-
High order harmonic generation (HHG) is an important phenomenon when atoms or molecules interact with an intense laser field. It can be used to generate ultrashort laser source, and can also be used to investigate the atomic and molecular dynamics and obtain the electric structure information of molecules. All these require to understand in depth the mechanism of HHG. There are complicated interference effects in HHG spectra of molecules due to multiple re-collision atomic centers in the molecule. In this paper, spectra of aligned O2 molecule in linearly polarized laser field is investigated by using the Lewenstein' s model. The dependence of the spectrum on the angle θ between the nuclear axis of the molecule and the laser polarization direction is obtained. It is shown that the maximum yield of HHG occurs at θ of 45°, which is in consistence with the experimental result. In addition, it is found that there exists a minimum value in the HHG spectrum for any given value of θ. The harmonic order corresponding to the minimum increases with θ increasing. It is found that the minimum comes from the coherent superposition of contributions from two channels. One channel refers to that the ionized electron from one atomic center, subjected to the electric field of the laser, moves back to its parent atomic center and there it combines with the molecule and emits harmonics; while the other channel is that the ionized electron generated from one atomic center move back to the other atomic center to complete the combination and emission of harmonics. The angle θ-dependent phase difference between contributions from these two channels is calculated and the harmonic order corresponding to the minimum value is obtained. Finally, the reason why the yield of HHG is low for the case of the molecular axis parallel to the laser polarization direction is different from that for the case of the molecular axis perpendicular to the polarization direction. For the parallel case, the contributions to HHG from the two channels are both small so that the amplitude of their coherent superposition is small. While for the perpendicular case, the individual contribution from each channel is not small but their destructive interference leads to small yield in harmonicspectrum.
[1] Skantzakis E, Chatziathanasiou S, Carpeggiani P A, Sansone G, Nayak A, Gray D, Tzallas P, Charalambidis D, Hertz E, Faucher O 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 39295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Popmintchev T, Chen M C, Popmintchev D et al. 2012 Science 336 1287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 宋浩, 吕孝源, 朱若碧, 陈高 2019 68 184201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H, Lv X Y, Zhu R B, Chen G 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 184201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Alexander M K, Marcin F, Maciej P, Stoyan K S, Kyle J M B, Bartosz A G 2006 Science 312 420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Itatani J, Levesque J, Zeidler D, Niikura H, Pepin H, Kieffer J C, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2004 Nature 432 867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Torres R, Kajumba N, Underwood J G, Robinson J S, Baker S, Tisch J W G, Nalda R D, Bryan W A, Velotta R, Altucci C, Turcu I C E, Marangos J P 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 203007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zair A, Siegel T, Sukiasyan S, Risoud F, Brugnera L, Hutchison C, Diveki Z, Auguste T, Tisch J W G, Salieres P, Ivanova M Y, Marangos J P 2013 Chem. Phys. 414 184
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chatziathanasiou S, Liontos I, Skantzakis E, Kahaly S, Kahaly M U, Tsatrafyllis N, Faucher O, Witzel B, Papadakis N, Charalambidis D, Tzallas P 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 061404
[10] Lein M, Hay N, Velotta R, Marangos J P, Knight P L 2002 Phys. Rev. A 66 023805
[11] Lein M, Hay N, Velotta R, Marangos J P, Knight P L 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 183903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kanai T, Minemoto S, Sakai H 2005 Nature 435 470
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Faria C F D M 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 043407
[14] 袁仲, 郭迎春, 王兵兵 2016 65 114205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan Z, Guo Y C, Wang B B 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 114205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou X X, Tong X M, Zhao Z X, Lin C D 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 033412
[16] Itatani J, Zeidler D, Levesque J, Spanner M, Villeneuve D M, Corkum P B 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 123902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lewenstein M, Balcou P, Ivanov M Y, Huillier A L, Corkum P B 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2117
[18] Molpro A Package of Ab Initio Programs, Werner H J, Knowles P J, Lindh R, Manby F R, Schutz M, Celani P, Korona T, Rauhut G, Amos R D, Bernhardsson A, Berning A, Cooper D L, Deegan M J O, Dobbyn A J, Eckert F, Hampel C, Hetzer G, Lloyd A W, McNicholas S J, Meyer W, Mura M E, Nicklass A, Palmieri P http://www.molpro.net/ [2020-12-12]
[19] 邓华依, 周效信 2009 原子与分子 26 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng H Y, Zhou X X 2009 J. At. Mol. Phys. 26 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 李忠元, 郭迎春, 王兵兵 2021 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版) 1 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z Y, Guo Y C, Wang B B 2021 Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Sciences) 1 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cooper J W 1962 Phys. Rev. 128 681
[22] Carlson T A, Krause M O, Grimm F A, Keller P, Taylor J W 1982 J. Chem. Phys. 77 5340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Worner H J, Niikura H, Bertrand J B, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 103901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Shiner A D, Schmidt B E, Herrero C T, Corkum P B, Kieffer J C, Legare F, Villeneuve D M 2012 J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 45 074010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wong M C H, Le A T, Alharbi A F, Boguslavskiy A E, Lucchese R R, Brichta J P, Lin C D, Bhardwaj V R 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 033006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
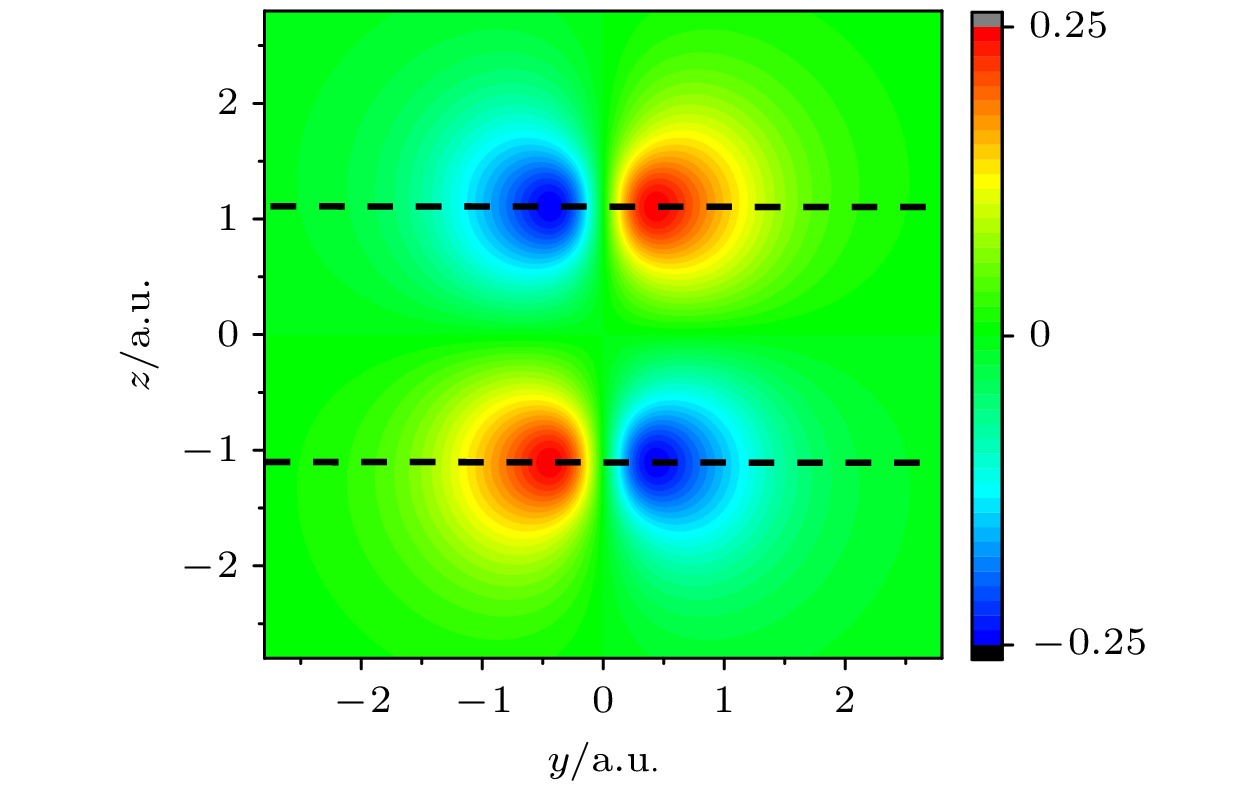
图 3 O2在激光偏振与核轴成不同夹角
$\theta $ 下的高次谐波谱, 每幅图中的黑色划线为第一类通道的贡献$\log |{X_1} + {X_2}{|^2}$ ; 红色点划线为第二类通道的贡献$\log |{X_3} + {X_4}{|^2}$ ; 蓝色实线为两类通道叠加的结果$\log |{X_1} + {X_2} + {X_3} + {X_4}{|^2}$ Figure 3. The HHG spectrum of O2 with different
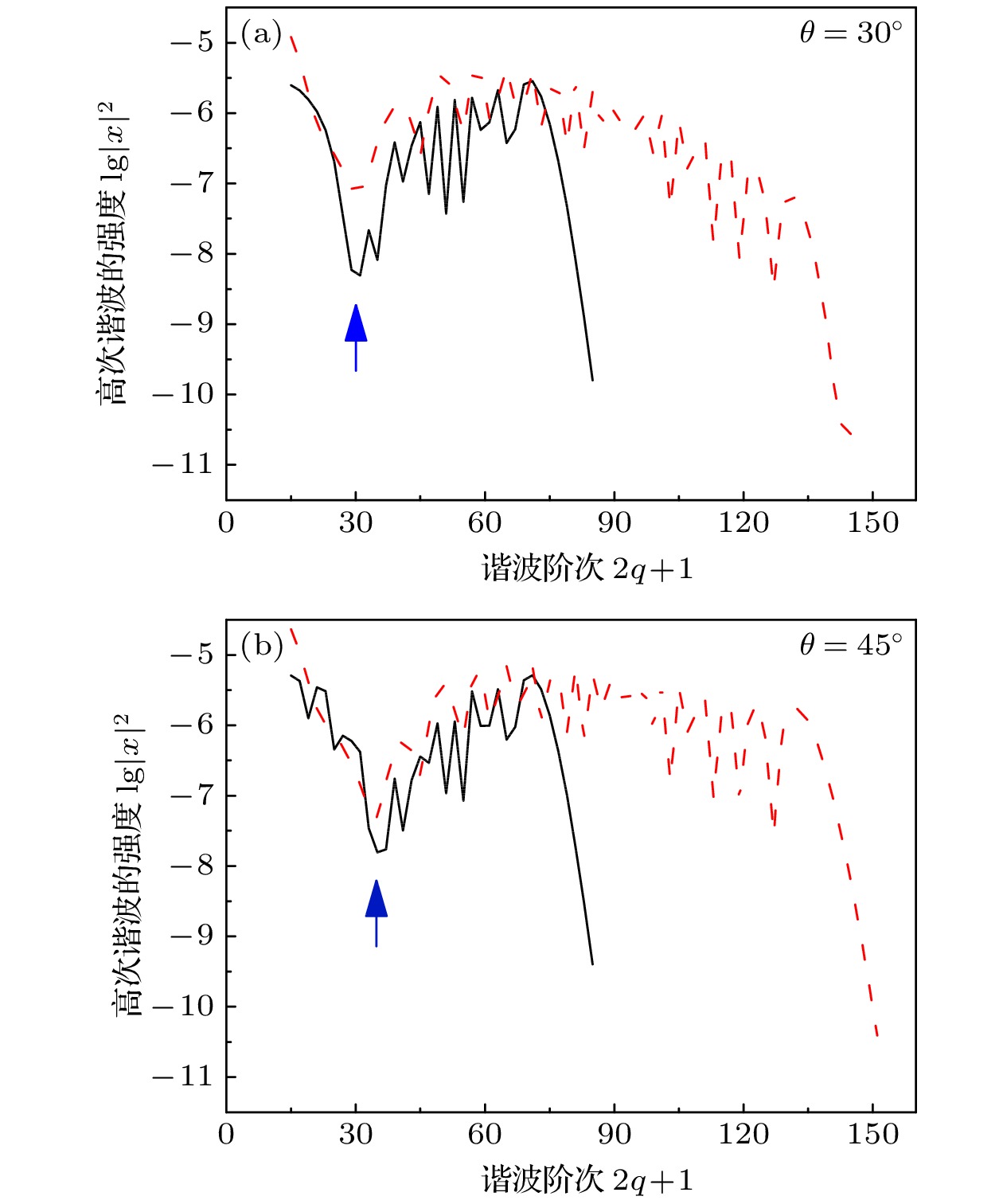
$\theta $ between the polarizing direction of laser electric field and the nuclear axis of O2: In each panel, black dash line is the contribution from the first path$\log |{X_1} + {X_2}{|^2}$ , red dot line represent that from the second path$\log |{X_3} + {X_4}{|^2}$ , and blue solid line represents the addition of the above two paths$\log |{X_1} + {X_2} + {X_3} + {X_4}{|^2}$ .图 5 核轴和偏振方向的夹角 θ 分别为30°(图(a))和45°(图(b))时O2的高次谐波谱, 黑色实线对应的激光强度为
$5.18 \times $ $ {10^{14}}\, {{\rm{{W/c}}}}{{{{\rm{m}}}}^{{2}}}$ , 红色虚线对应$1.036 \times {10^{15}}\, {{\rm{{W/c}}}}{{{\rm{{m}}}}^{{2}}}$ Figure 5. The HHG spectrum of O2 with different
$ \theta $ between the polarizing direction of laser electric field and the nuclear axis of O2 , in panel (a)$ \theta $ is 30° and in (b)$ \theta $ is 45°. In each panel, black solid line is for the laser intensity of$5.18 \times {10^{14}}\, {{\rm{{W/c}}}}{{{\rm{{m}}}}^{{2}}}$ and short dash line is for the laser intensity of$1.036 \times {10^{15}}\, {{\rm{{W/c}}}}{{{\rm{{m}}}}^{{2}}}$ -
[1] Skantzakis E, Chatziathanasiou S, Carpeggiani P A, Sansone G, Nayak A, Gray D, Tzallas P, Charalambidis D, Hertz E, Faucher O 2016 Sci. Rep. 6 39295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Popmintchev T, Chen M C, Popmintchev D et al. 2012 Science 336 1287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 宋浩, 吕孝源, 朱若碧, 陈高 2019 68 184201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H, Lv X Y, Zhu R B, Chen G 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 184201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Alexander M K, Marcin F, Maciej P, Stoyan K S, Kyle J M B, Bartosz A G 2006 Science 312 420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Itatani J, Levesque J, Zeidler D, Niikura H, Pepin H, Kieffer J C, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2004 Nature 432 867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Torres R, Kajumba N, Underwood J G, Robinson J S, Baker S, Tisch J W G, Nalda R D, Bryan W A, Velotta R, Altucci C, Turcu I C E, Marangos J P 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 203007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zair A, Siegel T, Sukiasyan S, Risoud F, Brugnera L, Hutchison C, Diveki Z, Auguste T, Tisch J W G, Salieres P, Ivanova M Y, Marangos J P 2013 Chem. Phys. 414 184
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chatziathanasiou S, Liontos I, Skantzakis E, Kahaly S, Kahaly M U, Tsatrafyllis N, Faucher O, Witzel B, Papadakis N, Charalambidis D, Tzallas P 2019 Phys. Rev. A 100 061404
[10] Lein M, Hay N, Velotta R, Marangos J P, Knight P L 2002 Phys. Rev. A 66 023805
[11] Lein M, Hay N, Velotta R, Marangos J P, Knight P L 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 183903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kanai T, Minemoto S, Sakai H 2005 Nature 435 470
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Faria C F D M 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 043407
[14] 袁仲, 郭迎春, 王兵兵 2016 65 114205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan Z, Guo Y C, Wang B B 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 114205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhou X X, Tong X M, Zhao Z X, Lin C D 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 033412
[16] Itatani J, Zeidler D, Levesque J, Spanner M, Villeneuve D M, Corkum P B 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 123902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lewenstein M, Balcou P, Ivanov M Y, Huillier A L, Corkum P B 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2117
[18] Molpro A Package of Ab Initio Programs, Werner H J, Knowles P J, Lindh R, Manby F R, Schutz M, Celani P, Korona T, Rauhut G, Amos R D, Bernhardsson A, Berning A, Cooper D L, Deegan M J O, Dobbyn A J, Eckert F, Hampel C, Hetzer G, Lloyd A W, McNicholas S J, Meyer W, Mura M E, Nicklass A, Palmieri P http://www.molpro.net/ [2020-12-12]
[19] 邓华依, 周效信 2009 原子与分子 26 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng H Y, Zhou X X 2009 J. At. Mol. Phys. 26 101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 李忠元, 郭迎春, 王兵兵 2021 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版) 1 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Z Y, Guo Y C, Wang B B 2021 Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Sciences) 1 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Cooper J W 1962 Phys. Rev. 128 681
[22] Carlson T A, Krause M O, Grimm F A, Keller P, Taylor J W 1982 J. Chem. Phys. 77 5340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Worner H J, Niikura H, Bertrand J B, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 103901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Shiner A D, Schmidt B E, Herrero C T, Corkum P B, Kieffer J C, Legare F, Villeneuve D M 2012 J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 45 074010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wong M C H, Le A T, Alharbi A F, Boguslavskiy A E, Lucchese R R, Brichta J P, Lin C D, Bhardwaj V R 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 033006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7102
- PDF Downloads: 92
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: