-
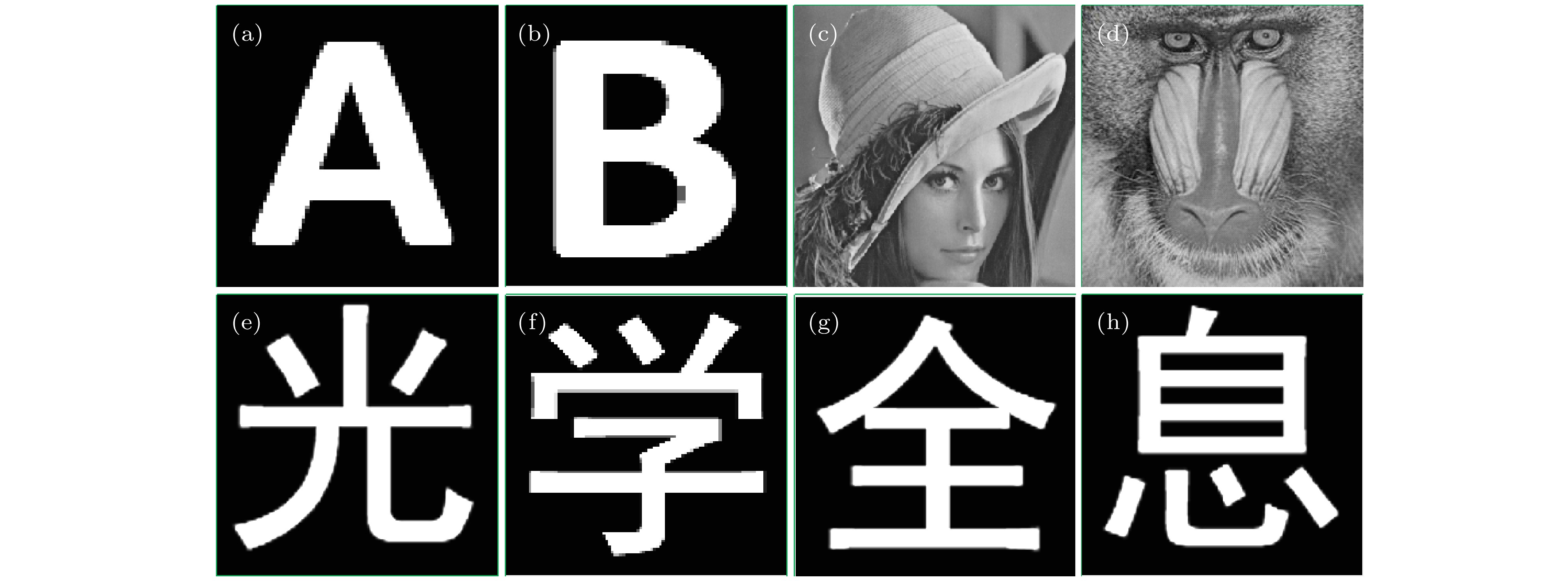
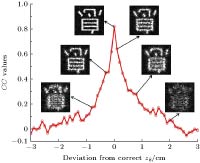
提出了基于空间角度复用和双随机相位的多图像光学加密新方法. 加密过程中, 首先将原始图像进行随机相位调制和不同距离的菲涅耳衍射; 其次, 将携带调制后图像的参考光与携带随机相位且具有不同立体角的参考光相干叠加, 产生干涉条纹; 最后, 将不同方向的干涉条纹叠加形成复合加密图像. 解密为加密的逆过程, 将复合加密图像置于空间滤波和菲涅耳衍射系统中, 经过不同相位密钥解调和正确距离的菲涅耳衍射完成解密, 得到多幅解密图像. 该方法可以同时对多幅图像进行高效的加密, 计算简单、安全可靠、抗噪声能力强. 利用相关系数评估了该方法的加密效果, 并通过仿真实验验证了该方法的有效性和安全性.An optical encryption method of multiple-image based on spatial angle multiplexing and double random phase encoding is proposed in this paper. In the encryption process, firstly the original images are modulated by random phase in Fresnel transform with different diffraction distances. Secondly, the modulated images are coherently superposed with reference beams which have different spatial angles and random phases, to generate interference fringes. Finally, the interference fringes from different directions are superposed to form a compound encrypted image. In the decryption process, the compound image is placed in a spatial filtering and Fresnel diffraction system, and the decrypted images are obtained after implementing the different phase keys’ demodulation and Fresnel diffraction with correct distance. This method encrypts multiple images into a single gray-scale image, which is easy to save and transmit. The double random phases are placed in object light and reference light respectively, which reduces the complexity of the encryption system and overcomes the difficulty of pixel-by-pixel alignment of random phase keys in traditional decryption experiment. At the same time, the multiplexing capacity of the proposed encryption system is analyzed, and the result shows that the system has sufficient encryption capacity. So the proposed method possesses the characteristics of high storage efficiency, simple calculation and strong anti-noise ability, and thus can encrypt multiple images simultaneously. In this paper, the encryption effect is evaluated by correlation coefficient, while the effectiveness and security are verified by simulation experiment.
-
Keywords:
- multiple-image encryption /
- spatial angle multiplexing /
- digital holography /
- interference encryption
[1] Refregier P, Javidi B 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Liu Z, Chen H, Blondel W, Shen Z, Liu S 2018 Opt. Lasers Eng. 105 1
[3] Chen L, Zhao D 2006 Opt. Express 14 8552
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao D, Li X, Chen L 2008 Opt. Commun. 281 5326
[5] Xu S J, Wang J Z, Yang S X 2008 Chin. Phys. B 17 4027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Borujeni S E, Eshghi M 2013 J. Telecommun. Syst. 52 525
[7] Toto-Arellano N, Rodriguez-Zurita G, Meneses-Fabian C, Vazquez-Castillo J 2008 Opt. Express 16 19330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nomura T, Javidi B 2000 Opt. Eng. 39 2031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shi Y S, Li T, Wang Y L, Gao Q K, Zhang S G, Li H F 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 1425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gopinathan U, Naughton T, Sheridan J 2006 Appl. Opt. 45 5693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Javidi B, Nomura T 2000 Opt. Lett. 25 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 席思星, 于娜娜, 王晓雷, 朱巧芬, 董昭, 王微, 刘秀红, 王华英 2019 68 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xi S X, Yu N N, Wang X L, Zhu Q F, Dong Z, Wang W, Liu X H, Wang H Y 2019 Acta. Phys. Sin. 68 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li X, Meng X, Yang X, Wang Y, Yin Y, Peng X, He W, Dong G, Chen H 2018 Opt. Lasers Eng. 102 106
[14] Xiao D, Li X, Liu S, Wang Q 2018 Opt. Commun. 410 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shao Z, Shu H, Wu J, Dong Z, Coatrieux G 2014 Opt. Express 22 4932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Situ G, Zhang J 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 1306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xu D, Lu M, Jia C, Hu Z 2017 J. Russ. Laser Res. 38 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Deepan B, Quan C, Wang Y, Tay C 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 4539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tang Z, Song J, Zhang X 2016 Opt. Lasers Eng. 80 1
[20] Kong D, Shen X, Xu Q, Wang X, Guo H 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 2619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Javidi B, Carnicer A, Yamaguchi M, Nomura T, Pérez-Cabré E, Millán M S, Nishchal N K, Torroba R, Barrera J F, He W, Peng X, Stern A, Rivenson Y, Alfalou A, Brosseau C, Guo C, Sheridan J T, Situ G, Naruse M, Matsumoto T, Juvells L, Tajahuerce E, Lancis J, Chen W, Chen X, Pinkse P W, Mosk A P, Markman A 2016 J. Opt. 18 083001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
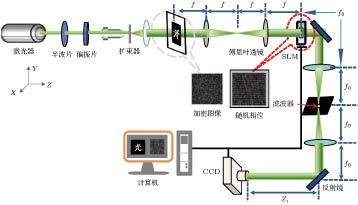
图 1 多图像光学加密系统(SLM是空间光调制器,
$f$ 是透镜焦距,${z_i}$ 是菲涅耳衍射距离,$R(\theta )$ 表示CCD旋转后与x轴的夹角,${\alpha _i}$ 是物光O与参考光R的夹角)Fig. 1. Optical setup of multiple-image encryption process. SLM is spatial light modulator,
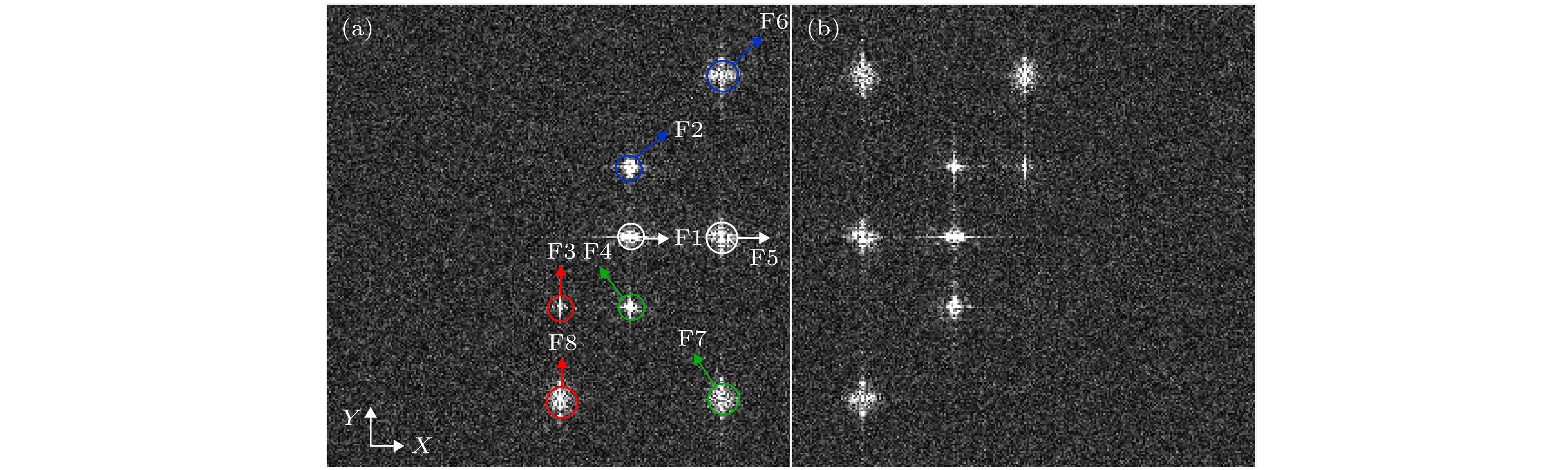
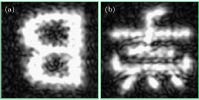
$f$ is focal length,${z_i}$ is the distance of Fresnel diffraction,$R(\theta )$ is the rotation angle of CCD,${\alpha _i}$ is angle between object light O and reference light R.图 8 (a)随机相位密钥
$p_2^ * $ 错误时原始图“A”解密结果; (a')随机相位密钥$p_2^ * $ 错误且无滤波器时原始图“A”解密结果; (b)随机相位密钥$p_2^ * $ 错误时原始图“光”解密结果; (b')随机相位密钥$p_2^ * $ 错误且无滤波器时原始图“光”解密结果Fig. 8. Decrypted results with wrong key
$p_2^ * $ : (a) For original image “A”; (a') for original image “A” without filter; (b) for original image “光”; (b') for original image “光” without filter. -
[1] Refregier P, Javidi B 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 767
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Liu Z, Chen H, Blondel W, Shen Z, Liu S 2018 Opt. Lasers Eng. 105 1
[3] Chen L, Zhao D 2006 Opt. Express 14 8552
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao D, Li X, Chen L 2008 Opt. Commun. 281 5326
[5] Xu S J, Wang J Z, Yang S X 2008 Chin. Phys. B 17 4027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Borujeni S E, Eshghi M 2013 J. Telecommun. Syst. 52 525
[7] Toto-Arellano N, Rodriguez-Zurita G, Meneses-Fabian C, Vazquez-Castillo J 2008 Opt. Express 16 19330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nomura T, Javidi B 2000 Opt. Eng. 39 2031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shi Y S, Li T, Wang Y L, Gao Q K, Zhang S G, Li H F 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 1425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gopinathan U, Naughton T, Sheridan J 2006 Appl. Opt. 45 5693
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Javidi B, Nomura T 2000 Opt. Lett. 25 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 席思星, 于娜娜, 王晓雷, 朱巧芬, 董昭, 王微, 刘秀红, 王华英 2019 68 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xi S X, Yu N N, Wang X L, Zhu Q F, Dong Z, Wang W, Liu X H, Wang H Y 2019 Acta. Phys. Sin. 68 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li X, Meng X, Yang X, Wang Y, Yin Y, Peng X, He W, Dong G, Chen H 2018 Opt. Lasers Eng. 102 106
[14] Xiao D, Li X, Liu S, Wang Q 2018 Opt. Commun. 410 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shao Z, Shu H, Wu J, Dong Z, Coatrieux G 2014 Opt. Express 22 4932
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Situ G, Zhang J 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 1306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xu D, Lu M, Jia C, Hu Z 2017 J. Russ. Laser Res. 38 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Deepan B, Quan C, Wang Y, Tay C 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 4539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tang Z, Song J, Zhang X 2016 Opt. Lasers Eng. 80 1
[20] Kong D, Shen X, Xu Q, Wang X, Guo H 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 2619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Javidi B, Carnicer A, Yamaguchi M, Nomura T, Pérez-Cabré E, Millán M S, Nishchal N K, Torroba R, Barrera J F, He W, Peng X, Stern A, Rivenson Y, Alfalou A, Brosseau C, Guo C, Sheridan J T, Situ G, Naruse M, Matsumoto T, Juvells L, Tajahuerce E, Lancis J, Chen W, Chen X, Pinkse P W, Mosk A P, Markman A 2016 J. Opt. 18 083001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 12488
- PDF下载量: 142
- 被引次数: 0






















 下载:
下载: