-
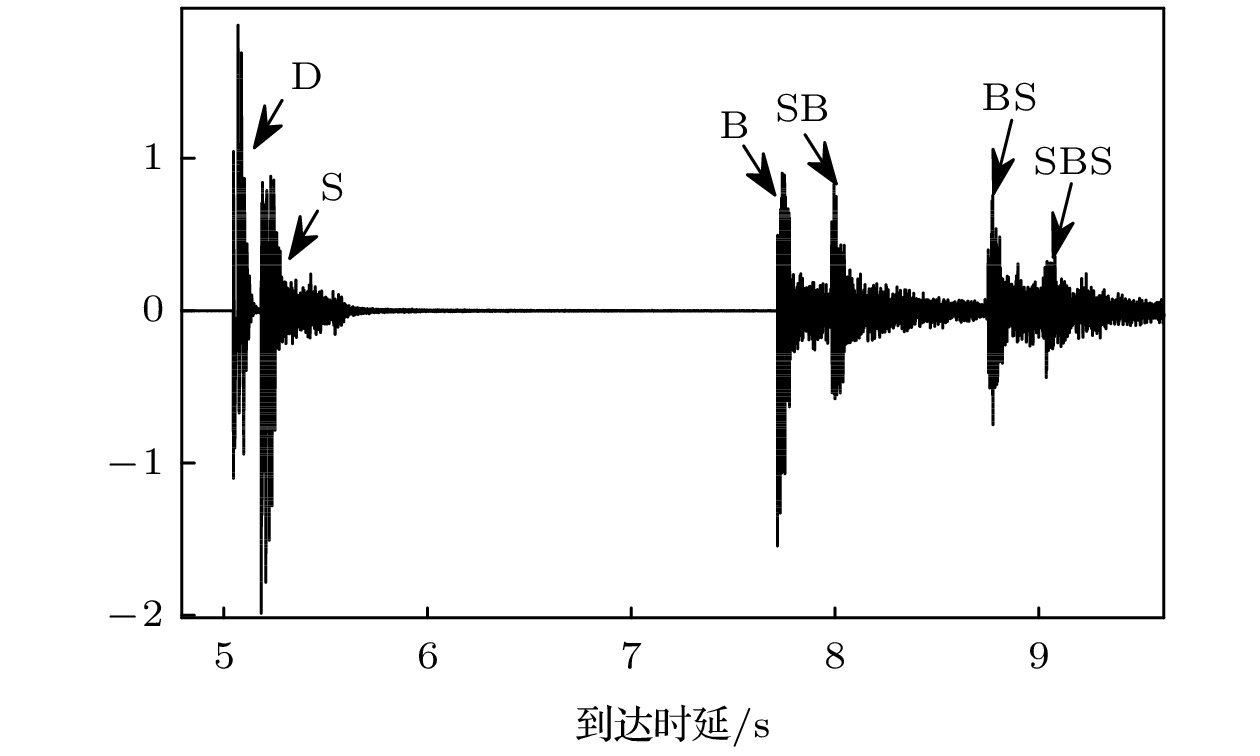
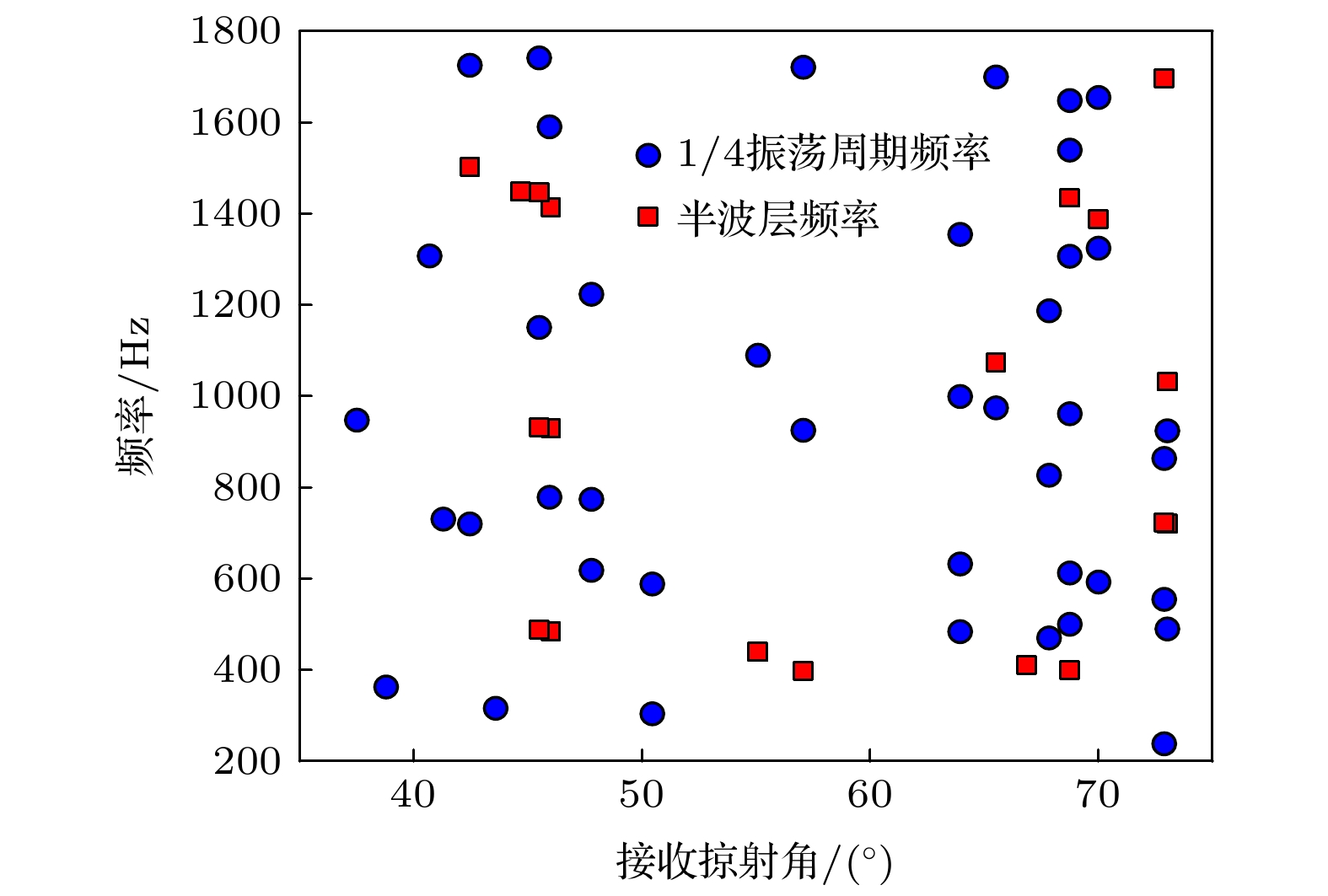
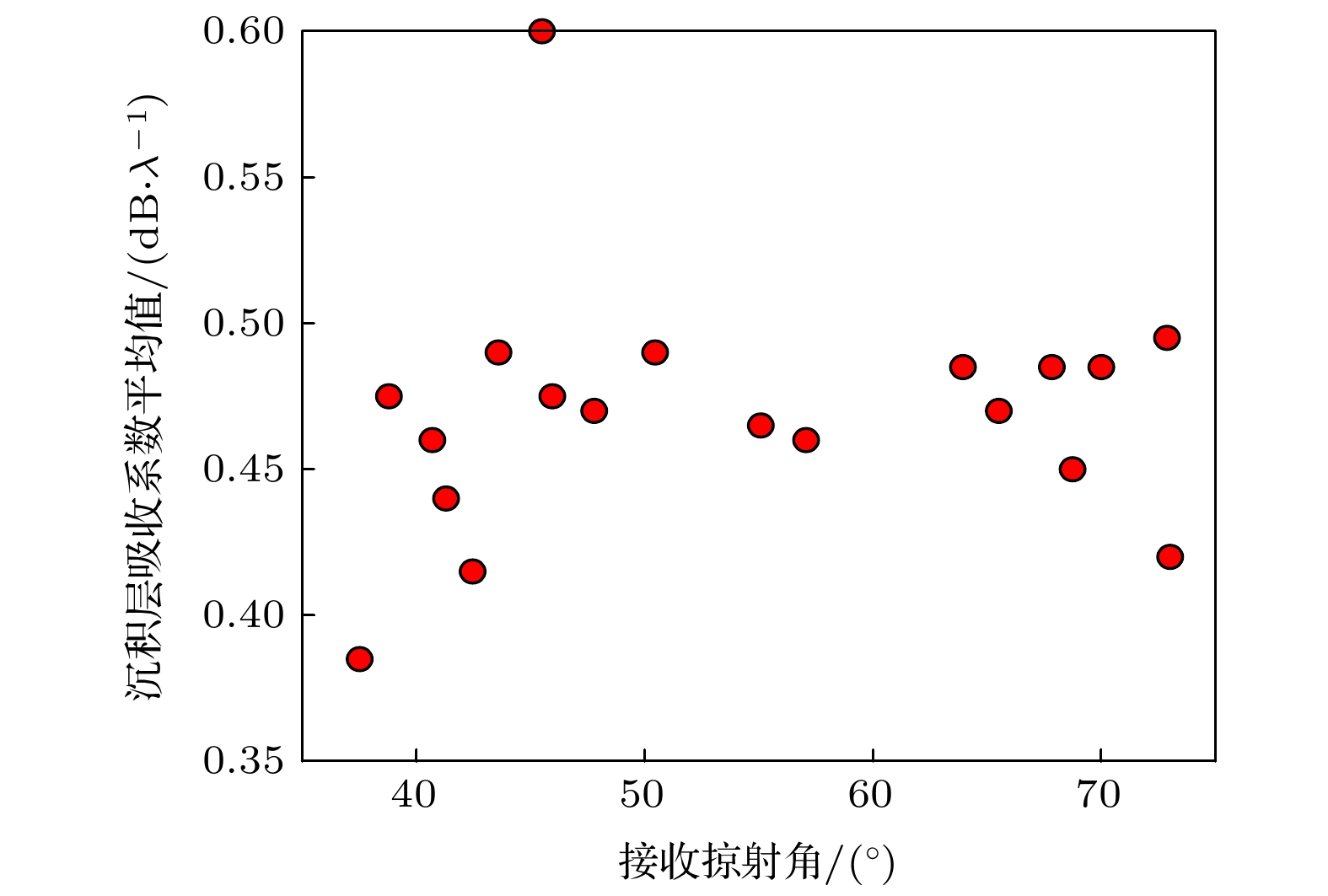
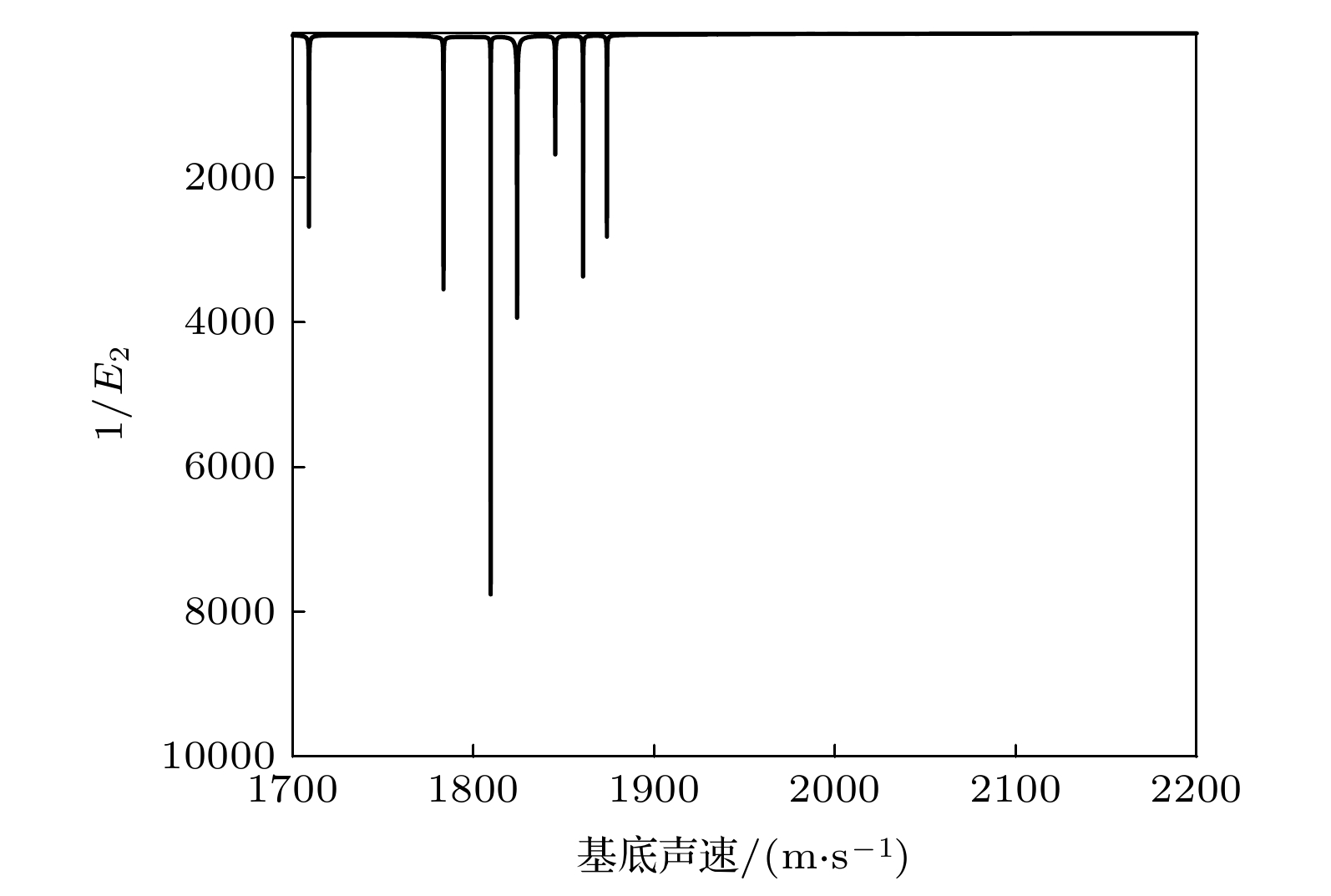
The acquisition of geoacoustic parameters is of great significance in studying ocean acoustics. On the basis of deducing the seabed reflection coefficient under the layered absorbing medium, the influence of the absorption coefficient on the seabed reflection coefficient under the condition of large grazing angles is analyzed. The seabed reflection coefficient oscillates at a frequency. When it is equal to the reflection coefficient of the contact interface between seawater and sediment, the corresponding frequency point is defined as the 1/4 oscillation period frequency. At this frequency, the coupling degree between absorption coefficient of sedimentary layer and substrate geoacoustic parameters is less than those at other frequencies. In this paper, a stepwise optimization inversion method for deep water geoacoustic parameters is proposed based on the seabed reflection characteristics of large grazing angles. Firstly, the interference period of the seabed reflection coefficient is extracted by the correlation method, and the sound speed and thickness of the deposited layer are inverted by the interference period. The density is obtained from the inversion result of sound speed combined with Hamilton empirical formula. Secondly, the value of the absorption coefficient of the sedimentary layer is calculated by combining the search boundary of the substrate sound speed. The one-dimensional inversion of the substrate sound speed is realized by using the substrate reflection coefficient at 1/4 oscillation period frequency. Finally, the one-dimensional inversion of the absorption coefficient of the sedimentary layer is realized by using the seabed reflection coefficient at a half-wave layer frequency. The seabed reflection characteristics of large glancing angles are combined with stepwise inversion to reduce the coupling degree of the substrate sound speed and the absorption coefficient of the sedimentary layer. Experimental results show that the geoacoustic parameters retrieved by this method can be effectively applied to the prediction of propagation loss in a certain range under the condition of large grazing angle measurement.
-
Keywords:
- geoacoustic inversion in the deep water /
- seabed reflection coefficient /
- stepwise inversion
[1] 杨坤德, 马远良 2009 58 1798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang K, Ma Y L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 1798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 黎雪刚, 杨坤德, 张同伟, 等 2009 58 7741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X G, Yang K D, Zhang T W, et al. 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 7741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 周天, 李海森, 朱建军, 等 2014 63 084302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou T, Li H S, Zhu J J, et al. 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 084302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 李赫, 郭新毅, 马力 2019 63 214303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li H, Guo X Y, Ma L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 214303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Belcourt J, Holland C W, Dosso S E, et al. 2020 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 45 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 陈勃, 赵梅, 胡长青, Zygmunt Klusek 2018 声学学报 43 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen B, Zhao M, Hu C Q, Zygmunt K 2018 Acta Acoustica 43 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chiu L, Chang A, Chen H H, et al. 2020 Cont. Shelf Res. 201 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 徐丽亚, 杨坤德 2020 声学技术 39 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L Y, Yang K D 2020 Technical Acoustics 39 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Quijano J E, Dosso S E, Dettmer J, et al. 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 133 EL47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Qin J X, Katsnelson B, Godin O, Li Z L 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 094301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 江鹏飞, 林建恒, 孙军平, 等 2019 66 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang P G, Lin J H, Sun J P, et al. 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 薄连坤, 罗来源, 熊瑾煜 2018 声学学报 43 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L K, Luo L Y, Xiong J Y 2018 Acta Acoustica 43 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Barclay D R, Bevans D A, Buckingham M J 2019 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 99 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 李风华, 张仁和 2000 声学学报 4 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li F H, Zhang R H 2000 Acta Acoustica 4 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张学磊, 李整林, 黄晓砥 2009 声学学报 1 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X L, Li Z L, Huang X D 2009 Acta Acoustica 1 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wu S L, Li Z L, Qin J X 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李梦竹, 李整林, 周纪浔 2019 68 094301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M Z, Li Z L, Zhou J X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 094301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 李梦竹, 李整林, 李倩倩 2019 声学学报 44 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M Z, Li Z L, Li Q Q 2019 Acta Acoustica 44 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fialkowski L T, Lingevitch J F, Perkins J S, et al. 2003 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 28 370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang Y M, Chapman N R, Badiey M 2007 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 121 1879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 布列霍夫斯基赫 L 著 (杨训仁 译) 1985 分层介质中的波 (北京: 科学出版社) 第10—16页
Л. М. Бреховских L (translated by Yang X R) 1985 Waves In Layered Medium (Beijing: Science Press) pp10–16 (in Chinese)
[22] Hamilton E L, Bachman R T 1982 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 72 1891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 布列霍夫斯基赫 L著 (中国海洋大学, 中国科学院声学研究所 译) 1983 海洋声学 (北京: 科学出版社) 第309—314页
Л. М. Бреховских L (translated by OUC & IACAS) 1983 Ocean Acoustic (Beijing: Science Press) pp309–314 (in Chinese)
-
图 2 各项参数随频率和沉积层吸收系数的变化 (a) 海水-沉积层界面反射系数相位; (b) 沉积层-基底界面反射系数相位; (c) 垂直相移实部
Figure 2. Various parameters vary with frequency and the absorption coefficient of the sedimentary layer: (a) Phase of the reflection coefficient of the seawater-sedimentary layer interface; (b) phase of the reflection coefficient of the sedimentary layer-substrate interface; (c) real part of the vertical phase shift.
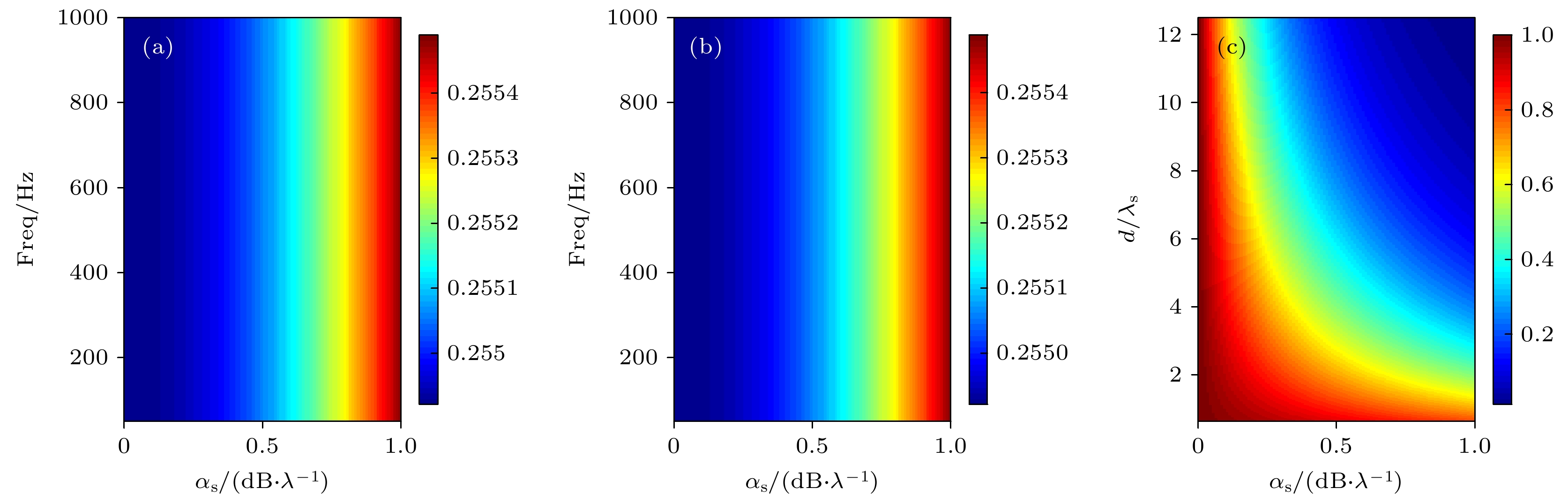
图 3 各项参数随频率和沉积层吸收系数的变化 (a) 海水-沉积层界面反射系数模; (b)沉积层-基底界面反射系数模; (c) 衰减项
Figure 3. Various parameters vary with frequency and the absorption coefficient of the sediment layer: (a) Reflection coefficient of the seawater-sedimentary layer interface; (b) reflection coefficient of the sedimentary layer- substrate interface; (c) attenuation term.
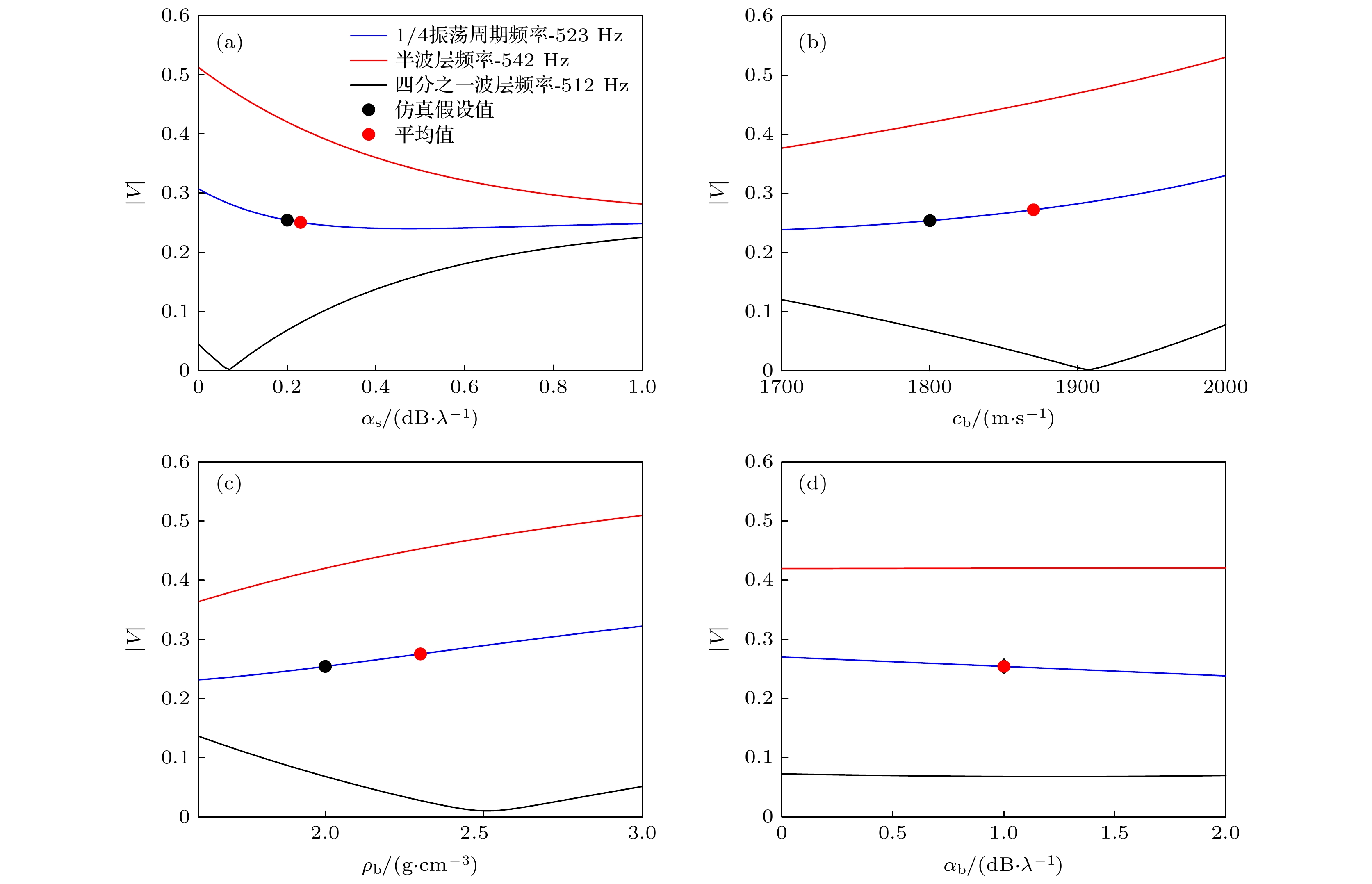
图 5 不同频点下海底反射系数随各地声参数的变化 (a) 沉积层吸收系数; (b) 基底声速; (c) 基底密度; (d) 基底吸收系数
Figure 5. Seabed reflectance coefficient varies with the various GA parameters at different frequency points: (a) Absorption coefficient of sedimentary layer; (b) sound speed of substrate; (c) density of substrate; (d) absorption coefficient of substrate.
表 1 海底反射系数仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of seabed reflection coefficient.
参数 $ {c_{\text{s}}} $/(m·s–1) $ {\rho _{\text{s}}} $/(g·cm–3) $ {d_{}} $/m $ {\alpha _{\text{s}}} $/(dB·λ–1) $ {c_{\text{b}}} $/(m·s–1) $ {\rho _{\text{b}}} $/(g·cm–3) $ {\alpha _{\text{b}}} $/(dB·λ–1) 数值 1600 1.5 20 0—1.0 1800 2.0 1.0 表 2 本文方法反演结果
Table 2. Inversion results obtained by using the method in this paper.
反演参数 参数穷举空间 反演结果 沉积层声速/(m·s–1) 1450 —1800 1570.6 沉积层密度/(g·cm–3) — 1.61 沉积层厚度/m 0—50 2.40 沉积层吸收系数/(dB·λ–1) 0—1.0 0.18 基底声速/(m·s–1) 1700 —2200 1809.5 基底密度/(g·cm–3) — 2.06 基底吸收系数/(dB·λ–1) — 1.0 表 3 Hamilton沉积分类参数
Table 3. Hamilton sedimentary classification parameters.
沉积物类型 声速
/(m·s–1)密度
/(g·cm–3)衰减系数
/(dB·m–1·kHz–1)粗砂 1836 2.034 0.479 细砂 1753 1.957 0.510 极细砂 1697 1.866 0.673 粉砂质砂 1668 1.806 0.692 砂质粉砂 1664 1.787 0.756 粉砂 1623 1.767 0.673 砂-粉砂-粘土 1579 1.590 0.113 粘土质粉砂 1549 1.488 0.095 粉砂质粘土 1520 1.421 0.078 -
[1] 杨坤德, 马远良 2009 58 1798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang K, Ma Y L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 1798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 黎雪刚, 杨坤德, 张同伟, 等 2009 58 7741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X G, Yang K D, Zhang T W, et al. 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 7741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 周天, 李海森, 朱建军, 等 2014 63 084302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou T, Li H S, Zhu J J, et al. 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 084302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 李赫, 郭新毅, 马力 2019 63 214303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li H, Guo X Y, Ma L 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 214303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Belcourt J, Holland C W, Dosso S E, et al. 2020 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 45 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 陈勃, 赵梅, 胡长青, Zygmunt Klusek 2018 声学学报 43 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen B, Zhao M, Hu C Q, Zygmunt K 2018 Acta Acoustica 43 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chiu L, Chang A, Chen H H, et al. 2020 Cont. Shelf Res. 201 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 徐丽亚, 杨坤德 2020 声学技术 39 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L Y, Yang K D 2020 Technical Acoustics 39 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Quijano J E, Dosso S E, Dettmer J, et al. 2013 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 133 EL47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Qin J X, Katsnelson B, Godin O, Li Z L 2017 Chin. Phys. Lett. 34 094301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 江鹏飞, 林建恒, 孙军平, 等 2019 66 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang P G, Lin J H, Sun J P, et al. 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 薄连坤, 罗来源, 熊瑾煜 2018 声学学报 43 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao L K, Luo L Y, Xiong J Y 2018 Acta Acoustica 43 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Barclay D R, Bevans D A, Buckingham M J 2019 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 99 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 李风华, 张仁和 2000 声学学报 4 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li F H, Zhang R H 2000 Acta Acoustica 4 297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张学磊, 李整林, 黄晓砥 2009 声学学报 1 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X L, Li Z L, Huang X D 2009 Acta Acoustica 1 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wu S L, Li Z L, Qin J X 2015 Chin. Phys. Lett. 32 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李梦竹, 李整林, 周纪浔 2019 68 094301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M Z, Li Z L, Zhou J X 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 094301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 李梦竹, 李整林, 李倩倩 2019 声学学报 44 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M Z, Li Z L, Li Q Q 2019 Acta Acoustica 44 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fialkowski L T, Lingevitch J F, Perkins J S, et al. 2003 IEEE J. Oceanic Eng. 28 370
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Jiang Y M, Chapman N R, Badiey M 2007 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 121 1879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 布列霍夫斯基赫 L 著 (杨训仁 译) 1985 分层介质中的波 (北京: 科学出版社) 第10—16页
Л. М. Бреховских L (translated by Yang X R) 1985 Waves In Layered Medium (Beijing: Science Press) pp10–16 (in Chinese)
[22] Hamilton E L, Bachman R T 1982 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 72 1891
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 布列霍夫斯基赫 L著 (中国海洋大学, 中国科学院声学研究所 译) 1983 海洋声学 (北京: 科学出版社) 第309—314页
Л. М. Бреховских L (translated by OUC & IACAS) 1983 Ocean Acoustic (Beijing: Science Press) pp309–314 (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8564
- PDF Downloads: 170
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: