-
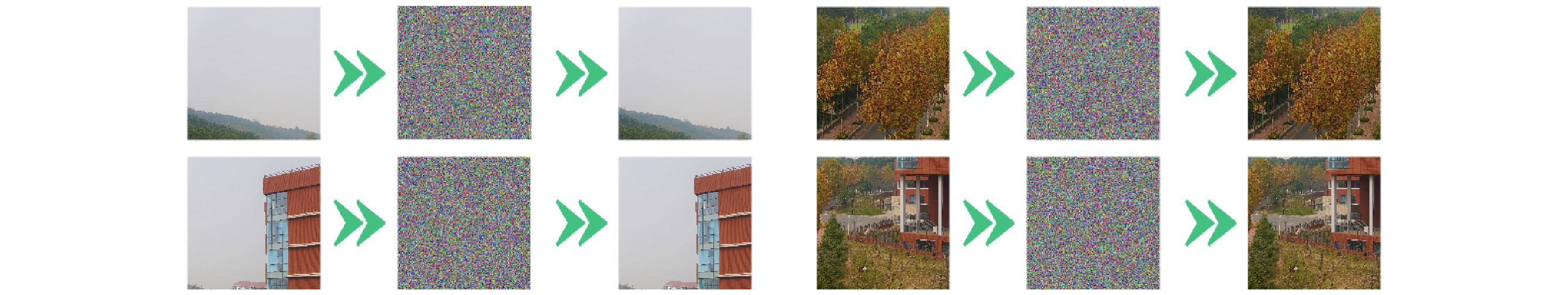
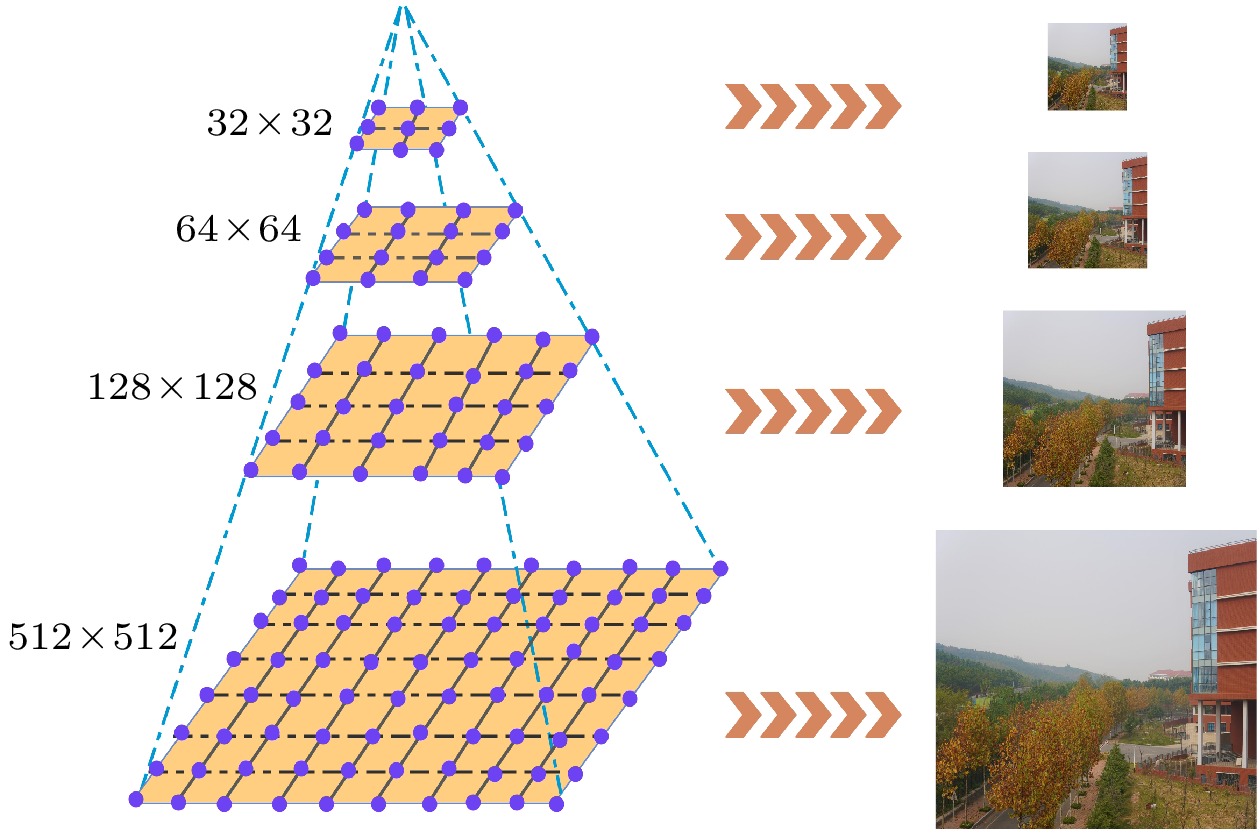
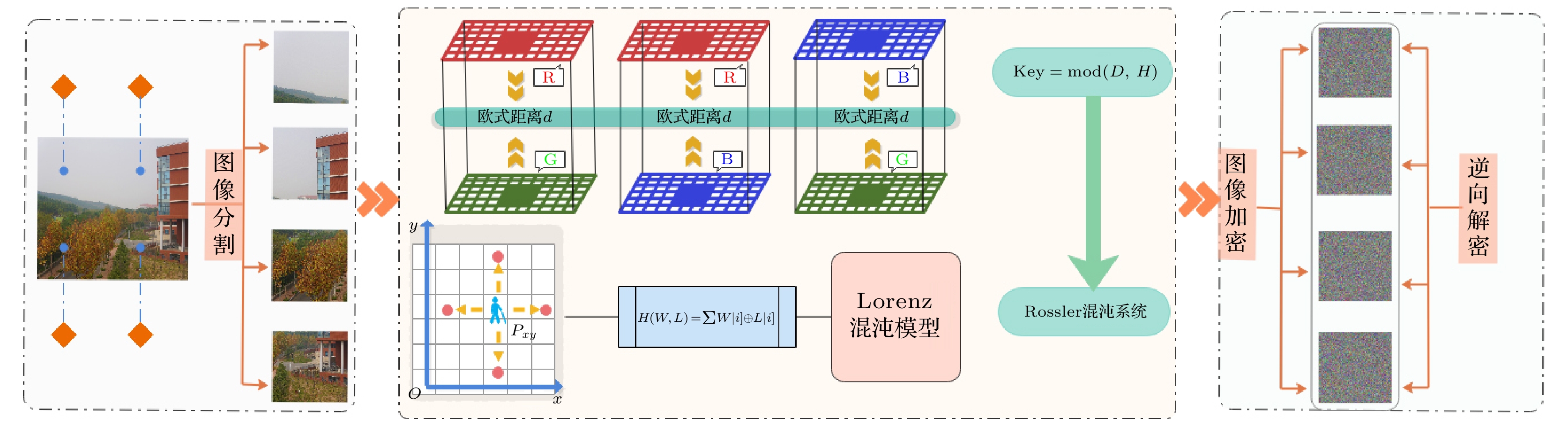
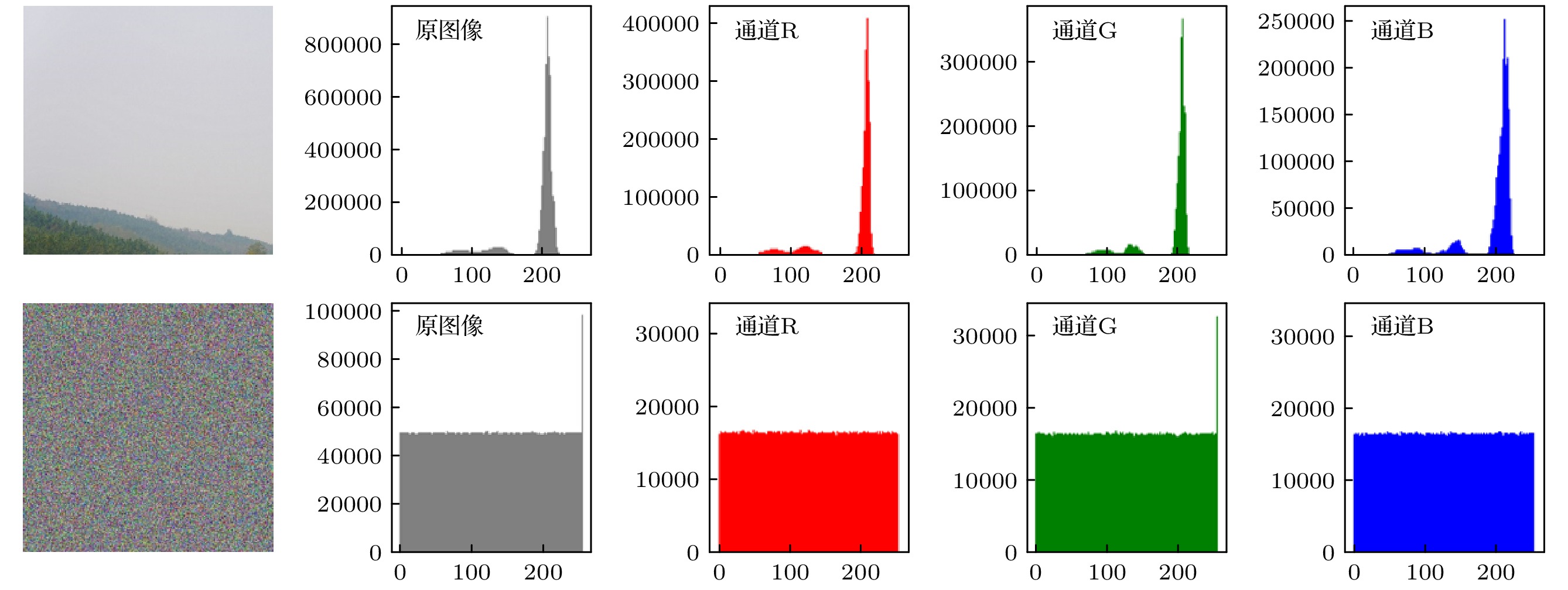
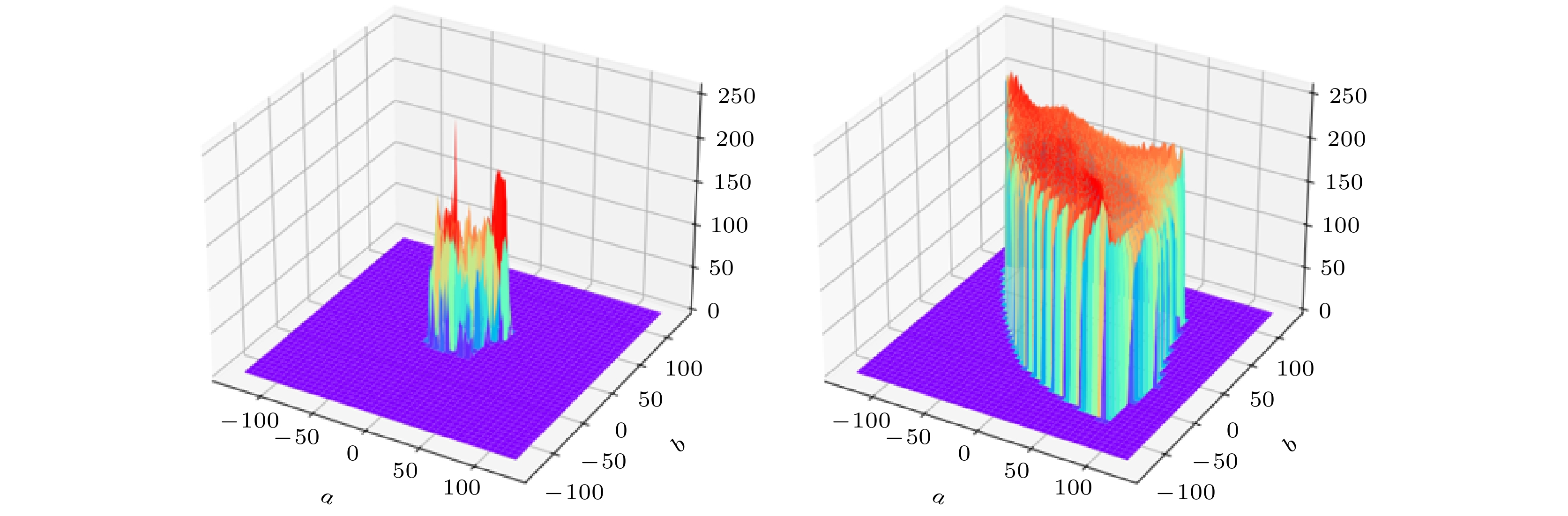
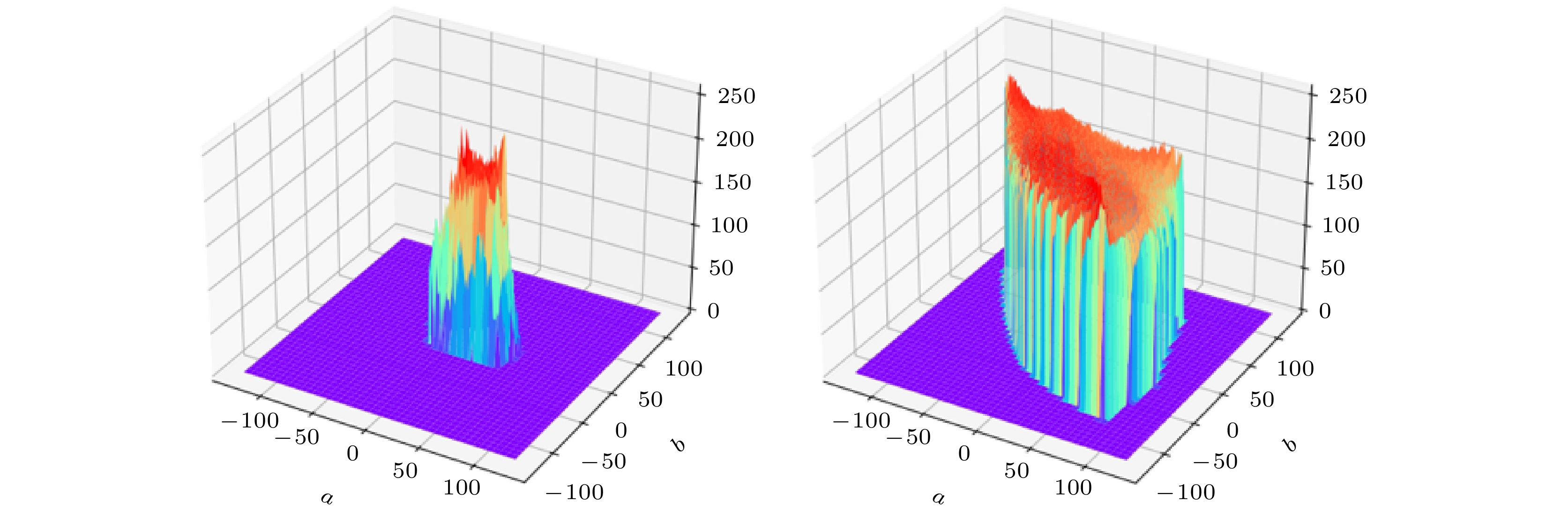
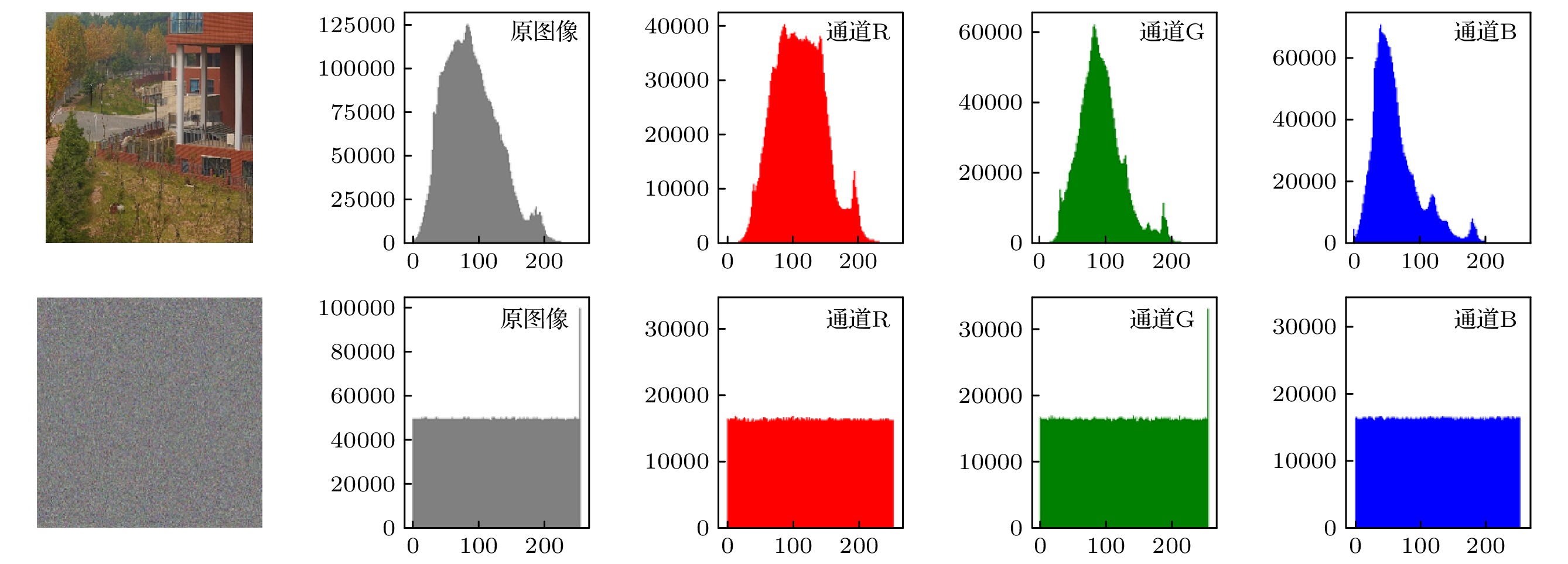
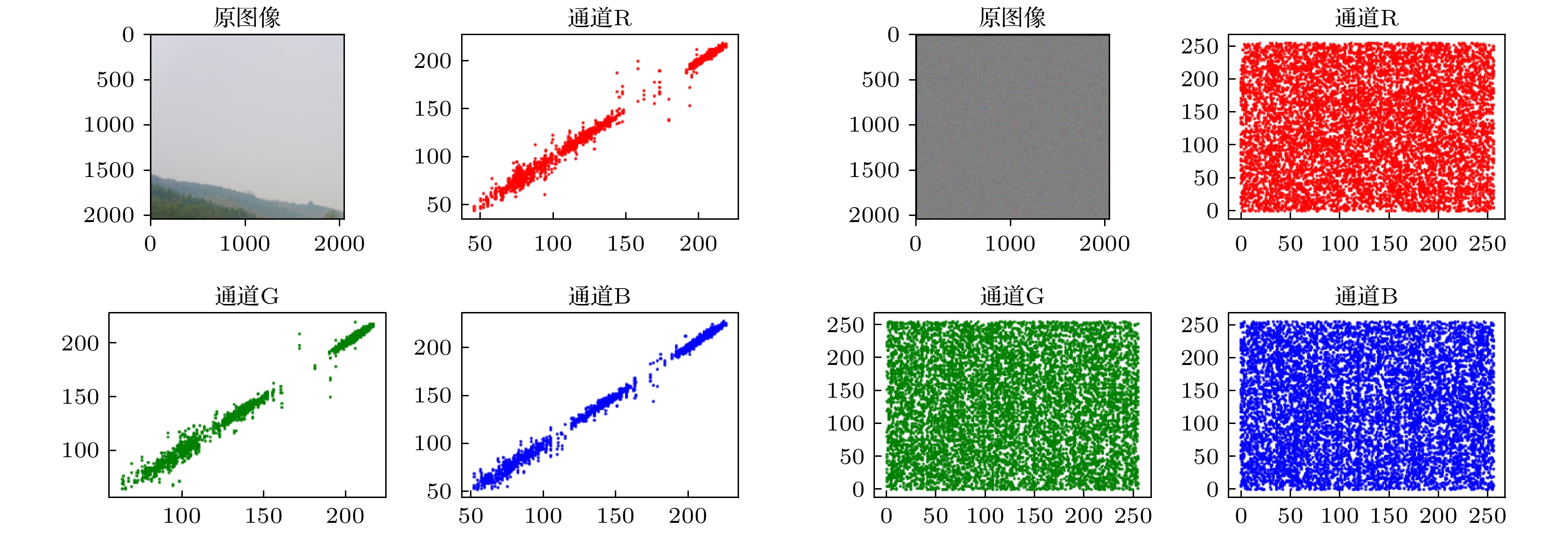
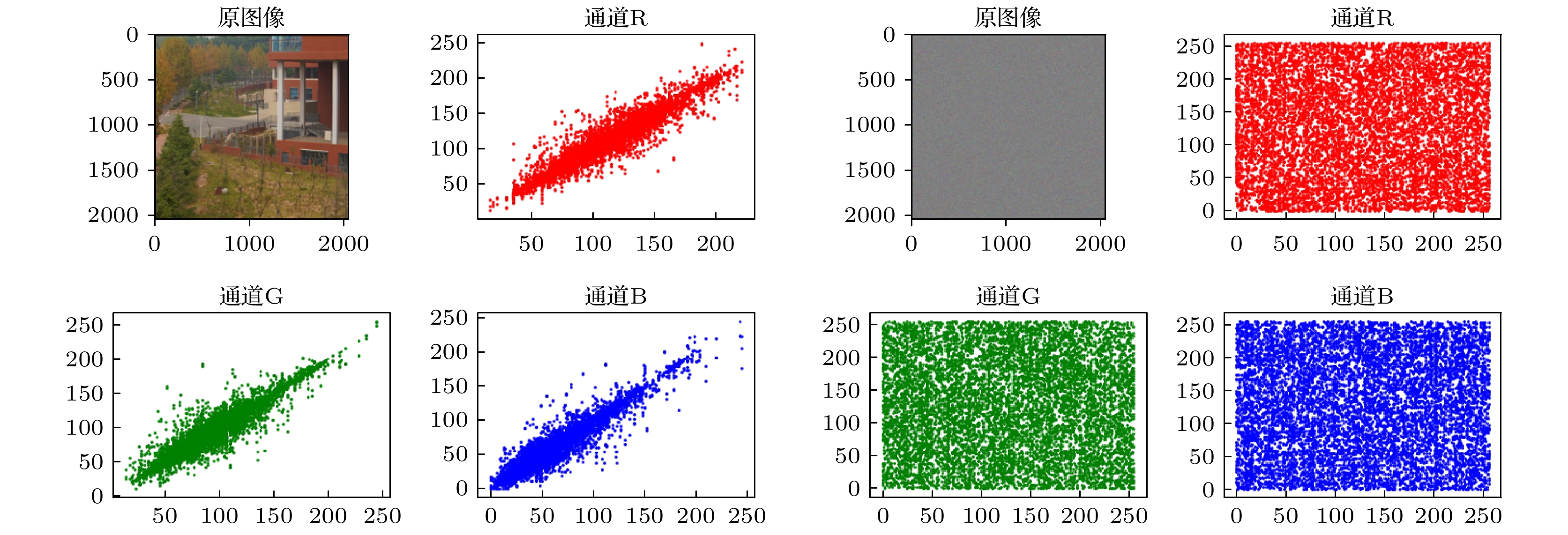
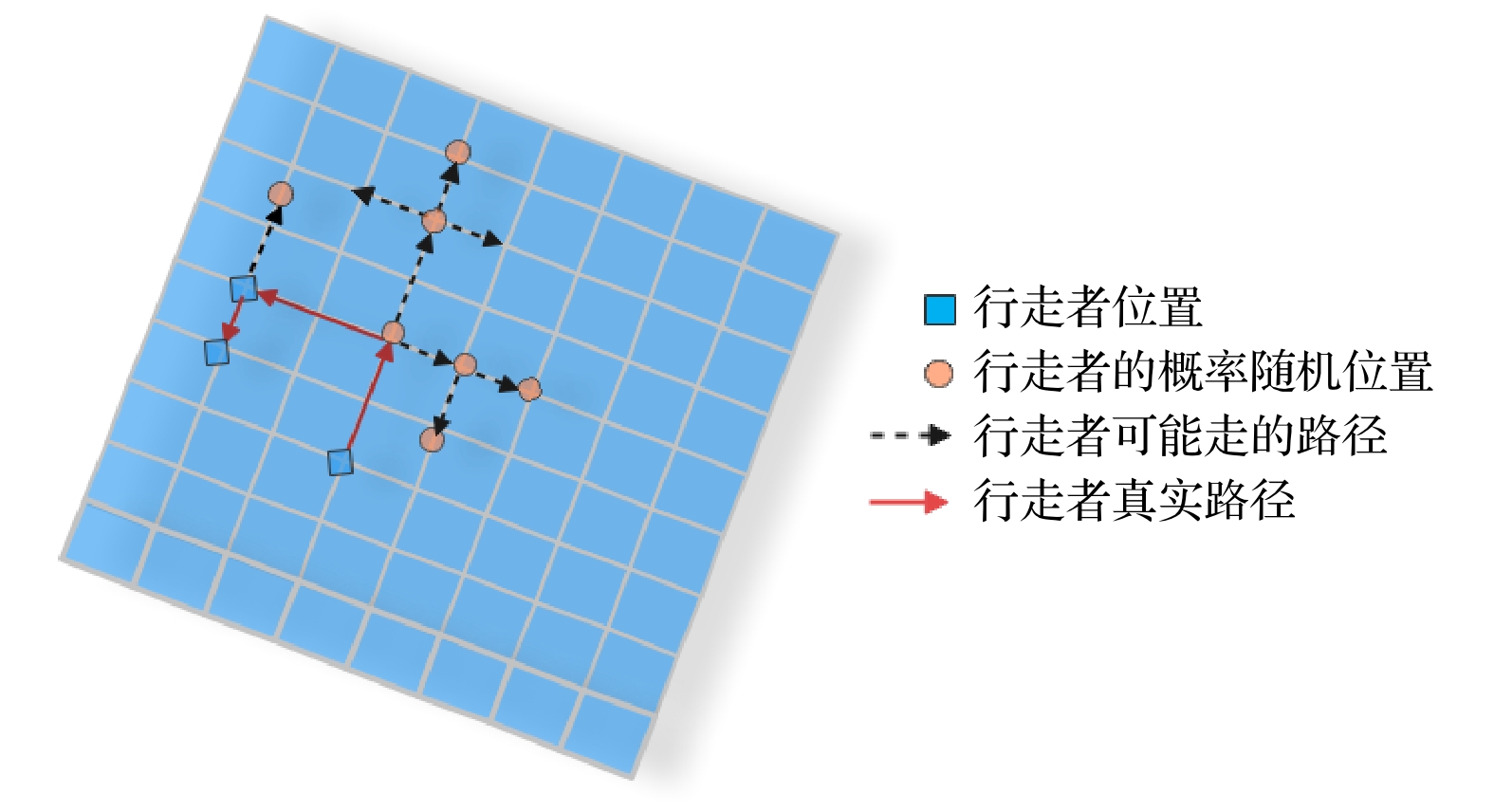
With the development of computer network technology, people’s requirements for information security is increasing day by day. However, the classical encryption technology has the defects of small key space and easy crack. The problems of image encryption technology in protecting image information security and private content need solving urgently. As a new type of quantum key generator, quantum random walk has a large key space. Compared with the classical random walk, the computing speed and security are significantly improved. This paper presents a three-dimensional image encryption algorithm that is based on quantum random walk and involves Lorenz and Rossler multidimensional chaos. Firstly, Gaussian pyramid is used to segment the image. Secondly, the Hamming distances of several sub images are calculated by using the random sequence generated by quantum random walk and the random sequence generated by Lorenz chaotic system in multi-dimensional chaos, and then synthesized, and the Euclidean distances between the three RGB channels of the image are calculated. Finally, the sequence value obtained from the remainder of Hamming distance and Euclidean distance, as an initial value is input into the Rossler system in multi-dimensional chaos to generate a random sequence which is used as the key to XOR the RGB channel of the image so as to create an encrypted image. The corresponding decryption scheme is the inverse process of the encryption process. In addition, in terms of transmission security, this paper uses a blind watermark embedding algorithm based on DCT and SVD to embed the watermark information into the encrypted image, so that the receiver can extract the watermark and judge whether the image is damaged by the attack in the transmission process according to the integrity of the watermark information. If it is not attacked maliciously, the image will be decrypted. This operation further improves the protection of image information security.The experimental results show that the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the encrypted image is stable between 7 and 9 and the encryption effect is good, the GVD score is close to 1, the correlation of the encrypted image is uniformly distributed, and the correlation coefficient is close to 0, and the key space is 2128 in size and the encrypted histogram is evenly distributed, showing a high ability to resist statistical analysis attacks.
-
Keywords:
- quantum walk /
- chaotic model /
- image encryption /
- blind watermarking
[1] Zheng R H, Xiao Y, Su S L, Chen Y H, Shi Z C, Song J, Xia Y, Zheng S B 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 052402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kang Y H, Shi Z C, Huang B H, Song J, Xia Y 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 032322
[3] Long G L 2001 Phys. Rev. A 64 022307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Long G L, Li X, Sun Y 2002 Phys. Lett. A 294 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Aharonov Y, Davidovich L, Zagury N 1993 Phys. Rev. A 48 1687
[6] Farhi E, Gutmann S 1998 Phys. Rev. A 58 915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Childs A M, Cleve R, Deotto E, Farhi E, Gutmann S, Spielman D A 2003 STOC’03: Proceedings of the Thirty-fifth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (New York: Association for Computing Machinery) pp59–68
[8] Castagnoli G 2016 Found. Phys. 46 360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Castagnoli G 2016 Quanta. 5 34
[10] Gong L H, Song H C, He C S, Liu Y, Zhou N R 2014 Phys. Scr. 89 035101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li H H, Gong L H, Zhou N R 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 110304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Watrous J 2001 J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 62 376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Abd El-Latif A A, Abd-El-Atty B, Venegas-Andraca S E, Elwahsh H, Piran M J, Bashir A K, Song O Y, Mazurczyk W, 2020 IEEE Access 8 92687
[14] Abd-El-Atty B, Iliyasu A M, Alaskar H, Alaskar H, Abd-El-Latif A A 2020 Sensors 20 3108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Abd El-Latif A A, Abd-El-Atty B, Mazurczyk W, Fung C, Venegas-Andraca S E 2020 IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manage. 17 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Abd El-Latif A A, Abd-El-Atty B, Elseuofi S, Khalifa H S, Alghamdi A S, Polat K, Amin M 2020 Physica A 541 123687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Abd El-Latif A A, Abd-El-Atty B, Amin M, Iliyasu A M 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Abd-El-Atty B, Iliyasu A M, Alanezi A, Abd El-latif AA 2021 Opt. Lasers Eng. 138 106403
[19] Smith J D, Hill A J, Reeder L E, Franke B C, Lehoucp R B, Parekh O, Severa, M, Aimone J B 2022 Nat. Electron. 5 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Godsil C, Zhan H M 2019 J. Comb. Theory A 167 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Singh S, Chawla P, Sarkar A, Chandrashekar C M 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 1
[22] Tsafack N, Kengne J, Abd-El-Atty B, Iliyasu A M, Hirota K, Abd EL-Latif A A 2020 Inf. Sci. 515 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 王一诺, 宋昭阳, 马玉林, 华南, 马鸿洋 2021 70 10
Wang Y N, Song Z Y, Ma Y L, Hua N, Ma H Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 10
[24] Kocarev L 2001 IEEE. Circ. Syst. Mag. 1 6
[25] Guan Z H, Huang F J, Guan W J 2005 Phys. Lett. A 346 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lian S G, Sun J S, Wang Z Q 2005 Physica A 351 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Xiao D, Liao X F, Wei P C 2009 Chaos. Solitons Fractals 40 2191
[28] Zhang X P, Zhao Z M, Wang J Y 2014 Signal Process. Image Commun. 29 902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Assad S E, Farajallah M 2016 Signal Process. Image Commun. 41 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang M G, Wang X Y, Zhang Y Q, Zhou S, Zhao T T, Yao N M 2019 Opt. Lasers Eng. 121 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Kumar V, Girdhar A 2021 Multimed Tools Appl. 80 3749
[32] Huang W, Jiang D H, An Y S, Liu L D, Wang X Y 2021 IEEE Access 9 41704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Rakesh S, Kaller A A, Shadakshari B C, Annappa B 2012 IJCIS 2 49
[34] Huang X L, Ye G D 2014 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 19 4094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wang M X, Wang X Y, Zhang Y Q, Zheng G 2018 Opt. Laser Technol. 108 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Zhou W J, Wang X Y, Wang M X, Li D Y 2022 Opt. Laser Eng. 149 106782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 原始图像1和加密图像1的相关性数值分析
Table 1. Numerical analysis of correlation between original image 1 and encrypted image 1
图像 通道 Horizontal Vertical Diagonal 图像1 R 0.9985 0.9990 0.9976 G 0.9980 0.9988 0.9973 B 0.9980 0.9991 0.9975 加密图像1 R –0.0136 –0.0325 –0.0304 G 0.0304 0.0014 0.0251 B –0.0234 0.0221 0.0051 表 2 原始图像2和加密图像2的相关性数值分析
Table 2. Numerical analysis of correlation between original image 2 and encrypted image 2
图像 通道 Horizontal Vertical Diagonal 图像2 R 0.9910 0.9858 0.9752 G 0.9954 0.9941 0.9883 B 0.9969 0.9962 0.9930 加密图像2 R –0.0136 –0.0325 –0.0304 G 0.0304 0.0014 0.0251 B –0.0234 0.0221 0.0051 表 3 原始图像3和加密图像3的相关性数值分析
Table 3. Numerical analysis of correlation between original image 3 and encrypted image 3
图像 通道 Horizontal Vertical Diagonal 图像3 R 0.9293 0.9631 0.8961 G 0.9077 0.9522 0.8648 B 0.9011 0.9379 0.8484 加密图像3 R –0.0069 –0.0081 –0.0218 G –0.0070 0.0065 –0.0245 B –0.0117 0.0249 –0.0134 表 4 原始图像4和加密图像4的相关性数值分析
Table 4. Numerical analysis of correlation between original image 4 and encrypted image 4
图像 通道 Horizontal Vertical Diagonal 图像4 R 0.9568 0.9750 0.9379 G 0.9449 0.9665 0.9170 B 0.9540 0.9746 0.9346 加密图像4 R –0.0162 –0.0055 0.0147 G 0.0006 0.0003 –0.0060 B 0.0207 –0.0291 0.0017 表 5 GVD
Table 5. GVD
GVD 原始-加密
图像1原始-加密
图像2原始-加密
图像3原始-加密
图像4R 0.9993 0.995 0.9755 0.9809 G 0.9993 0.9947 0.9763 0.9815 B 0.9993 0.995 0.9804 0.9826 表 6 密钥敏感性分析
Table 6. Key sensitivity analysis
图像 通道 NPCR/% UACI/% 图像1 R 99.5687 33.4381 G 99.6098 33.4594 B 99.6180 33.4347 图像2 R 99.5690 33.4386 G 99.6100 33.4598 B 99.6186 33.4350 图像3 R 99.5684 33.4378 G 99.6094 33.4588 B 99.6174 33.4437 图像4 R 99.5688 33.4376 G 99.6088 33.4590 B 99.6170 33.4347 表 7 峰值信噪比
Table 7. Peak signal to noise ratio
PSNR 原始-加密
图像1原始-加密
图像2原始-加密
图像3原始-加密
图像4R 7.691 8.376 9.369 9.582 G 7.755 8.132 8.686 9.193 B 7.479 7.747 6.782 7.782 表 8 嵌入水印的峰值信噪比
Table 8. Peak signal to noise ratio of embedded watermark
PSNR 加密-嵌入
水印1加密-嵌入
水印2加密-嵌入
水印3加密-嵌入
水印4R 38.81 38.81 38.8 38.79 G 40.28 40.29 40.26 40.28 B 35.46 35.48 35.47 35.47 -
[1] Zheng R H, Xiao Y, Su S L, Chen Y H, Shi Z C, Song J, Xia Y, Zheng S B 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 052402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kang Y H, Shi Z C, Huang B H, Song J, Xia Y 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 032322
[3] Long G L 2001 Phys. Rev. A 64 022307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Long G L, Li X, Sun Y 2002 Phys. Lett. A 294 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Aharonov Y, Davidovich L, Zagury N 1993 Phys. Rev. A 48 1687
[6] Farhi E, Gutmann S 1998 Phys. Rev. A 58 915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Childs A M, Cleve R, Deotto E, Farhi E, Gutmann S, Spielman D A 2003 STOC’03: Proceedings of the Thirty-fifth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (New York: Association for Computing Machinery) pp59–68
[8] Castagnoli G 2016 Found. Phys. 46 360
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Castagnoli G 2016 Quanta. 5 34
[10] Gong L H, Song H C, He C S, Liu Y, Zhou N R 2014 Phys. Scr. 89 035101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li H H, Gong L H, Zhou N R 2020 Chin. Phys. B 29 110304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Watrous J 2001 J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 62 376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Abd El-Latif A A, Abd-El-Atty B, Venegas-Andraca S E, Elwahsh H, Piran M J, Bashir A K, Song O Y, Mazurczyk W, 2020 IEEE Access 8 92687
[14] Abd-El-Atty B, Iliyasu A M, Alaskar H, Alaskar H, Abd-El-Latif A A 2020 Sensors 20 3108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Abd El-Latif A A, Abd-El-Atty B, Mazurczyk W, Fung C, Venegas-Andraca S E 2020 IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manage. 17 118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Abd El-Latif A A, Abd-El-Atty B, Elseuofi S, Khalifa H S, Alghamdi A S, Polat K, Amin M 2020 Physica A 541 123687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Abd El-Latif A A, Abd-El-Atty B, Amin M, Iliyasu A M 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Abd-El-Atty B, Iliyasu A M, Alanezi A, Abd El-latif AA 2021 Opt. Lasers Eng. 138 106403
[19] Smith J D, Hill A J, Reeder L E, Franke B C, Lehoucp R B, Parekh O, Severa, M, Aimone J B 2022 Nat. Electron. 5 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Godsil C, Zhan H M 2019 J. Comb. Theory A 167 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Singh S, Chawla P, Sarkar A, Chandrashekar C M 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 1
[22] Tsafack N, Kengne J, Abd-El-Atty B, Iliyasu A M, Hirota K, Abd EL-Latif A A 2020 Inf. Sci. 515 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 王一诺, 宋昭阳, 马玉林, 华南, 马鸿洋 2021 70 10
Wang Y N, Song Z Y, Ma Y L, Hua N, Ma H Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 10
[24] Kocarev L 2001 IEEE. Circ. Syst. Mag. 1 6
[25] Guan Z H, Huang F J, Guan W J 2005 Phys. Lett. A 346 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lian S G, Sun J S, Wang Z Q 2005 Physica A 351 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Xiao D, Liao X F, Wei P C 2009 Chaos. Solitons Fractals 40 2191
[28] Zhang X P, Zhao Z M, Wang J Y 2014 Signal Process. Image Commun. 29 902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Assad S E, Farajallah M 2016 Signal Process. Image Commun. 41 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wang M G, Wang X Y, Zhang Y Q, Zhou S, Zhao T T, Yao N M 2019 Opt. Lasers Eng. 121 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Kumar V, Girdhar A 2021 Multimed Tools Appl. 80 3749
[32] Huang W, Jiang D H, An Y S, Liu L D, Wang X Y 2021 IEEE Access 9 41704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Rakesh S, Kaller A A, Shadakshari B C, Annappa B 2012 IJCIS 2 49
[34] Huang X L, Ye G D 2014 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 19 4094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wang M X, Wang X Y, Zhang Y Q, Zheng G 2018 Opt. Laser Technol. 108 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Zhou W J, Wang X Y, Wang M X, Li D Y 2022 Opt. Laser Eng. 149 106782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8648
- PDF Downloads: 186
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: