-
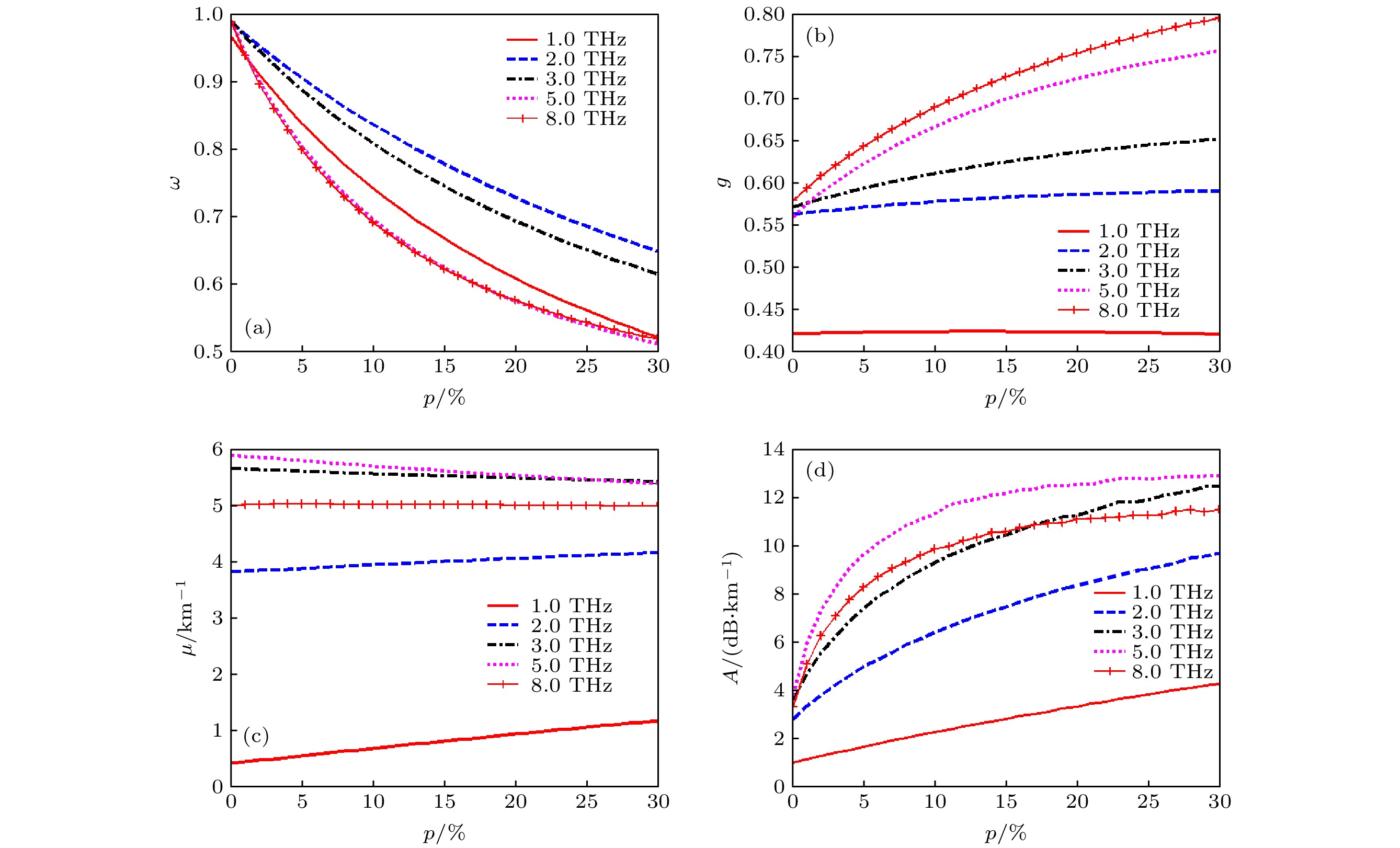
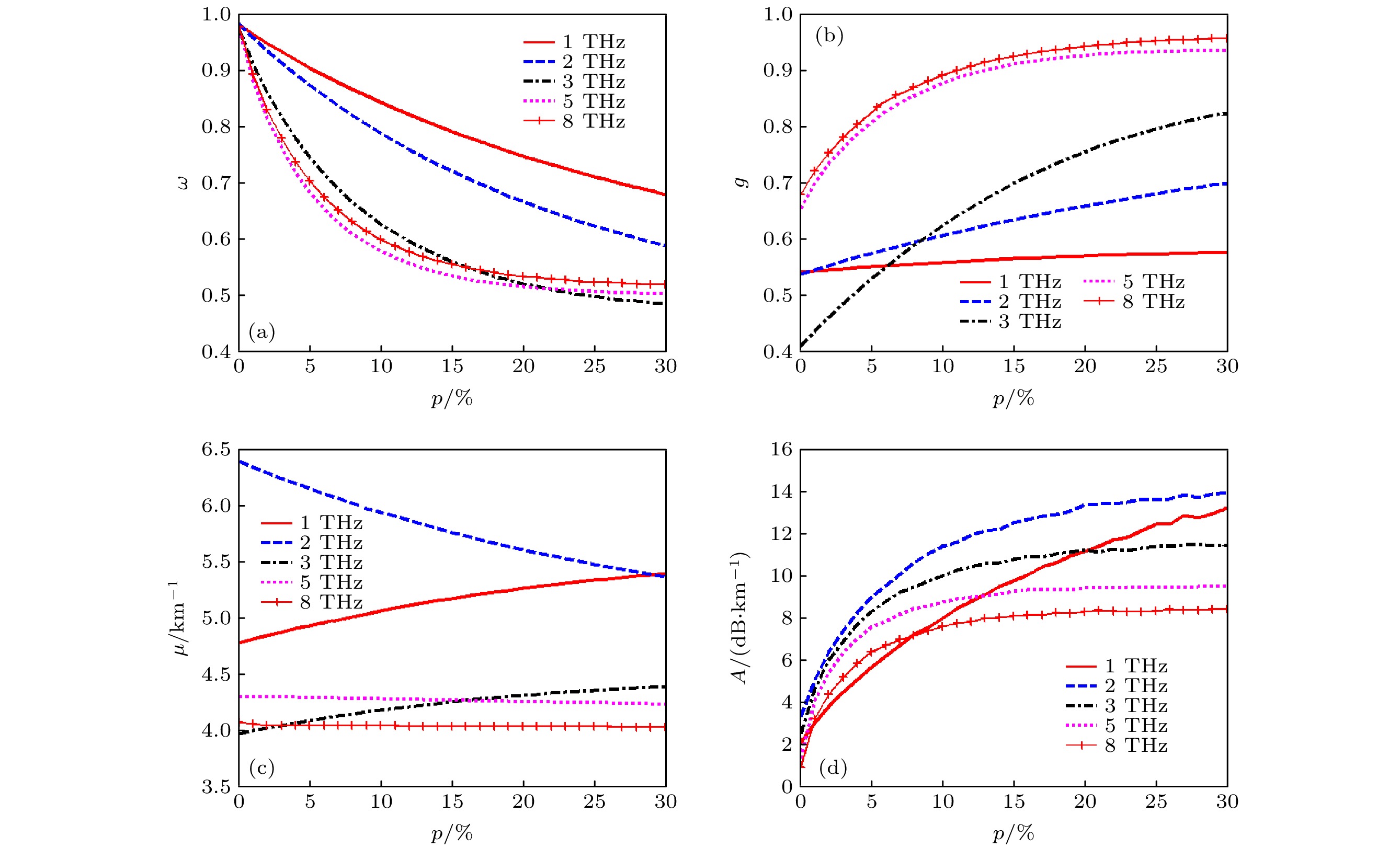
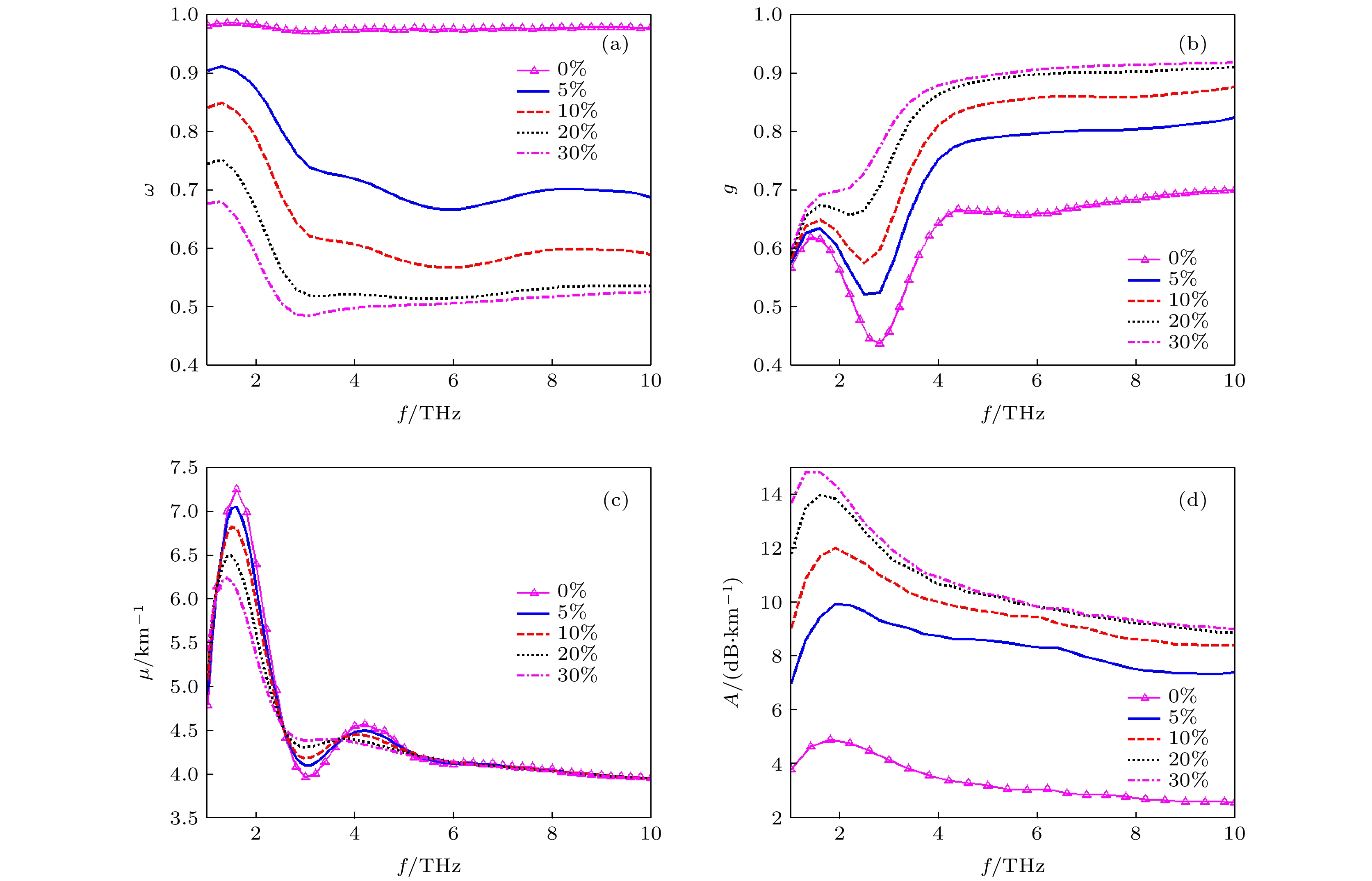
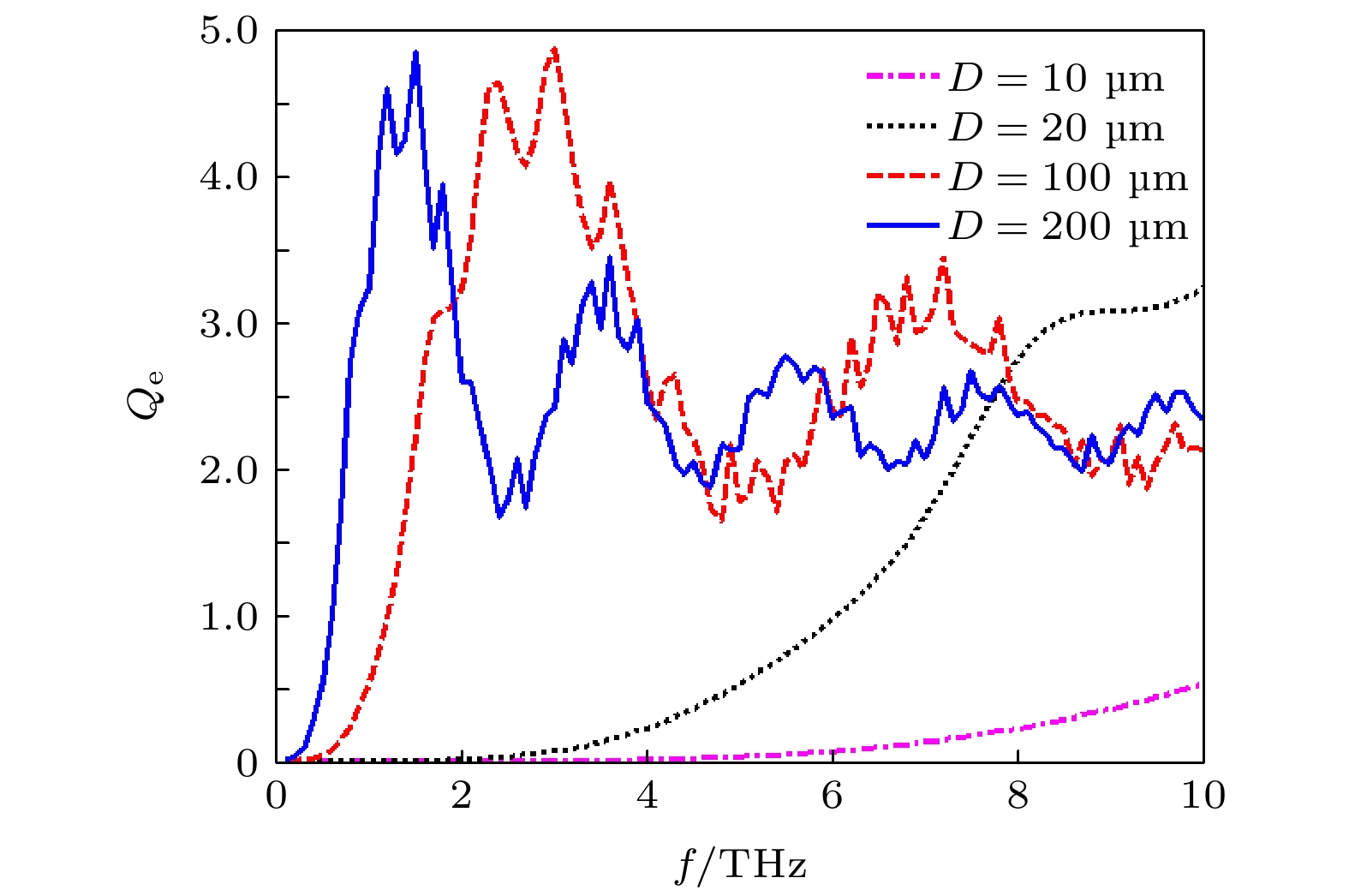
The research on space transmission characteristics of terahertz wave is of great significance for the application of terahertz wave in space. In order to study the transmission characteristics of terahertz wave in sand and dust storm weather, according to the lognormal distribution of dust particle sizes, Mie scattering theory and Monte Carlo method are used to analyze the attenuation characteristics of six dry sand modes of sand and dust storm in different regions of China in a frequency band of 1–10 THz, and the relationship of the extinction parameters and attenuation rate to the frequency is given. The results show that with the increase of frequency, the attenuation rate of 1–10 THz terahertz wave first increases and then decreases. Different mode of sand and dust storm leads to different frequency range of strong attenuation of terahertz wave. In order to analyze the influence of sand dust particle moisture content on terahertz wave propagation attenuation, the relationship of three efficiency factors to water content of sand dust particles with different sizes is calculated. The results show that the influence of water content on extinction is different from that of the particle size. Monte Carlo method is used to calculate the attenuation of terahertz wave by sand and dust storm in two kinds of wet sand modes, and the relationship of the attenuation rate and water content to the frequency is given, the results are compared with those from the dry sand mode, showing that the albedo of wet sand mode is obviously lower than that of dry sand mode with the same size distribution. The absorption of wet sand particles increases with water content increasing. The extinction of wet sand and dust storm results from scattering and absorption. With the increase of water content in sand particles, the frequency band with strong attenuation of terahertz wave by wet sand and dust storm moves toward low frequency. When the water content is less than 5%, the attenuation rate of terahertz wave increases significantly with the increase of water content. Sand and dust storms with higher humidity have a greater influence on the transmission attenuation of terahertz wave.
-
Keywords:
- terahertz wave /
- sand and dust storm /
- Monte Carlo /
- attenuation rate
[1] Sarieddeen H, Alouini M S, Al-Naffouri T Y 2019 IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 37 2040
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chong H, Yi C 2018 IEEE Commun. Mag. 56 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jiang Y, Deng B, Wang H 2016 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 28 1684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hu B B, Nuss M C 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 1716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mellinger J S, Yang Y, Mandehgar M 2012 Opt. Express 20 6788
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Elsheikh E A A, Islam M R, Habaebi M H 2017 IEEE Trans. Anten. Propag. 65 4200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen H Y, Ku C C 2011 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 10 469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chiou M M, Kiang J F 2016 IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 13 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chu T S 2013 Bell Labs Tech. J. 58 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li X C, Gao X, Wang J 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 34208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dong Q F, Li Y L, Xu J D, Zhang H, Wang M J 2013 IEEE Trans. Anten. Propag. 61 910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴振森, 由金光, 杨瑞科 2004 中国激光 31 1075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Zh S, You J G, Yang R K 2004 Chin. J. Las. 31 1075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王红霞, 孙红辉, 张清华 2020 红外与激光工程 49 20201022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H X, Sun H H, Zhang Q H 2020 Infrared Laser Eng. 49 20201022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 杨瑞科, 李茜茜, 姚荣辉 2016 65 094205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang R K, Li Q Q, Yao R H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 094205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李宇晔, 王新柯, 张平 2008 激光与红外 9 921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y H, Wang H K, Zhang P 2008 Laser Infr. 9 921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 许文忠, 钟凯, 梅嘉林 2015 红外与激光工程 44 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu W Z, Zhong K, Mei J L 2015 Infrared Laser Eng. 44 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 董群锋, 郭立新, 李应乐, 王明军 2018 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报 16 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Q F, Guo L X, Li Y L, Wang M J 2018 J. Terahertz Sci. Electron. Inf. Technol. 16 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 周旺, 周东方, 侯德亭 2005 强激光与粒子束 17 1259
Zhou W, Zhong D F, Hou D T 2005 High Pow. Las. Part. Beam. 17 1259
[19] Sihvola A H, Kong J A 1988 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 26 420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liebe H J, Hufford G A, Manabe T 1991 Int. J. Infrared Millimeter Waves 12 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ahmed A S 1987 IEE Proc. H 134 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 董庆生 1997 电波科学学报 12 15
Dong Q S 1997 Chin. J. Radio Sci. 12 15
[23] Ansari A J, Evans B G 1982 IEE Proc. F 129 315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Seyoung M, Dongyun K, Eunji S 2008 Appl. Opt. 47 336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 王红霞, 竹有章, 田涛, 李爱君 2013 62 024214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H X, Zhu Y Z, Tian T, Li A J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 024214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 高志文, 周又和, 郑晓静 2008 中国科学G辑 38 955
Gao Z W, Zhou Y H, Zheng X J 2008 Sci. Chin. Ser. G 38 955
[27] Prahl S A, Keijzer M, Jacques S L 1989 SPIE Proceedings IS 5 102
[28] Binzoni T, Leung T S, Gandjbakhche A H 2006 Phys. Med. Biol. 51 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 沙粒的尺度分布参数
Table 1. Size distribution parameters of sand particles.
Sand source m0 σ Loess –3.08 0.491 Maowusu –2.96 0.380 Tengger –2.31 0.296 Taklimakan –2.26 0.276 Gansu –2.19 0.279 Coast –1.83 0.166 -
[1] Sarieddeen H, Alouini M S, Al-Naffouri T Y 2019 IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 37 2040
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Chong H, Yi C 2018 IEEE Commun. Mag. 56 96
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jiang Y, Deng B, Wang H 2016 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 28 1684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hu B B, Nuss M C 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 1716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mellinger J S, Yang Y, Mandehgar M 2012 Opt. Express 20 6788
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Elsheikh E A A, Islam M R, Habaebi M H 2017 IEEE Trans. Anten. Propag. 65 4200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen H Y, Ku C C 2011 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 10 469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Chiou M M, Kiang J F 2016 IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 13 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chu T S 2013 Bell Labs Tech. J. 58 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li X C, Gao X, Wang J 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 34208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dong Q F, Li Y L, Xu J D, Zhang H, Wang M J 2013 IEEE Trans. Anten. Propag. 61 910
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 吴振森, 由金光, 杨瑞科 2004 中国激光 31 1075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Zh S, You J G, Yang R K 2004 Chin. J. Las. 31 1075
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 王红霞, 孙红辉, 张清华 2020 红外与激光工程 49 20201022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H X, Sun H H, Zhang Q H 2020 Infrared Laser Eng. 49 20201022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 杨瑞科, 李茜茜, 姚荣辉 2016 65 094205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang R K, Li Q Q, Yao R H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 094205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李宇晔, 王新柯, 张平 2008 激光与红外 9 921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y H, Wang H K, Zhang P 2008 Laser Infr. 9 921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 许文忠, 钟凯, 梅嘉林 2015 红外与激光工程 44 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu W Z, Zhong K, Mei J L 2015 Infrared Laser Eng. 44 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 董群锋, 郭立新, 李应乐, 王明军 2018 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报 16 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Q F, Guo L X, Li Y L, Wang M J 2018 J. Terahertz Sci. Electron. Inf. Technol. 16 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 周旺, 周东方, 侯德亭 2005 强激光与粒子束 17 1259
Zhou W, Zhong D F, Hou D T 2005 High Pow. Las. Part. Beam. 17 1259
[19] Sihvola A H, Kong J A 1988 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 26 420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liebe H J, Hufford G A, Manabe T 1991 Int. J. Infrared Millimeter Waves 12 659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ahmed A S 1987 IEE Proc. H 134 55
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 董庆生 1997 电波科学学报 12 15
Dong Q S 1997 Chin. J. Radio Sci. 12 15
[23] Ansari A J, Evans B G 1982 IEE Proc. F 129 315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Seyoung M, Dongyun K, Eunji S 2008 Appl. Opt. 47 336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 王红霞, 竹有章, 田涛, 李爱君 2013 62 024214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H X, Zhu Y Z, Tian T, Li A J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 024214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 高志文, 周又和, 郑晓静 2008 中国科学G辑 38 955
Gao Z W, Zhou Y H, Zheng X J 2008 Sci. Chin. Ser. G 38 955
[27] Prahl S A, Keijzer M, Jacques S L 1989 SPIE Proceedings IS 5 102
[28] Binzoni T, Leung T S, Gandjbakhche A H 2006 Phys. Med. Biol. 51 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8197
- PDF Downloads: 119
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: