-
Tin oxide (SnO2) has attracted a lot of attention among lithium ion battery anode materials due to its rich reserves, high theoretical capacity, and safe potential. However, the mechanism of the SnO2 nano materials in the lithiation-delithiation reaction, especially whether the first-step conversion reaction is reversible, is still controversial. In this paper, SnO2 nanoparticles with an average particle size of 4.4 nm are successfully prepared via a simple hydrothermal method. A nanosized lithium ion battery that enables the in situ electrochemical experiments of SnO2 nanoparticles is constructed to investigate the electrochemical behavior of SnO2 in lithiation-delithiation process. Briefly, the nanosized electrochemical cell consists of a SnO2 working electrode, a metal lithium (Li) counter electrode on a sharp tungsten probe, and a solid electrolyte of lithium oxide (Li2O) layer naturally grown on the surface of metal Li. Then, the whole lithiation-delithiation process of SnO2 nanocrystals is tracked in real time. When a constant potential of –2 V is applied to the SnO2 with respect to lithium, lithium ions begin to diffuse from one side of the nanoparticles, which is in contact with the Li/Li2O layer, and gradually propagate to the other side. Upon the lithiation, a two-step conversion reaction mechanism is revealed: SnO2 is first converted into intermediate phase of Sn with an average diameter of 4.2 nm which is then further converted into Li22Sn5. Upon the delithiation, a potential of 2 V is applied and Li22Sn5 phase can be reconverted into SnO2 phase when completely delithiated. It is because the interfaces and grain boundaries of nano-sized SnO2 may impede the Sn diffusing from one grain into another during lithiation/delithiation and then suppress the coarsening of Sn, and enable the Li2O and Sn to be sufficiently contacted with each other and then converted into SnO2. This work provides a valuable insight into an understanding of phase evolution in the lithiation-delithiation process of SnO2 and the results are of great significance for improving the reversible capacity and cycle performance of lithium ion batteries with SnO2 electrodes.
[1] Paek S M, Yoo E, Honma I 2009 Nano Lett. 9 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kojima T, Ishizu T, Horiba T, Yoshikawa M 2009 J. Power Sources 189 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nitta N, Yushin G 2014 Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 31 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Armand M, Tarascon J M 2008 Nature 451 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Shao-Horn Y, Croguennec L, Delmas C, Nelson E C, O'Keefe M A 2003 Nat. Mater. 2 464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 季怡汝, 张庆华, 谷林 2018 电子显微学报 37 532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ji Y R, Zhang Q H, Gu L 2018 J. Chin. Electron Microsc. Soc. 37 532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 侯贤华, 余洪文, 胡社军 2010 59 8226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou X H, Yu H W, Hu S J 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 8226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 侯贤华, 胡社军, 石璐 2009 59 2109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou X H, Hu S J, Shi L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 2109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu F, Li X, Wang Z, Guo H J, He Z J, Zhang Q, Xiong X H, Yue P 2012 J. Power Sources 202 374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu F, Li X, Wang Z, Guo H J 2013 Nanoscale 5 6936
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sun L, Gao Y M, Xiao B, Li Y F, Wang G L 2013 J. Alloy. Compd. 579 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tian Q H, Tian Y, Zhang Z X, Yang L, Hirano S I 2014 J. Power Sources 269 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Guo X W, Fang X P, Sun Y, Shen L Y, Wang Z X, Chen L Q 2013 J. Power Sources 226 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen L, Wu P, Wang H, Ye Y, Xu B, Cao G P, Zhou Y M, Lu T H, Yang Y S 2014 J. Power Sources 247 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Han Q Y, Zai J T, Xiao Y L, Li B, Xu M, Qian X F 2013 RSC Adv. 3 20573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen J S, Lou X W 2013 Small 9 1877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ye H J, Li H Q, Jiang F Q, Yin J, Zhu H 2018 Electrochim. Acta 266 170
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 刘美梅, 钱翔英 2018 电子显微学报 37 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiu M M, Qian X Y 2018 J. Chin. Electron Microsc. Soc. 37 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Youn S G, Lee I H, Yoon C S, Kim C K, Sun Y K, Lee Y S, Yoshio M 2002 J. Power Sources 108 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kraytsberg A, Ein-Eli Y 2011 J. Power Sources 196 886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Thackeray M M, Johnson C S, Kahaian A J, Kepler K D, Vaughey J T, Shao-Horn Y, Hackney S A 1999 J. Power Sources 81-82 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Idota Y, Kubota T, Matsufuji A, Maekawa Y, Miyasaka T 1997 Science 276 1395
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hu R Z, Sun W, Liu H, Zeng M Q, Zhu M 2013 Nanoscale 5 11971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Brousse T, Retoux R, Herterich U, Schleich D M 1998 J. Electrochem. Soc. 145 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Retoux R, Brousse T, Schleich D M 1999 J. Electrochem. Soc. 146 2472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lou X W, Li C M, Archer L A 2009 Adv. Mat. 21 2536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Holmberg V C, Panthani M G, Korgel B A 2009 Science 326 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zheng H M, Smith R K, Jun Y W, Kisielowski C, Dahmen U, Alivisatos A P 2009 Science 324 1309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Huang J Y, Zhong L, Wang C M, Sullivan J P, Xu W, Zhang L Q, Mao Scott X, Hudak N S, Liu X H, Subramanian A, Fan H Y, Qi L, Kushima A, Li J 2010 Science 330 1515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Hu R Z, Zhang H P, Lu Z C, Liu J, Zeng M Q, Yang L C, Yuan B, Zhu M 2018 Nano Energy 45 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Hu R Z, Chen D C, Waller G, Ouyang Y P, Chen Y, Zhao B, Rainwater B, Yang C H, Zhu M, Liu M L 2016 Energy Environ. Sci. 9 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Li B S, Feng J K, Qian Y T, Xiong S L 2015 J. Mater. Chem. A 3 10336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wang C M, Xu W, Liu J, Zhang J G, Saraf L V, Arey B W, Choi D, Yang Z G, Xiao J, Thevuthasan S, Baer D R 2011 Nano Lett. 11 1874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Meduri P, Clark E, Dayalan E, Sumanasekera G U, Sunkara M K 2011 Energy Environ. Sci. 4 1695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Meduri P, Pendyala C, Kumar V, Sumanasekera G U, Sunkara M K 2009 Nano Lett. 9 612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Haines J, Leger J M 1997 Phys. Rev. B 55 11144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Liu L G 1978 Science 199 422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Chen Z W, Lai J K L, Shek C H 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 231902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Carvalho M H, Pereira E C, de Oliveira A J A 2018 RSC Adv. 8 3958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 SnO2纳米颗粒的表征 (a) SnO2纳米颗粒的XRD图谱; (b) 低倍率下的SnO2纳米颗粒的TEM像, 比例尺为50 nm; (c) SnO2纳米颗粒的高分辨像, 比例尺为2 nm; (d) SnO2纳米颗粒的SAED图像; (e) 四方相SnO2纳米颗粒的晶体结构; (f) SnO2纳米颗粒粒径尺寸分布
Figure 2. Characterization of SnO2 nanoparticles: (a) XRD pattern of the as-prepared SnO2 nanoparticles; (b) TEM image of SnO2 nanopaticles; (c) HRTEM of SnO2 nanoparticles; (d) SAED of SnO2 nanoparticles; (e) crystal structure of the tetracoral SnO2; (f) distribution of SnO2 nanoparticles size.
图 3 SnO2纳米颗粒第一次嵌锂前后的变化 (a) SnO2嵌锂前的形貌, 比例尺为15 nm; (b) SnO2第一次嵌锂后的形貌, 比例尺为15 nm; (c) SnO2嵌锂一段时间后的HRTEM像, 比例尺为1 nm; (d) SnO2嵌锂一段时间后的SAED图; (e) SnO2第一次嵌锂结束后的HRTEM图, 比例尺为5 nm; (f) SnO2第一次嵌锂结束后的SAED图; (g)−(k) SnO2纳米颗粒第一次锂化过程, 比例尺为10 nm
Figure 3. Changes of SnO2 nanoparticles during the first lithiation: (a) Morphology of SnO2 before lithiation; (b) morphology of SnO2 after first lithiation; (c) HRTEM image of SnO2 after a moment; (d) SAED pattern of SnO2 after a moment; (e) HRTEM image of SnO2 after first completely lithiated; (f) SAED pattern of SnO2 after first completely lithiated; (g)−(k) SnO2 nanoparticle first lithiation process.
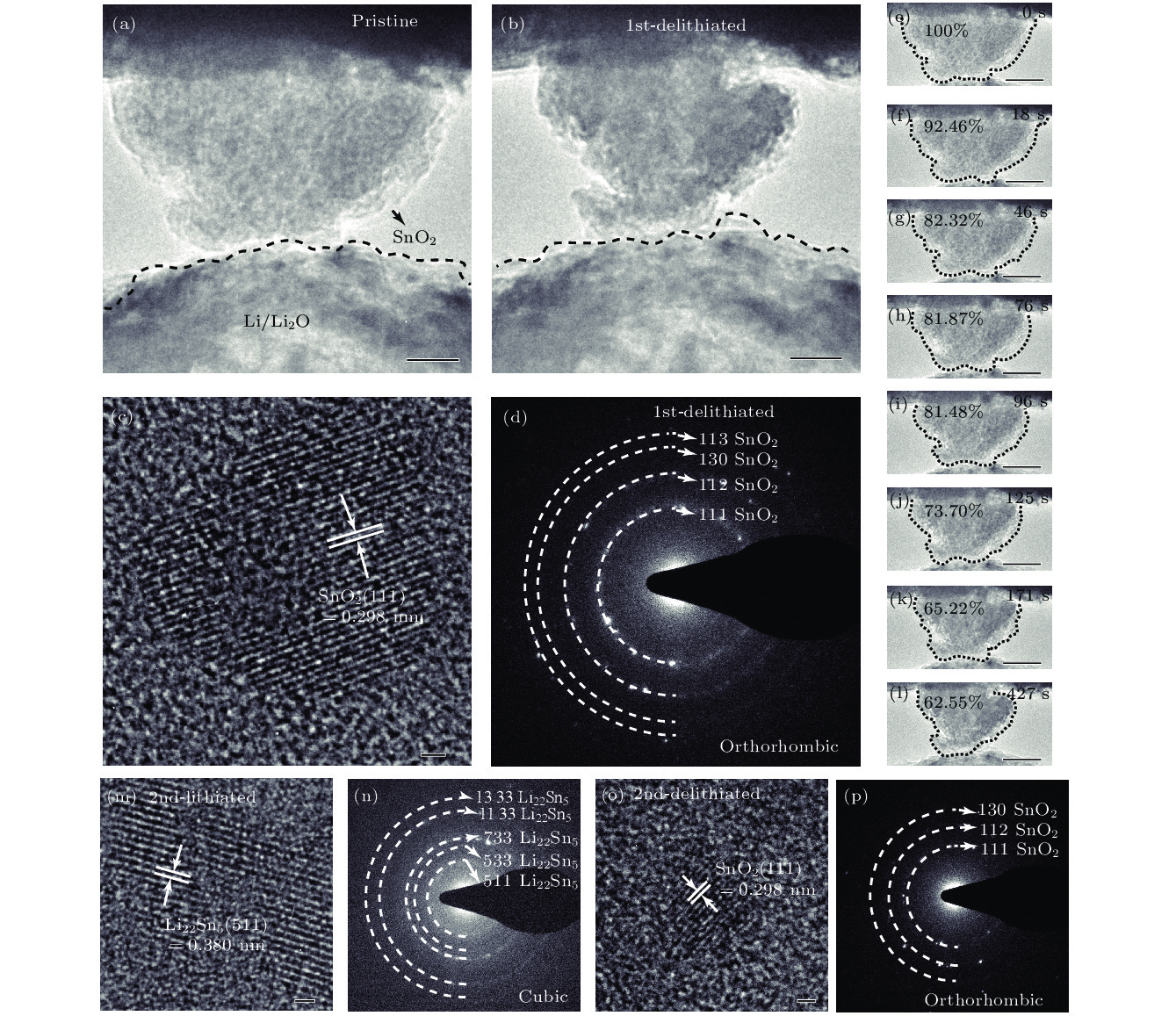
图 4 SnO2纳米颗粒脱锂前后的变化 (a) SnO2第一次脱锂前的形貌, 比例尺为40 nm; (b) SnO2第一次脱锂后的形貌, 比例尺为40 nm; (c) SnO2第一次脱锂结束后的HRTEM图, 比例尺为1 nm; (d) SnO2第一次脱锂结束后的SAED图; (e)—(l) SnO2纳米颗粒第一次脱锂过程, 比例尺为40 nm; (m) SnO2纳米颗粒第二次嵌锂后的HRTEM图, 比例尺为1 nm; (n) SnO2纳米颗粒第二次嵌锂后的SAED图; (o) SnO2纳米颗粒第二次脱锂后的HRTEM图, 比例尺为1 nm; (p) SnO2纳米颗粒第二次脱锂后的SAED图
Figure 4. Changes of SnO2 nanoparticles during the delithiation: (a) Morphology of SnO2 before delithiation; (b) morphology of SnO2 after first delithiated; (c) HRTEM image of SnO2 after completely first delithiated; (d) SAED pattern of SnO2 after first completely delithiated; (e)–(l) SnO2 nanoparticle first delithiation process; (m) HRTEM image of SnO2 after second lithiated; (n) SAED pattern of SnO2 after second lithiated; (o) HRTEM image of SnO2 after second delithiated; (p) SAED pattern of SnO2 after second delithiated.
-
[1] Paek S M, Yoo E, Honma I 2009 Nano Lett. 9 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Kojima T, Ishizu T, Horiba T, Yoshikawa M 2009 J. Power Sources 189 859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nitta N, Yushin G 2014 Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 31 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Armand M, Tarascon J M 2008 Nature 451 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Shao-Horn Y, Croguennec L, Delmas C, Nelson E C, O'Keefe M A 2003 Nat. Mater. 2 464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 季怡汝, 张庆华, 谷林 2018 电子显微学报 37 532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ji Y R, Zhang Q H, Gu L 2018 J. Chin. Electron Microsc. Soc. 37 532
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 侯贤华, 余洪文, 胡社军 2010 59 8226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou X H, Yu H W, Hu S J 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 8226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 侯贤华, 胡社军, 石璐 2009 59 2109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou X H, Hu S J, Shi L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 2109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu F, Li X, Wang Z, Guo H J, He Z J, Zhang Q, Xiong X H, Yue P 2012 J. Power Sources 202 374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu F, Li X, Wang Z, Guo H J 2013 Nanoscale 5 6936
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sun L, Gao Y M, Xiao B, Li Y F, Wang G L 2013 J. Alloy. Compd. 579 457
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tian Q H, Tian Y, Zhang Z X, Yang L, Hirano S I 2014 J. Power Sources 269 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Guo X W, Fang X P, Sun Y, Shen L Y, Wang Z X, Chen L Q 2013 J. Power Sources 226 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chen L, Wu P, Wang H, Ye Y, Xu B, Cao G P, Zhou Y M, Lu T H, Yang Y S 2014 J. Power Sources 247 178
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Han Q Y, Zai J T, Xiao Y L, Li B, Xu M, Qian X F 2013 RSC Adv. 3 20573
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chen J S, Lou X W 2013 Small 9 1877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ye H J, Li H Q, Jiang F Q, Yin J, Zhu H 2018 Electrochim. Acta 266 170
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 刘美梅, 钱翔英 2018 电子显微学报 37 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiu M M, Qian X Y 2018 J. Chin. Electron Microsc. Soc. 37 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Youn S G, Lee I H, Yoon C S, Kim C K, Sun Y K, Lee Y S, Yoshio M 2002 J. Power Sources 108 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kraytsberg A, Ein-Eli Y 2011 J. Power Sources 196 886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Thackeray M M, Johnson C S, Kahaian A J, Kepler K D, Vaughey J T, Shao-Horn Y, Hackney S A 1999 J. Power Sources 81-82 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Idota Y, Kubota T, Matsufuji A, Maekawa Y, Miyasaka T 1997 Science 276 1395
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hu R Z, Sun W, Liu H, Zeng M Q, Zhu M 2013 Nanoscale 5 11971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Brousse T, Retoux R, Herterich U, Schleich D M 1998 J. Electrochem. Soc. 145 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Retoux R, Brousse T, Schleich D M 1999 J. Electrochem. Soc. 146 2472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lou X W, Li C M, Archer L A 2009 Adv. Mat. 21 2536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Holmberg V C, Panthani M G, Korgel B A 2009 Science 326 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zheng H M, Smith R K, Jun Y W, Kisielowski C, Dahmen U, Alivisatos A P 2009 Science 324 1309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Huang J Y, Zhong L, Wang C M, Sullivan J P, Xu W, Zhang L Q, Mao Scott X, Hudak N S, Liu X H, Subramanian A, Fan H Y, Qi L, Kushima A, Li J 2010 Science 330 1515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Hu R Z, Zhang H P, Lu Z C, Liu J, Zeng M Q, Yang L C, Yuan B, Zhu M 2018 Nano Energy 45 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Hu R Z, Chen D C, Waller G, Ouyang Y P, Chen Y, Zhao B, Rainwater B, Yang C H, Zhu M, Liu M L 2016 Energy Environ. Sci. 9 595
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Li B S, Feng J K, Qian Y T, Xiong S L 2015 J. Mater. Chem. A 3 10336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wang C M, Xu W, Liu J, Zhang J G, Saraf L V, Arey B W, Choi D, Yang Z G, Xiao J, Thevuthasan S, Baer D R 2011 Nano Lett. 11 1874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Meduri P, Clark E, Dayalan E, Sumanasekera G U, Sunkara M K 2011 Energy Environ. Sci. 4 1695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Meduri P, Pendyala C, Kumar V, Sumanasekera G U, Sunkara M K 2009 Nano Lett. 9 612
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Haines J, Leger J M 1997 Phys. Rev. B 55 11144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Liu L G 1978 Science 199 422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Chen Z W, Lai J K L, Shek C H 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 231902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Carvalho M H, Pereira E C, de Oliveira A J A 2018 RSC Adv. 8 3958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12638
- PDF Downloads: 160
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: