-
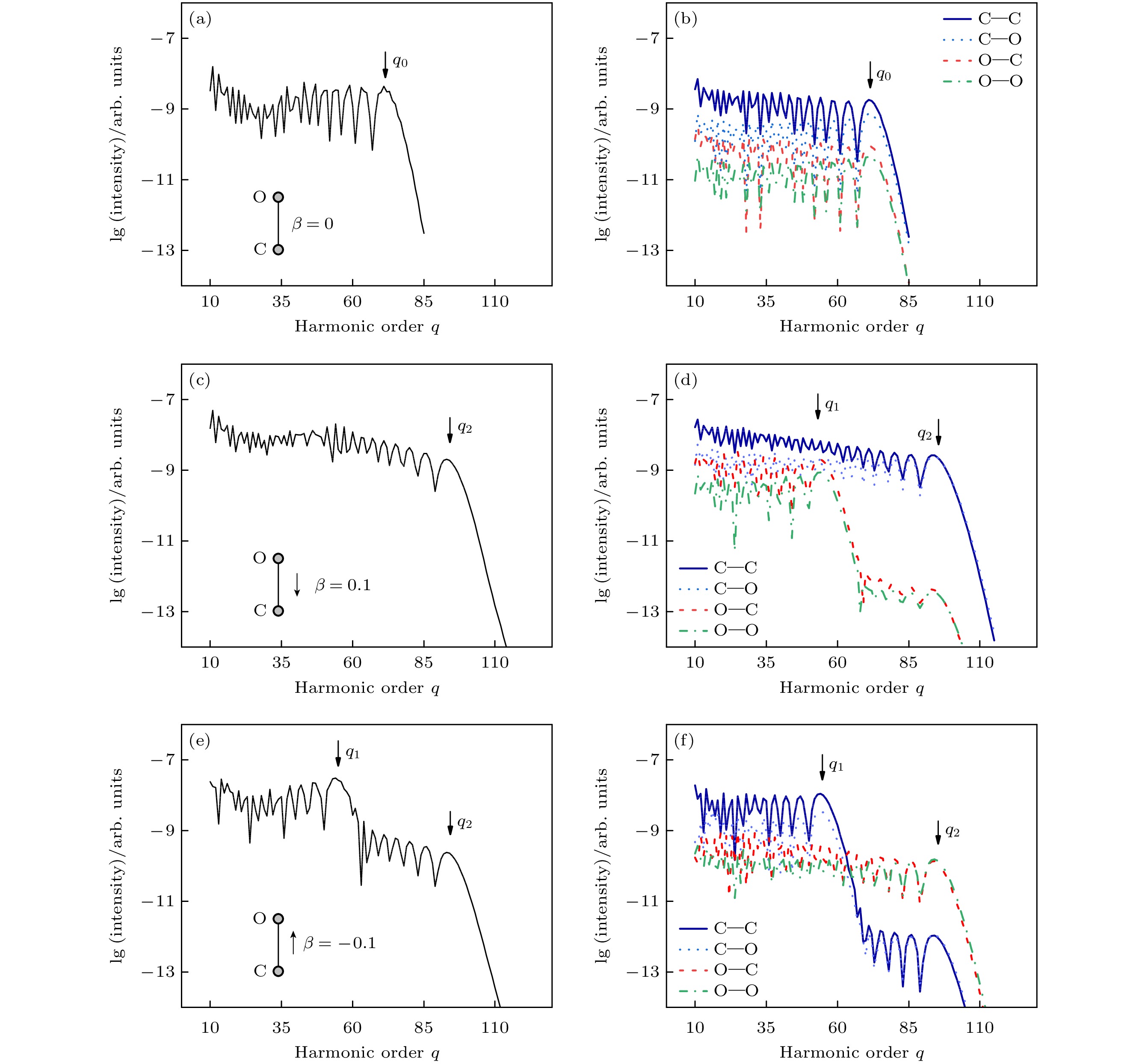
In this work, we use Lewenstein’s theory to calculate the high order harmonic spectra of CO molecule in a linearly polarized laser field combined with an external electrostatic field. The results show that the characteristics of the high order harmonic spectra of CO molecule depend strongly on the direction of the external static electric field relative to the orientation of CO. Especially, when the direction of the external static electric field points from O to C, the plateau of the harmonic spectrum becomes wider and the cutoff frequency reaches a larger value than the scenario without external static electric field. When the direction of the external static electric field points from C to O, the harmonic spectrum shows a double-plateau structure. Using Lewenstein theory, these phenomena can be understood from the viewpoint that the harmonic generation comes from a coherent superposition of the contributions of two kinds of channels characterized by C-end ionization and O-end ionization. The C(O)-end ionization channel means that the electron is ionized from C(O) end, then accelerated by the driving electric field, finally recombines with its parent molecular ion at either C or O end, emitting the harmonics. For the same harmonic order, the contribution of the C-end ionization channel is greater than that of the the O-end ionization channel. The two kinds of channels emit harmonics in adjacent half period of laser, where the external static electric field causes the cutoff frequency of the harmonic spectrum to increase and decrease in the adjacent half period of the laser field. Especially, when the direction of external static electric field is from the C to O, the cutoff frequency of the harmonic spectrum of the C-end ionization channel decreases, resulting in a higher first plateau in the spectrum. While, the increase of cut-off frequency of the O-end ionization channel will result in a lower second plateau. When the direction of external static electric field is reversed, the cutoff frequency of the harmonics of the C-end channel increases, leading the plateau of CO harmonic spectrum to become wider than that without the external static electric field. The cut-off frequency of the O-end ionization channel decreases. Because the contribution of the O-end ionization channel can be ignored compared with that of C-end ionization channel, the C-end channel dominates the contribution to harmonic generation and hence there is only one plateau in the harmonic spectrum. This work provides a clear physical picture for the formation of a double-plateau structure of CO harmonic spectra under the action of an external static electric field.
-
Keywords:
- high order harmonic spectra of CO /
- external static electric field /
- molecular orientation /
- double plateau structure
[1] Phan N L, Le C T, Hoang V H, Le V H 2019 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21 24177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hu H T, Li N, Liu P, Li R X, Xu Z Z 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 173201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Le C T, Hoang V H, Tran L P, Le V H 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 043405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang B, Yuan J M, Zhao Z X 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 035402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Koushki A M, Bonabi R S, Nia M M, Irani E 2018 Laser Phys. 28 075404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pan Y, Zhao S F, Zhou X X 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 035805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen Y J, Fu L B, Liu J 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 073902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhu X S, Zhang Q B, Hong W Y, Lan P F, Lu P X 2011 Opt. Express 19 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Augstein B B, Faria C F M 2011 J. Mod. Optic. 58 1173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 杨艳, 张斌, 任仲雪, 白光如, 刘璐, 赵增秀 2022 71 234204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y, Zhang B, Ren Z X, Bai G R, Liu L, Zhao Z X 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 234204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang B B, Li X F, Fu P M 1998 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 31 1961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Silaev A A, Romanov A A, Vvedenskii N V 2022 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2249 012004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Odžak S, Milošević D B 2006 Phys. Lett. A 355 368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hong W Y, LuP X, Cao W, Lan P F, Wang X L 2007 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 40 2321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yuan K J, Bandrauk A D 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 063422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Miao X Y, Liu S S 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 013301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Serrat C, Biegert J 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 073901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 陈基根, 陈高, 曾思良, 杨玉军, 朱颀人 2008 57 4104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen J G, Chen G, Zeng S L, Yang Y J, Zhu Q R 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 4104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Odžak S, Milošević D B 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 033407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao G J, Guo X L, Shao T J, Xue K 2011 New J. Phys. 13 093035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shi Y Z, Zhang B, Li B Y, Yu S J, Chen Y J 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 033406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lewenstein M, Balcou P, Ivanov M Y, Huillier A L, Corkum P B 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Majety V P, Scrinzi A 2015 J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 48 245603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 袁长全, 郭迎春, 王兵兵 2021 70 204206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan C Q, Guo Y C, Wang B B 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 204206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 不同外加静电场情况下的CO高次谐波谱 (a) 不外加静电场; (c) 外加静电场的方向从O指向C, 且β = 0.1; (e) 外加静电场的方向从C指向O, 且β = –0.1; (b), (d), (f) 3种情况对应各个通道的谐波谱
Figure 1. High order harmonic spectra of CO with different external static electric field: (a) Without external static electric field; (c) static field pointed from O to C and β = 0.1; (e) static field pointed from C to O and β = –0.1; (b), (d), (f) harmonic spectra of each channel for the former three cases.
图 2 不同外加静电场下 (a)—(l) 各通道在一个周期内发射的谐波合成的脉冲; (m)—(o) 经典情况发射的谐波阶次q和发射时间的关系(蓝色实线和红色短划线)以及总电场强度E随时间的关系(点线)
Figure 2. Under different external static electric fields: (a)–(l) Pulses from all harmonics emitted in each channel within an optical period; (m)–(o) harmonic order q versus harmonic emission time for classical situation (blue solid lines and red dash lines), and also present total electric field E versus time (dot lines).
-
[1] Phan N L, Le C T, Hoang V H, Le V H 2019 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21 24177
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hu H T, Li N, Liu P, Li R X, Xu Z Z 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 173201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Le C T, Hoang V H, Tran L P, Le V H 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 043405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang B, Yuan J M, Zhao Z X 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 035402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Koushki A M, Bonabi R S, Nia M M, Irani E 2018 Laser Phys. 28 075404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pan Y, Zhao S F, Zhou X X 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 035805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chen Y J, Fu L B, Liu J 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 073902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhu X S, Zhang Q B, Hong W Y, Lan P F, Lu P X 2011 Opt. Express 19 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Augstein B B, Faria C F M 2011 J. Mod. Optic. 58 1173
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 杨艳, 张斌, 任仲雪, 白光如, 刘璐, 赵增秀 2022 71 234204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y, Zhang B, Ren Z X, Bai G R, Liu L, Zhao Z X 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 234204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang B B, Li X F, Fu P M 1998 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 31 1961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Silaev A A, Romanov A A, Vvedenskii N V 2022 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2249 012004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Odžak S, Milošević D B 2006 Phys. Lett. A 355 368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hong W Y, LuP X, Cao W, Lan P F, Wang X L 2007 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 40 2321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yuan K J, Bandrauk A D 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 063422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Miao X Y, Liu S S 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 013301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Serrat C, Biegert J 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 073901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 陈基根, 陈高, 曾思良, 杨玉军, 朱颀人 2008 57 4104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen J G, Chen G, Zeng S L, Yang Y J, Zhu Q R 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 4104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Odžak S, Milošević D B 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 033407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao G J, Guo X L, Shao T J, Xue K 2011 New J. Phys. 13 093035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Shi Y Z, Zhang B, Li B Y, Yu S J, Chen Y J 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 033406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Lewenstein M, Balcou P, Ivanov M Y, Huillier A L, Corkum P B 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Majety V P, Scrinzi A 2015 J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 48 245603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 袁长全, 郭迎春, 王兵兵 2021 70 204206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan C Q, Guo Y C, Wang B B 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 204206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4251
- PDF Downloads: 125
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad:

