-
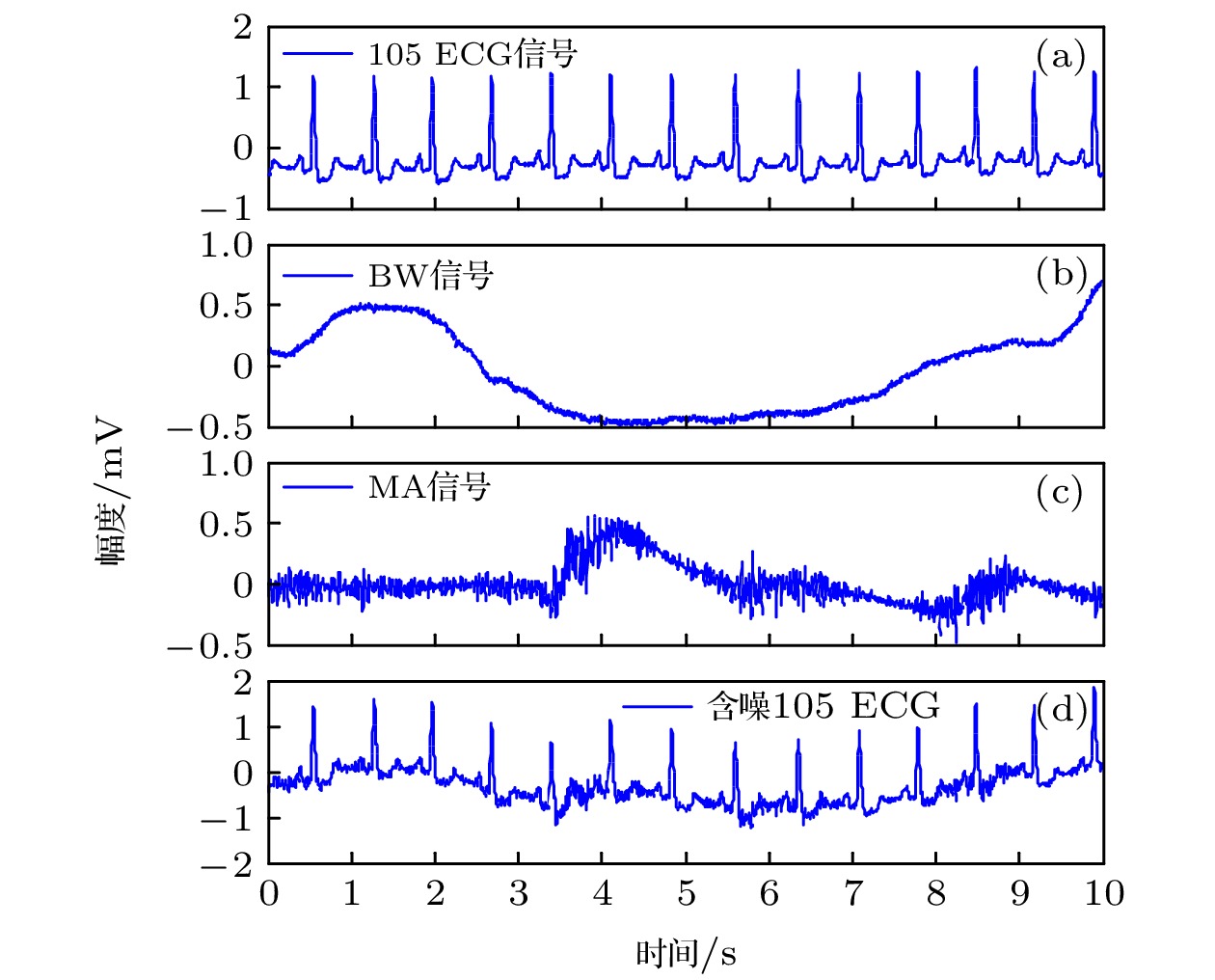
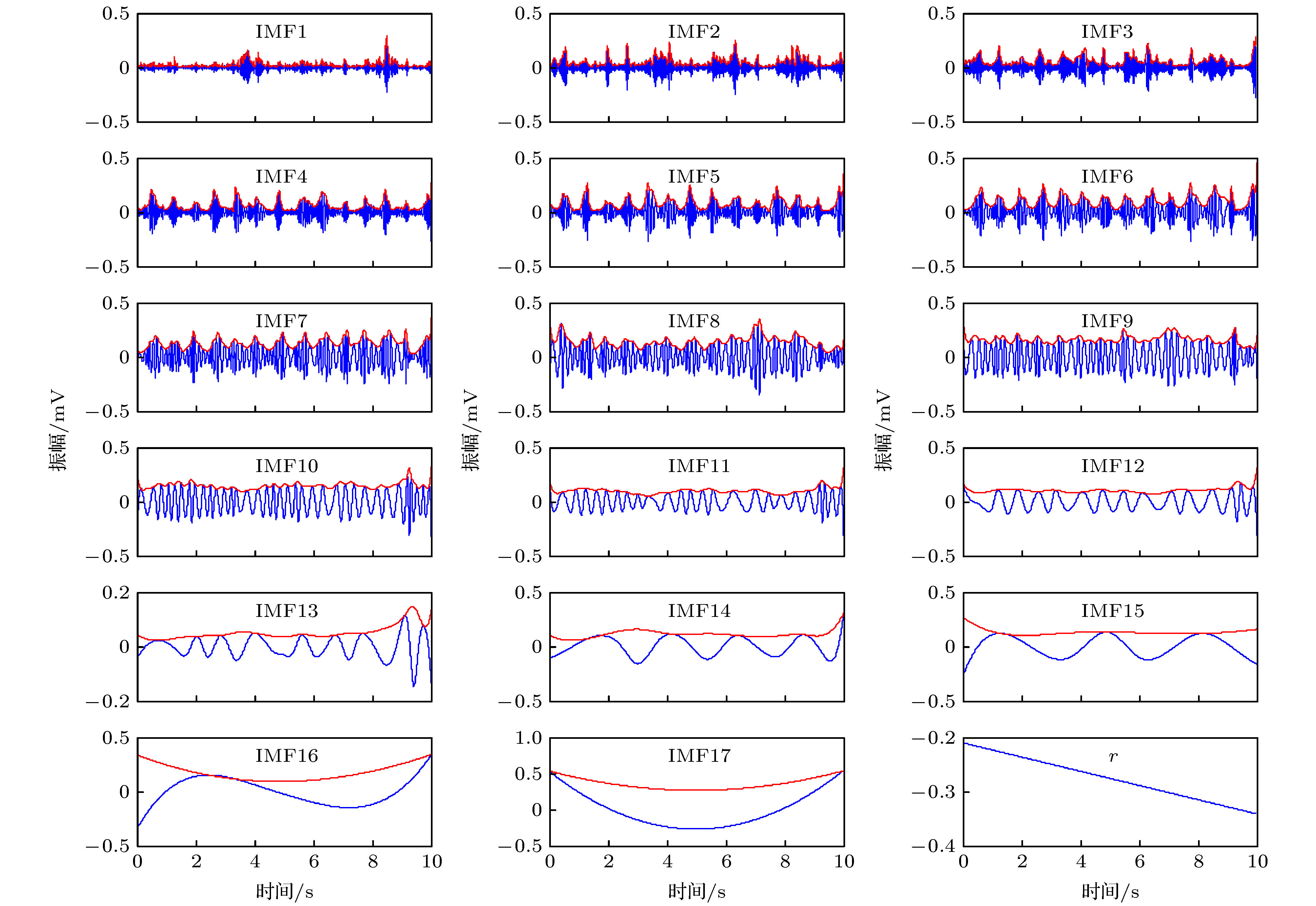
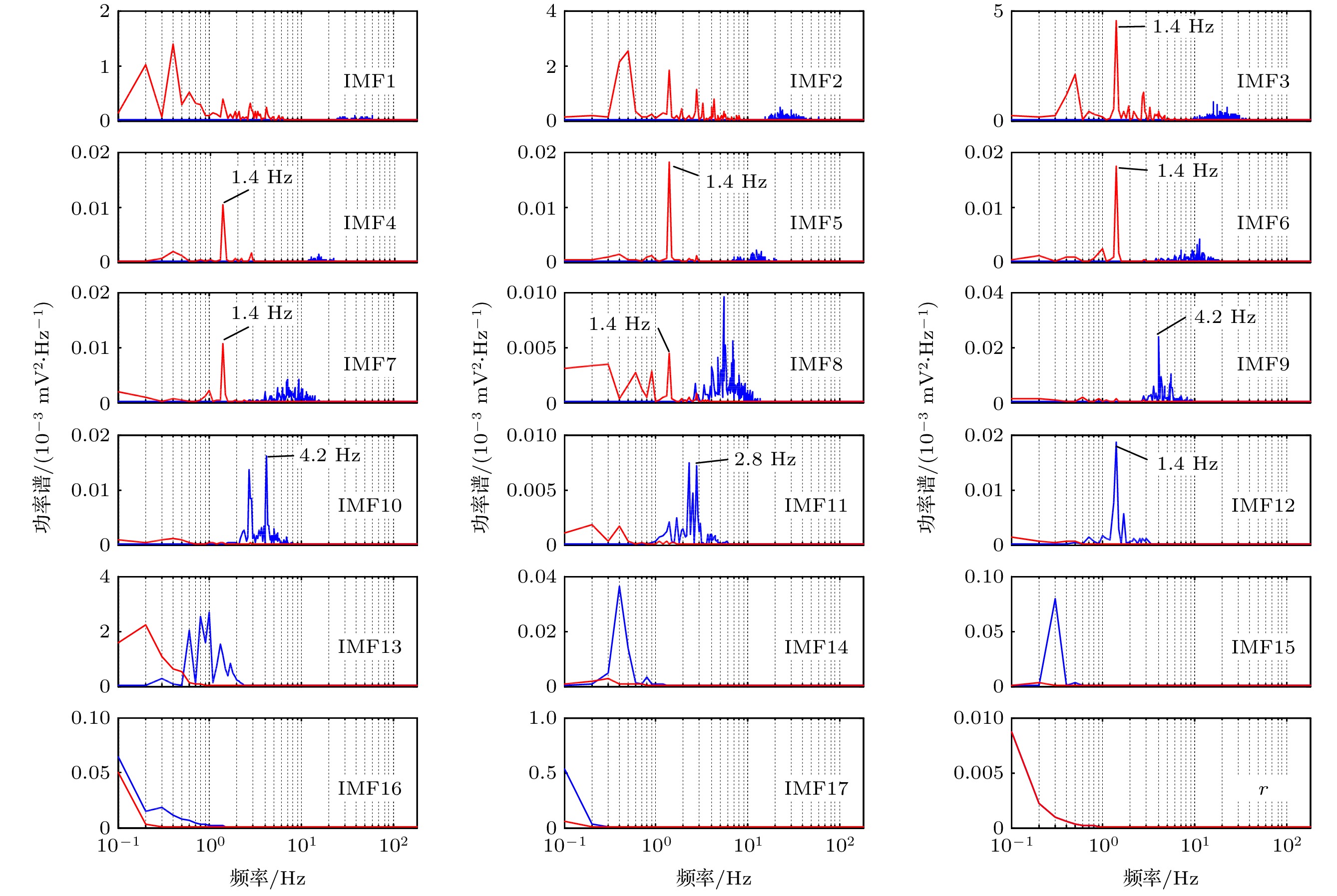
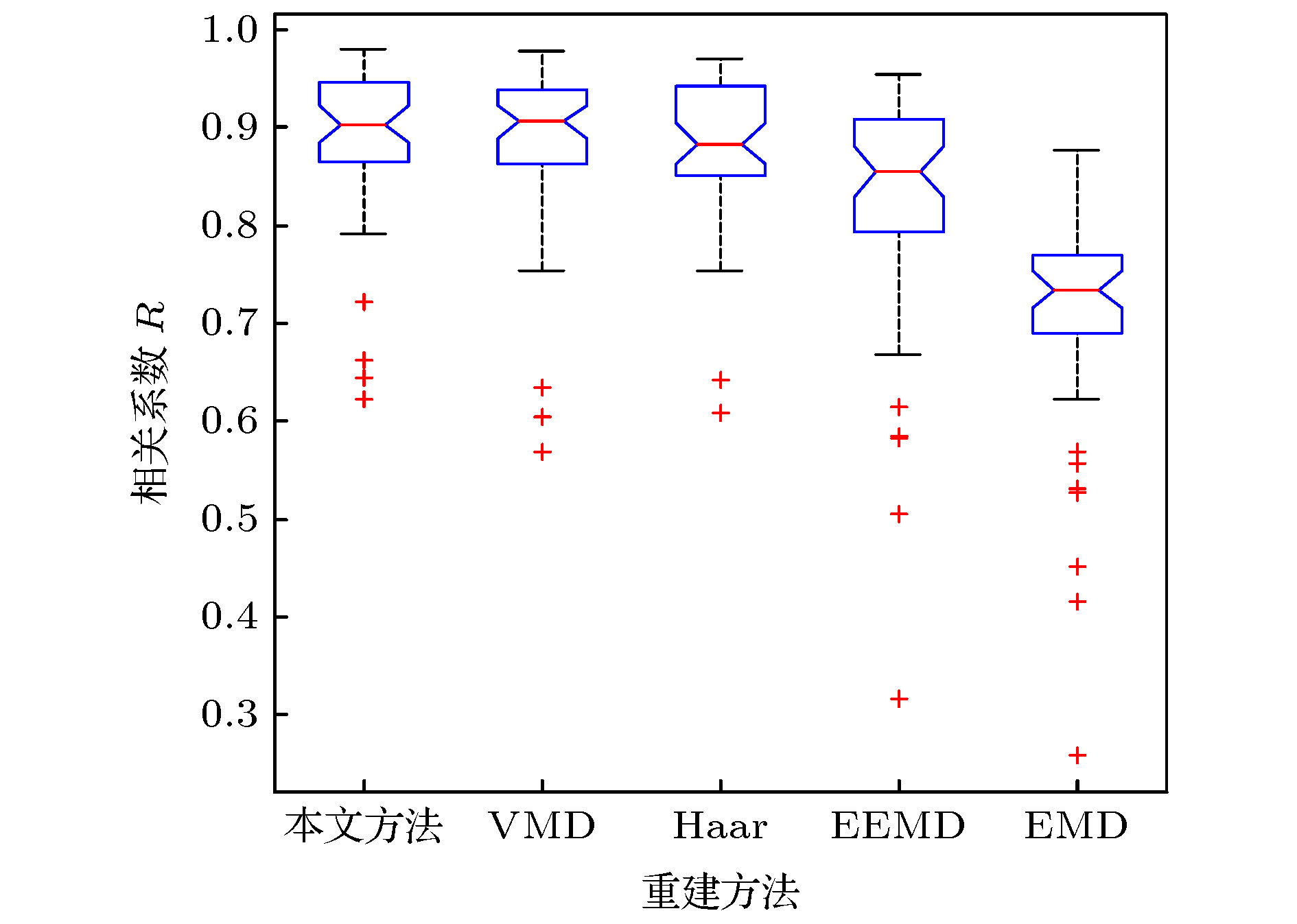
Electrocardiogram (ECG) diagnosis is based on the waveform, duration and amplitude of characteristic wave, which are required to have a high accuracy for ECG signal reconstruction. As an effective nonlinear signal processing method, empirical mode decomposition (EMD) has been widely used for diagnosing and reconstructing the ECG signal, but there are two problems arising here. One is the mode mixing, and the other is that the mode components used in reconstruction are identified by experience. Therefore, the method of reconstruction is not adaptive and universal, and reconstructed ECG signal loses accuracy. Firstly, we propose an improved EMD method, which is called integral mean mode decomposition (IMMD). The analysis of 5000 samples of Gaussian white noise shows that IMMD has better multi-resolution analysis ability than EMD, and it can effectively alleviate mode mixing consequently. Secondly, based on the inherent physical characteristics of ECG signal, cardiac cycle or heart rate (HR), it has practical physical significance to identify the mode components used in ECG signal reconstruction. The cardiac cycle feature acts as the intrinsic mode function (IMF) component through two modes. 1) For the low-order IMF that belongs to the ECG signal, the cardiac cycle feature acts as the amplitude modulation. The envelope of the IMF component has the characteristics of the cardiac cycle, and the frequency corresponding to the maximum amplitude in the spectrum of the envelope is equal to HR. 2) For the high-order IMF that belongs to the ECG signal, the cardiac cycle feature acts as frequency modulation. Those IMF components have the harmonic characteristics of periodic heartbeats, and the maximum amplitude in the spectrum corresponds to an integral multiple of HR (usually 1-3 times). The noise attributed to IMF component cannot show the above two cardiac cycle characteristics. Thus the proposed method is adaptive and universal. The 47 ECG signals with baseline drift and muscle artifact noise are tested. The results show that the proposed method is more effective than the variational mode decomposition (VMD), Haar wavelet with soft threshold, ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) and EMD. Among the 47 correlation coefficients between reconstructed and original ECG signals, the proposed method has 31 better than VMD, 33 better than Haar wavelet, 42 better than EEMD and 45 better than EMD. The mean of 47 correlation coefficients from the proposed method is 0.8904, and the variance is 0.0071, which shows that the proposed method has good performance and stability.
-
Keywords:
- electrocardiogram /
- reconstruction /
- heart rate /
- integral mean mode decomposition
[1] 黄宛 1998 临床心电图学 (第5版) (北京: 人民卫生出版社) 第22, 428页
Huang W 1998 Clinical Electrocardiography (5th Ed.) (Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House Press) pp22, 428 (in Chinese)
[2] Poungponsri S, Yu X H 2013 Neurocomputing 117 206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 庞宇, 邓璐, 林金朝, 李章勇, 周前能, 李国权, 黄华伟, 张懿, 吴炜 2014 63 098701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pang Y, Deng L, Lin J C, Li Z Y, Zhou Q N, Li G Q, Huang H W, Zhang Y, Wu W 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 098701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sharma R R, Pachori R B 2018 Biomed. Signal Process. Control 45 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] de Oliveira B R, Duarte M A Q, de Abreu C C E, Vieira F J 2018 Res. Biomed. Eng. 34 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zou C, Qin Y, Sun C, Li W, Chen W 2017 Pervasive Mob. Comput. 40 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jung W H, Lee S G 2012 Comput. Meth. Programs Biomed. 108 1121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yadav S K, Sinha R, Bora P K 2015 IET Signal Proc. 9 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yu Q, Guan Q, Li P, Liu T B, Si J F, Zhao Y, Liu H X, Wang Y Q 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 118702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Satija U, Ramkumar B, Manikandan M S 2018 IEEE J. Biomed. Health 22 722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, Wu M C, Shih H H, Zheng Q, Yen N C, Tung C C, Liu H H 1998 Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454 903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fu M J, Zhuang J J, Hou F Z, Zhan Q B, Shao Y, Ning X B 2010 Chin. Phys. B 19 058701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhu Y H, Yuan J, Stephen Z P, Oliver D K, Cheng Q, Wang X D, Tao C, Liu X J, Xu G, Paul L C 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 064301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu Z, Huang N E 2009 Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 531
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 曾彭, 刘红星, 宁新宝, 庄建军, 张兴敢 2015 64 078701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng P, Liu H X, Ning X B, Zhuang J J, Zhang X G 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 078701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nazari M, Sakhaei S M 2018 IEEE J. Biomed. Health 22 1059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ibtehaz N, Rahman M S, Rahman M S 2019 Biomed. Signal Process. Control 49 349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jarchi D, Casson A J 2017 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64 2042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lee J, McManus D D, Merchant S, Chon K H 2012 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59 1499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 盖强 2001 博士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Gai Q 2001 Ph. D. Dissertation (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[22] Huang N E, Wu M L C, Long S R, Shen S S P, Qu W, Gloersen P, Fan K L 2003 Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 459 2317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Flandrin P, Rilling G, Goncalves P 2004 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Flandrin P, Goncalves P 2004 Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolution. Inf. Process. 2 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huang N E, Hu K, Yang A C C, Chang H C, Jia D, Liang W K, Yeh J R, Kao C L, Juan C H, Peng C K, Meijer J H, Wang Y H, Long S R, Wu Z 2016 Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 374 20150206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Moody G B, Mark R G 2001 IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 20 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Moody G B, Muldrow W E, Mark R G 1984 Comput Cardiol 11 381
[28] Motin M A, Karmakar C, Palaniswami M 2019 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26 592
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li H Y, Wang C J, Zhao D 2018 IET Signal Proc. 12 844
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 IMMD和EMD方法分解高斯白噪声的等效滤波器组特性 (a) IMMD (实线)和EMD (虚线)的IMF分量的平均功率谱; (b) 基于(5)式, IMMD (实线)和EMD (虚线)的IMF分量的平均功率谱坍缩重合
Figure 1. Equivalent filter banks of IMMD and EMD decomposing Gauss white noises: (a) Averaged power spectra of IMFs from IMMD (solid curves) and EMD (dotted curves); (b) collapse and coincidence of the average power spectrum of IMFs from IMMD (solid curves) and EMD (dotted curves) based on Eq. (5).
图 5 原105 ECG信号(蓝色点虚线)与由五种方法重建的105 ECG信号(红色实线) (a) 本文方法; (b) VMD; (c) Haar小波软阈值; (d) EMMD; (e) EMD
Figure 5. Original No. 105 ECG signal (blue dotted curves) and the No. 105 ECG signals (red solid curves) reconstructed by 5 methods: (a) The proposed method; (b) VMD; (c) Haar wavelet with soft threshold; (d) EEMD; (e) EMD.
表 1 五种方法重建105 ECG信号的特征量值
Table 1. Characteristic values of No. 105 ECG signals reconstructed by 5 methods.
重建方法 R SNR/dB MSE/mV2 本文方法 0.9577 10.7740 0.0076 VMD 0.9572 10.6602 0.0078 Haar 0.9434 9.0070 0.0114 EEMD 0.9204 8.1126 0.0140 EMD 0.7638 3.6982 0.0388 表 2 实验采用的部分ECG信号对应心律失常类型
Table 2. Type of arrhythmia corresponding to some ECG signals used in the experiment.
心律失常类别 ECG索引号 房性早搏 100, 232 P波峰值和
起搏心搏102, 104, 107, 217 心房颤动 201, 203, 210, 219, 221 预激综合征 230 左束支传导阻滞 109, 111, 214 右束支传导阻滞 118, 124, 207, 212, 231, 232 室性早搏 119, 200, 203, 207, 208, 210,
214, 221, 233表 3 五种方法重建47个ECG信号的R值的均值与方差
Table 3. Means and variances of R values of 47 ECG signals reconstructed by 5 methods.
重建方法 均值 方差 本文方法 0.8904 0.0071 VMD 0.8826 0.0081 Haar 0.8804 0.0058 EEMD 0.8222 0.0166 EMD 0.7100 0.0143 -
[1] 黄宛 1998 临床心电图学 (第5版) (北京: 人民卫生出版社) 第22, 428页
Huang W 1998 Clinical Electrocardiography (5th Ed.) (Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House Press) pp22, 428 (in Chinese)
[2] Poungponsri S, Yu X H 2013 Neurocomputing 117 206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 庞宇, 邓璐, 林金朝, 李章勇, 周前能, 李国权, 黄华伟, 张懿, 吴炜 2014 63 098701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pang Y, Deng L, Lin J C, Li Z Y, Zhou Q N, Li G Q, Huang H W, Zhang Y, Wu W 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 098701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sharma R R, Pachori R B 2018 Biomed. Signal Process. Control 45 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] de Oliveira B R, Duarte M A Q, de Abreu C C E, Vieira F J 2018 Res. Biomed. Eng. 34 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zou C, Qin Y, Sun C, Li W, Chen W 2017 Pervasive Mob. Comput. 40 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jung W H, Lee S G 2012 Comput. Meth. Programs Biomed. 108 1121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yadav S K, Sinha R, Bora P K 2015 IET Signal Proc. 9 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yu Q, Guan Q, Li P, Liu T B, Si J F, Zhao Y, Liu H X, Wang Y Q 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 118702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Satija U, Ramkumar B, Manikandan M S 2018 IEEE J. Biomed. Health 22 722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, Wu M C, Shih H H, Zheng Q, Yen N C, Tung C C, Liu H H 1998 Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454 903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fu M J, Zhuang J J, Hou F Z, Zhan Q B, Shao Y, Ning X B 2010 Chin. Phys. B 19 058701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhu Y H, Yuan J, Stephen Z P, Oliver D K, Cheng Q, Wang X D, Tao C, Liu X J, Xu G, Paul L C 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 064301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu Z, Huang N E 2009 Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 531
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 曾彭, 刘红星, 宁新宝, 庄建军, 张兴敢 2015 64 078701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zeng P, Liu H X, Ning X B, Zhuang J J, Zhang X G 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 078701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nazari M, Sakhaei S M 2018 IEEE J. Biomed. Health 22 1059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ibtehaz N, Rahman M S, Rahman M S 2019 Biomed. Signal Process. Control 49 349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jarchi D, Casson A J 2017 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64 2042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Lee J, McManus D D, Merchant S, Chon K H 2012 IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59 1499
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 盖强 2001 博士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Gai Q 2001 Ph. D. Dissertation (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[22] Huang N E, Wu M L C, Long S R, Shen S S P, Qu W, Gloersen P, Fan K L 2003 Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 459 2317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Flandrin P, Rilling G, Goncalves P 2004 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Flandrin P, Goncalves P 2004 Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolution. Inf. Process. 2 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huang N E, Hu K, Yang A C C, Chang H C, Jia D, Liang W K, Yeh J R, Kao C L, Juan C H, Peng C K, Meijer J H, Wang Y H, Long S R, Wu Z 2016 Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 374 20150206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Moody G B, Mark R G 2001 IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 20 45
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Moody G B, Muldrow W E, Mark R G 1984 Comput Cardiol 11 381
[28] Motin M A, Karmakar C, Palaniswami M 2019 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26 592
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Li H Y, Wang C J, Zhao D 2018 IET Signal Proc. 12 844
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9362
- PDF Downloads: 120
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: