-
With the rapid development of computer science, the storage and dissemination of information are often carried out between various types of computer hardwares and various networks. The traditional information encryption scheme has gradually disappeared. Therefore, computer-based information encryption algorithms have gradually become a research hotspot in recent years. By combining the theory of wavelet packet transform, compressed sensing and chaotic system, a multi-process image encryption scheme based on compressed sensing and multi-dimensional chaotic system is proposed. The encryption scheme implements compression and encryption for grayscale images and corresponding decompression and decryption process. The wavelet packet transform theory is applied to the image preprocessing stage to perform wavelet packet decomposition on the original image. At the same time, the image signal components obtained by the decomposition are classified according to the threshold processing method, and the characteristics of the image signal components are processed in the subsequent processing. They are compressed, encrypted, or reserved in a differentiated manner. In the image compression stage, by introducing the compressed sensing algorithm to overcome the shortcomings of the traditional Nyquist sampling theorem, such as high sampling cost and low reconstruction quality, the compression efficiency and compression quality are improved while the ciphertext image reconstruction quality is guaranteed. In the image encryption stage, the encryption scheme combines multi-class and multi-dimensional chaotic systems to confuse and scramble the related image signal components, and introduces a high-dimensional chaotic system to make the encryption scheme have a large enough key space to further enhance the ciphertext image reliability. Finally, the complete reconstruction of the original image is achieved by applying the inverse of compression, encryption and wavelet packet transform. The simulation results show that the image encryption scheme effectively protects the basic information about ciphertext images by virtue of algorithm robustness against external interference, and does not reveal any useful information when dealing with cracking methods such as plaintext attacks. In addition, the information entropy and correlation coefficient of ciphertext images encrypted by this encryption scheme are closer to ideal values than those of the encryption algorithm in the references, and its encryption performance is significantly improved.
-
Keywords:
- digital image /
- encryption /
- wavelet packet transform /
- compressed sensing
[1] 吴成茂 2014 63 090504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu C M 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 090504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 林青, 王延江, 王珺 2016 中国科学: 技术科学 46 910
Lin Q, Wang Y J, Wang J 2016 Sci. China: Technol. Sci. 46 910
[3] 李静, 向菲, 张军朋 2019 电子设计工程 27 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J, Xian F, Zhang J P 2019 Int. Electr. Elem. 27 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Donoho D L 2006 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52 1289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chai X L, Zheng X Y, Gan Z H, Han D J, Chen Y R 2018 Signal Process 148 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhu S Q, Zhu C X, Wang W H 2018 IEEE Access. 6 67095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lü X P, Liao X F, Yang B 2018 Multimed Tools Appl. 77 28633
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hilton M L 1997 IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 44 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张祥, 张达永, 张刘辉, 潘栋 2016 气象水文海洋仪器 33 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang D Y, Zhang L H, Pan D 2016 Meteorol. Hydrol. Mar. Instrum. 33 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Goklani H S 2017 Int. J. Image, Graphics and Signal Processing 9 30
[11] Huang R, Rhee K H, Uchida S 2012 Multimed Tools Appl. 7 2
[12] Zhou N, Pan S, Cheng S, et al. 2016 Opt. Laser Technol. 82 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 禹思敏 2008 57 3374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu S M 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 3374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 禹思敏 2011 混沌系统与混沌电路 (西安:西安电子科技大学出版社) 第136−137页
Yu S M 2011 Chaotic Systems and Chaotic Circuits (Xi’ an: Xi 'an University of Electronic Science and Technology Press) pp136−137 (in Chinese)
[15] Chen G R 1999 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 9 1465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王鸣天, 郭玉奇 2017 电子技术 46 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang M T, Guo Y Q 2017 Electr. Technol. 46 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Li C Q 2013 Nonlinear Dyn. 73 2083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 高展鸿, 徐文波 2011 基于MATLAB的图像处理案例教程 (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第99−101页
Gao Z H, Xu W B 2011 MATLAB-Based Image Processing Case Tutorial (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp99−101 (in Chinese)
[19] 张勇 2016 混沌数字图像加密 (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第50−59页
Zhang Y 2016 Chaotic Digital Image Crptosystem (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp50−59 (in Chinese)
[20] 王静, 蒋国平 2011 60 060503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Jiang G P 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 060503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang Y, Xiao D 2013 Opt. Lasers Eng. 51 472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
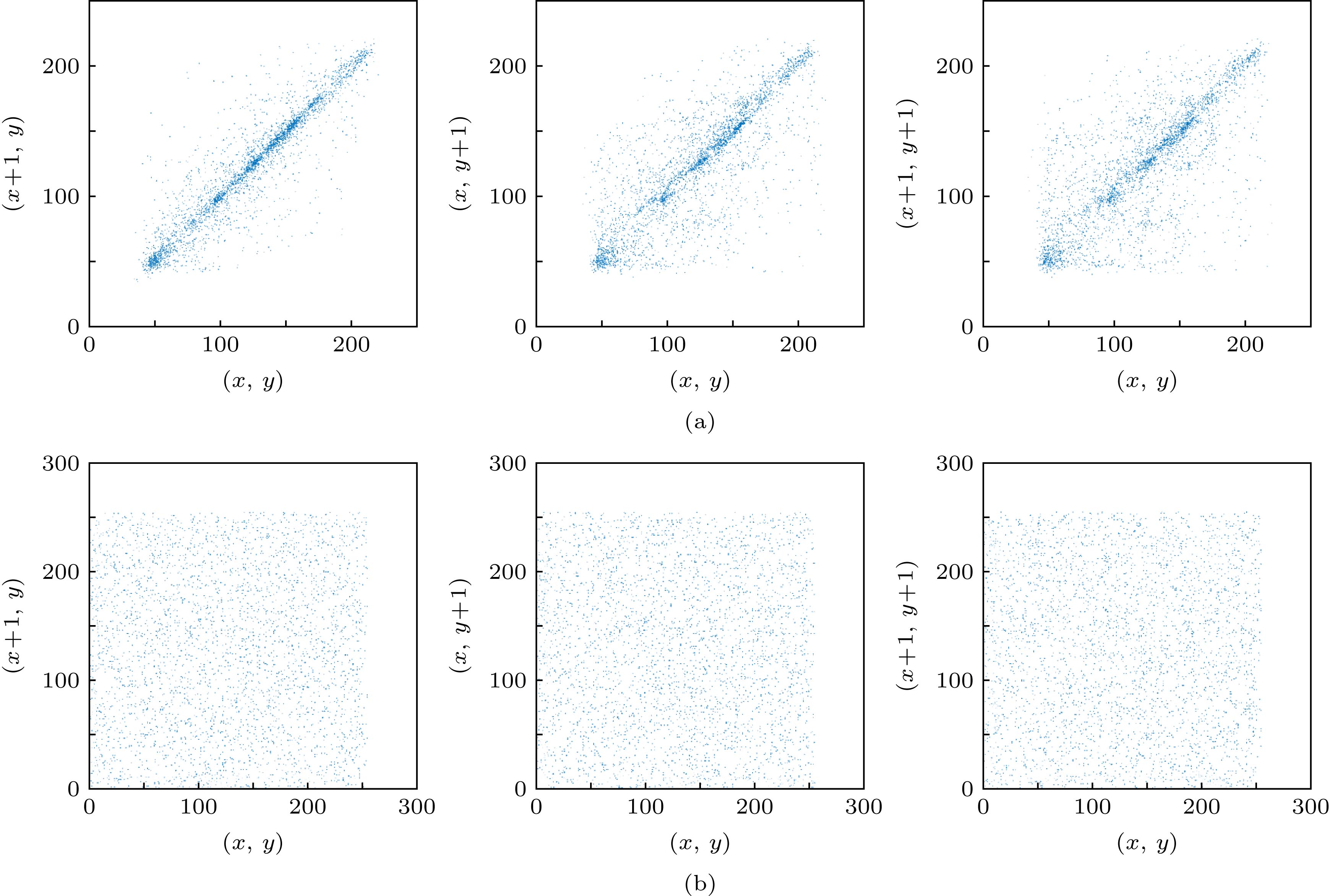
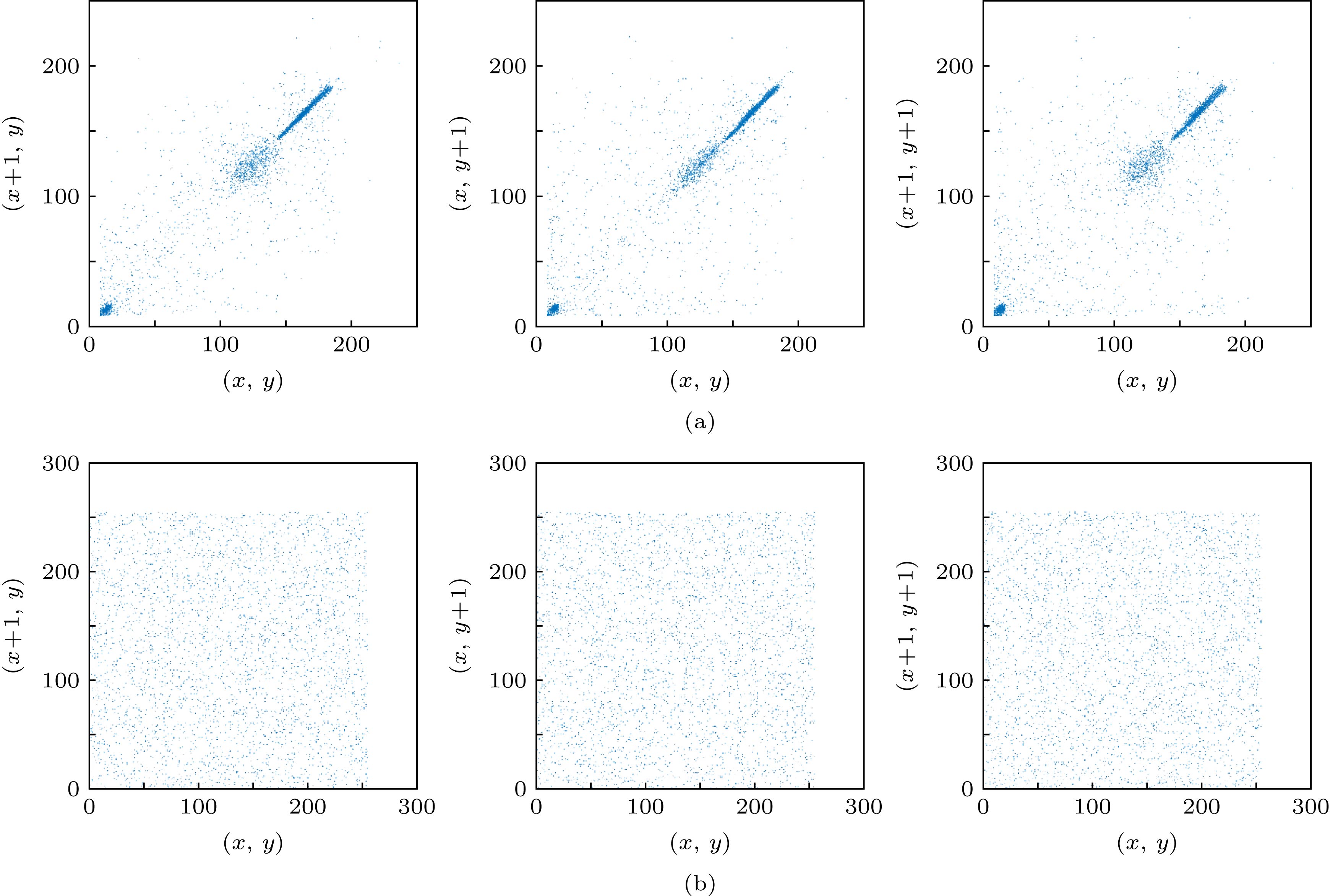
图 9 Lena图像的明文(S信号)、密文图像在水平、竖直、斜线三个方向的相关分布图 (a)明文图像相关分布图; (b) S信号的密文图像相关分布图
Figure 9. Correlation distribution of plaintext, ciphertext image in horizontal, vertical and oblique directions of S signal of Lena: (a) Correlation distribution of plaintext of S signal; (b) correlation distribution of ciphertext of S signal.
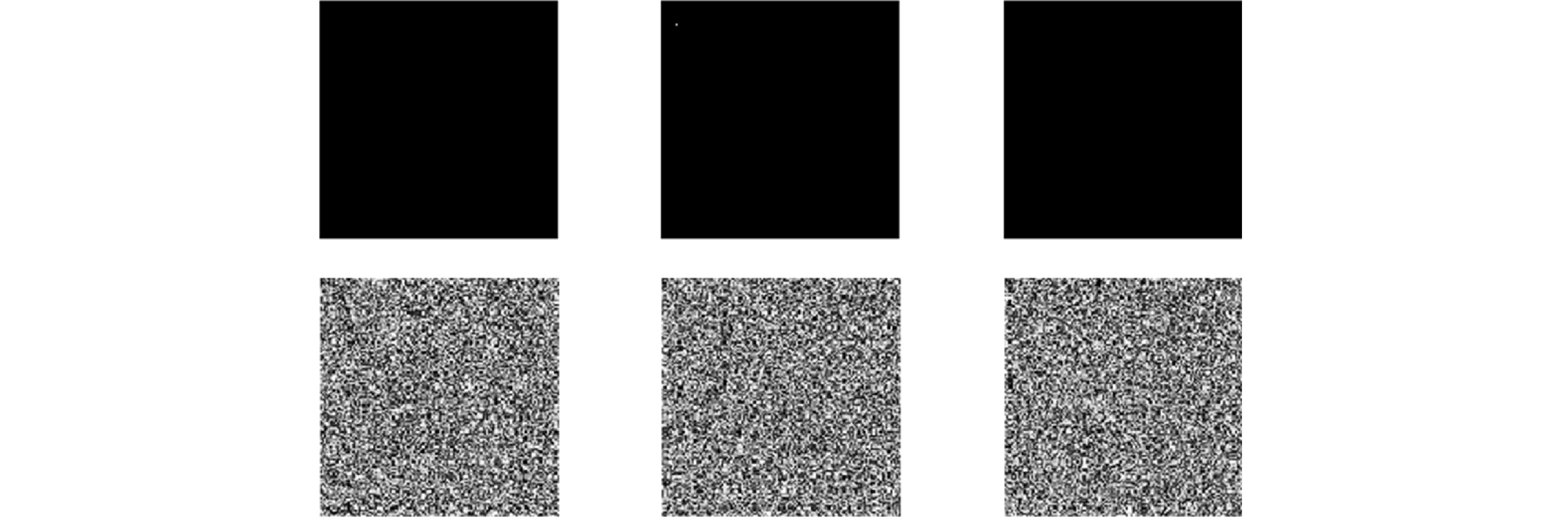
图 11 Cameraman图像的明文(S信号)、密文图像在水平、竖直、斜线三个方向的相关分布图 (a)明文图像相关分布图; (b) S信号的密文图像相关分布图
Figure 11. Correlation distribution of plaintext, ciphertext image in horizontal, vertical and oblique directions of S signal of Cameraman: (a) Correlation distribution of plaintext of S signal; (b) correlation distribution of ciphertext of S signal
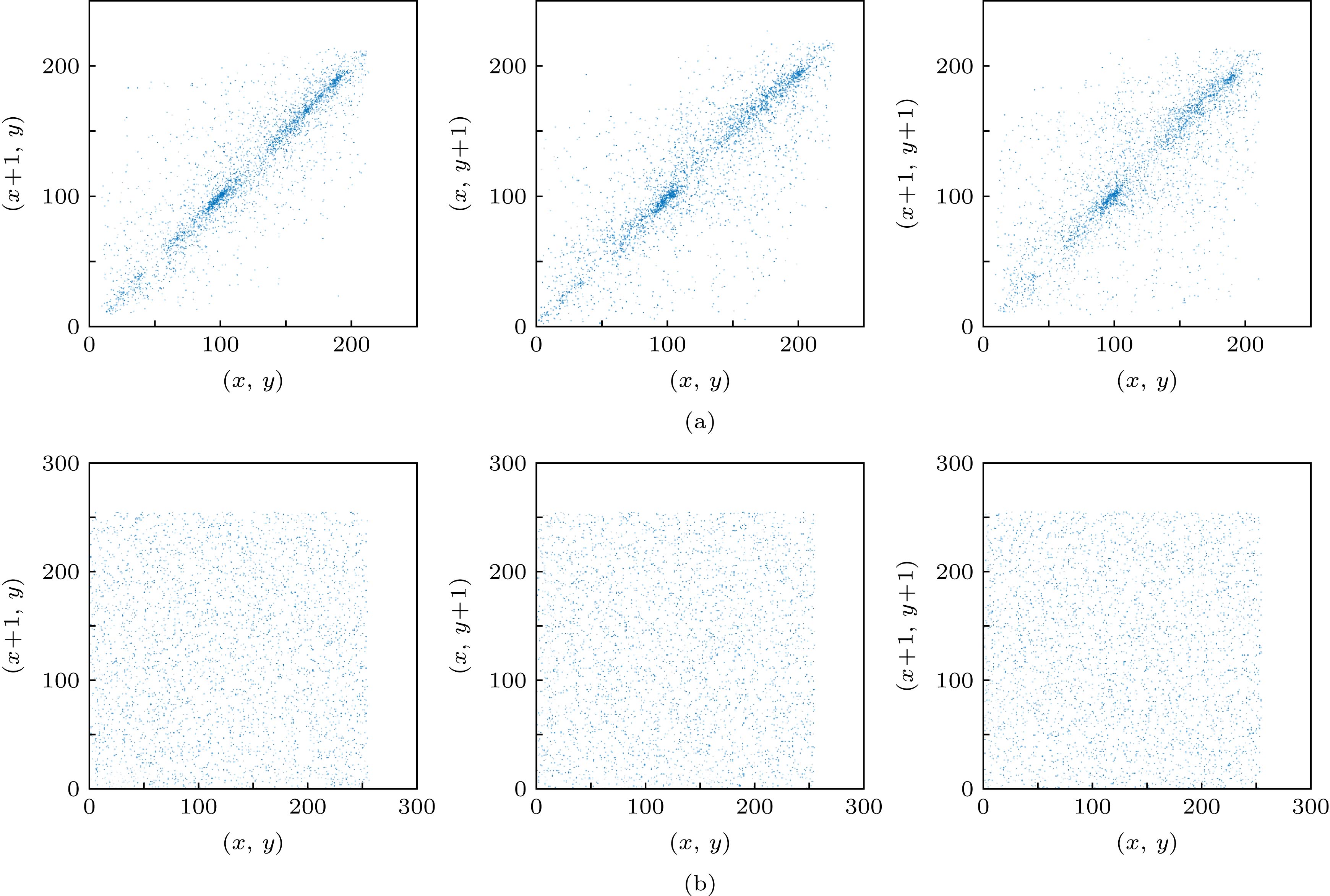
图 10 Pepper图像的明文(S信号)、密文图像在水平、竖直、斜线三个方向的相关分布图 (a)明文图像相关分布图; (b) S信号的密文图像相关分布图
Figure 10. Correlation distribution of plaintext, ciphertext image in horizontal, vertical and oblique directions of S signal of Pepper: (a) Correlation distribution of plaintext of S signal; (b) correlation distribution of ciphertext of S signal.
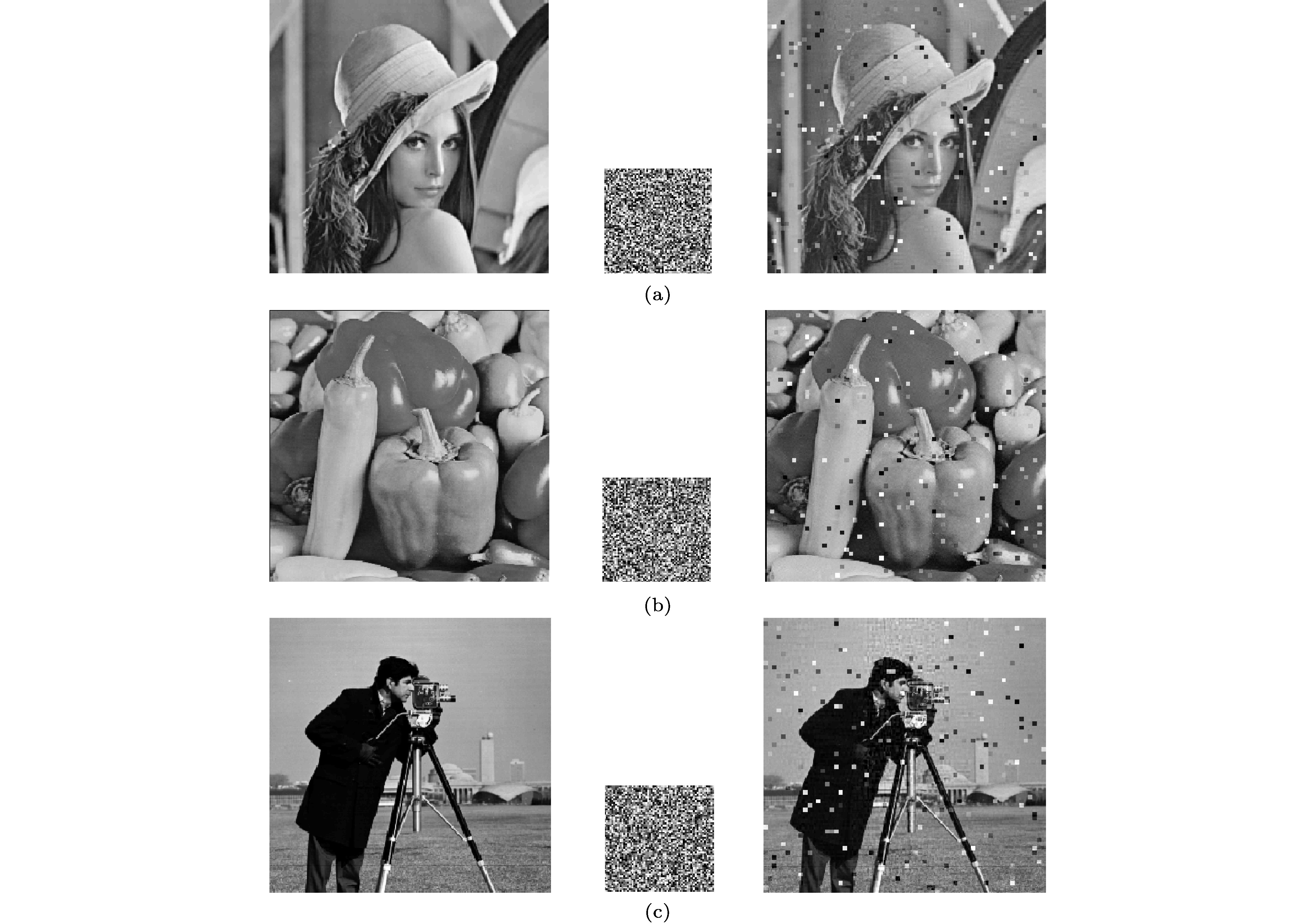
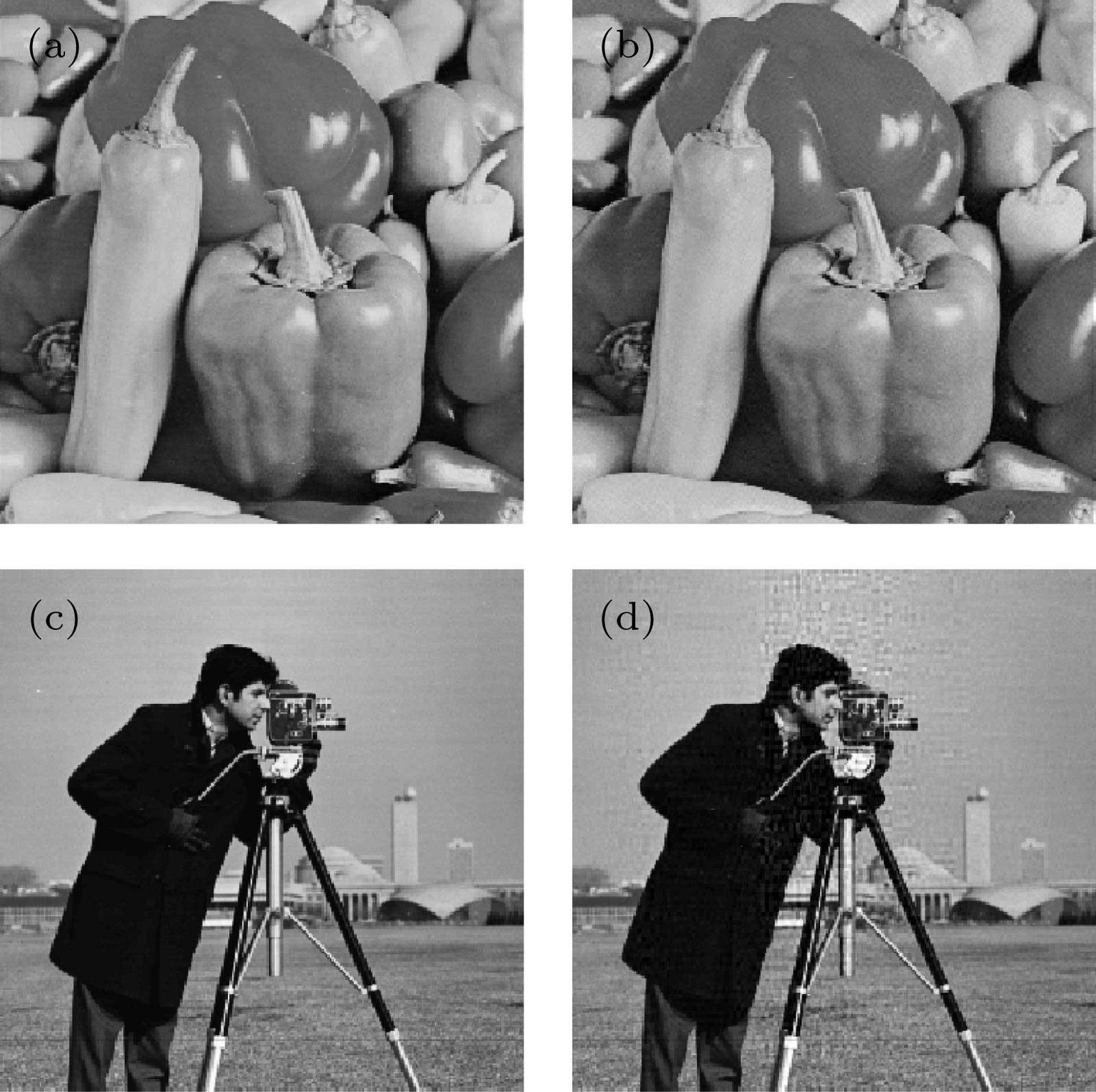
图 13 不同图像的S信号嵌入噪声后的重构结果 (a) Lena原始图像、嵌入噪声的S信号密文、重构图像; (b) Pepper原始图像、嵌入噪声的S信号密文、重构图像; (c) Cameraman原始图像、嵌入噪声的S信号密文、重构图像
Figure 13. Reconstruction results of S signals of different images embedded with noise: (a) Reconstruction results of Lena with corresponding Cipher S signal embedded noise; (b) reconstruction results of Pepper with corresponding Cipher S signal embedded noise; (c) reconstruction results of Cameraman with corresponding Cipher S signal embedded noise
图 14 不同图像的S信号像素剪切后的重构结果 (a) Lena原始图像、剪切12.5%像素点后的S信号密文、重构图像; (b) Pepper原始图像、剪切12.5%像素点后的S信号密文、重构图像; (c) Cameraman原始图像、剪切12.5%像素点后的S信号密文、重构图像
Figure 14. Reconstruction results of S signals of different images after pixel shearing: (a) Reconstruction results of Lena with corresponding Cipher S signal with 12.5% pixels lost; (b) reconstruction results of Pepper with corresponding Cipher S signal with 12.5% pixels lost; (c) reconstruction results of Cameraman with corresponding Cipher S signal with 12.5% pixels lost
表 1 Lena图像Ci信号分量0像素点的个数及占比
Table 1. The number and proportion of 0 pixels in Ci signals in Lena.
信号分量 0像素点个数 0像素点占比/% C1 329 8.03 C2 554 13.53 C3 703 17.16 C4 682 16.65 C5 436 10.64 C6 917 22.39 C7 842 20.56 C8 789 19.26 表 2 比较不同加密方案的相关系数
Table 2. Comparisons for the correlation coefficients of different encryption scheme.
图像 明文图像 密文图像 水平 竖直 斜线 水平 竖直 斜线 Lena (本文) 0.9189 0.7339 0.8097 –0.0002 –0.0004 0.0001 Lena[16] 0.9180 0.7345 0.8083 0.0032 0.0025 –0.0173 Lena[17] 0.9151 0.8097 0.7484 –0.0274 0.0051 –0.0117 Pepper (本文) 0.8849 0.7567 0.8323 –0.0003 –0.0004 0.0003 Pepper[16] 0.8827 0.8374 0.7482 0.0210 0.0010 0.0071 Pepper[17] 0.8864 0.8398 0.7466 0.0070 –0.0198 –0.0228 Cameraman (本文) 0.9275 0.8364 0.8866 0.0004 0.0001 0.0002 Cameraman [16] 0.9339 0.8898 0.8459 –0.0035 –0.0014 0.0159 Cameraman[17] 0.9280 0.8835 0.8411 0.0277 0.0141 0.0281 表 3 比较不同加密方案的信息熵
Table 3. Comparisons for the entropy of different encryption scheme.
表 4 修改1 bit像素点后不同图像(S信号)的NPCR, UACI, BACI
Table 4. NPCR, UACI, BACI of different images after changed 1 bit.
图像 NPCR UACI BACI Lena 0.9954 0.3303 0.2682 Pepper 0.9944 0.3305 0.2657 Cameraman 0.9966 0.3394 0.2684 表 5 本文算法处理下不同图像的wPSNR和SSIM
Table 5. wPSNR and SSIM of different images after processed by scheme in this paper.
图像 wPSNR SSIM Lena 48.90 0.9898 Pepper 50.33 0.9927 Cameraman 43.34 0.9736 表 6 本文算法处理不同图像时的时间复杂度
Table 6. Algorithm proposed deals with the time complexity of different images.
图像 WPT分解及分类 压缩及重构 加密及解密 整体重构 总耗时/s Lena 0.600 s 8.893 s 1.098 s 0.377 s 10.968 Pepper 0.734 s 7.815 s 1.105 s 0.362 s 10.016 Cameraman 0.617 s 3.908 s 1.901 s 0.353 s 6.799 -
[1] 吴成茂 2014 63 090504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu C M 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 090504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 林青, 王延江, 王珺 2016 中国科学: 技术科学 46 910
Lin Q, Wang Y J, Wang J 2016 Sci. China: Technol. Sci. 46 910
[3] 李静, 向菲, 张军朋 2019 电子设计工程 27 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J, Xian F, Zhang J P 2019 Int. Electr. Elem. 27 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Donoho D L 2006 IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52 1289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chai X L, Zheng X Y, Gan Z H, Han D J, Chen Y R 2018 Signal Process 148 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhu S Q, Zhu C X, Wang W H 2018 IEEE Access. 6 67095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lü X P, Liao X F, Yang B 2018 Multimed Tools Appl. 77 28633
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hilton M L 1997 IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 44 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张祥, 张达永, 张刘辉, 潘栋 2016 气象水文海洋仪器 33 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang D Y, Zhang L H, Pan D 2016 Meteorol. Hydrol. Mar. Instrum. 33 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Goklani H S 2017 Int. J. Image, Graphics and Signal Processing 9 30
[11] Huang R, Rhee K H, Uchida S 2012 Multimed Tools Appl. 7 2
[12] Zhou N, Pan S, Cheng S, et al. 2016 Opt. Laser Technol. 82 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 禹思敏 2008 57 3374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu S M 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 3374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 禹思敏 2011 混沌系统与混沌电路 (西安:西安电子科技大学出版社) 第136−137页
Yu S M 2011 Chaotic Systems and Chaotic Circuits (Xi’ an: Xi 'an University of Electronic Science and Technology Press) pp136−137 (in Chinese)
[15] Chen G R 1999 Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 9 1465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王鸣天, 郭玉奇 2017 电子技术 46 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang M T, Guo Y Q 2017 Electr. Technol. 46 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Li C Q 2013 Nonlinear Dyn. 73 2083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 高展鸿, 徐文波 2011 基于MATLAB的图像处理案例教程 (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第99−101页
Gao Z H, Xu W B 2011 MATLAB-Based Image Processing Case Tutorial (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp99−101 (in Chinese)
[19] 张勇 2016 混沌数字图像加密 (北京: 清华大学出版社) 第50−59页
Zhang Y 2016 Chaotic Digital Image Crptosystem (Beijing: Tsinghua University Press) pp50−59 (in Chinese)
[20] 王静, 蒋国平 2011 60 060503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang J, Jiang G P 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 060503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang Y, Xiao D 2013 Opt. Lasers Eng. 51 472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 13507
- PDF Downloads: 205
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: