-
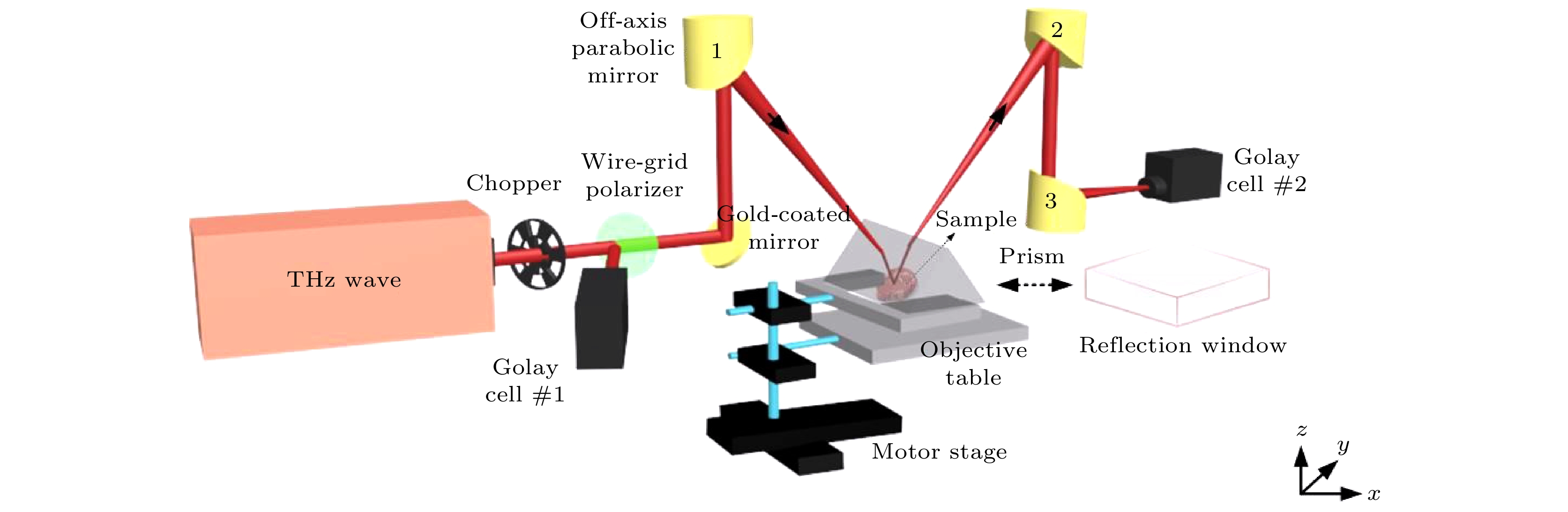
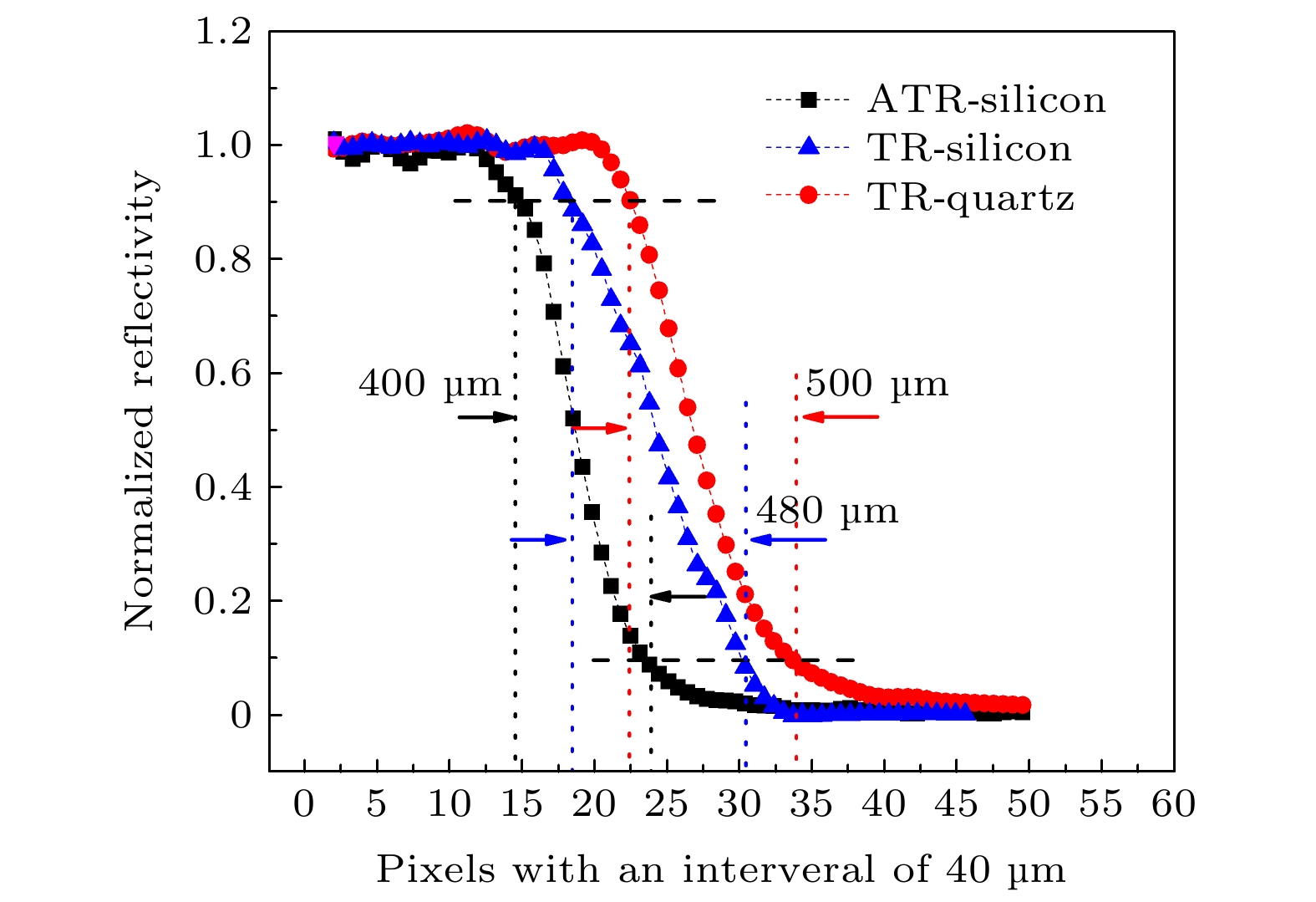
Terahertz imaging technology is one of the candidate technologies for medical imaging. In particular, continuous terahertz reflection and attenuated total reflection imaging are expected to achieve rapid intraoperative imaging, which is hot research topic at present. In order to realize the rapid multi-dimensional and high-quality terahertz imaging detection of sample, it is necessary to study the common optical path continuous terahertz reflection/attenuated total reflection dual-mode imaging system based on point scanning. By using the Fresnel formula and the penetration depth formula of evanescent wave, the influence of imaging angle on the reflected signal and the penetration depth of attenuated total reflection are studied theoretically in this paper. The imaging angle of terahertz wave suitable for both reflection and attenuation total reflection imaging is obtained. Based on this, an isoscele total reflection prism with a base angle of 49° is designed. The dual-mode imaging of common optical path continuous terahertz reflection and attenuated total reflection is realized by quickly switching between reflection window and total reflection prism. The reflection and attenuation total reflection imaging modes have imaging resolutions of 400 μm and 500 μm, respectively. Continuous terahertz reflection and attenuated total reflection imaging are experimentally studied by using distilled water and pork as samples. The results show that the relative reflectance of the sample obtained in the attenuated total reflection imaging mode fluctuates within a range of 1%, and the image contrast is 9 times that of the reflection imaging mode. Moreover, attenuated total reflection imaging can effectively identify the sample with the length less than 1 mm. Thus, compared with reflection imaging, continuous terahertz attenuated total reflection imaging has the advantages of high image resolution, high image contrast and highr signal stability, and can accurately obtain the reflectivity of sample. The terahertz attenuated total reflection imaging technology is more helpful in achieving high sensitivity imaging of samples. By combining reflection and attenuated total reflection imaging modes, the advantages of different imaging modes can be compensated for and the performance of the imaging system can be further improved. This common path continuous terahertz reflection and attenuated total reflection dual mode imaging system is expected to achieve a high sensitivity detection of sample.
[1] Son J H 2009 J. Appl. Phys. 105 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hu B B, Nuss M C 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bowman T, Shenawee M, Campbell L K 2016 Biomed. Opt. Express 7 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ji Y B, Park C H, Kim H, Kim S H, Lee G M, Noh S K, Jeon T I, Son J H, Huh Y M, Haam S, Oh S J, Lee S K, Suh J S 2015 Biomed. Opt. Express 6 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ishikawa Y, Minamide H, Ikari T, Miura Y, Ito H 2005 Proceedings of the International Quantum Electronics Conference San Jose, USA, July 11−11, 2005, p1236
[6] Nishizawa J, Sasaki T, Suto K, Yamada T, Tanabe T, Tanno T, Sawai T, Miura Y 2005 Opt. Commun. 244 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 杨昆, 赵国忠, 梁承森, 武利忠 2009 中国激光 25 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang K, Zhao G, Liang C S, Wu L Z 2009 J. Lasers 25 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wahaia F, Kasalynas I, Venckevicius R, Seliuta D, Granja P L 2016 J. mol. Struct. 5 1107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hartwick T S, Hodges D T, Barker D H, Foote F B 1976 Appl. Optics 15 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Park J Y, Choi H J, Cho K S, Kim K R, Son J H 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu H, Wang Y, Xu D, Wu L, Yan C, Yan D, Tang L, He Y, Feng H, Yao J 2017 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 50 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Gerasimov V V, Knyazev B A and Cherkassky V S 2010 Opt. Spectrosc. 108 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bowman T, Walter A, EI-Shenawee M 2016 Proceedings Volume 9700, Design and Quality for Biomedical Technologies IX San Francisco, California, United States, February 13−14, 2016 p97000J-1–5
[14] Wallace V P, Fitzgerald A J, Shankar S, Flanagan N, Arnone D D 2015 Brit J. of Dermatol. 151 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sim Y C, Park J Y, Ahn K M, Park C, Son J H 2013 Biomed. Opt. Express 4 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang Y, Chen L, Chen T, Jia S, Ren Y, Li C, Chao Z, Liu H, Wu L 2018 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 51 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chan K L A and Kazarian S G 2003 Appl. Spectrosc. 57 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wojdyla A, Gallot G 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Catherine Z 2003 Nature 14 721
[20] Lee A W, Hu Q 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Watts C M, Shrekenhamer D, Montoya J, Lipworth G, Hunt J, Sleasman T, Krishna S, Smith D R, Padilla W J 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Doradla P, Alavi K, Joseph C S, Giles R 2013 J. Biomed. Opt. 18 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chernomyrdin N V, Kucheryavenko A S, Kolontaeva G S, G M Katyba, I N Dolganova, P A Karalkin, D S Ponomarev, V N Kurlov, I V Reshetov, Skorobogatiy M 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu L, Xu D, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang H, Liao B, Gong S, Chen T, Wu N, Feng H, Yao J 2020 Neurophotonics 7 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Johnk C T 1988 Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves (2nd Ed.) (Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley) pp247−251
[26] Wang Y, Wang Y, Xu D, Wu L, Wang G, Jiang B, Yu T, Chang C, Chen T, Yao J 2020 Opt. Express 28 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Shikata J, Handal H, Nawaharal A, Minamide H, Ito H 2007 Conference on Lasers and Electro Optics Pacific Rim, Seoul, South Korea, August 26–31, 2007 p1406
[28] Liu H, Wang Y, Xu D, Jiang Z, Wu L, Yan C, Tang L, He Y, Yan D, Ding X, Feng H, Yao J 2018 Opt. Express 26 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
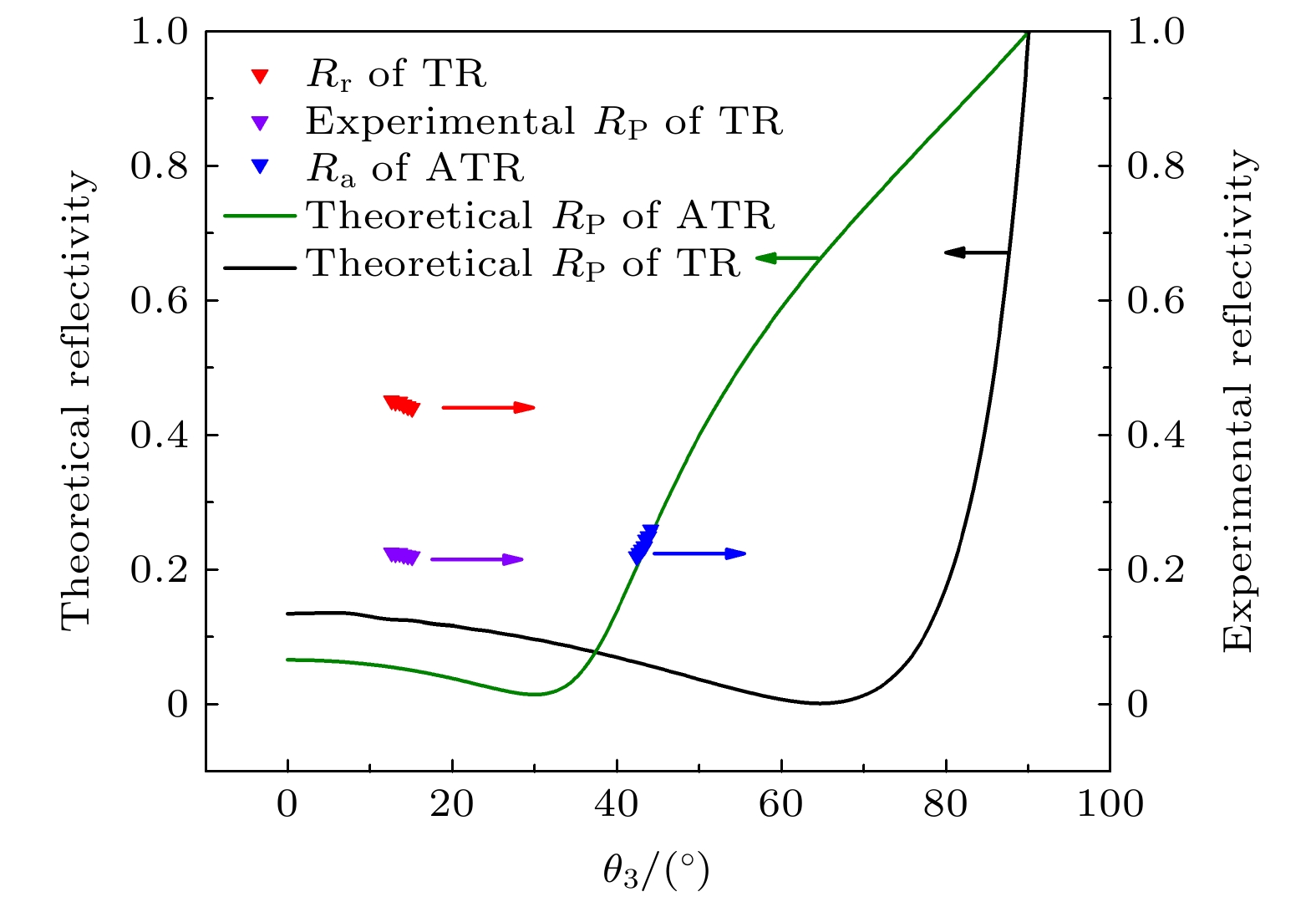
图 2 (a) S和P偏振波在界面处的反射系数和透射系数与入射角θ1的关系; (b)太赫兹波经反射窗口前表面透射、后表面反射和前表面透射后的反射系数r与入射角θ1的关系
Figure 2. (a) The relation between the reflection coefficient and transmission coefficient of S and P polarized waves at the interface and the incident angle θ1; (b) the relation between the reflection coefficient r and incident angle θ1 of terahertz wave after the front surface transmission, back surface reflection and front surface transmission through reflection window.
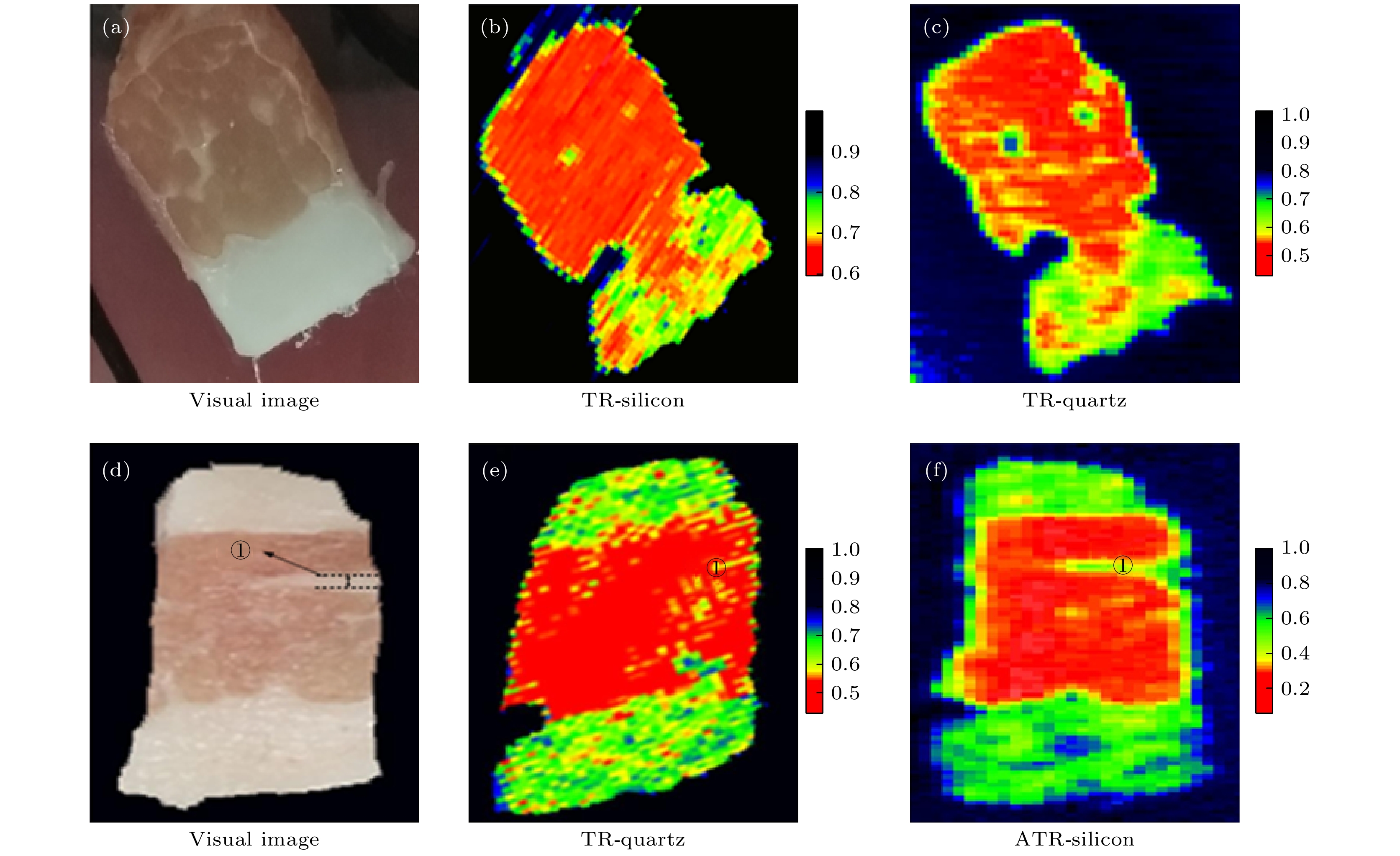
图 8 (a) 猪肉组织与反射窗口紧密接触可见光图; (b), (c) 采用高阻硅和石英材料为反射窗口时的太赫兹成像图; (d) 未覆盖成像窗口时猪肉组织可见光图; (e), (f) 反射和衰减全反射模式下猪肉组织的太赫兹成像图
Figure 8. (a) Visible image of pork tissue in close contact with the reflection window; (b), (c) the terahertz images of pork tissue in reflective and attenuated total reflection modes using high resistance silicon and quartz materials as reflection windows, (d) visible image of pork tissue when the imaging window is not covered; (e), (f) the terahertz images of pork tissue in reflective and attenuated total reflection modes respectively.
-
[1] Son J H 2009 J. Appl. Phys. 105 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Hu B B, Nuss M C 1995 Opt. Lett. 20 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Bowman T, Shenawee M, Campbell L K 2016 Biomed. Opt. Express 7 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ji Y B, Park C H, Kim H, Kim S H, Lee G M, Noh S K, Jeon T I, Son J H, Huh Y M, Haam S, Oh S J, Lee S K, Suh J S 2015 Biomed. Opt. Express 6 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ishikawa Y, Minamide H, Ikari T, Miura Y, Ito H 2005 Proceedings of the International Quantum Electronics Conference San Jose, USA, July 11−11, 2005, p1236
[6] Nishizawa J, Sasaki T, Suto K, Yamada T, Tanabe T, Tanno T, Sawai T, Miura Y 2005 Opt. Commun. 244 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 杨昆, 赵国忠, 梁承森, 武利忠 2009 中国激光 25 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang K, Zhao G, Liang C S, Wu L Z 2009 J. Lasers 25 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wahaia F, Kasalynas I, Venckevicius R, Seliuta D, Granja P L 2016 J. mol. Struct. 5 1107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hartwick T S, Hodges D T, Barker D H, Foote F B 1976 Appl. Optics 15 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Park J Y, Choi H J, Cho K S, Kim K R, Son J H 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu H, Wang Y, Xu D, Wu L, Yan C, Yan D, Tang L, He Y, Feng H, Yao J 2017 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 50 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Gerasimov V V, Knyazev B A and Cherkassky V S 2010 Opt. Spectrosc. 108 6
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bowman T, Walter A, EI-Shenawee M 2016 Proceedings Volume 9700, Design and Quality for Biomedical Technologies IX San Francisco, California, United States, February 13−14, 2016 p97000J-1–5
[14] Wallace V P, Fitzgerald A J, Shankar S, Flanagan N, Arnone D D 2015 Brit J. of Dermatol. 151 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Sim Y C, Park J Y, Ahn K M, Park C, Son J H 2013 Biomed. Opt. Express 4 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang Y, Chen L, Chen T, Jia S, Ren Y, Li C, Chao Z, Liu H, Wu L 2018 J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 51 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chan K L A and Kazarian S G 2003 Appl. Spectrosc. 57 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wojdyla A, Gallot G 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Catherine Z 2003 Nature 14 721
[20] Lee A W, Hu Q 2005 Opt. Lett. 30 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Watts C M, Shrekenhamer D, Montoya J, Lipworth G, Hunt J, Sleasman T, Krishna S, Smith D R, Padilla W J 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Doradla P, Alavi K, Joseph C S, Giles R 2013 J. Biomed. Opt. 18 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chernomyrdin N V, Kucheryavenko A S, Kolontaeva G S, G M Katyba, I N Dolganova, P A Karalkin, D S Ponomarev, V N Kurlov, I V Reshetov, Skorobogatiy M 2018 Appl. Phys. Lett. 113 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu L, Xu D, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang H, Liao B, Gong S, Chen T, Wu N, Feng H, Yao J 2020 Neurophotonics 7 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Johnk C T 1988 Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves (2nd Ed.) (Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley) pp247−251
[26] Wang Y, Wang Y, Xu D, Wu L, Wang G, Jiang B, Yu T, Chang C, Chen T, Yao J 2020 Opt. Express 28 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Shikata J, Handal H, Nawaharal A, Minamide H, Ito H 2007 Conference on Lasers and Electro Optics Pacific Rim, Seoul, South Korea, August 26–31, 2007 p1406
[28] Liu H, Wang Y, Xu D, Jiang Z, Wu L, Yan C, Tang L, He Y, Yan D, Ding X, Feng H, Yao J 2018 Opt. Express 26 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6988
- PDF Downloads: 126
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: