-
Ellipticity properties of high-order harmonic generation (HHG) from symmetric molecules
$ {\text{H}}_{\text{2}}^ + $ in strong and short wavelength (less than 800nm) laser fields are numerically investigated. In this study, the ellipticity of harmonic is compared with the corresponding harmonic spectrum and dipole, and the calculation results are analyzed and the results obtained at different laser intensities, different laser wavelengths, different internuclear distances and different orientation angles are compared with each other. Our numerical simulations show that the influences of laser intensity, laser wavelength, internuclear distance and orientation angle on the ellipticity of harmonic are different. Especially in a two-center interference region, the excited state plays an important role in the HHG, but the effects of the excited state on the ellipticity of harmonic are different at different orientation angles. Further analysis shows that these different effects are due to the influence of the excited state on the harmonic yield. Using the numerical scheme, it is determined that in the two-center interference region, the excited state plays an important role in the parallel harmonic spectrum, while the effects of the excited state on the perpendicular harmonics at different angles are all very small, which results in different phase differences between the accurate harmonic spectrum and the harmonic spectrum only returning to the ground state. Overall, the relative yields of the accurate perpendicular harmonics are lower (higher) than those of the accurate parallel harmonics, but the intensities of the perpendicular harmonics, which only return to the ground state, are comparable to (or farther away from) those of the parallel harmonics which are only to return to ground state in the two-center interference regions. Therefore, the small (large) intensity ratio between the accurate perpendicular harmonic and accurate parallel harmonic can be attributed to the contributions of the excited state to harmonics. Then we can conclude that the harmonic spectra that only go back to the ground state show high (small) ellipticity, whereas the accurate harmonic spectra show small (high) ellipticity, resulting in a strong angle dependence of the influence of the excited state on the ellipticity of harmonic. In addition, in the high-order harmonic plateau region, the relative yields of harmonics can be well predicted by the corresponding dipoles, indicating the applicability of tunneling pictures and plane wave approximation in the strong and short-wave laser fields. When the ellipticity of harmonic occurs in the interference region due to the two-center characteristics of the symmetric potential, the results show that the polarization measurement can also be used to detect the structures of symmetric molecules and track the dynamic behaviors of excited states.-
Keywords:
- high-order harmonic generation /
- strong and short wave laser field /
- the polarization properties of harmonics /
- dipole
[1] L’Huillier A, Schafer K J, Kulander K C 1991 J. Phys. B 24 3315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Itatani J, Levesque J, Zeidler Hiromichi Niikura D, Pepin H, Kieffer J C, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2004 Nature 432 867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Krausz F, Ivanov M 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Le V H, Le A T, Xie R H, Lin C D 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 013414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Vozzi C, Negro M, Calegari F, Sansone G, Nisoli M, Silvestri S De, Stagira S 2011 Nat. Phys. 7 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Smirnova O, Mairesse Y, Patchkovskii S, Dudovich N, Villeneuve D, Corkum P, Ivanov M Yu 2009 Nature 460 972
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shafifir D, Soifer H, Bruner B D, Dagan M, Mairesse Y, Patchkovskii S, Ivanov M Yu, Smirnova O, Dudovich N 2012 Nature 485 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lewenstein M, Balcou Ph, Ivanov M Yu, L'Huillier Anne, Corkum P B 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Keldysh L V 1965 Sov. Phys. JETP 20 1307
[11] Kim V V, Ganeev R A, Boltaev G S, Alnaser A S 2020 J. Phys. B 53 155405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dong F L, Tian Y Q, Yu S J, Wang S, Yang S P, Chen Y J 2015 Opt. Express 23 18106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhou X, Lock R, Wagner N, Li W, Kapteyn H C, Murnane M M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 073902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Levesque J, Mairesse Y, Dudovich N, epin H P, Kieffer J C, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 243001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ramakrishna S, Sherratt P A J, Dutoi A D, Seideman T 2010 Phys. Rev. A 81 021802(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Strelkov V V, Gonoskov A A, Gonoskov I A, Ryabikin M Yu 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 043902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Akagi H, Otobe T, Staudte A, Shiner A, Turner F, Dörner R, Villeneuve D M, Corkum P B 2009 Science 325 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bian X B, Bandrauk A D 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 093903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chen Y J, Zhang B 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 053402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Qin M, Zhu X, Zhang Q, Hong W, Lu P 2011 Opt. Express 19 25084
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Du H, Luo L, Wang X, Hu B 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 013846
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yu S J, Zhang B, Li Y P, Yang S P, Chen Y J 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 053844
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Barreau L, Veyrinas K, Gruson V, Weber S J, Auguste T, Hergott J F, Lepetit F, Carré B, Houver J -C, Dowek D, Salières P 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 4727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun F J, Chen C, Li W Y, Liu X, Li W, Chen Y J 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 053108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Habibović D, Milošević D B 2020 Photonics 7 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huo X X, Xing Y H, Qi T, Sun Y, Li Bo, Zhang J, Liu X S 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 053116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen Y J 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 043423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen Y J, Zhang B 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 023415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bian X B, Bandrauk A D 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 053417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Miao X Y, Zhang C P 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 033410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Han Y C 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 043404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Feit M D, Jr Fleck J A, Steiger A 1982 J. Comput. Phys. 47 412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Shiner A D, Trallero-Herrero C, Kajumba N, Bandulet H C, Comtois D, Légaré F, Giguère M, Kieffffer J C, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 073902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Yu S J, Li W Y, Li Y P, Chen Y J 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 013432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen Y J, Hu B 2009 J. Chem. Phys. 131 244109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen Y J, Chen J, Liu J 2006 Phys. Rev. A 74 063405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1
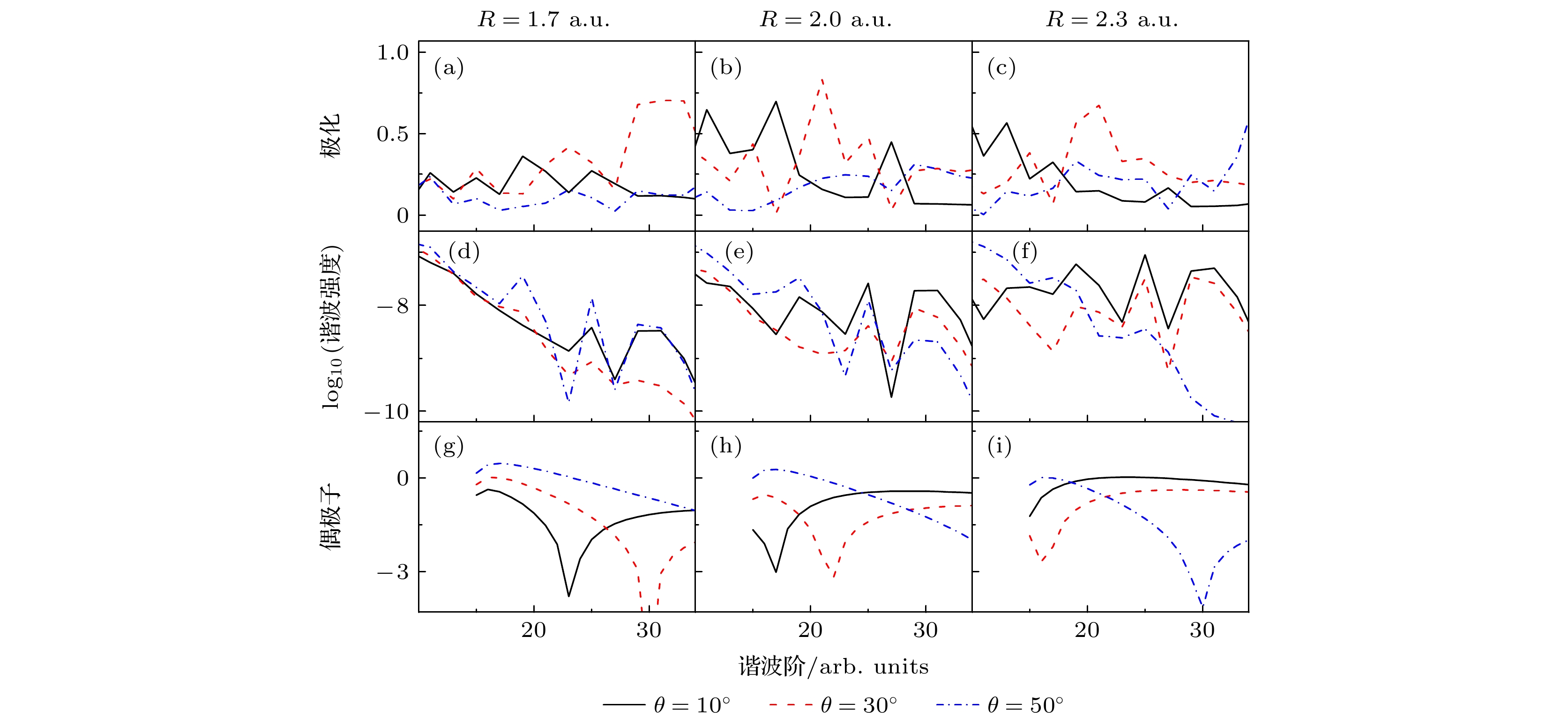
${\text{H}}_2^ + $ 分子在激光强度$ I = 4 \times {10^{14}}{\text{ W}}/{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} $ 及波长$ \lambda = 600{\text{nm}} $ 时谐波的椭偏率、谐波谱及偶极子的比较 (a), (d), (g) 核间距为$ R = 1.7{\text{ a}}{\text{.u}}{\text{. }} $ ; (b), (e), (h) 核间距为$ R = 2{\text{ a}}{\text{.u}}{\text{. }} $ ; (c), (f), (i) 核间距为$ R = 2.3{\text{ a}}{\text{.u}}{\text{. }} $ Figure 1. Comparison of the harmonic ellipticity, harmonic spectra and corresponding dipole for
${\text{H}}_2^ + $ molecules at the laser intensity$ I = 4 \times {10^{14}}{\text{ W}}/{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} $ and wavelength$ \lambda = 600{\text{ nm}} $ : (a), (d), (g)$ R = 1.7{\text{ a}}. {\text{u}}. $ ; (b), (e), (h)$ R = 2{\text{ a}}. {\text{u}}. $ ; (c), (f), (i)$ R = 2.3{\text{ a}}. {\text{u}}. $ .图 4
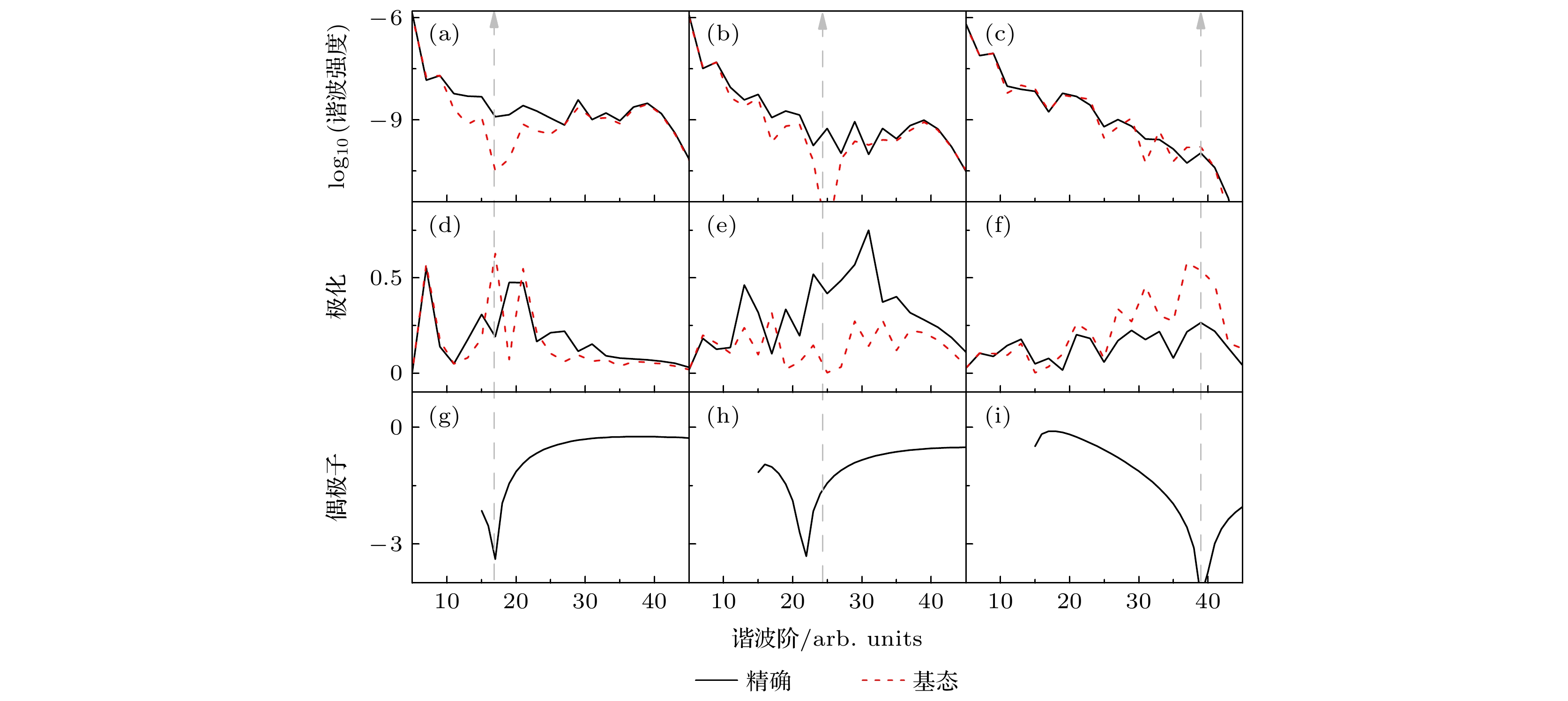
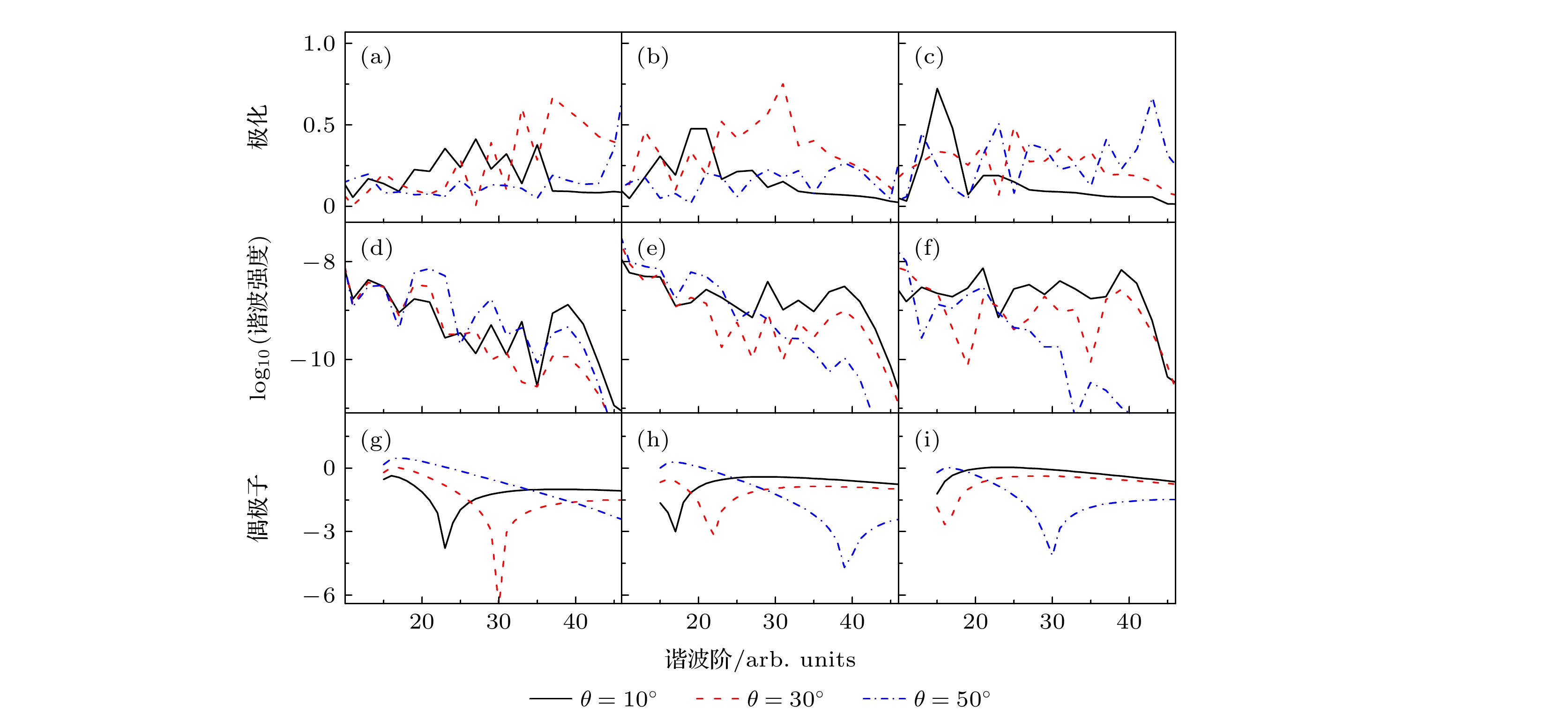
${\text{H}}_2^ + $ 分子$I = 4 \times {10^{14}}\;{\text{W}}/{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ ,$ \lambda = 600{\text{ nm}} $ 及R=2 a.u.时谐波谱、偶极子和谐波椭偏率的比较 (a), (d), (g)$ \theta = {10^\circ} $ ; (b), (e), (h)$ \theta = {30^\circ} $ ; (c), (f), (i)$ \theta = {50^\circ} $ Figure 4. Comparison of the harmonic ellipticity, harmonic spectra and corresponding dipole for
${\text{H}}_2^ + $ molecules with R=2 a.u. at the laser intensity$ I = 4 \times {10^{14}}{\text{ W}}/{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} $ and wavelength$ \lambda = 600{\text{ nm}} $ : (a), (d), (g)$ \theta = {10^\circ} $ ; (b), (e), (h)$ \theta = {30^\circ} $ ; (c), (f), (i)$ \theta = {50^\circ} $ .图 5
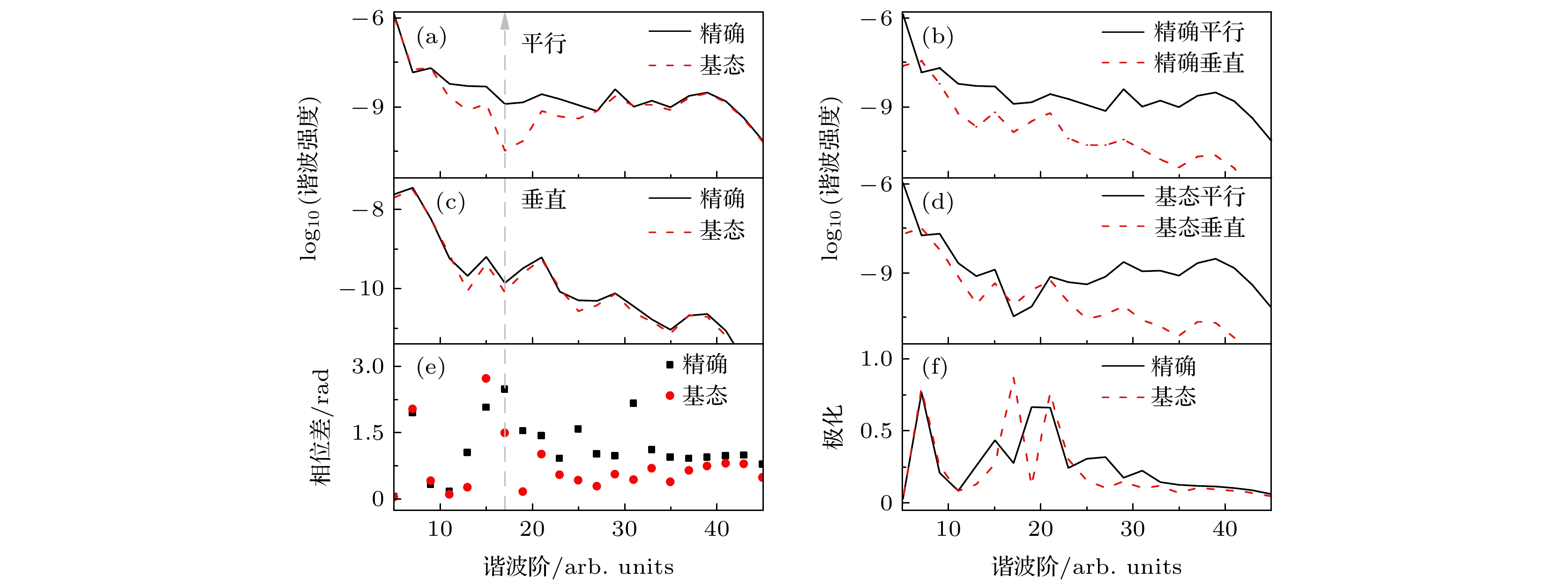
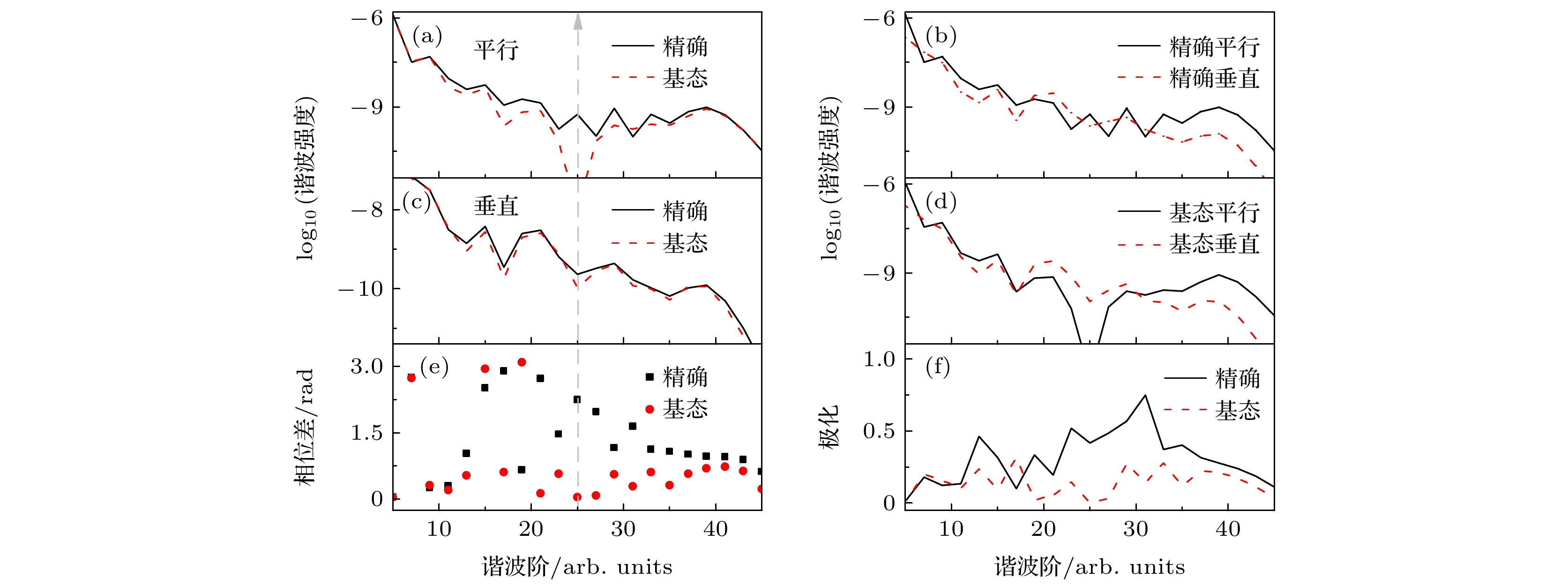
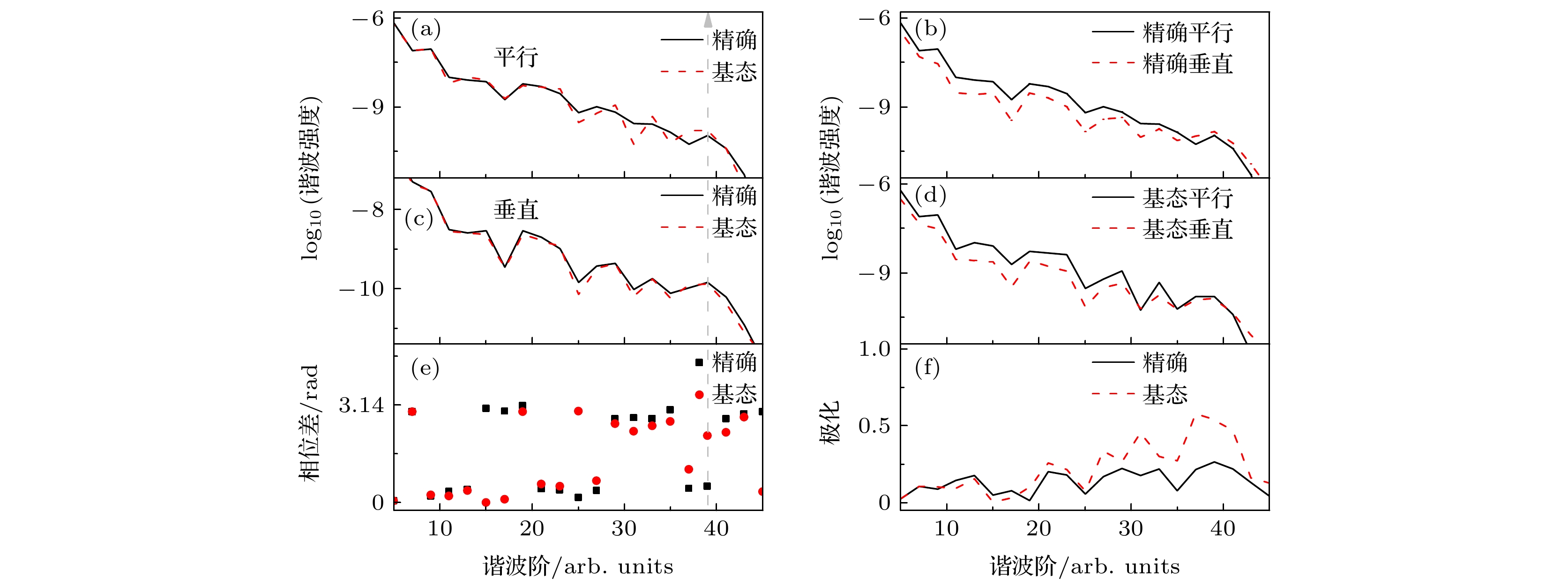
${\text{H}}_2^ + $ 分子$I = 4 \times {10^{14}}\;{\text{ W}}/{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ ,$\lambda = 600\;{\text{nm}}$ , R=2 a.u.及$ \theta = {10^\circ} $ 时谐波谱、相位差和谐波椭偏率的比较 (a) 精确平行与跃迁回基态的平行谐波谱(基态平行谐波)比较; (b) 精确平行与精确垂直谐波谱的比较; (c) 精确与基态垂直谐波谱的比较; (d) 基态平行与基态垂直谐波谱的比较; (e) 精确与基态谐波相位差比较; (f) 精确与基态谐波椭偏率比较Figure 5. The comparison of the harmonic spectra, the phase differences
$ {\delta _1}\left( d \right) $ and the ellipticity of harmonic for${\text{H}}_2^ + $ molecules with R=2 a.u. and$ \theta = {10^\circ} $ at the laser intensity$I = 4 \times {10^{14}}\;{\text{W}}/{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ and wavelength$\lambda = 600\;{\text{ nm}}$ : (a) The comparison of accurate parallel harmonic and the parallel harmonic that transition back to ground state (ground-state parallel harmonic); (b) the comparison of accurate parallel and perpendicular harmonic; (c) comparison between accurate and ground state perpendicular harmonic spectrum; (d) comparison between ground-state parallel and ground-state perpendicular harmonic; (e) the comparison of the phase difference of accurate and ground-state harmonic; (f) comparison between accurate and ground-state harmonic ellipticity. -
[1] L’Huillier A, Schafer K J, Kulander K C 1991 J. Phys. B 24 3315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Itatani J, Levesque J, Zeidler Hiromichi Niikura D, Pepin H, Kieffer J C, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2004 Nature 432 867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Krausz F, Ivanov M 2009 Rev. Mod. Phys. 81 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Le V H, Le A T, Xie R H, Lin C D 2007 Phys. Rev. A 76 013414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Vozzi C, Negro M, Calegari F, Sansone G, Nisoli M, Silvestri S De, Stagira S 2011 Nat. Phys. 7 822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Smirnova O, Mairesse Y, Patchkovskii S, Dudovich N, Villeneuve D, Corkum P, Ivanov M Yu 2009 Nature 460 972
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shafifir D, Soifer H, Bruner B D, Dagan M, Mairesse Y, Patchkovskii S, Ivanov M Yu, Smirnova O, Dudovich N 2012 Nature 485 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Corkum P B 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 1994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lewenstein M, Balcou Ph, Ivanov M Yu, L'Huillier Anne, Corkum P B 1994 Phys. Rev. A 49 2117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Keldysh L V 1965 Sov. Phys. JETP 20 1307
[11] Kim V V, Ganeev R A, Boltaev G S, Alnaser A S 2020 J. Phys. B 53 155405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Dong F L, Tian Y Q, Yu S J, Wang S, Yang S P, Chen Y J 2015 Opt. Express 23 18106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhou X, Lock R, Wagner N, Li W, Kapteyn H C, Murnane M M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 073902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Levesque J, Mairesse Y, Dudovich N, epin H P, Kieffer J C, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 243001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ramakrishna S, Sherratt P A J, Dutoi A D, Seideman T 2010 Phys. Rev. A 81 021802(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Strelkov V V, Gonoskov A A, Gonoskov I A, Ryabikin M Yu 2011 Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 043902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Akagi H, Otobe T, Staudte A, Shiner A, Turner F, Dörner R, Villeneuve D M, Corkum P B 2009 Science 325 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bian X B, Bandrauk A D 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 093903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chen Y J, Zhang B 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 053402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Qin M, Zhu X, Zhang Q, Hong W, Lu P 2011 Opt. Express 19 25084
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Du H, Luo L, Wang X, Hu B 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 013846
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yu S J, Zhang B, Li Y P, Yang S P, Chen Y J 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 053844
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Barreau L, Veyrinas K, Gruson V, Weber S J, Auguste T, Hergott J F, Lepetit F, Carré B, Houver J -C, Dowek D, Salières P 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 4727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Sun F J, Chen C, Li W Y, Liu X, Li W, Chen Y J 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 053108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Habibović D, Milošević D B 2020 Photonics 7 110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huo X X, Xing Y H, Qi T, Sun Y, Li Bo, Zhang J, Liu X S 2021 Phys. Rev. A 103 053116
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen Y J 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 043423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen Y J, Zhang B 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 023415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bian X B, Bandrauk A D 2012 Phys. Rev. A 86 053417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Miao X Y, Zhang C P 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 033410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Han Y C 2013 Phys. Rev. A 87 043404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Feit M D, Jr Fleck J A, Steiger A 1982 J. Comput. Phys. 47 412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Shiner A D, Trallero-Herrero C, Kajumba N, Bandulet H C, Comtois D, Légaré F, Giguère M, Kieffffer J C, Corkum P B, Villeneuve D M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 073902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Yu S J, Li W Y, Li Y P, Chen Y J 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 013432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Chen Y J, Hu B 2009 J. Chem. Phys. 131 244109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen Y J, Chen J, Liu J 2006 Phys. Rev. A 74 063405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3886
- PDF Downloads: 94
- Cited By: 0




























 DownLoad:
DownLoad: