-
Quantum key distribution (QKD) enables the establishment of shared keys between two distant users, Alice and Bob, based on the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics, and it has proven to possess information-theoretic security. In most of QKD systems, Alice and Bob require a shared reference frame, and real-time calibration of the reference frame increases system costs and reduces its performance. Fortunately, the reference-frame-independent QKD protocol has been proposed, overcoming reference-frame drift issues and receiving widespread attention. However, in practical QKD systems, the non-ideal characteristics of realistic devices introduce certain inconsistency between the theory and the practice. In real-world quantum key distribution systems, device imperfections can lead to security vulnerabilities, thereby reducing system security. For example, imperfections in the encoding apparatus at the source end may result in errors in the quantum states. The inherent defects in the detection part may cause after-pulse effects and dead-time effects, thus reducing the key rate. Therefore, in this work, we propose a practical state-preparation error tolerant reference-frame-independent quantum key distribution protocol by taking imperfections in both the source and the detectors into account. Moreover, a three-intensity decoy-state scheme for modeling analysis and numerical simulations is employed. In this protocol, we reduce the influence of state-preparation errors on the key rate by utilizing virtual state methods to precisely estimate the phase-error rate. Furthermore, by characterizing the effects of after-pulses and dead-time on the key rate, our protocol exhibits higher robustness and can effectively address issues related to detector imperfections. This approach can also be extended to other quantum key distribution protocols with higher security levels, such as measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution protocol and twin-field quantum key distribution, further mitigating the influence of device imperfections on practical implementation of QKD system. Therefore, our present work provide important reference value for putting the quantum key distributions into practical application.
-
Keywords:
- quantum key distribution /
- state preparation error /
- reference-frame-independent protocol /
- after-pulse effect /
- dead-time effect
[1] Bennett C H, Brassard G 1984 Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, System and Signal Processing (Vol. 1 of 3) (Bangalore: IEEE) pp175–179
[2] Brassard G, Lütkenhaus N, Mor T, Sanders B C 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 1330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yuan Z, Plews A, Takahashi R, Doi K, Tam W, Sharpe A W, Dixon A R, Lavelle E, Dynes J F, Murakami A, Kujiraoka M, Lucamarini M, Tanizawa Y, Sato H, Shields A J 2018 J. Light. Technol. 36 16
[4] Boaron A, Korzh B, Houlmann R, Boso G, Rusca D, Gray S, Li M, Nolan D, Martin A, Zbinden H 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Minder M, Pittaluga M, Roberts G, Lucamarini M, Dynes J F, Yuan Z L, Shields A J 2019 Nat. Photonics 13 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu Y, Yu Z W, Zhang W, Guan J Y, Chen J P, Zhang C, Hu X L, Li H, Jiang C, Lin J, Chen T Y, You L, Wang Z, Wang X B, Zhang Q, Pan J W 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 100505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bennett C H, Bessette F, Brassard G, Salvail L, Smolin J 1992 J Cryptol 5 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kurtsiefer C, Zarda P, Halder M, Weinfurter H, Gorman P M, Tapster P R, Rarity J G 2002 Nature 419 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Laing A, Scarani V, Rarity J G, O’Brien J L 2018 Phys. Rev. A 82 012304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gottesman D, Lo H K, Lütkenhaus N, Preskill J 2004 Quantum Inf. Comput. 4 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tamaki K, Curty M, Kato G, Lo H K, Azuma K 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 052314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang C, Sun S H, Ma X C, Tang G Z, Liang L M 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 042319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xu F H, Wei K J, Sajeed S, Kaiser S, Sun S H, Tang Z Y, Qian L, Makarov V, Lo H K 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 032305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tang Z Y, Wei K J, Bedroya O, Qian L, Lo H K 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 042308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou X Y, Ding H J, Zhang C H, Li J, Zhang C M, Wang Q 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 4176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fan Y G J, Wang C, Wang S, Yin Z Q, Liu H, Chen W, He D Y, Han Z F, Guo G C 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 064032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Campbell L 1992 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 63 5794
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Rusca D, Boaron A, Grünenfelder F, Martin A, Zbinden H 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 171104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 莫小范 2006 博士毕业论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Mo X F 2006 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China
[20] Wang W J, Zhou X Y, Zhang C H, Ding H J, Wang Q 2022 Quantum Inf. Process 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 范元冠杰 2020 博士毕业论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Fan Y G J 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China
[22] Wang X B 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 30503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 马啸, 孙铭铄, 刘靖阳, 丁华建, 王琴 2022 71 030301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma X, Sun M S, Liu J Y, Ding H J, Wang Q 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 030301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Fung C F, Tamaki K, Qi B, Lo H K, Ma X F 2009 Quantum Inf. Comput. 9 1533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sun S H, Xu F H 2021 New J. Phys. 23 023011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhou Y H, Yu Z W, Wang X B 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 042324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhang C H, Zhang C M, Guo G C, Wang Q 2018 Opt. Express 26 4219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhou X Y, Zhang C H, Zhang C M, Wang Q 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 052337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Jiang C, Yu Z W, Hu X L, Wang X B 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 012402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Huang L Y, Zhang Y C, Yu S 2021 Chin. Phys. Lett. 38 040301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Lucamarini M, Yuan Z L, Dynes J F, Shields A J 2018 Nature 557 400
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang X B, Yu Z W, Hu X L 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 062323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
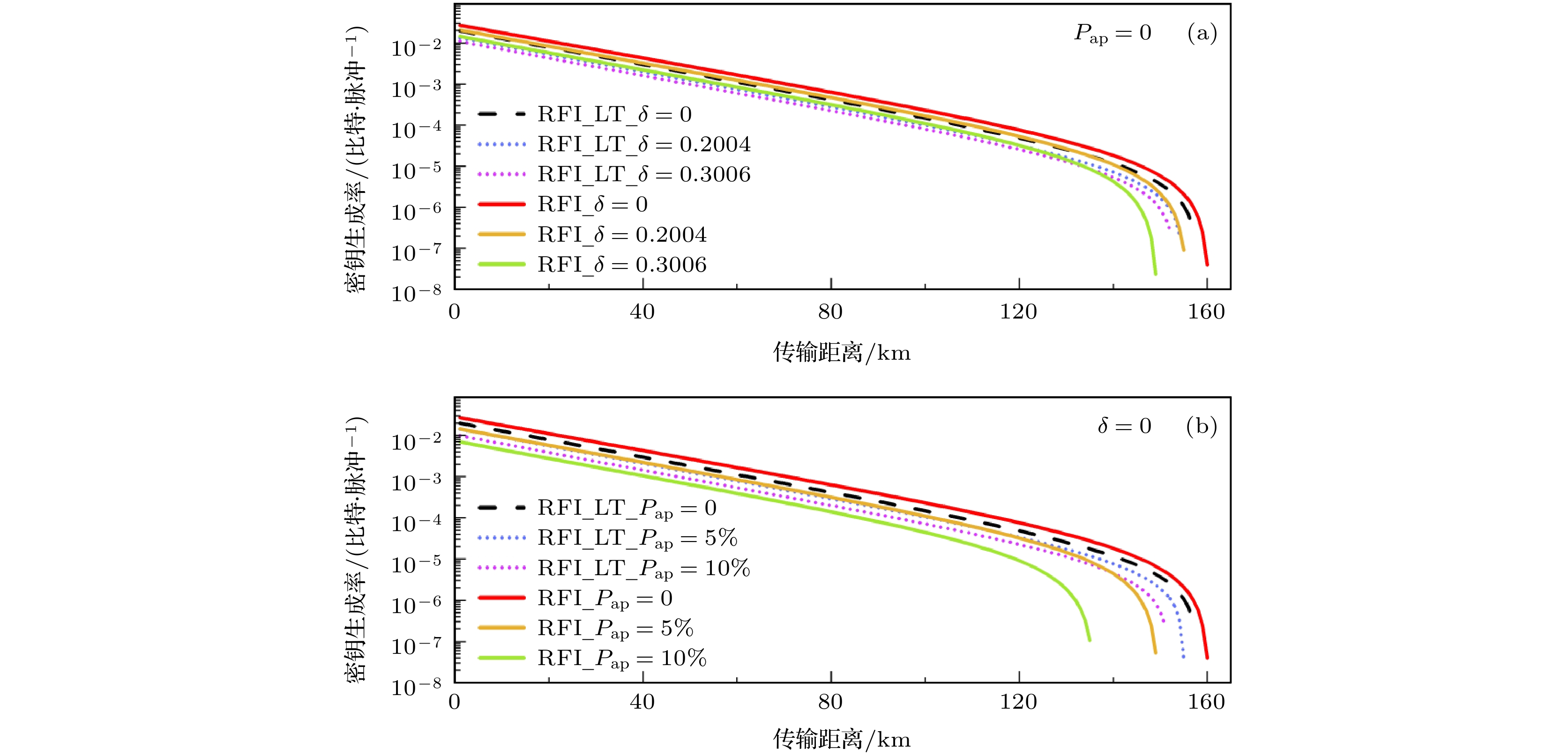
图 1 (a) 基于态制备缺陷$ \delta $的RFI协议以及LT-RFI协议的密钥生成率图; (b)基于后脉冲效应$ {P_{{\text{ap}}}} $的RFI协议以及LT-RFI协议的密钥生成率图
Figure 1. (a) Key generation rates of the RFI protocol and LT-RFI protocol based on state preparation flaws $ \delta $; (b) the key generation rates of the RFI protocol and LT-RFI protocol based afterpulse effect $ {P_{{\text{ap}}}} $.
表 1 基于后脉冲效应和死时间效应的LT-RFI协议仿真参数列表
Table 1. Parameter list used in simulation of LT-RFI protocol based on after-pulse effect and dead time effect.
Bob探测器
暗计数率$ {P_{{\text{dc}}}} $Bob探测器
效率$ {\eta _{{\text{Bob}}}} $系统纠错
系数fAlice发送的
总脉冲数N系统
重复频率F信道损耗系数
$ \alpha $/(dB·km–1)系统
本底误码$ {e_{\text{d}}} $3×10–6 0.145 1.16 1012 109 0.2 0.0015 -
[1] Bennett C H, Brassard G 1984 Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, System and Signal Processing (Vol. 1 of 3) (Bangalore: IEEE) pp175–179
[2] Brassard G, Lütkenhaus N, Mor T, Sanders B C 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 1330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yuan Z, Plews A, Takahashi R, Doi K, Tam W, Sharpe A W, Dixon A R, Lavelle E, Dynes J F, Murakami A, Kujiraoka M, Lucamarini M, Tanizawa Y, Sato H, Shields A J 2018 J. Light. Technol. 36 16
[4] Boaron A, Korzh B, Houlmann R, Boso G, Rusca D, Gray S, Li M, Nolan D, Martin A, Zbinden H 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Minder M, Pittaluga M, Roberts G, Lucamarini M, Dynes J F, Yuan Z L, Shields A J 2019 Nat. Photonics 13 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu Y, Yu Z W, Zhang W, Guan J Y, Chen J P, Zhang C, Hu X L, Li H, Jiang C, Lin J, Chen T Y, You L, Wang Z, Wang X B, Zhang Q, Pan J W 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 100505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bennett C H, Bessette F, Brassard G, Salvail L, Smolin J 1992 J Cryptol 5 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kurtsiefer C, Zarda P, Halder M, Weinfurter H, Gorman P M, Tapster P R, Rarity J G 2002 Nature 419 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Laing A, Scarani V, Rarity J G, O’Brien J L 2018 Phys. Rev. A 82 012304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gottesman D, Lo H K, Lütkenhaus N, Preskill J 2004 Quantum Inf. Comput. 4 325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tamaki K, Curty M, Kato G, Lo H K, Azuma K 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 052314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang C, Sun S H, Ma X C, Tang G Z, Liang L M 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 042319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xu F H, Wei K J, Sajeed S, Kaiser S, Sun S H, Tang Z Y, Qian L, Makarov V, Lo H K 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 032305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tang Z Y, Wei K J, Bedroya O, Qian L, Lo H K 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 042308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou X Y, Ding H J, Zhang C H, Li J, Zhang C M, Wang Q 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 4176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Fan Y G J, Wang C, Wang S, Yin Z Q, Liu H, Chen W, He D Y, Han Z F, Guo G C 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 064032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Campbell L 1992 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 63 5794
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Rusca D, Boaron A, Grünenfelder F, Martin A, Zbinden H 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 171104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 莫小范 2006 博士毕业论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Mo X F 2006 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China
[20] Wang W J, Zhou X Y, Zhang C H, Ding H J, Wang Q 2022 Quantum Inf. Process 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 范元冠杰 2020 博士毕业论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Fan Y G J 2020 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China
[22] Wang X B 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 30503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 马啸, 孙铭铄, 刘靖阳, 丁华建, 王琴 2022 71 030301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma X, Sun M S, Liu J Y, Ding H J, Wang Q 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 030301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Fung C F, Tamaki K, Qi B, Lo H K, Ma X F 2009 Quantum Inf. Comput. 9 1533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sun S H, Xu F H 2021 New J. Phys. 23 023011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhou Y H, Yu Z W, Wang X B 2016 Phys. Rev. A 93 042324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zhang C H, Zhang C M, Guo G C, Wang Q 2018 Opt. Express 26 4219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhou X Y, Zhang C H, Zhang C M, Wang Q 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 052337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Jiang C, Yu Z W, Hu X L, Wang X B 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 012402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Huang L Y, Zhang Y C, Yu S 2021 Chin. Phys. Lett. 38 040301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Lucamarini M, Yuan Z L, Dynes J F, Shields A J 2018 Nature 557 400
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang X B, Yu Z W, Hu X L 2018 Phys. Rev. A 98 062323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3580
- PDF Downloads: 152
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad:



