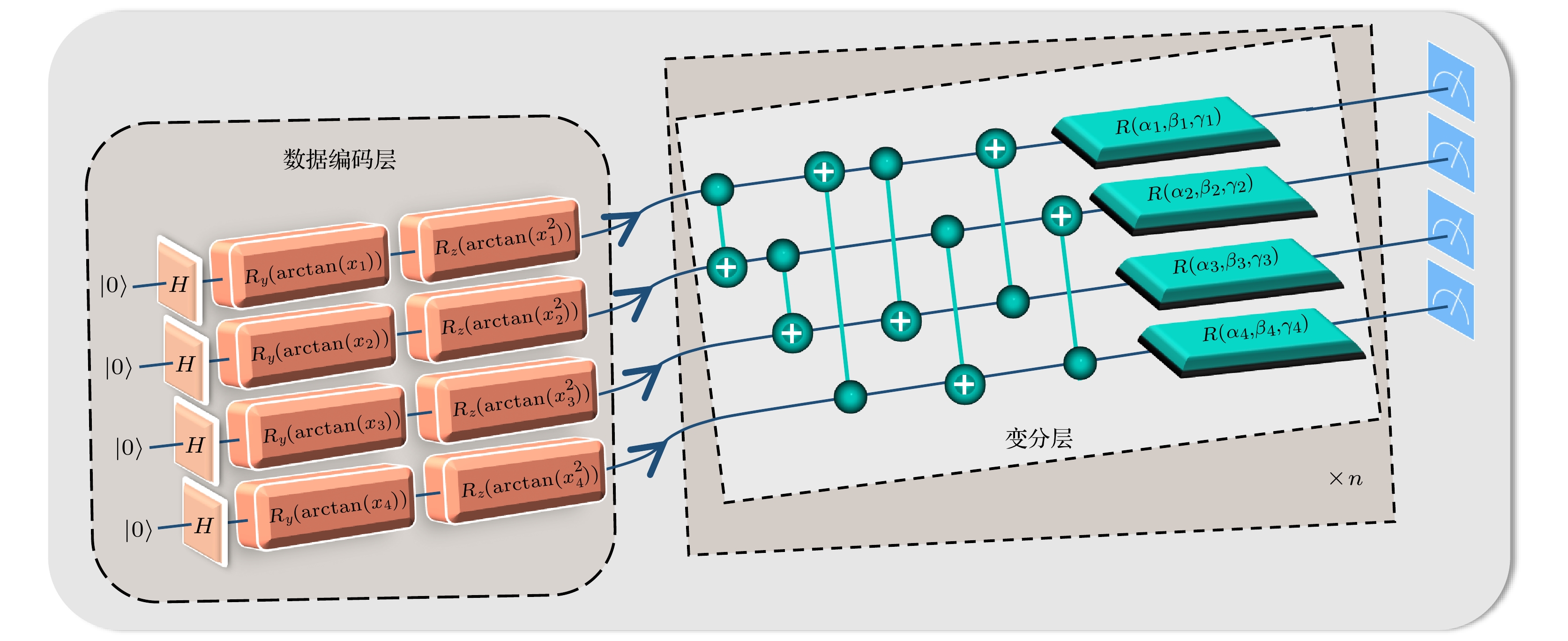
-
近年来, 图像信息的传输安全性已经成为互联网领域的重要研究方向. 本文提出了一种基于量子长短期记忆(quantum long-short term memory, QLSTM)网络的量子图像混沌加密方案. 结果发现, 因为QLSTM网络具有复杂的结构和较多的参数, 应用QLSTM网络对Lorenz混沌序列进行改进, 其最大Lyapunov指数比原序列提高2.5465%, 比经典长短期记忆(long-short term memory, LSTM)网络改进的序列提高0.2844%, 同时在0—1测试中结果更接近1且更稳定, 因此QLSTM网络改进的序列具备更优异的混沌性能, 更难以被预测, 提高了单一混沌系统加密的安全性. 运用NCQI (novel quantum representation of color digital images) 量子图像表示模型, 将原始图像存储为量子态形式, 利用QLSTM网络改进的序列分别控制三级径向扩散、量子广义Arnold变换和量子W变换, 改变量子图像的灰度值与像素位置, 生成最终的加密图像. 本文提出的加密方案在统计学特性测试中, 实现了RGB三通道平均信息熵均大于7.999, 像素数改变率的平均值达99.6047%, 统一平均变化强度的平均值为33.4613%, 平均相关性为0.0038等, 比其他一些传统方法具有更高的安全性, 能够抵抗常见的攻击方式.In recent years, the transmission security of image information has become an important research direction in the internet field. In this work, we propose a quantum image chaos encryption scheme based on quantum long-short term memory (QLSTM) network. We find that because the QLSTM network has a complex structure and more parameters, when the QLSTM network is used to improve the Lorenz chaotic sequence, its largest Lyapunov exponent is 2.5465% higher than that of the original sequence and 0.2844% higher than that the sequence improved by the classical long-short term memory (LSTM) network, while its result is closer to 1 and more stable in the 0–1 test. The improved sequence of QLSTM network has better chaotic performance and is predicted more difficultly, which improves the security of single chaotic system encryption. The original image is stored in the form of quantum states by using the NCQI quantum image representation model, and the improved sequence of QLSTM network is used to control the three-level radial diffusion, quantum generalized Arnold transform and quantum W-transform respectively, so that the gray value and pixel position of the quantum image are changed and the final encrypted image is obtained. The encryption scheme proposed in this work obtains the average information entropy of all three channels of RGB of greater than 7.999, the average value of pixel number change rate of 99.6047%, the average value of uniform average change intensity of 33.4613%, the average correlation of 0.0038, etc. In the test of statistical properties, the encryption scheme has higher security than some other traditional methods and can resist the common attacks.
[1] Shakir H R, Mehdi S A A, Hattab A A 2022 Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 11 2645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王一诺, 宋昭阳, 马玉林, 华南, 马鸿洋 2021 70 230302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y N, Song Z Y, Ma Y L, Hua N, Ma H Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 230302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu G Z, Li W, Fan X K, Li Z, Wang Y X, Ma H Y 2022 Entropy 24 608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao J B, Zhang T, Jiang J W, Fang T, Ma H Y 2022 Sci. Rep. 12 14253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li C Q, Lin D D, Lu J H 2017 IEEE MultiMedia 24 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li C M, Yang X Z 2022 Optik 260 169042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Xian Y J, Wang X Y 2021 Inf. Sci. 547 1154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhou N R, Hu Y Q, Gong L H, Li G Y 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu H, Zhao B, Huang L Q 2019 Entropy 21 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Song X H, Wang S, Abd El-Latif A A, Niu X M 2014 Quantum Inf. Process. 13 1765
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Akhshani A, Akhavan A, Lim S C, Hassan Z 2012 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17 4653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou N R, Huang L X, Gong L H, Zeng Q W 2020 Quantum Inf. Process. 19 284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang X Y, Su Y I, Luo C, Nian F Z, Teng L 2022 Multimedea Tools Appl. 81 13845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gao Y J, Xie H W, Zhang J, Zhang H 2022 Physia A 598 127334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu X B, Xiao D, Liu C 2021 Quantum Inf. Process. 20 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang J W, Zhang T, Li W, Wang S M 2023 Quantum Eng. 2023 3746357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhao J F, Wang S Y, Chang Y X, Li X F 2015 Nonlinear Dyn. 80 1721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chai X L, Fu J Y, Zhang J T, Han D J, Gan Z H 2021 Neural. Comput. Appl. 33 10371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chai X L, Gan Z H, Yuan K, Lu Y, Chen Y R 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 020504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang N, Dong X, Hu H, Ji Z X, Zhang W Y 2019 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ge B, Luo H B 2020 Int. J. Autom. Comput. 17 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hu W B, Dong Y M 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 131 114402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 刘瀚扬, 华南, 王一诺, 梁俊卿, 马鸿洋 2022 71 170303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H Y, Hua N, Wang Y N, Liang J Q, Ma H Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 170303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Faqih A, Kamanditya B, Kusumoputro B 2018 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (Alsace: IEEE) p1
[25] Qu J Y, Zhao T, Ye M, Li J Y, Liu C 2020 Neural Process. Lett. 52 1461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yang G C, Zhu T, Wang H, Yang F B 2021 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 69 1487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li Y T, Li Y 2022 Neurocomputing 491 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li W, Chu P C, Liu G Z, Tian Y B, Qiu T H, Wang S M 2022 Quantum Eng. 2022 5701479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Chen G M, Long S, Yuan Z D, Li W Y, Peng J F 2023 Quantum Eng. 2023 2842217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang Y, Ni Q 2021 Quantum Eng. 3 e75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wei S J, Chen Y H, Zhou Z R, Long G L 2022 AAPPS Bulletin 32 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J 1997 Neural Comput. 9 1735
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Kandala A, Mezzacapo A, Temme K, Takita M, Brink M, Chow J M, Gambetta J M 2017 Nature 549 242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] McClean J R, Romero J, Babbush R, Aspuru-Guzik A 2016 New J. Phys. 18 023023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen S Y C, Yang C H H, Qi J, Chen P Y, Ma X L, Goan H S 2020 IEEE Access 8 141007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Schuld M, Bocharov A, Svore K M, Wiebe N 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 032308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Benedetti M, Lloyd E, Sack S, Fiorentini M 2019 Quantum Sci. Technol. 4 043001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Havlicek V, Corcoles A D, Temme K, Harrow A W, Kandala A, Chow J M, Gambetta J M 2019 Nature 567 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Di Sipio R, Huang J H, Chen S Y C, Mangini S, Worring M 2022 ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (Singapore: IEEE) p8612
[40] Sang J Z, Wang S, Li Q 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 42
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Wu Y L 2008 Electron. Sci. 21 69
[42] Wolf A, Swift J B, Swinney H L, Vastano J A 1985 Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenomena 16 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] 赵智鹏, 周双, 王兴元 2021 70 230502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Z P, Zhou S, Wang X Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 230502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Gottwald G A, Melbourne I 2004 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 460 603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Sun K H, Liu X, Zhu C X 2010 Chin. Phys. B 19 110510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Boriga R, Dascalescu A C, Priescu I 2014 Signal Process. Image Commun. 29 887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Raja S S, Mohan V 2014 Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. 8 1
[48] Yang Y G, Tian J, Lei H, Zhou Y H, Shi W M 2016 Inf. Sci. 345 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 LLE数据对比
Table 1. Comparison of LLE data
序列来源 LLE Henon映射 0.4192 超混沌Lorenz系统 0.3381 LSTM网络改进的序列[43] 2.6002 QLSTM网络改进的序列 2.8846 表 2 0—1测试的数据对比
Table 2. Comparison of from 0–1 test data
表 3 加密图像的相关性分析
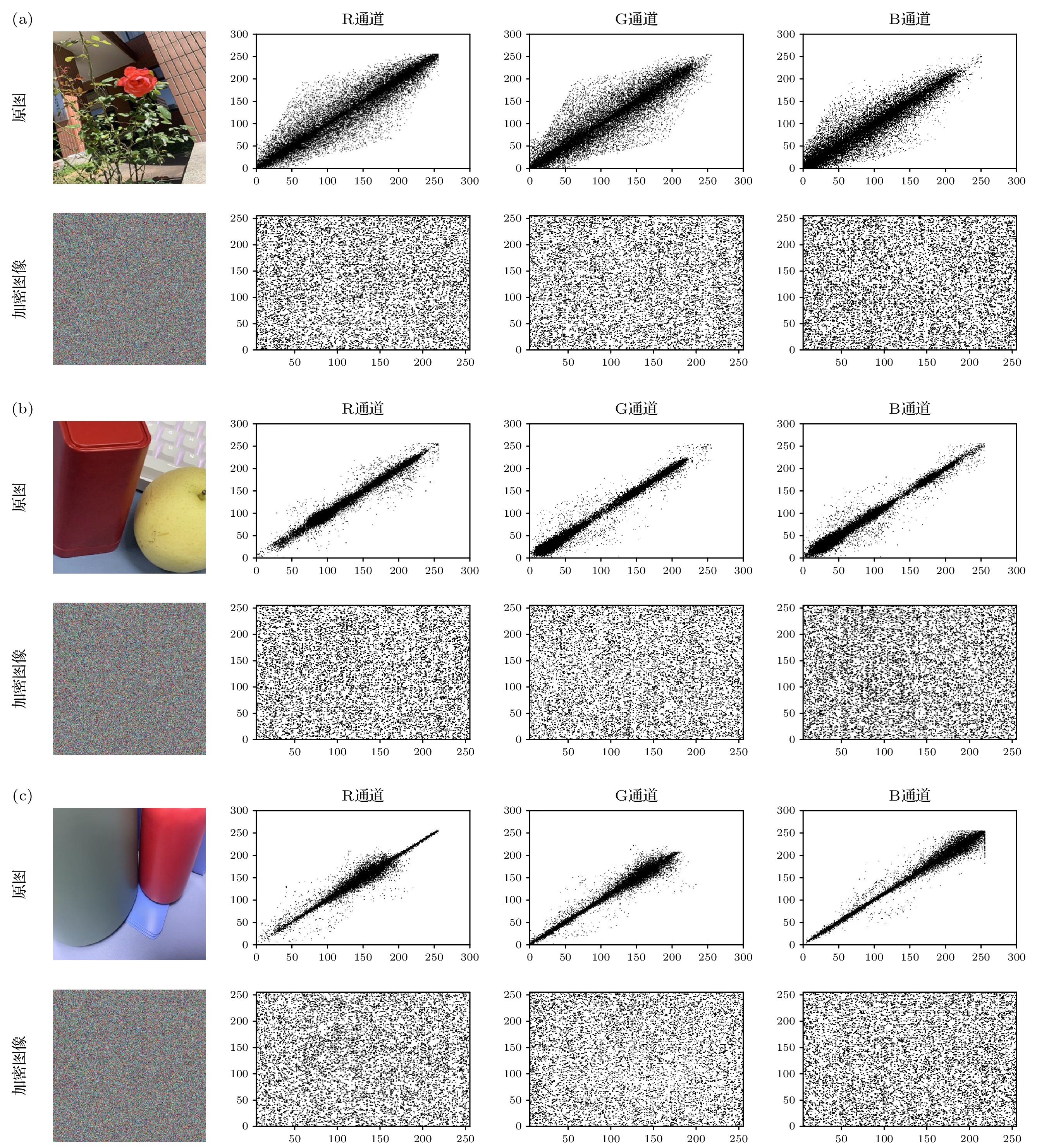
Table 3. Pixel correlation analysis of encrypted images
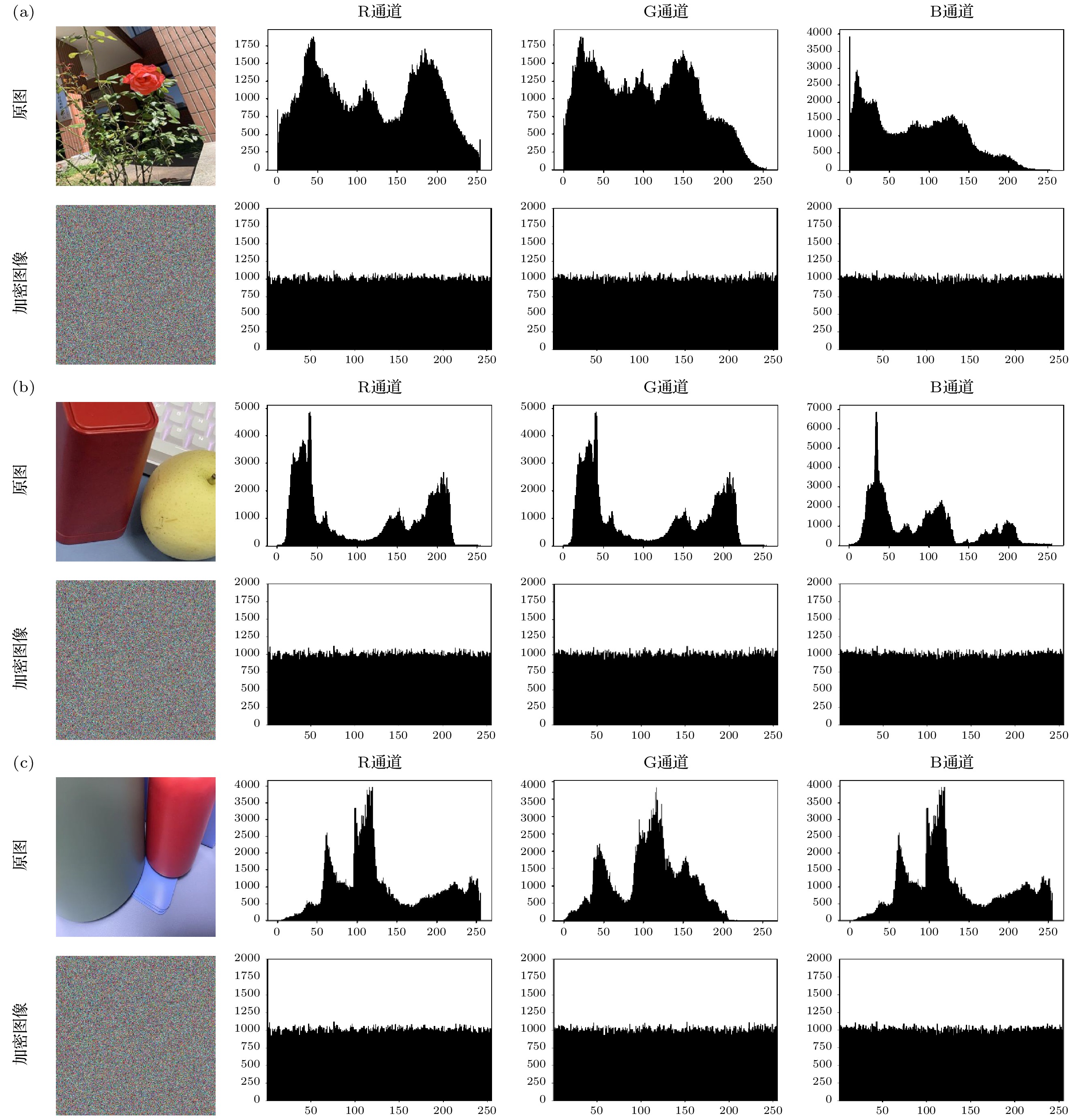
图像 通道 水平 垂直 对角 R 0.0074 0.0031 0.0064 1 G 0.0039 0.0021 0.0019 B 0.0044 0.0013 0.0058 R 0.0006 0.0067 0.0026 2 G 0.0017 0.0049 0.0047 B 0.0057 0.0006 0.0069 R 0.0003 0.0052 0.0013 3 G 0.0035 0.0005 0.0042 B 0.0090 0.0029 0.0045 表 4 加密图像的信息熵
Table 4. Information entropy of encrypted images
图像 R G B 1 7.99928 7.99973 7.99951 2 7.99935 7.99908 7.99975 3 7.99912 7.99949 7.99921 表 5 加密图像的NPCR与UACI
Table 5. NPCR and UACI of encrypted images.
图像 NPCR UACI 1 99.6048% 33.4604% 2 99.6063% 33.4609% 3 99.6029% 33.4627% 表 6 NPCR与UACI的对比分析
Table 6. Comparison of NPCR and UACI
算法 平均NPCR 平均UACI 本文 99.6047% 33.4613% 文献[43] 99.604% 33.46% -
[1] Shakir H R, Mehdi S A A, Hattab A A 2022 Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 11 2645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 王一诺, 宋昭阳, 马玉林, 华南, 马鸿洋 2021 70 230302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Y N, Song Z Y, Ma Y L, Hua N, Ma H Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 230302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu G Z, Li W, Fan X K, Li Z, Wang Y X, Ma H Y 2022 Entropy 24 608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao J B, Zhang T, Jiang J W, Fang T, Ma H Y 2022 Sci. Rep. 12 14253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li C Q, Lin D D, Lu J H 2017 IEEE MultiMedia 24 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li C M, Yang X Z 2022 Optik 260 169042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Xian Y J, Wang X Y 2021 Inf. Sci. 547 1154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhou N R, Hu Y Q, Gong L H, Li G Y 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Liu H, Zhao B, Huang L Q 2019 Entropy 21 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Song X H, Wang S, Abd El-Latif A A, Niu X M 2014 Quantum Inf. Process. 13 1765
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Akhshani A, Akhavan A, Lim S C, Hassan Z 2012 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17 4653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou N R, Huang L X, Gong L H, Zeng Q W 2020 Quantum Inf. Process. 19 284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang X Y, Su Y I, Luo C, Nian F Z, Teng L 2022 Multimedea Tools Appl. 81 13845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Gao Y J, Xie H W, Zhang J, Zhang H 2022 Physia A 598 127334
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu X B, Xiao D, Liu C 2021 Quantum Inf. Process. 20 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiang J W, Zhang T, Li W, Wang S M 2023 Quantum Eng. 2023 3746357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhao J F, Wang S Y, Chang Y X, Li X F 2015 Nonlinear Dyn. 80 1721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chai X L, Fu J Y, Zhang J T, Han D J, Gan Z H 2021 Neural. Comput. Appl. 33 10371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chai X L, Gan Z H, Yuan K, Lu Y, Chen Y R 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 020504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang N, Dong X, Hu H, Ji Z X, Zhang W Y 2019 Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ge B, Luo H B 2020 Int. J. Autom. Comput. 17 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hu W B, Dong Y M 2022 J. Appl. Phys. 131 114402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 刘瀚扬, 华南, 王一诺, 梁俊卿, 马鸿洋 2022 71 170303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H Y, Hua N, Wang Y N, Liang J Q, Ma H Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 170303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Faqih A, Kamanditya B, Kusumoputro B 2018 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (Alsace: IEEE) p1
[25] Qu J Y, Zhao T, Ye M, Li J Y, Liu C 2020 Neural Process. Lett. 52 1461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yang G C, Zhu T, Wang H, Yang F B 2021 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 69 1487
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Li Y T, Li Y 2022 Neurocomputing 491 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li W, Chu P C, Liu G Z, Tian Y B, Qiu T H, Wang S M 2022 Quantum Eng. 2022 5701479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Chen G M, Long S, Yuan Z D, Li W Y, Peng J F 2023 Quantum Eng. 2023 2842217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang Y, Ni Q 2021 Quantum Eng. 3 e75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Wei S J, Chen Y H, Zhou Z R, Long G L 2022 AAPPS Bulletin 32 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J 1997 Neural Comput. 9 1735
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Kandala A, Mezzacapo A, Temme K, Takita M, Brink M, Chow J M, Gambetta J M 2017 Nature 549 242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] McClean J R, Romero J, Babbush R, Aspuru-Guzik A 2016 New J. Phys. 18 023023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen S Y C, Yang C H H, Qi J, Chen P Y, Ma X L, Goan H S 2020 IEEE Access 8 141007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Schuld M, Bocharov A, Svore K M, Wiebe N 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 032308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Benedetti M, Lloyd E, Sack S, Fiorentini M 2019 Quantum Sci. Technol. 4 043001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Havlicek V, Corcoles A D, Temme K, Harrow A W, Kandala A, Chow J M, Gambetta J M 2019 Nature 567 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Di Sipio R, Huang J H, Chen S Y C, Mangini S, Worring M 2022 ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (Singapore: IEEE) p8612
[40] Sang J Z, Wang S, Li Q 2017 Quantum Inf. Process. 16 42
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Wu Y L 2008 Electron. Sci. 21 69
[42] Wolf A, Swift J B, Swinney H L, Vastano J A 1985 Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenomena 16 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] 赵智鹏, 周双, 王兴元 2021 70 230502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Z P, Zhou S, Wang X Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 230502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Gottwald G A, Melbourne I 2004 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 460 603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Sun K H, Liu X, Zhu C X 2010 Chin. Phys. B 19 110510
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Boriga R, Dascalescu A C, Priescu I 2014 Signal Process. Image Commun. 29 887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Raja S S, Mohan V 2014 Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. 8 1
[48] Yang Y G, Tian J, Lei H, Zhou Y H, Shi W M 2016 Inf. Sci. 345 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5740
- PDF下载量: 163
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: