-
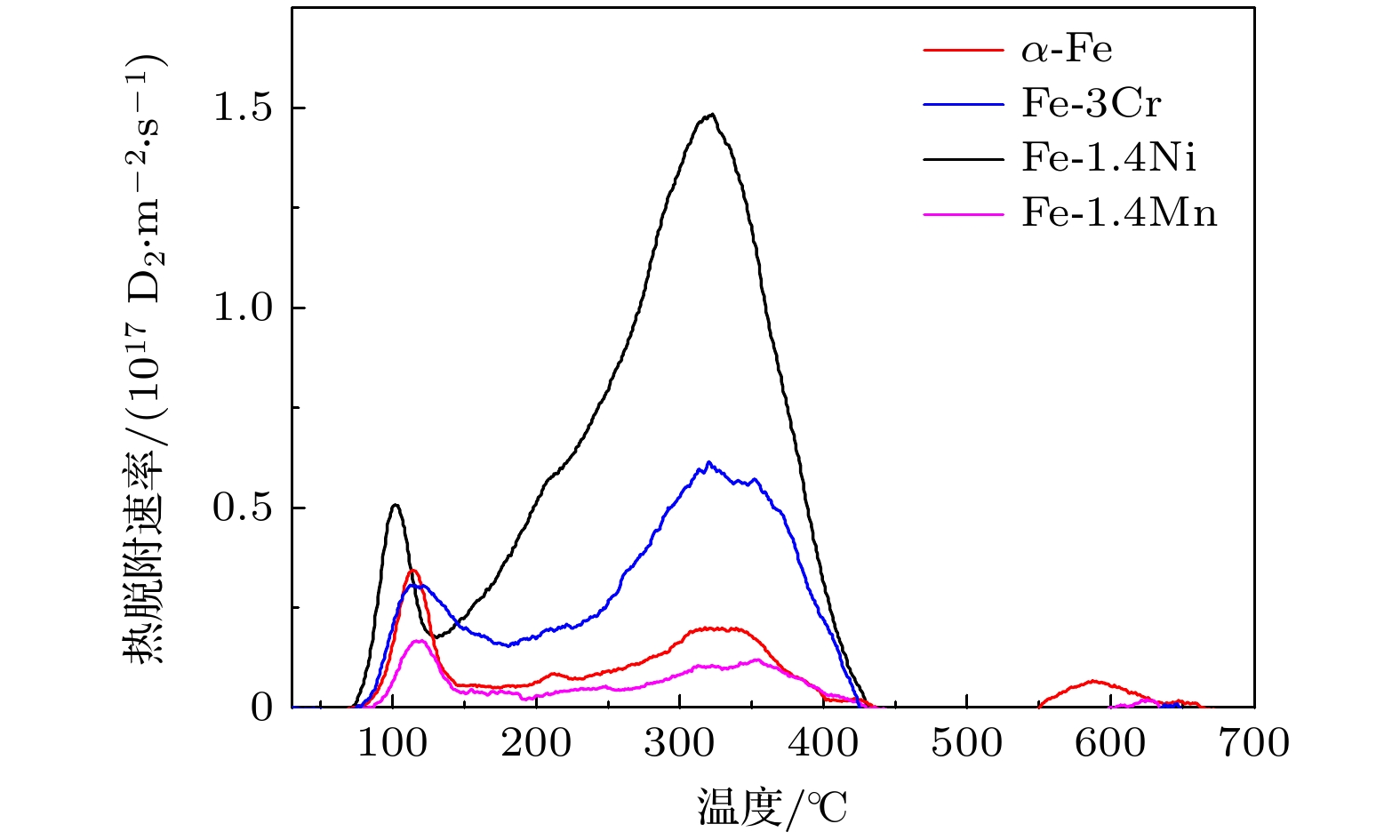
Reduced activation ferritic/martensitic (RAFM) steels have been considered as a family of prime candidate structural materials for fusion reactors due to low radioactivity and good resistance to irradiation swelling. Various types of defects such as dislocation loops can form in these materials during irradiation. Effects of alloying elements in iron on the formation and migration of dislocation loops have been widely investigated. However, most studies dealt with interstitial-type dislocation loops in iron alloys, while very few focused on vacancy-type dislocation loops. Previous high voltage electron microscope (HVEM) studies from the authors' group have shown that interstitial loops are fully eliminated in hydrogen-ion-implanted α-Fe at 500 ℃, only vacancy loops remain and can achieve up to 100 nm in size. The addition of Ni in α-Fe can reduce the formation temperature of vacancy-type dislocation loops (Tc) to ~450 ℃, while the addition of Cr can increase the temperature to above 600 ℃. However, these experiments are usually difficult to perform due to the scarce resource of HVEM facilities. In this work, in-situ observations by conventional transmission electron microscope (CTEM, 200 kV) are systematically carried out on the hydrogen-ion-implanted α-Fe and Fe-based binary alloys (Fe-3wt.%Cr, Fe-1.4wt.%Ni and Fe-1.4wt.%Mn). The evolutions of morphology and average size of dislocation loops under different annealing temperatures are investigated. The formation temperatures of vacancy-type dislocation loops are determined from the change of average loop size with annealing temperature. The results are consistent with previous studies by HVEM. The effect of Mn atoms in α-Fe is similar to that of Cr atoms, which leads to Tc increase, and the addition of Ni in α-Fe can reduce Tc. Furthermore, the results of D thermal desorption spectrum analysis show that Tc is affected by the binding and release process of hydrogen isotopes to vacancies in α-Fe. Alloying element Ni promotes the binding and release of hydrogen isotopes to vacancies, which leads to Tc decrease. Cr and Mn inhibit the binding and release of hydrogen isotopes to vacancies, causing Tc to increase.
-
Keywords:
- Fe-based binary alloy /
- H+/D+ ion implantation /
- vacancy-type dislocation loop /
- TEM
[1] Kano S, Yang H L, Suzue R, Matsukawa Y, Satoh Y, Sakasegawa H, Tanigawa H, Abe H 2016 Nucl. Mater. Energy 9 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hishinuma A, Kohyama A, Klueh R, Gelles D, Dietz W, Ehrlich K 1998 J. Nucl. Mater. 258–263 193
[3] Sojak S, Slugeň V, Petriska M, Veterníková JŠ, Stacho M, Sabelová V 2013 22nd International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe Bled, Slovenia September 8–13, 2013 p314
[4] 杜玉峰 2019 博士学位论文 (北京: 北京科技大学)
Du Y F 2019 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing) (in Chinese)
[5] Kohno Y, Kohyama A, Hirose T, Hamilton M, Narui M 1999 J. Nucl. Mater. 272 145
[6] Klueh R, Alexander D, Rieth M 1999 J. Nucl. Mater. 273 146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sacksteder I, Schneider H C, Materna-Morris E 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 417 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Schäublin R, Henry J, Dai Y 2008 Cr. Phys. 9 389
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Dubinko V I, Kotrechko S A, Klepikov V F 2009 Radiat. Eff. Defect. S. 164 647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 姜少宁, 万发荣, 龙毅 刘传歆, 詹倩, 大貫惣明 2013 62 166801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang S N, Wan F R, Long Y, Liu C X, Zhan Q, Ohnuki S. 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 166801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Osetsky Y N, Serra A, Singh B N, Golubov S I 2000 Philos. Mag. A 80 2131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kim S M, Buyers W 1978 J. Phys. F:Metal Physics 8 L103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Willaime F, Fu C C, Marinica M C, Dalla Torre J 2005 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 228 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hashimoto N, Sakuraya S, Tanimoto J, Ohnuki S 2014 J. Nucl. Mater. 445 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 万发荣 2020 工程科学学报 42 1535
Wan F R 2020 Chinese J. Eng. 42 1535
[16] Hoelzer D T, Ebrahimi F 1994 MRS Online Proceedings Library 373 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ward A, Fisher S B 1989 J. Nucl. Mater. 166(3) 227
[18] Chen L, Murakami K, Chen D, Abe H, Li Z, Sekimura N 2020 Scripta Mater. 187 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Mizandrontsev D B, Vasiliev A A 2000 Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering 4064 220
[20] Eyre B L, Bartlett A F 1965 Philos. Mag. 12 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Masters B C 1965 Philos. Mag. 11 881
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yabuuchi K, Saito M, Kasada R, Kimura A 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 414 498
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yabuuchi K, Kasada R, Kimura A 2013 Acta Mater. 61 6517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Watanabe H, Masaki S, Masubuchi S, Yoshida N, Dohi K 2013 J. Nucl. Mater. 439 268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Horton L L, Bentley J, Farrell K 1982 J. Nucl. Mater. 108 222
[26] Wirth B D, Odette G R, Maroudas D, Lucas G E 2000 J. Nucl. Mater. 276 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Terentyev D, Grammatikopoulos P, Bacon D J, Osetsky Y N 2008 Acta Mater. 56 5034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang W P, Song L G, Zhu T, Xiong Y, Ma H L, Yan Q Z, Cao X Z, Wang B Y, Jin S X 2021 J. Nucl. Mater. 548 152862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gao N, Perez D, Lu G H, Wang Z G 2018 J. Nucl. Mater. 498 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Kiritani M, Yoshiie T, Iseki M, Kojima S, Hamada K, Horiki M, Kizuka Y, Inoue H, Tada T, Ogasawara Y 1994 J. Nucl. Mater. 212 241
[31] Wei Y X, Gao N, Shen Z Y, Chen C, Xie Z Y, Guo L P 2020 Comp. Mater. Sci. 180 109724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pan X D, Lu T, Lyu Y M, Xu Y P, Zhou H S, Yang Z S, Niu G J, Li X C, Gao F, Luo G N 2020 J. Nucl. Mater. 542 152500
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wei Y X, Gao N, Wang D, Chen C, Guo L P 2019 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 461 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Huang Y N, Wan F R, Xiao X, Shi S, Long Y, Ohnuki S, Hashimoto N 2010 Fusion Eng. Des. 85 2203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wan F R, Ohnuki S, Takahashi H, Takeyama T, Nagasaki R 1986 Philos. Mag. A 53 L21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Gao J, Du Y, Ohnuki S, Wan F 2016 J. Nucl. Mater. 481 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wan F R, Zhan Q, Long Y, Yang S W, Zhang G W, Du Y F, Jiao Z J, Ohnuki S 2014 J. Nucl. Mater. 455 253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Du Y F, Cui L J, Han W T, Wan F R 2019 Acta Metall. Sin-Engl. 32 566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Foll H, Wilkens M 1975 Phys. Status Solidi A 31 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] 黄依娜, 万发荣, 焦治杰 2011 60 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang Y N, Wan F R, Jiao Z J 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Stoller R E, Toloczko M B, Was G S, Certain A G, Dwaraknath S, Garner F A 2013 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 310 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] ASTM-Committee 2003 Standard Practice for Neutron Radiation Damage Simulation by Charged-particle Irradiation (West Conshohocken: Copyright © ASTM International) p8
[43] 颜强 2017 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Yan Q 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
[44] 万发荣 1993 金属材料的辐照损伤 (北京: 科学出版社) 第85页
Wan F R 1993 Irradiation Damage of Metal Materials (Beijing: Science Press) p85 (in Chinese)
[45] Morishita K, Sugano R, Wirth B D, de La Rubia T D 2003 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 202 76
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] 徐玉平 2017 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Xu Y P 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[47] Sugano R, Morishita K, Iwakiri H, Yoshida N 2002 J. Nucl. Mater. 307 941
[48] Sugano R, Morishita K, Kimura A, Iwakiri H, Yoshida N 2004 J. Nucl. Mater. 329 942
-
图 1 实验过程示意图 (a)不同退火温度下位错环的TEM原位观察; (b) TDS实验. 铁基合金指Fe-3Cr, Fe-1.4Ni和Fe-1.4Mn
Figure 1. A schematic illustration of experiment procedures: (a) In-situ TEM observation of dislocation loops at different annealing temperatures; (b) TDS experiment. Fe-based binary alloys refer to Fe-3Cr, Fe-1.4Ni and Fe-1.4Mn.
图 2 SRIM 2013模拟注氢纯铁的辐照损伤量(dpa)和氢离子浓度(H, at.%)随注入深度的分布情况. 纯铁离位阈能为40 eV[43]. 辐照条件: 30 keV H+, 1.0 × 1021 ions /m2
Figure 2. SRIM 3013 calculated depth profiles of displacement damage (dpa) and hydrogen concentration (H, at.%) in H+ ion implanted pure Fe. Displacement threshold energy of pure Fe: 40 eV[43]. Irradiation condition: 30 keV H+, 1.0 × 1021 ions /m2.
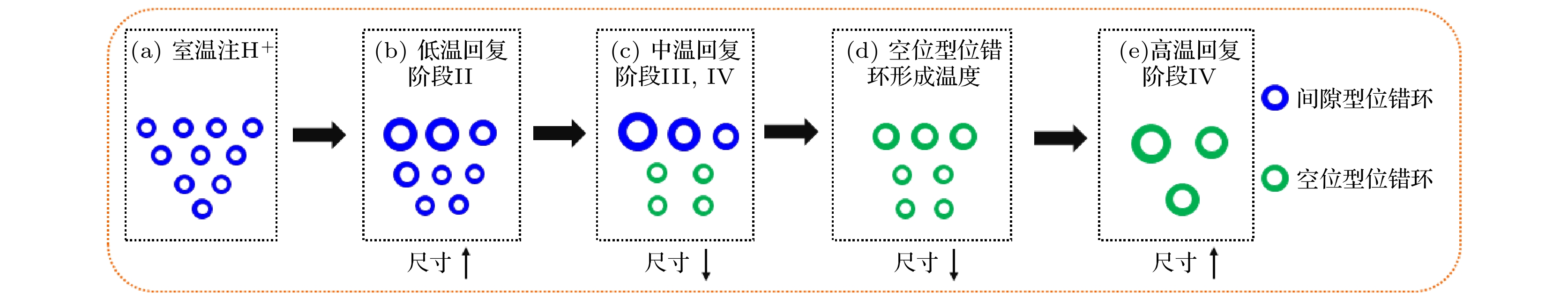
图 3 辐照位错环在恒定时间内(本文指20 min)、不同退火温度下的形态和尺寸演化示意图. 尺寸表示位错环的平均尺寸, 阶段II-IV指辐照缺陷的第II至IV热回复阶段[44]
Figure 3. A schematic diagram illustrating the morphology/size evolution of irradiation-induced dislocation loops during post-irradiation isochronal annealing for 20 min. ‘Loop size’ refers to the average size of dislocation loops. Stages ‘II-IV’ refer to the thermal recovery stages of radiation defects [44].
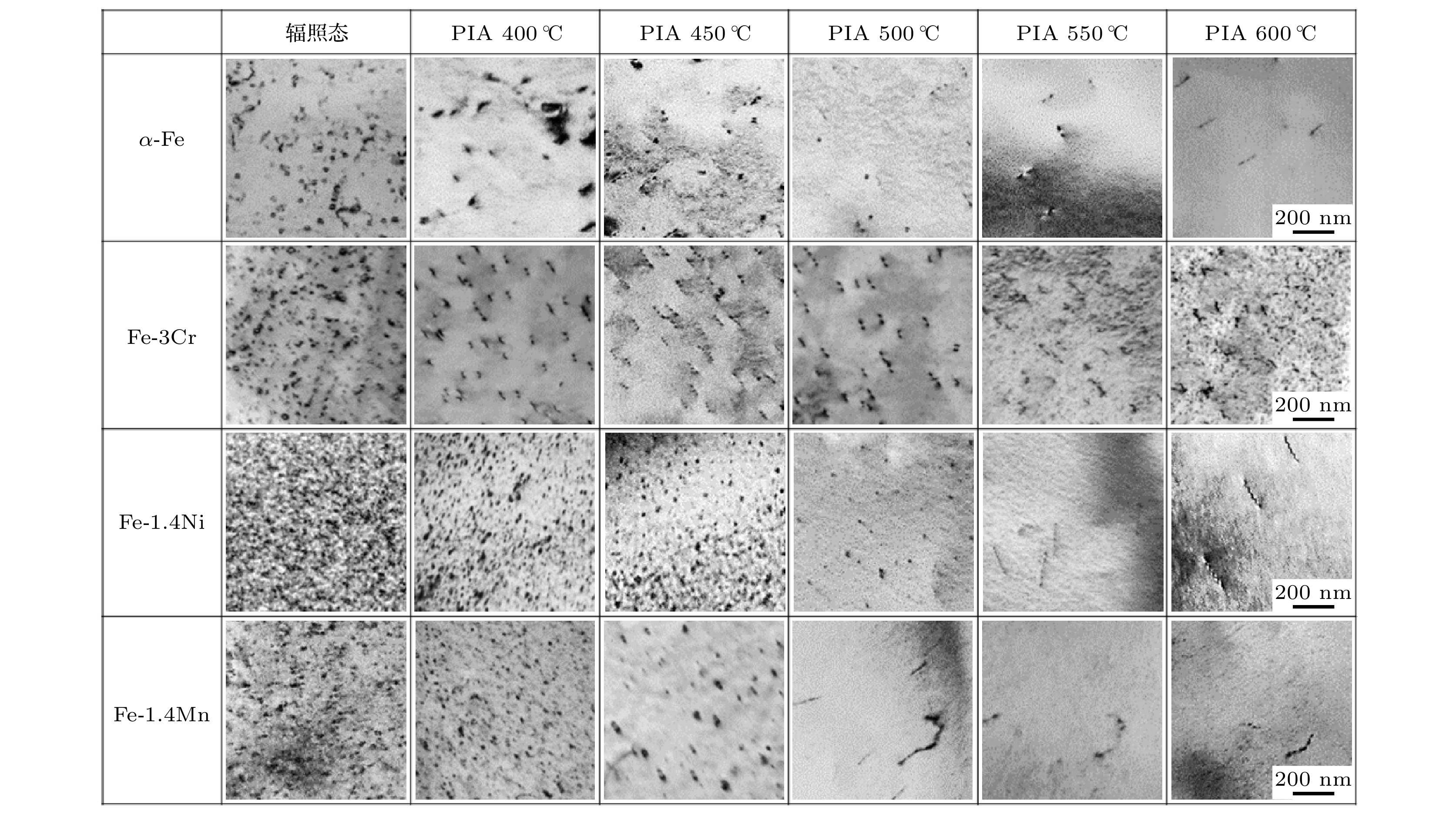
图 4 注氢纯铁/铁基二元合金中位错环在辐照后退火过程中的演化. 辐照条件: 30 keV H+, 1.0 × 1021 ions/m2, 25 ℃; 辐照后退火条件: 400—600 ℃, 20 min; 成像条件: 双束运动学明场像, g = 200
Figure 4. Loop evolution in H+ ion implanted Fe/Fe-based binary alloys during post-irradiation annealing (PIA) treatment. Irradiation condition: 30 keV H+, 1.0 × 1021 ions/m2, 25 ℃. PIA condition: 400–600 ℃, 20 min. Imaging condition: two-beam kinematical bright-field, g = 200.
图 5 注氢纯铁/铁基二元合金中位错环在辐照后退火过程中的平均尺寸变化. 辐照条件: 30 keV H+, 1.0 × 1021 ions/m2, 25 ℃. 辐照后退火条件: 400—600 ℃, 20 min.
Figure 5. Average loop size changes in H+ ion implanted Fe/Fe-based binary alloys during post-irradiation annealing (PIA) treatment. Irradiation condition: 30 keV H+, 1.0 × 1021 ions/m2, 25 ℃. PIA condition: 400–600 ℃, 20 min.
表 1 纯铁/铁基二元合金离子辐照条件
Table 1. Ion irradiation conditions of Fe/Fe-based binary alloys.
材料 用途 温度/℃ 注入离子 注入能量/keV 注入剂量/(ions·m–2) 纯铁/铁基二元合金* TEM 25 H+ 30 1×1021 TDS 25 D+ 30 1×1021 注: *铁基二元合金指Fe-3Cr, Fe-1.4Ni和Fe-1.4Mn合金. -
[1] Kano S, Yang H L, Suzue R, Matsukawa Y, Satoh Y, Sakasegawa H, Tanigawa H, Abe H 2016 Nucl. Mater. Energy 9 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hishinuma A, Kohyama A, Klueh R, Gelles D, Dietz W, Ehrlich K 1998 J. Nucl. Mater. 258–263 193
[3] Sojak S, Slugeň V, Petriska M, Veterníková JŠ, Stacho M, Sabelová V 2013 22nd International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe Bled, Slovenia September 8–13, 2013 p314
[4] 杜玉峰 2019 博士学位论文 (北京: 北京科技大学)
Du Y F 2019 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing) (in Chinese)
[5] Kohno Y, Kohyama A, Hirose T, Hamilton M, Narui M 1999 J. Nucl. Mater. 272 145
[6] Klueh R, Alexander D, Rieth M 1999 J. Nucl. Mater. 273 146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sacksteder I, Schneider H C, Materna-Morris E 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 417 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Schäublin R, Henry J, Dai Y 2008 Cr. Phys. 9 389
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Dubinko V I, Kotrechko S A, Klepikov V F 2009 Radiat. Eff. Defect. S. 164 647
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 姜少宁, 万发荣, 龙毅 刘传歆, 詹倩, 大貫惣明 2013 62 166801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang S N, Wan F R, Long Y, Liu C X, Zhan Q, Ohnuki S. 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 166801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Osetsky Y N, Serra A, Singh B N, Golubov S I 2000 Philos. Mag. A 80 2131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kim S M, Buyers W 1978 J. Phys. F:Metal Physics 8 L103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Willaime F, Fu C C, Marinica M C, Dalla Torre J 2005 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 228 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hashimoto N, Sakuraya S, Tanimoto J, Ohnuki S 2014 J. Nucl. Mater. 445 224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 万发荣 2020 工程科学学报 42 1535
Wan F R 2020 Chinese J. Eng. 42 1535
[16] Hoelzer D T, Ebrahimi F 1994 MRS Online Proceedings Library 373 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ward A, Fisher S B 1989 J. Nucl. Mater. 166(3) 227
[18] Chen L, Murakami K, Chen D, Abe H, Li Z, Sekimura N 2020 Scripta Mater. 187 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Mizandrontsev D B, Vasiliev A A 2000 Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering 4064 220
[20] Eyre B L, Bartlett A F 1965 Philos. Mag. 12 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Masters B C 1965 Philos. Mag. 11 881
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yabuuchi K, Saito M, Kasada R, Kimura A 2011 J. Nucl. Mater. 414 498
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yabuuchi K, Kasada R, Kimura A 2013 Acta Mater. 61 6517
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Watanabe H, Masaki S, Masubuchi S, Yoshida N, Dohi K 2013 J. Nucl. Mater. 439 268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Horton L L, Bentley J, Farrell K 1982 J. Nucl. Mater. 108 222
[26] Wirth B D, Odette G R, Maroudas D, Lucas G E 2000 J. Nucl. Mater. 276 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Terentyev D, Grammatikopoulos P, Bacon D J, Osetsky Y N 2008 Acta Mater. 56 5034
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang W P, Song L G, Zhu T, Xiong Y, Ma H L, Yan Q Z, Cao X Z, Wang B Y, Jin S X 2021 J. Nucl. Mater. 548 152862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gao N, Perez D, Lu G H, Wang Z G 2018 J. Nucl. Mater. 498 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Kiritani M, Yoshiie T, Iseki M, Kojima S, Hamada K, Horiki M, Kizuka Y, Inoue H, Tada T, Ogasawara Y 1994 J. Nucl. Mater. 212 241
[31] Wei Y X, Gao N, Shen Z Y, Chen C, Xie Z Y, Guo L P 2020 Comp. Mater. Sci. 180 109724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pan X D, Lu T, Lyu Y M, Xu Y P, Zhou H S, Yang Z S, Niu G J, Li X C, Gao F, Luo G N 2020 J. Nucl. Mater. 542 152500
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wei Y X, Gao N, Wang D, Chen C, Guo L P 2019 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 461 83
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Huang Y N, Wan F R, Xiao X, Shi S, Long Y, Ohnuki S, Hashimoto N 2010 Fusion Eng. Des. 85 2203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Wan F R, Ohnuki S, Takahashi H, Takeyama T, Nagasaki R 1986 Philos. Mag. A 53 L21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Gao J, Du Y, Ohnuki S, Wan F 2016 J. Nucl. Mater. 481 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wan F R, Zhan Q, Long Y, Yang S W, Zhang G W, Du Y F, Jiao Z J, Ohnuki S 2014 J. Nucl. Mater. 455 253
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Du Y F, Cui L J, Han W T, Wan F R 2019 Acta Metall. Sin-Engl. 32 566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Foll H, Wilkens M 1975 Phys. Status Solidi A 31 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] 黄依娜, 万发荣, 焦治杰 2011 60 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang Y N, Wan F R, Jiao Z J 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Stoller R E, Toloczko M B, Was G S, Certain A G, Dwaraknath S, Garner F A 2013 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 310 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] ASTM-Committee 2003 Standard Practice for Neutron Radiation Damage Simulation by Charged-particle Irradiation (West Conshohocken: Copyright © ASTM International) p8
[43] 颜强 2017 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Yan Q 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
[44] 万发荣 1993 金属材料的辐照损伤 (北京: 科学出版社) 第85页
Wan F R 1993 Irradiation Damage of Metal Materials (Beijing: Science Press) p85 (in Chinese)
[45] Morishita K, Sugano R, Wirth B D, de La Rubia T D 2003 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 202 76
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] 徐玉平 2017 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Xu Y P 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
[47] Sugano R, Morishita K, Iwakiri H, Yoshida N 2002 J. Nucl. Mater. 307 941
[48] Sugano R, Morishita K, Kimura A, Iwakiri H, Yoshida N 2004 J. Nucl. Mater. 329 942
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6096
- PDF Downloads: 73
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: