-
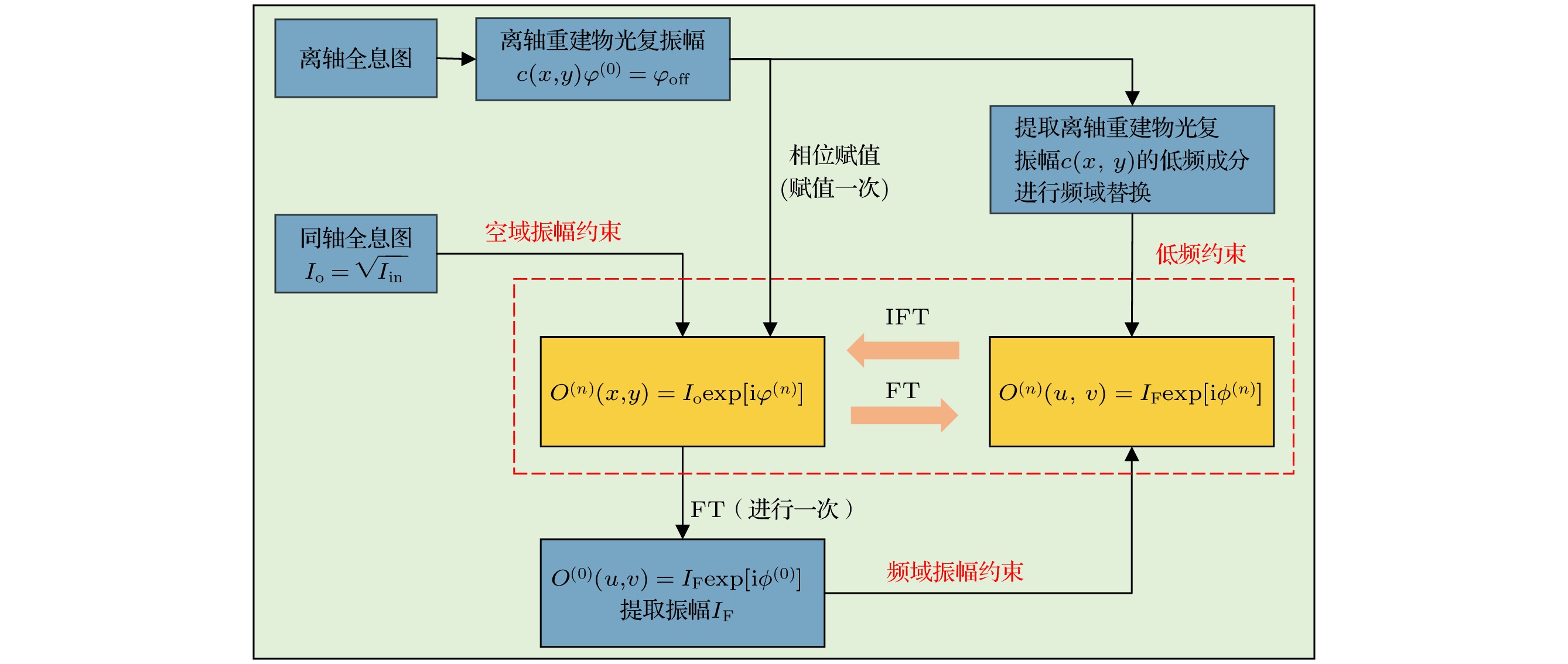
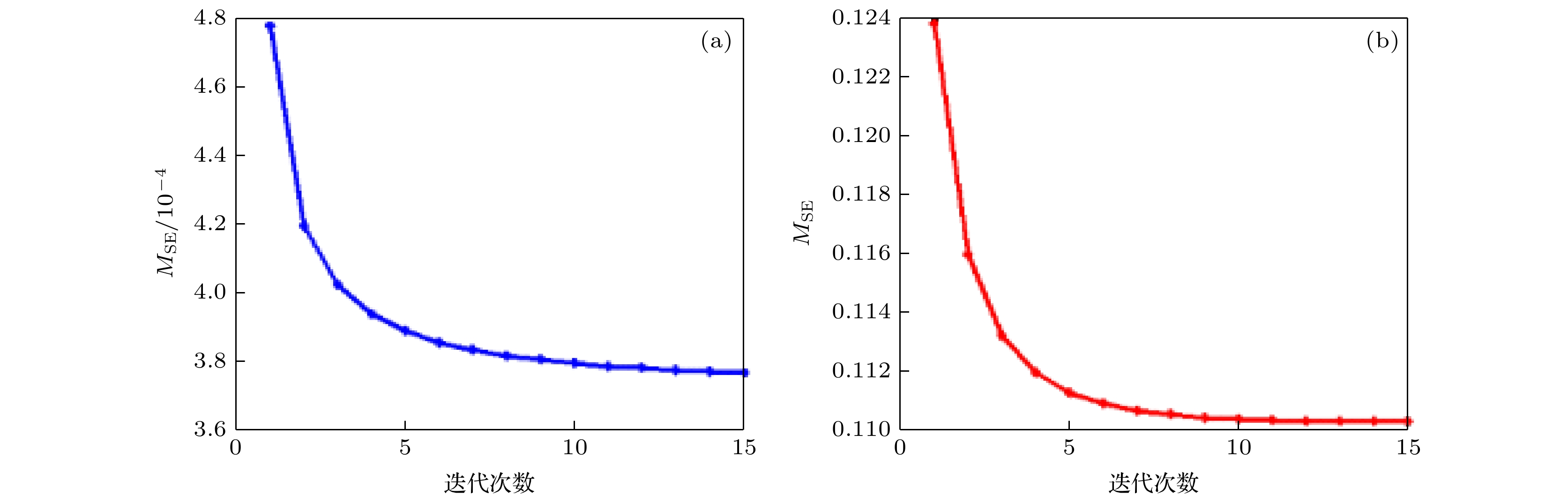
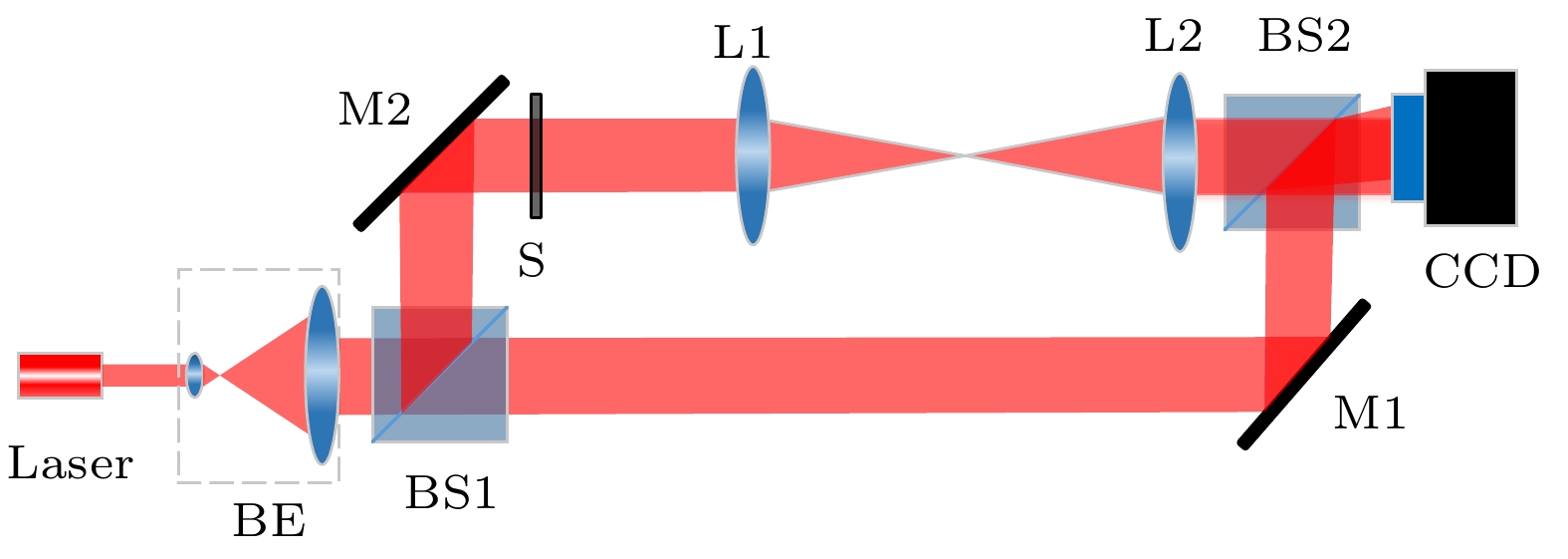
In-line digital holography usually employs a phase retrieval algorithm to decouple the phase information but fails to eliminate the unwanted DC and twin image terms when the measured sample does not agree with the sparsity. While the off-axis digital holography can efficiently remove the unwanted image terms but can not reserve the high frequencies of the sample to realize high resolution. The in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography was then developed to provide a relatively high resolution digital holographic imaging without considering the effect of the unwanted terms. In other words, the in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography merges all of the best virtues of the mentioned-above methods in an efficient and elegant way. However, this state-of-the-art method requires prior knowledge about the diffraction distance, which results in time-consuming and low accuracy. In other sense, telecentric technology can realize non-diffractive imaging without the knowledge about the diffraction distance or spherical aberration or defocusing aberration. Therefore, in this paper, a novel in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography is proposed by introducing telecentric imaging architecture, and the corresponding reconstruction method is further proposed by utilizing constrained iterative approach. In this method, telecentric in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography is first used to acquire focused off-axis and in-line holograms, respectively. The low resolution phase information is reconstructed from the off-axis hologram by using Fourier transform method with the help of the sample-free off-axis hologram, and then multiplexed with the amplitude information obtained from the in-line hologram to act as the initial complex amplitude in the iterative recovery process. As a result, constrained iterations are carried out in the spatial domain and frequency domain to realize high resolution and high speed reconstruction. After simulations, we build an experimental setup and demonstrate the operation of the method with USAF resolution target, onion cells and bee wings. Both the simulation and experimental results show that the proposed method can require no prior knowledge to suppress the phase disturbance caused by the unwanted image terms and optical aberrations, resulting in high speed and full utilization of spatial bandwidth product of the digital camera to yield high resolution reconstruction. We hope that the proposed method will have most practical applications in the case where large resolution, high speed and good quality are needed.
-
Keywords:
- digital holography /
- telecentric imaging /
- iterative recovery /
- high resolution
[1] Schnars U, Juptner W 1994 Appl. Opt. 33 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang Z, Millet L J, Gillette M U, Popescu G 2008 Opt. Lett. 33 1270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Aguilar J C, Raul Berriel-Valdos L, Felix Aguilar J 2013 Opt. Eng. 52 104103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kemper B, Vollmer A, Rommel C E, Schnekenburger J, Von B G, Biomed J 2011 J. Biomed. Opt. 16 026014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao W Q, Qiu L R, Xiao Y, Yang J M 2016 Opt. Express 24 22813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Donnarumma D, Brodoline A, Alexandre D 2016 Opt. Express 24 26887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang J W, Dai S Q, Ma C J, Di J L, Zhao J L 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 3462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang W J, Liu X J, Lu W L, Guo X T, Popescu G 2018 Precis. Eng. 51 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Qiu L R, Wang Y, Wu H X, Sun Y B, Cui H, Zhao W Q, Yuan L, Zhan C L 2018 Opt. Express 26 2314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hu C F, Zhu S S, Gao L 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 3373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 周宏强, 万玉红, 满天龙 2018 67 044202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou H Q, Wan Y H, Man T L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 044202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 张益溢, 吴佳琛, 郝然, 金尚忠, 曹良才 2020 69 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y Y, Wu J C, Hao R, Jin S Z, Cao L C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu J Q, Zhu L Q, Zhang F, Dong M L, Qu X H 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 4042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王华英, 刘飞飞, 宋修法, 廖微, 赵宝群, 于梦杰, 刘佐强 2013 62 024207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H Y, Liu F F, Liao W, Song X F, Yu M J, Liu Z Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 024207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cuche E, Marquet P, Depeursinge C 1999 Appl. Opt. 38 6994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Pham H V, Edwards C, Lynford L G, Popescu G 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 A97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gao P, Harder I, Nercissian V, Mantel K, Yao B 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bai H Y, Shan M G, Zhong Z, Guo L L, Zhang Y B 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 9513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yamaguchi I, Zhang T 1997 Opt. Lett. 22 1268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Oshima T, Matsudo Y, Kakue T, Arai D, Shimobaba T, Ito T 2015 Opt. Commun. 350 270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gerchberg R W, Saxton W O 1972 Optik 35 237
[22] Fienup J 1982 Appl. Opt. 21 2758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Latychevskaia T, Fink H W 2007 Phy. Rev. Lett. 98 233901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rong L, Li Y, Liu S, Xiao W, Pan F, Wang D Y 2013 Opt. Laser Eng. 51 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang G Z, Dong B Z, Gu B Y, Zhuang J Y, Ersoy O K 1994 Appl. Opt. 33 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang W H, Cao L C, David J B, Zhang H, Cang J, Jin G F 2018 Phy. Rev. Lett. 121 093902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Orzó L 2015 Opt. Express 23 16638
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 王凤鹏, 王大勇, 王云新, 戎路, 赵洁 2018 中国激光 45 0609001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang F P, Wang D Y, Wang Y X, Rong L, Zhao J 2018 Chinese Journal of Lasers 45 0609001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Khare K, Ali P T S, Joseph J 2013 Opt. Express 21 5634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wu X Y, Yu Y J, Zhou W J 2014 Opt. Express 22 19860
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhong M, Cui J, Hyun J S, Pan L, Duan P, Zhang S 2020 Meas. Sci. Technol. 31 085003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Sanchez-Ortiga E, Ferraro P, Martinez-Corral M 2011 Opt. Soc. Am. A 28 1410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhong Z, Bai H Y, Shan M G, Zhang Y B, Guo L L 2017 Opt. Laser Eng. 97 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Hao B G, Shan M G, Zhong Z, Diao M, Wang Y, Zhang Y B 2015 J. Opt. 17 035602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
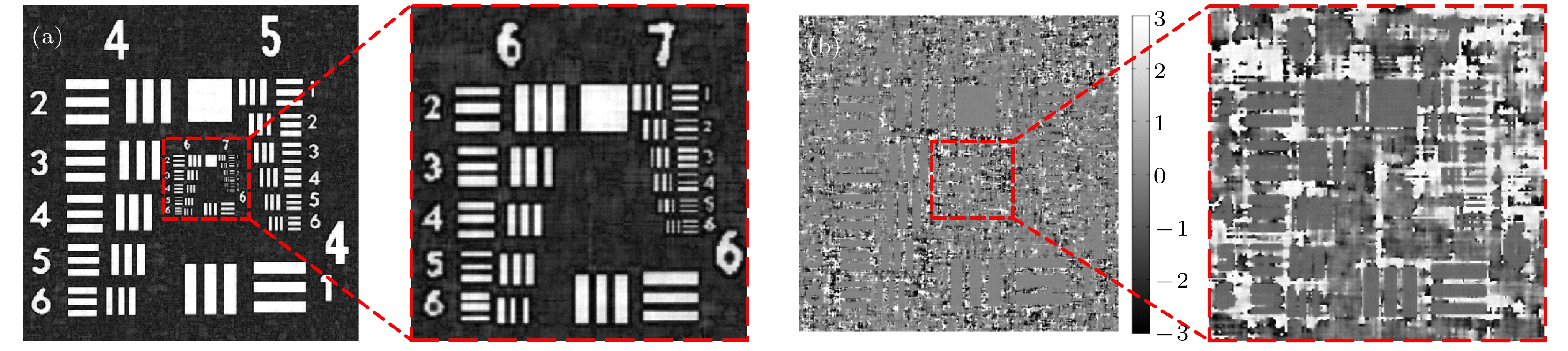
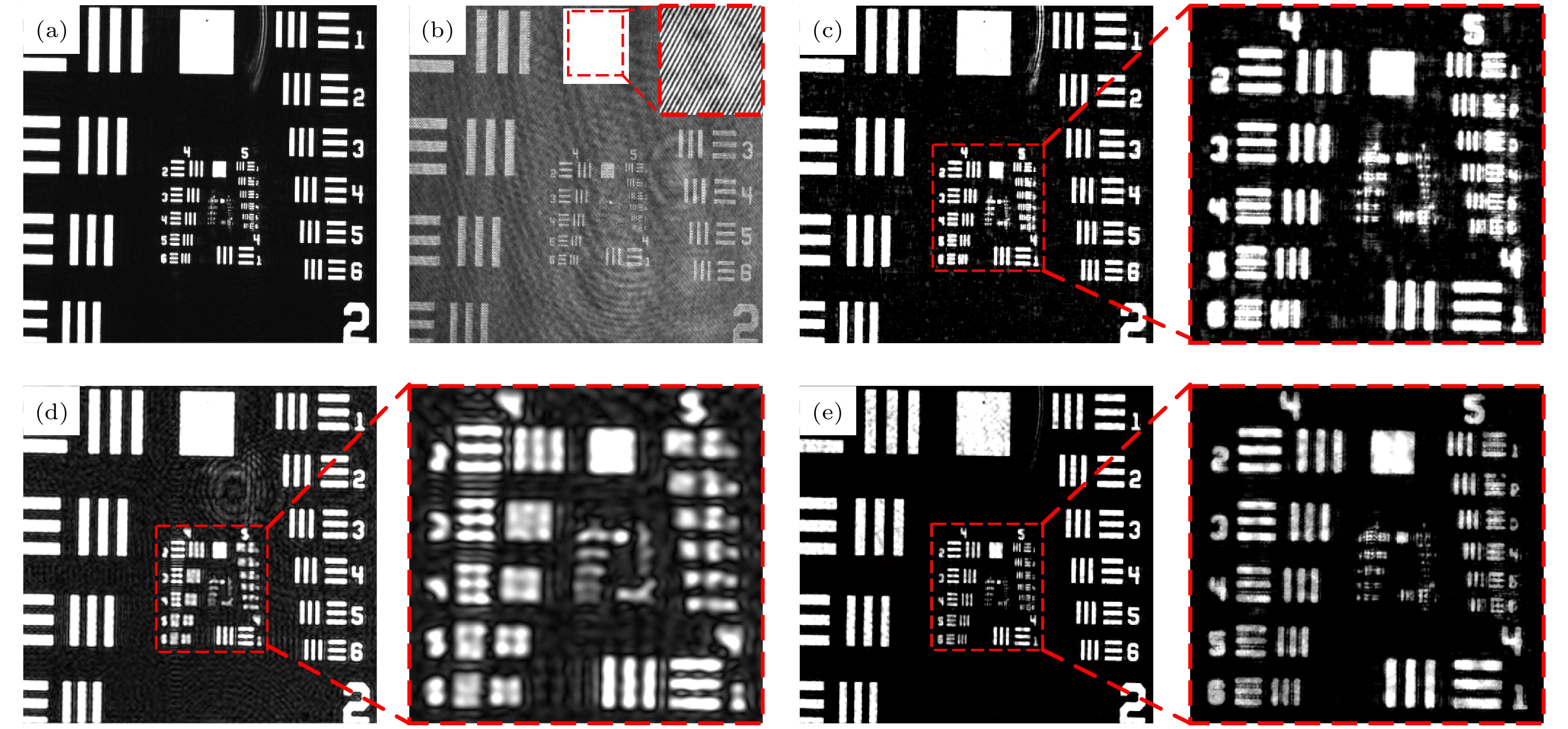
图 8 USAF分辨率板实验结果 (a)同轴全息图; (b)离轴全息图; (c) 同轴数字全息再现像; (d)离轴数字全息再现像; (e)同-离轴混合数字全息再现像
Figure 8. Experimental results of USAF resolution target: (a) In-line hologram; (b) off-axis hologram; (c) amplitude reconstructed image of the in-line hologram; (d) amplitude reconstructed image of the off-axis hologram; (e) amplitude reconstructed image of the in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography.
图 9 洋葱表皮细胞实验结果 (a)同轴全息图; (b)离轴全息图; (c)同轴数字全息再现强度像; (d)同轴数字全息再现相位像; (e) 离轴数字全息再现强度像; (f) 离轴数字全息再现相位像; (g) 混合数字全息再现强度像; (h) 混合数字全息再现相位像; (i)相位剖面曲线
Figure 9. Experimental results of onion epidermal cell: (a) In-line hologram; (b) off-axis hologram; (c) amplitude reconstructed image of the in-line hologram; (d) phase reconstructed image of the in-line hologram; (e) amplitude reconstructed image of the off-axis hologram; (f) phase reconstructed image of the off-axis hologram; (g) amplitude reconstructed image of the in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography; (h) phase reconstructed image of the in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography; (i) phase profile curves.
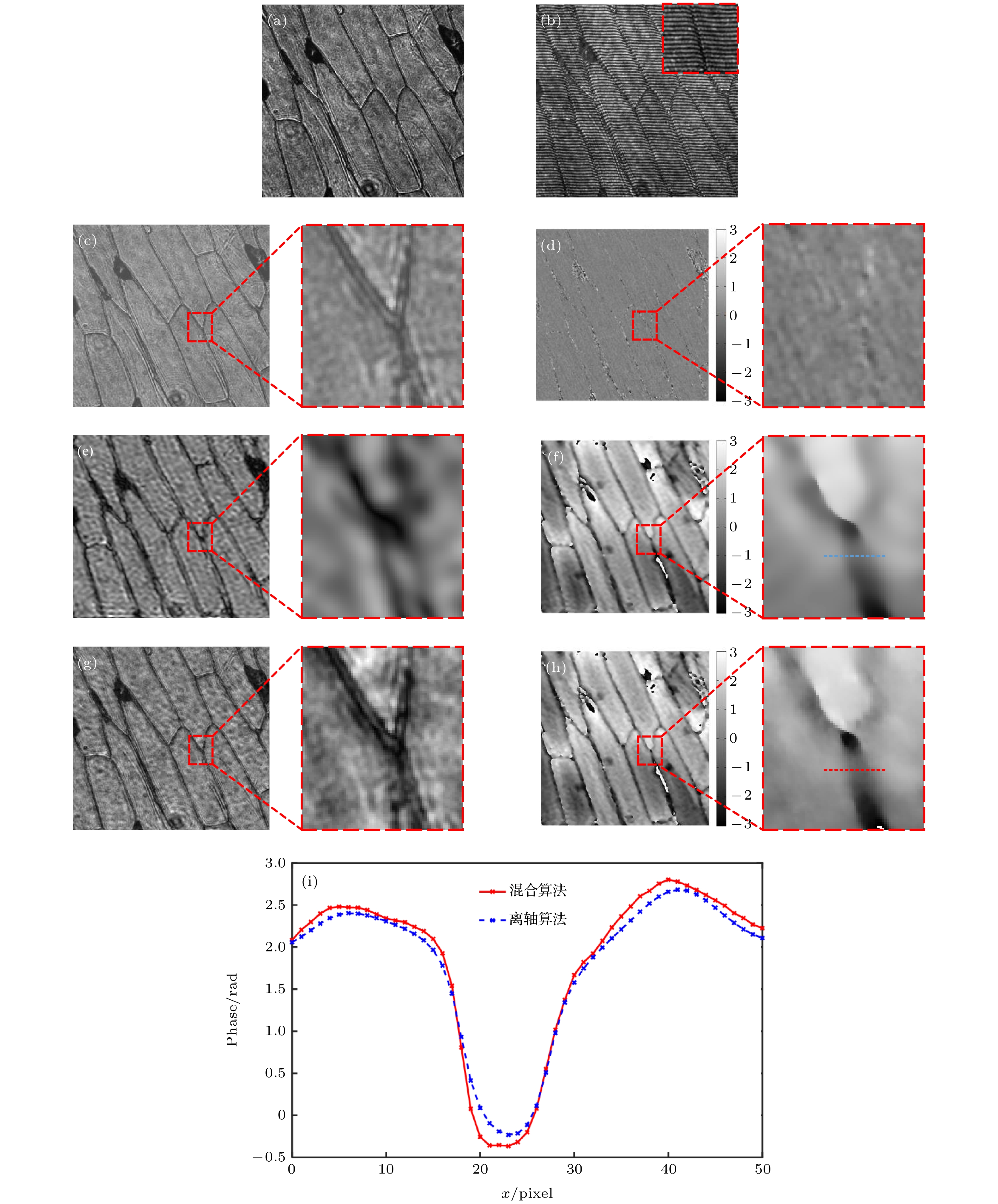
图 10 蜜蜂翅膀实验结果 (a)同轴全息图; (b)离轴全息图; (c)同轴数字全息再现强度像; (d)同轴数字全息再现相位像; (e) 离轴数字全息再现强度像; (f) 离轴数字全息再现相位像; (g) 混合数字全息再现强度像; (h) 混合数字全息再现相位像; (i)相位剖面曲线
Figure 10. Experimental results of bee wings: (a) In-line hologram; (b) off-axis hologram; (c) amplitude reconstructed image of the in-line hologram; (d) phase reconstructed image of the in-line hologram; (e) amplitude reconstructed image of the off-axis hologram; (f) phase reconstructed image of the off-axis hologram; (g) amplitude reconstructed image of the in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography; (h) phase reconstructed image of the in-line-and-off-axis hybrid digital holography; (i) phase profile curves
表 1 不同算法重建振幅和相位的峰值信噪比
Table 1. Peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of amplitudes and phases reconstructed by different algorithms.
同轴算法 离轴算法 混合算法 振幅PSNR/dB 71.55 66.54 82.37 相位PSNR/dB 43.69 55.29 57.70 -
[1] Schnars U, Juptner W 1994 Appl. Opt. 33 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang Z, Millet L J, Gillette M U, Popescu G 2008 Opt. Lett. 33 1270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Aguilar J C, Raul Berriel-Valdos L, Felix Aguilar J 2013 Opt. Eng. 52 104103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kemper B, Vollmer A, Rommel C E, Schnekenburger J, Von B G, Biomed J 2011 J. Biomed. Opt. 16 026014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao W Q, Qiu L R, Xiao Y, Yang J M 2016 Opt. Express 24 22813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Donnarumma D, Brodoline A, Alexandre D 2016 Opt. Express 24 26887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang J W, Dai S Q, Ma C J, Di J L, Zhao J L 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 3462
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang W J, Liu X J, Lu W L, Guo X T, Popescu G 2018 Precis. Eng. 51 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Qiu L R, Wang Y, Wu H X, Sun Y B, Cui H, Zhao W Q, Yuan L, Zhan C L 2018 Opt. Express 26 2314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Hu C F, Zhu S S, Gao L 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 3373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 周宏强, 万玉红, 满天龙 2018 67 044202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou H Q, Wan Y H, Man T L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 044202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 张益溢, 吴佳琛, 郝然, 金尚忠, 曹良才 2020 69 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y Y, Wu J C, Hao R, Jin S Z, Cao L C 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu J Q, Zhu L Q, Zhang F, Dong M L, Qu X H 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 4042
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王华英, 刘飞飞, 宋修法, 廖微, 赵宝群, 于梦杰, 刘佐强 2013 62 024207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H Y, Liu F F, Liao W, Song X F, Yu M J, Liu Z Q 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 024207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cuche E, Marquet P, Depeursinge C 1999 Appl. Opt. 38 6994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Pham H V, Edwards C, Lynford L G, Popescu G 2013 Appl. Opt. 52 A97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gao P, Harder I, Nercissian V, Mantel K, Yao B 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Bai H Y, Shan M G, Zhong Z, Guo L L, Zhang Y B 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 9513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yamaguchi I, Zhang T 1997 Opt. Lett. 22 1268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Oshima T, Matsudo Y, Kakue T, Arai D, Shimobaba T, Ito T 2015 Opt. Commun. 350 270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gerchberg R W, Saxton W O 1972 Optik 35 237
[22] Fienup J 1982 Appl. Opt. 21 2758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Latychevskaia T, Fink H W 2007 Phy. Rev. Lett. 98 233901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rong L, Li Y, Liu S, Xiao W, Pan F, Wang D Y 2013 Opt. Laser Eng. 51 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang G Z, Dong B Z, Gu B Y, Zhuang J Y, Ersoy O K 1994 Appl. Opt. 33 209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang W H, Cao L C, David J B, Zhang H, Cang J, Jin G F 2018 Phy. Rev. Lett. 121 093902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Orzó L 2015 Opt. Express 23 16638
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 王凤鹏, 王大勇, 王云新, 戎路, 赵洁 2018 中国激光 45 0609001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang F P, Wang D Y, Wang Y X, Rong L, Zhao J 2018 Chinese Journal of Lasers 45 0609001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Khare K, Ali P T S, Joseph J 2013 Opt. Express 21 5634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wu X Y, Yu Y J, Zhou W J 2014 Opt. Express 22 19860
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhong M, Cui J, Hyun J S, Pan L, Duan P, Zhang S 2020 Meas. Sci. Technol. 31 085003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Sanchez-Ortiga E, Ferraro P, Martinez-Corral M 2011 Opt. Soc. Am. A 28 1410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhong Z, Bai H Y, Shan M G, Zhang Y B, Guo L L 2017 Opt. Laser Eng. 97 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Hao B G, Shan M G, Zhong Z, Diao M, Wang Y, Zhang Y B 2015 J. Opt. 17 035602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8474
- PDF Downloads: 157
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: