-
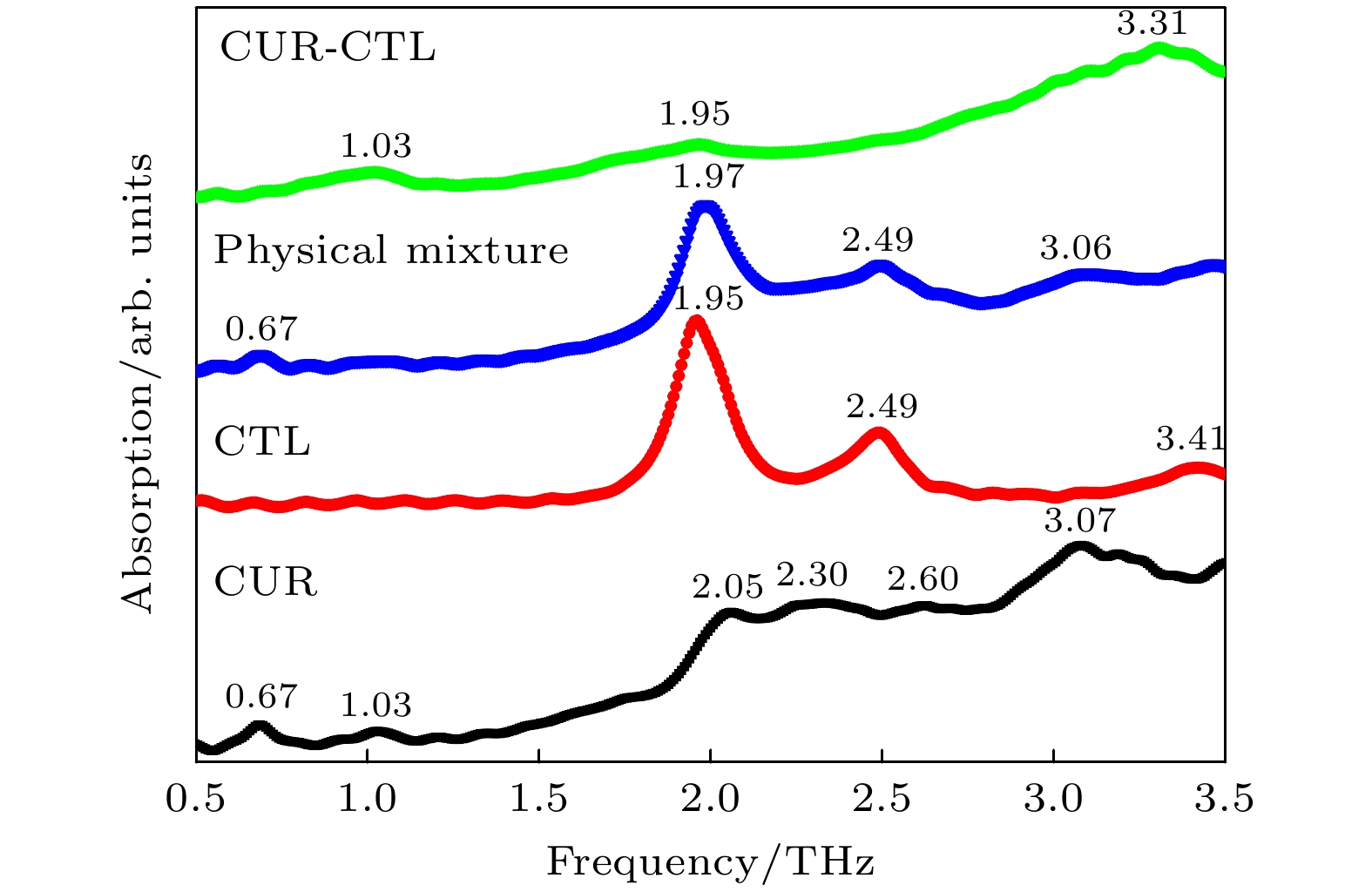
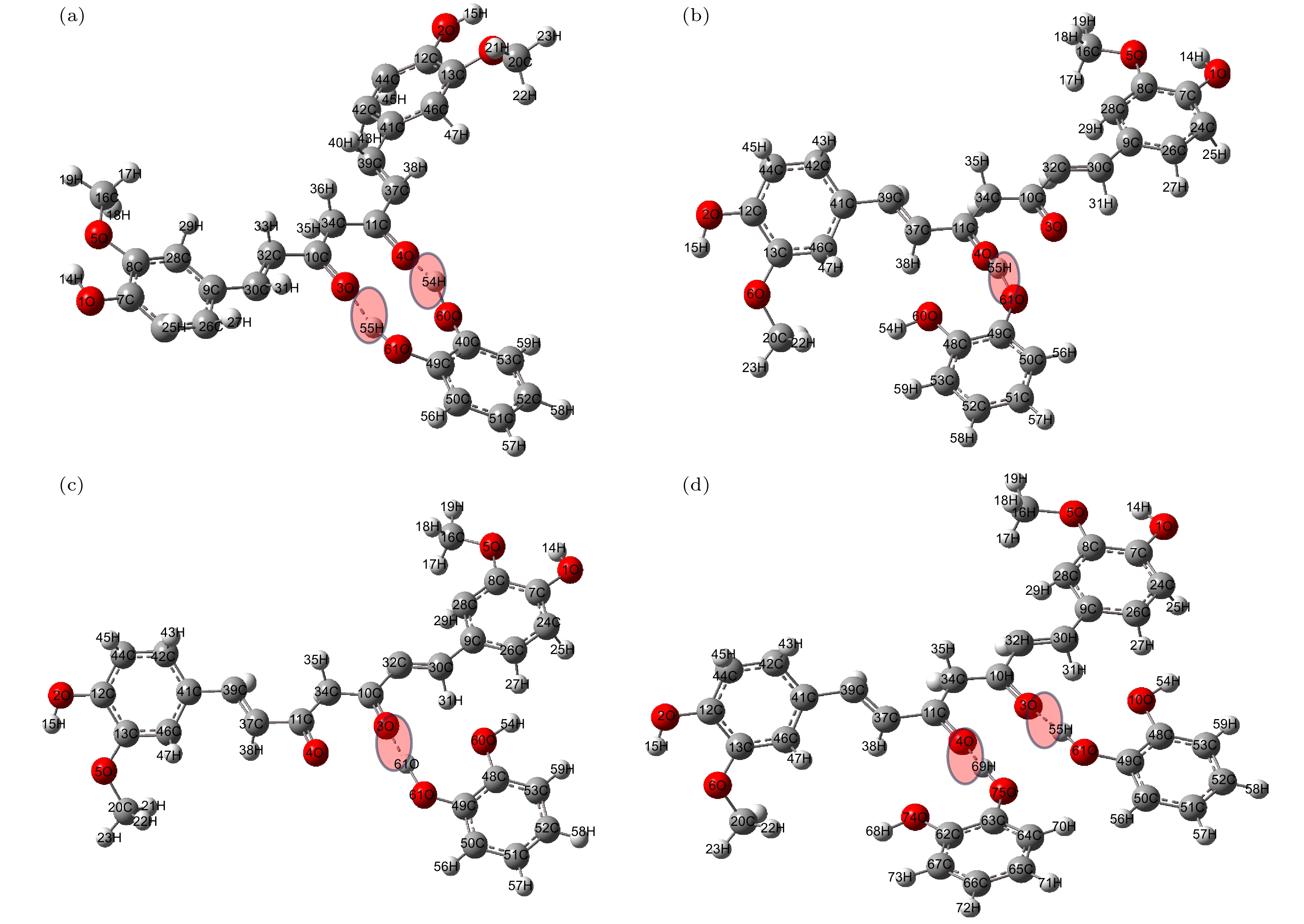
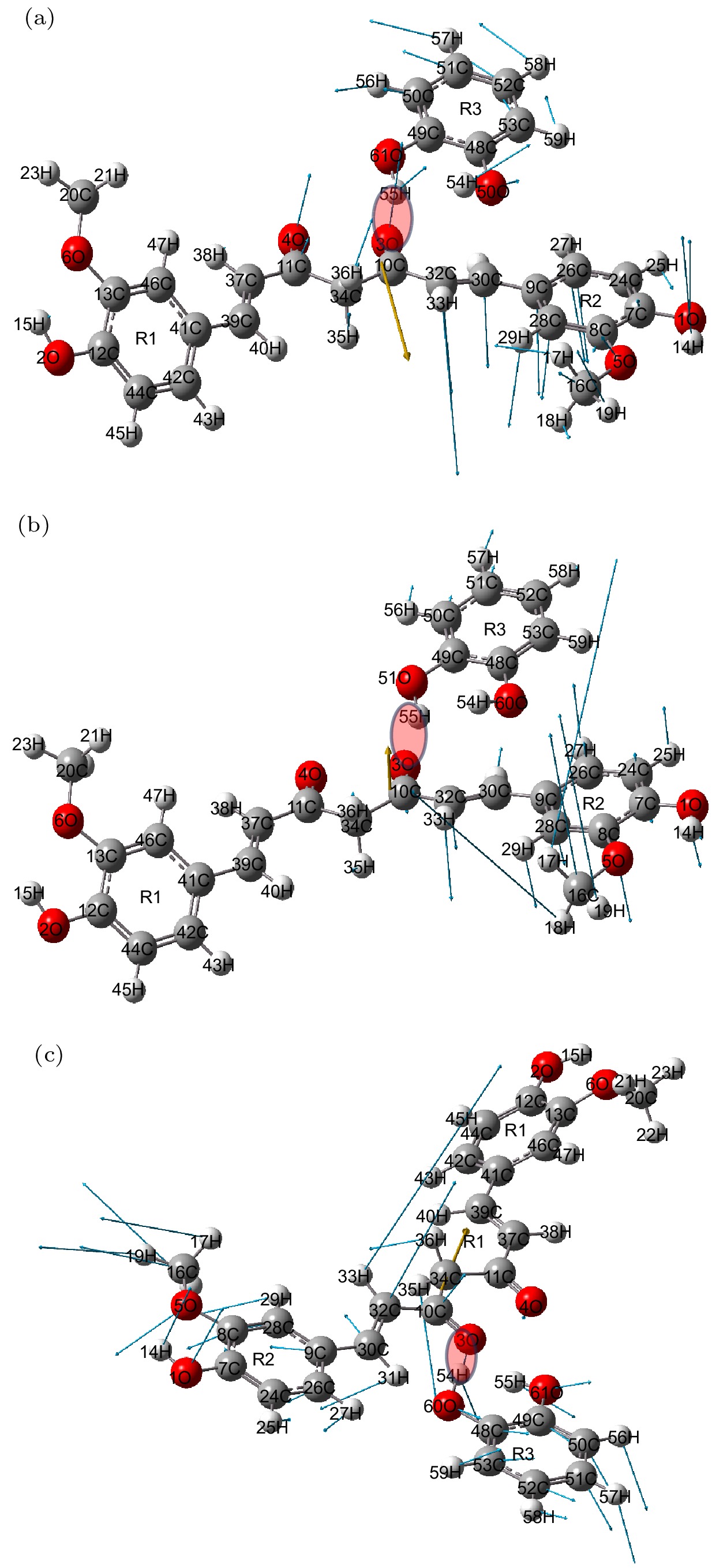
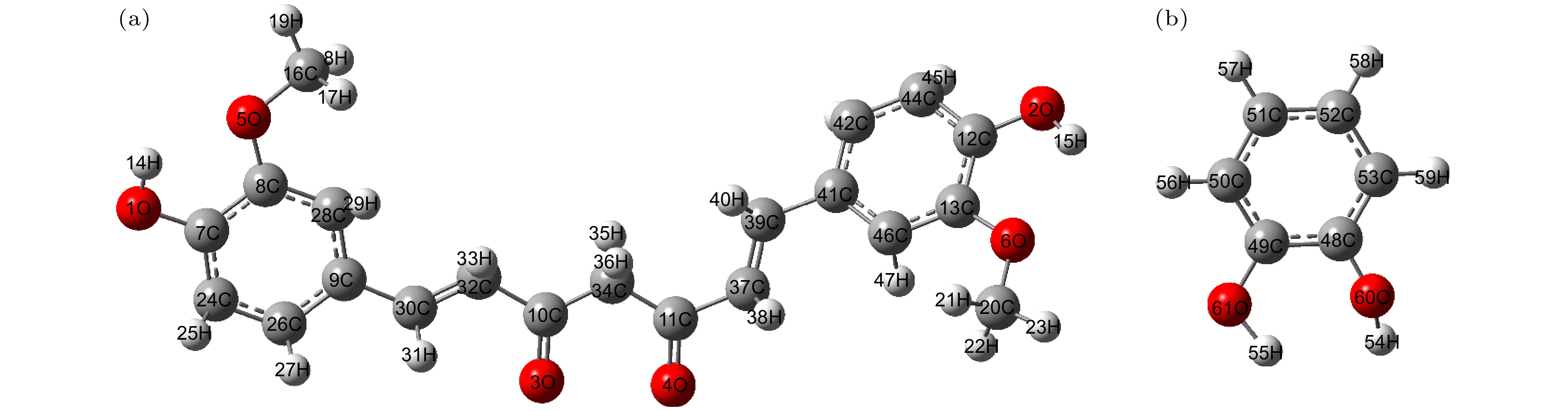
Curcumin (CUR) is a commonly used pharmaceutical with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-cancer effects, but its solubility in water is relatively low. In recent years, pharmaceutical co-crystal has been an effective method of enhancing the solubility of limited water-soluble pharmaceuticals. Based on this, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) is used to study the THz spectra of curcumin-catechol co-crystal. Firstly, the experimental spectra of curcumin, catechol (CTL), their physical mixture and their co-crystal are measured in a range of 0.5–3.5 THz, respectively. The experimental data show that CUR obtains six THz absorption peaks, while CTL possess three THz absorption peaks, the physical mixture obtains four absorption peaks, and their CUR-CTL co-crystal obtains three absorption peaks. These results indicate that THz-TDS can effectively identify curcumin, catechol and their co-crystals. The fact that the absorption peak at 3.31 THz obtained in co-crystal is entirely different from those of raw materials, implying that new weak interactional forces are generated between CUR molecule and CTL molecule, the co-crystal forms a new three-dimensional structure compared with their raw materials. These results are also verified by X-ray diffraction spectra of raw material and their Co-crystal. Moreover, four possible theoretical forms of curcumin-catechol co-crystal are optimized and simulated by using density functional theory (DFT). The calculated results indicate that the data of co-crystal form III are in good agreement with the experimental spectrum, and the simulation effectively reconstructs the experimental spectrum. So it can be inferred that the co-crystal is formed through the hydrogen bond between the carbonyl C10=O3 of CUR and the hydroxy O61-H55 of CTL. In addition, depending on the good match between experimental data and theoretical results, it is found that the three absorption peaks in the co-crystal do not origin from the action of a single molecule, but the joint action of the functional groups of the two molecules under the driving by the hydrogen bond. The existence of weak interaction forces, such as the hydrogen bond, not only changes the structural parameters of the two molecules, but also reestablishes a new intermolecular force, which then affects the interactional motions of the co-crystal. This fact directly leads the CUR-CTL co-crystal to exhibit THz absorption peaks different from those of raw materials in the THz band.
-
Keywords:
- curcumin /
- co-crystal /
- terahertz wave /
- absorption spectrum
[1] Kulkarni A, Shete S, Hol V, Bachhav R 2020 AJPS 13 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Prabhakar P, Giridhar S 2019 Indian J. Pharm. Educ. 53 563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Novena L. M, Athimoolam S, Anitha R, Bahadur S A 2021 J. Mol. Struct. 1249 2022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Akshita J, Mansi P, Neelima D, Kunal C, Maninder 2022 J. Pharm. 111 2788
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] George C P, Thorat S H, Shaligram P S, Suresha P R, Gonnade R G 2020 Crystengcomm 22 6137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sakamoto N, Tsuno N, Koyama R, Gato K, Titapiwatanakun V, Takatori K, Fukami T 2021 Chem. Pharm. Burl. 69 1995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu L X, Liu M, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Wu L, Zhang L, Zhang Y J, Liu Y L, Zou D Y 2022 J. Mol. Struct. 1250 1318
[8] Yong D, Hong X F, Qi Z, Hui L Z, Zhi H 2016 Spectrochim. Acta. A 153 580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wan M, Fang J Y, Xue J D, Liu J J, Qin J Y, Hong Z, Li J S, D Y 2022 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 8550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 段铜川, 闫韶健, 赵妍, 孙庭钰, 李阳梅, 朱智 2021 70 248702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan T C, Yan S j, Zhao Y, Sun T Y, Li Y G, Zhu Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 248702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 郑转平, 刘榆杭, 曾方, 赵帅宇, 朱礼鹏 2023 72 083201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Z P, Liu Y H, Zeng F, Zhao S Y, Zhu L P 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 083201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Cai Q, Xue J D, Wang Q, Du Y 2017 Spectrochim. Acta. A 186 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang P F, Zhao J T, Zhang Y M, Zhu Z J, Liu L Y, Zhao H G, Yang X C, Yang X N, Sun X H, He M G 2022 Int. J. Pharmaceut. 620 121759
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Margaret D, Mizuki M, Kei H, Timothy K 2020 J. Phys. Chem. A 124 9793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Luczynska, Katarzyna, Druzbicki, Kacper, Lyczko, Krzysztof, Dobrowolski 2015 J. Phys. Chem. B 119 6852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Adrieli S H, Matheus G L, Radharani B 2022 Ind. Crop. Prod. 177 114501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yao T M, Srinivas J W 2022 Food Hydrocolloids 126 107466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Saffarionpour S, Diosady L L 2022 Curr. Opin. Food. Sci. 43 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Sakineh M, Ali H A, Pouya M 2020 Chromatographia 83 1293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 程桂林, 邓彩赟, 蒋成君 2018 中国现代应用药学 35 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng G L, Deng G Y, Jiang C J 2018 Chin. J. Mod. Drug App. 35 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ribas M M, Sakata G S, Santos A E, Magro C D, Aguiar G P, Vladimir M L 2019 J. Supercrit. Fluid. 152 104564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Indumathi S, Jenna S M, Sohrab R, Sameer D V 2018 J. Chem. Data. 63 3652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 邓彩赟, 蒋成君 2018 浙江科技学院学报 30 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng C Y, Jiang C J 2018 J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 30 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Roothan C C 1951 Rev. Mod. Phys. 23 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Stephens P J, Devlin F J, Chabalowski C F 1994 J. Phys. Chem. 98 11623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chen T, Yu L X, Tang Z Q, Li Z, Hu F G 2022 Chem. Phys. 562 111676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Otsuka Y T, Ito A, Takeuchi M, Sasaki T, Tanaka H J 2020 J. Brug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 56 101215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hjorth H T, Jan K, Arvid M, Bertil S, Znzell C R, Eric J B 1982 Acta Chem. Sca. 36 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wunderlich H, Mootz D 1971 Acta Cry. Sect. B 27 1684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 姜黄素与邻苯二酚键长和键角
Table 1. Bond length and bond angle of curcumin and catechol.
表 2 CUR-CTL共晶体实验和理论计算数据
Table 2. The results of experimental and calculated data of CUR-CTL co-crystal.
Frequency/THz Vibrational mode Expt. Theo. 1.03 1.03 Bending of C34—C10—C32, Out-of-plane oscillation of R2 and R2, In plane oscillation of CTL 1.95 1.95 Out of plane torsion of -C16H3 and R2, Out of plane rocking oscillation of CTL 3.31 3.34 The stretching vibration of hydrogen bond C10=O30···H55—O61, Swing of C30—C32—C10, Out-of-plane oscillation of R2 and R1 -
[1] Kulkarni A, Shete S, Hol V, Bachhav R 2020 AJPS 13 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Prabhakar P, Giridhar S 2019 Indian J. Pharm. Educ. 53 563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Novena L. M, Athimoolam S, Anitha R, Bahadur S A 2021 J. Mol. Struct. 1249 2022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Akshita J, Mansi P, Neelima D, Kunal C, Maninder 2022 J. Pharm. 111 2788
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] George C P, Thorat S H, Shaligram P S, Suresha P R, Gonnade R G 2020 Crystengcomm 22 6137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sakamoto N, Tsuno N, Koyama R, Gato K, Titapiwatanakun V, Takatori K, Fukami T 2021 Chem. Pharm. Burl. 69 1995
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu L X, Liu M, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Wu L, Zhang L, Zhang Y J, Liu Y L, Zou D Y 2022 J. Mol. Struct. 1250 1318
[8] Yong D, Hong X F, Qi Z, Hui L Z, Zhi H 2016 Spectrochim. Acta. A 153 580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wan M, Fang J Y, Xue J D, Liu J J, Qin J Y, Hong Z, Li J S, D Y 2022 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 8550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 段铜川, 闫韶健, 赵妍, 孙庭钰, 李阳梅, 朱智 2021 70 248702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Duan T C, Yan S j, Zhao Y, Sun T Y, Li Y G, Zhu Z 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 248702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 郑转平, 刘榆杭, 曾方, 赵帅宇, 朱礼鹏 2023 72 083201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Z P, Liu Y H, Zeng F, Zhao S Y, Zhu L P 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 083201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Cai Q, Xue J D, Wang Q, Du Y 2017 Spectrochim. Acta. A 186 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang P F, Zhao J T, Zhang Y M, Zhu Z J, Liu L Y, Zhao H G, Yang X C, Yang X N, Sun X H, He M G 2022 Int. J. Pharmaceut. 620 121759
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Margaret D, Mizuki M, Kei H, Timothy K 2020 J. Phys. Chem. A 124 9793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Luczynska, Katarzyna, Druzbicki, Kacper, Lyczko, Krzysztof, Dobrowolski 2015 J. Phys. Chem. B 119 6852
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Adrieli S H, Matheus G L, Radharani B 2022 Ind. Crop. Prod. 177 114501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yao T M, Srinivas J W 2022 Food Hydrocolloids 126 107466
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Saffarionpour S, Diosady L L 2022 Curr. Opin. Food. Sci. 43 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Sakineh M, Ali H A, Pouya M 2020 Chromatographia 83 1293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 程桂林, 邓彩赟, 蒋成君 2018 中国现代应用药学 35 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cheng G L, Deng G Y, Jiang C J 2018 Chin. J. Mod. Drug App. 35 5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ribas M M, Sakata G S, Santos A E, Magro C D, Aguiar G P, Vladimir M L 2019 J. Supercrit. Fluid. 152 104564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Indumathi S, Jenna S M, Sohrab R, Sameer D V 2018 J. Chem. Data. 63 3652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 邓彩赟, 蒋成君 2018 浙江科技学院学报 30 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng C Y, Jiang C J 2018 J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 30 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Roothan C C 1951 Rev. Mod. Phys. 23 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Stephens P J, Devlin F J, Chabalowski C F 1994 J. Phys. Chem. 98 11623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Chen T, Yu L X, Tang Z Q, Li Z, Hu F G 2022 Chem. Phys. 562 111676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Otsuka Y T, Ito A, Takeuchi M, Sasaki T, Tanaka H J 2020 J. Brug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 56 101215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hjorth H T, Jan K, Arvid M, Bertil S, Znzell C R, Eric J B 1982 Acta Chem. Sca. 36 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Wunderlich H, Mootz D 1971 Acta Cry. Sect. B 27 1684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6017
- PDF Downloads: 83
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: