-
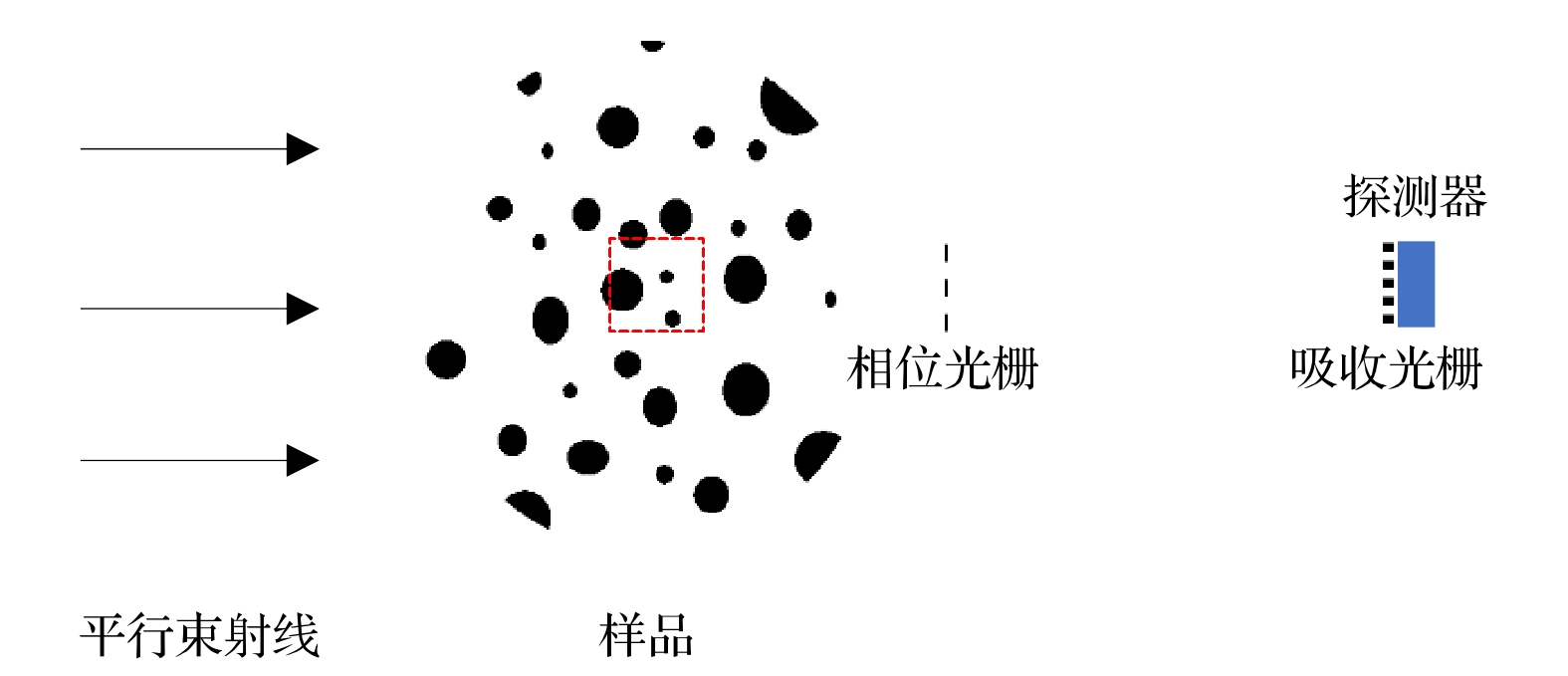
X-ray differential phase contrast computed tomography imaging based on grating interferometer system can reconstruct not only the linear attenuation coefficient, but also the phase shift coefficient and the linear scattering coefficient of the object. In practical application, it is very difficult to make a large area grating, so the sample is often larger than the grating. When the sample is scanned with a grating smaller than the sample, the part of the sample beyond the field of view of the grating will cause the differential phase projection information to be truncated. In this paper, a method of reconstructing the region of interest for differential phase contrast computed tomography is proposed. The method is based on the approximate linear relation between the phase shift coefficient of the object and the linear attenuation coefficient (i.e. the decrement in the real part of the refractive index and the imaginary part of the refractive index), the phase shift coefficient of the region of interest is approximately reconstructed by the polynomial of Lambda function of the phase shift coefficient and Lambda inverse function of linear attenuation coefficient. In this paper, according to the Fresnel diffraction theory and differential phase grating phase step-by-step method of imaging a simulation experiment is performed. In the experiment, conducted is the approximate reconstruction by using the first order polynomial and quadratic polynomial of Lambda function of the phase shift coefficient and Lambda inverse function of linear attenuation coefficient. The sample size is five times of grating imaging field, and the results show that this method can approximately reconstruct the region of interest for the sample image. We also carry out the actual data experiment. The actual data are obtained by the Talbot grating interferometer system of Shanghai synchrotron radiation BL13W1 station, and the standard model and biological sample are imaged. The method of reconstructing the region of interest is proposed in this paper. This method can be applied to the multi-material samples with a similar relationship between the decrement in the real part of the refractive index and the decrement in the imaginary part of the refractive index, and also to single-material samples. The comparison between the numerical simulations and the actual experimental results verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Keywords:
- differential phase contrast /
- computed tomography /
- reconstruction of region of interest /
- phase shift coefficient
[1] Momose A, Takeda T, Itai Y 1995 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66 1434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Momose A, Takeda T, Itai Y Hirano K 1996 Nat. Med. 2 473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] David C, Nohammer B, Solak H H, Ziegler, E 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 3287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Momose A, Kawamoto S, Koyama I, Hamaishi Y, Takai K, Suzuki Y 2003 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42 L866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 陈博, 朱佩平, 刘宜晋, 王寯越, 袁清习, 黄万霞, 明海, 吴自玉 2008 57 1576
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen B, Zhu P P, Liu Y J, Wang J Y, Yuan Q X, Huang W X, Ming H, Wu Z Y 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 1576
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zou Y, Pan X, Sidky E Y 2005 Phys. Med. Biol 50 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 张慧滔, 陈明, 张朋 2007 自然科学进展 17 1589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H T, Chen M, Zhang P 2007 Prog. Nat. Sci. 17 1589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Smith K T, Keinert F 1985 Appl. Optics 24 3950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Faridani A, Ritman E L, Smith K T 1992 SIAM J. Appl. Math. 52 459
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Faridani A, Finch D V, Ritman E L, Smith K T 1997 SIAM J. Appl. Math. 57 1095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Anastasio M A, Pan X 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 3167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Cong W, Yang J, Wang G 2011 Phys. Med. Biol. 57 2905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Pascal Thériault Lauzier, Qi Z, Zambelli J, Bevins N, Chen G H 2012 Phys. Med. Biol. 57 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yang Q, Cong W, Wang G Developments in X-Ray Tomography X San Diego, California, United States, August 28–September 1, 2016 p996709-1
[15] Felsner L, Berger M, Kaeppler S, Bopp J, Riess C 2018 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2018 (Springer: Cham) pp137−144
[16] Felsner L, Kaeppler S, Maier A, Riess C 2020 IEEE T Comput. Imag. 6 625
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hsieh J 2009. Computed Tomography Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent Advances (2nd Ed.) (Washington: Wiley) pp55−114
[18] Pan X, Xia D, Zou Y, Yu L 2004 Phys. Med. Biol. 49 4349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gordon R, Bender R, Herman G T 1970 J. Theor. Biol. 29 471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Pfeiffer F, David C, Bunk O, Donath T, Bech M, Duc G L, Bravin A, Cloetens P 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 168101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu X, Liu H, Yan A 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen R C, Dreossi D, Mancini L, Menk R, Rigon L, Xiao T Q, Longo R 2012 J. Synchrotron. Radiat. 19 836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zanette I, Bech M, Pfeiffer F, Weitkamp T 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rong F, Liang Y, Yang Y D, Ma X H 2017 Infrared Laser Eng. 46 1220002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zanette I, Bech M, Rack A, Le Duc G, Tafforeau P, David C 2012 PNAS 109 10199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 王圣浩 2015 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Wang S H 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation ((Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
-
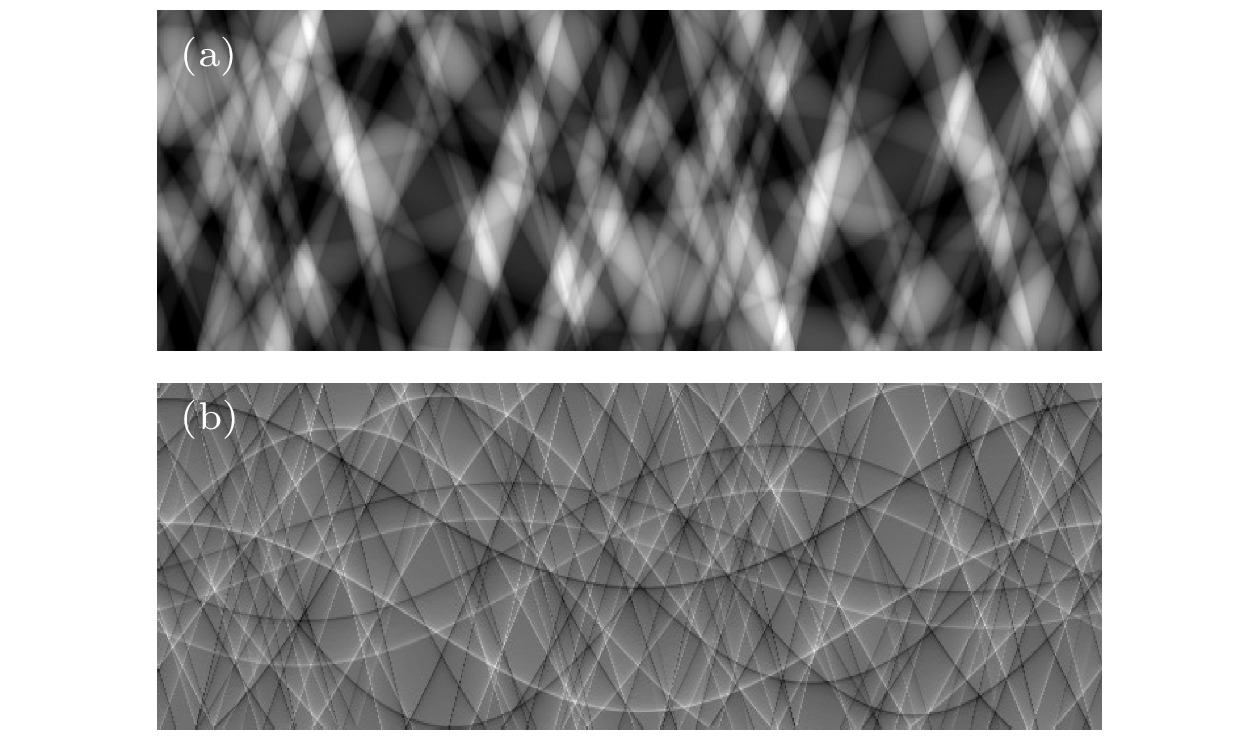
图 3 相移系数重建结果 (a) 采用一次多项式近似的重建图像; (b)采用二次多项式近似的重建图像; (c) 图3(a)和图3(b)在绿色虚线位置处的剖线图
Figure 3. Reconstruction results of phase shift coefficient: (a) The reconstruction image using a first order polynomial approximation; (b) the reconstruction image using a second order polynomial approximation; (c) Fig.3 (a) and Fig.3 (b) in the green dotted line location profile chart.
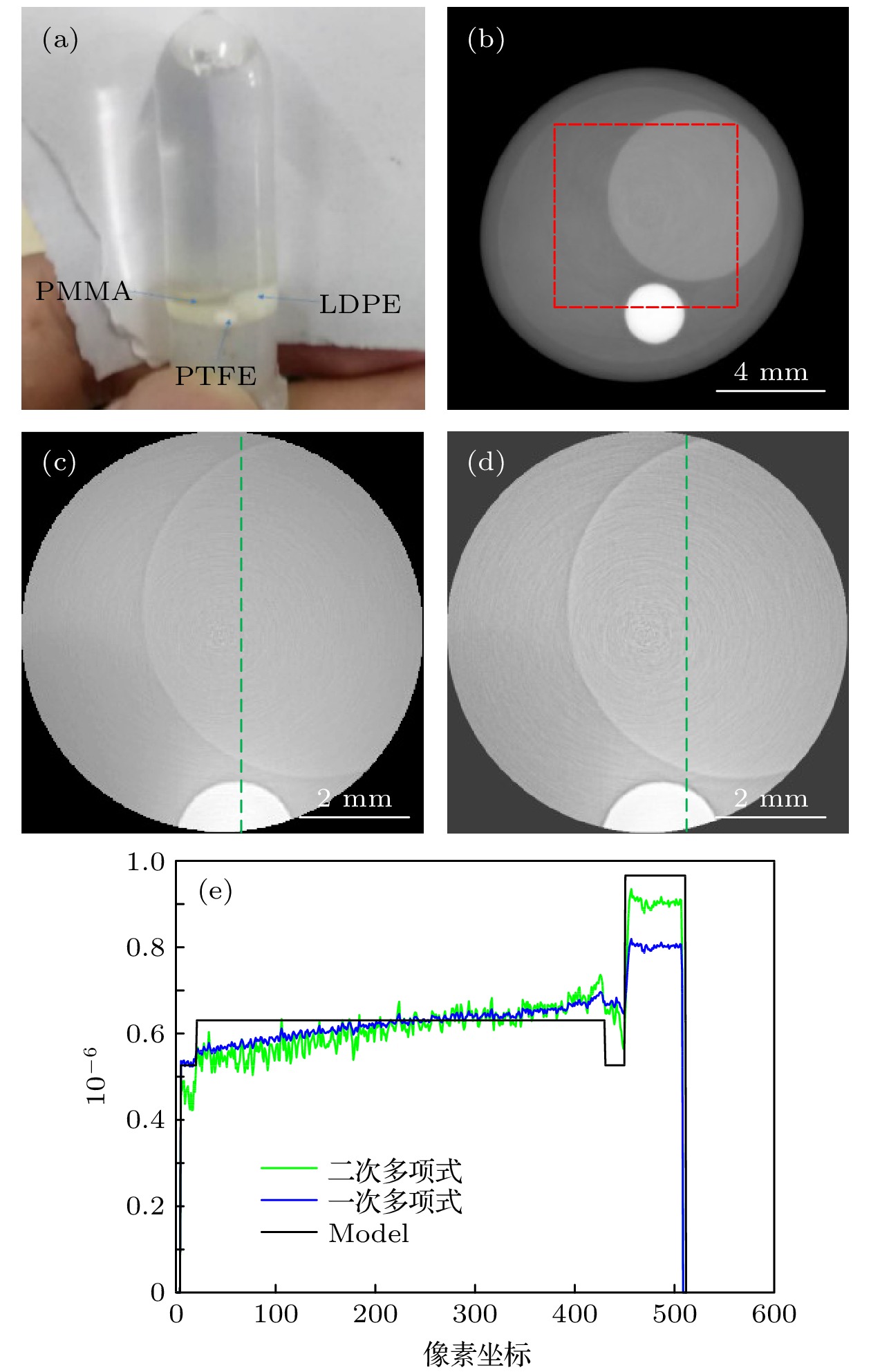
图 4 相移系数重建结果 (a)实验模体; (b)全局数据重建图像, 红色虚线内为感兴趣区域图像; (c)截断数据采用一次多项式近似的重建图像; (d)截断数据采用二次多项式近似的重建图像; (e) 图4(c)和图4(d)在绿色虚线位置处的剖线图
Figure 4. Reconstruction results of phase shift coefficient: (a) Experimental modle; (b) the reconstruction image of global data, the ROI image is in the red dotted line; (c) the reconstruction image of the truncated data using a first order polynomial approximation; (d) the reconstruction image of the truncated data using a second order polynomial approximation; (e) Fig.4 (c) and Fig.4 (d) in the green dotted line location profile chart.
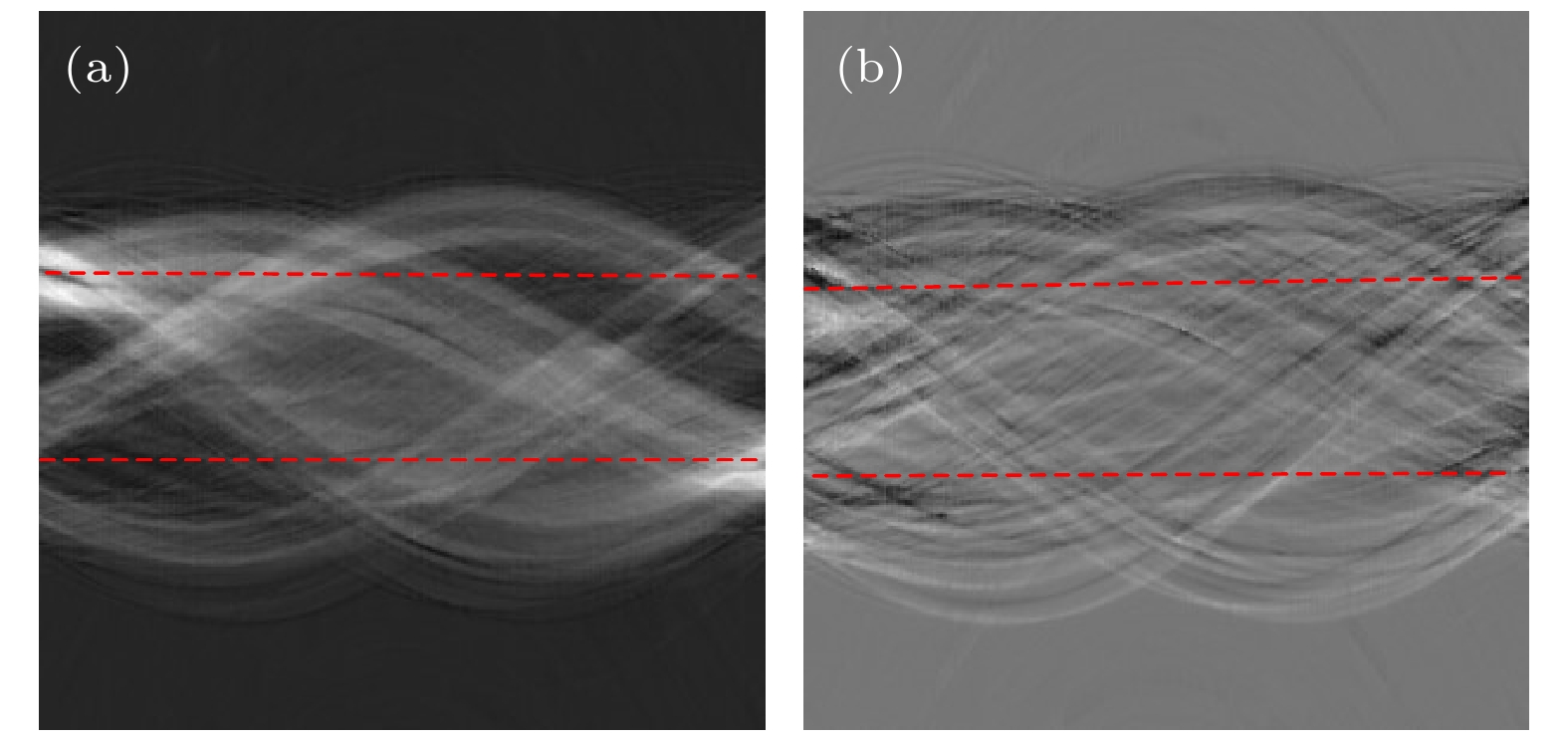
图 6 相移系数重建图像 (a) 全局数据重建图像, 红色虚线内为感兴趣区域图像; (b) 全局数据的感兴趣区域重建图像; (c) 截断数据采用一次多项式近似的重建图像
Figure 6. Reconstruction image of phase shift coefficient: (a) The reconstruction image of global data, the ROI image is in the red dotted line; (b) the reconstruction image of the ROI from the global data; (c) the reconstruction image of the truncated data using a first order polynomial approximation.
表 1 一次多项式和二次多项式重建结果的MSE和PSNR
Table 1. MSE and PSNR of reconstruction results of the first order polynomial and the second order polynomial.
方法 MSE PSNR 一次多项式 0.0796 10.9894 二次多项式 0.0271 15.6647 表 2 水、PTFE、PMMA、LDPE的折射率实部减小量
$\delta $ Table 2. The decrement of the real part of the refractive index of water, PTFE, PMMA, and LDPE.
材料 水(H2O) PTFE
(C2F4)PMMA
(C5O2H8)LDPE
(C2H4)$\delta $/10–7 5.26 9.65 6.30 5.46 -
[1] Momose A, Takeda T, Itai Y 1995 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66 1434
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Momose A, Takeda T, Itai Y Hirano K 1996 Nat. Med. 2 473
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] David C, Nohammer B, Solak H H, Ziegler, E 2002 Appl. Phys. Lett. 81 3287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Momose A, Kawamoto S, Koyama I, Hamaishi Y, Takai K, Suzuki Y 2003 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42 L866
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 陈博, 朱佩平, 刘宜晋, 王寯越, 袁清习, 黄万霞, 明海, 吴自玉 2008 57 1576
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen B, Zhu P P, Liu Y J, Wang J Y, Yuan Q X, Huang W X, Ming H, Wu Z Y 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 1576
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zou Y, Pan X, Sidky E Y 2005 Phys. Med. Biol 50 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 张慧滔, 陈明, 张朋 2007 自然科学进展 17 1589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H T, Chen M, Zhang P 2007 Prog. Nat. Sci. 17 1589
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Smith K T, Keinert F 1985 Appl. Optics 24 3950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Faridani A, Ritman E L, Smith K T 1992 SIAM J. Appl. Math. 52 459
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Faridani A, Finch D V, Ritman E L, Smith K T 1997 SIAM J. Appl. Math. 57 1095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Anastasio M A, Pan X 2007 Opt. Lett. 32 3167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Cong W, Yang J, Wang G 2011 Phys. Med. Biol. 57 2905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Pascal Thériault Lauzier, Qi Z, Zambelli J, Bevins N, Chen G H 2012 Phys. Med. Biol. 57 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yang Q, Cong W, Wang G Developments in X-Ray Tomography X San Diego, California, United States, August 28–September 1, 2016 p996709-1
[15] Felsner L, Berger M, Kaeppler S, Bopp J, Riess C 2018 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2018 (Springer: Cham) pp137−144
[16] Felsner L, Kaeppler S, Maier A, Riess C 2020 IEEE T Comput. Imag. 6 625
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hsieh J 2009. Computed Tomography Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent Advances (2nd Ed.) (Washington: Wiley) pp55−114
[18] Pan X, Xia D, Zou Y, Yu L 2004 Phys. Med. Biol. 49 4349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gordon R, Bender R, Herman G T 1970 J. Theor. Biol. 29 471
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Pfeiffer F, David C, Bunk O, Donath T, Bech M, Duc G L, Bravin A, Cloetens P 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 168101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu X, Liu H, Yan A 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chen R C, Dreossi D, Mancini L, Menk R, Rigon L, Xiao T Q, Longo R 2012 J. Synchrotron. Radiat. 19 836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zanette I, Bech M, Pfeiffer F, Weitkamp T 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rong F, Liang Y, Yang Y D, Ma X H 2017 Infrared Laser Eng. 46 1220002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zanette I, Bech M, Rack A, Le Duc G, Tafforeau P, David C 2012 PNAS 109 10199
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 王圣浩 2015 博士学位论文 (合肥: 中国科学技术大学)
Wang S H 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation ((Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China) (in Chinese)
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7714
- PDF Downloads: 90
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: