-
Due to the unique bacterial killing ability through membrane permeabilization and content leakage, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have been regarded as promising candidates against the severe threats of drug-resistant bacteria and even superbugs to public health. However, investigations of the mechanism underlying their membrane permeabilization like poration are still on the way. Here, from the perspective of molecular motion kinetics, we studied the interactions between melittin, as one of the most representative AMPs, and a bi-component lipid membrane based on the combination of single-molecule tracking and molecular dynamics simulations. Our results reveal that, the mobility of some lipids in membrane, in comparison of the other most molecules, is significantly decreased by the surface adsorption and transmembrane insertion of melittin. Moreover, melittin tends to work at the boundary region between phase domains, disturb and blur the phase separation behavior and consequently lower the confinement of phase boundary on lipid motions. This work demonstrates the correlation between membrane activity of melittin and the motion kinetics of lipids as well as phase behavior of the membrane. These results would be helpful not only for understanding the molecular mechanism of AMPs from a new perspective but also for the development of new antibacterial agents with improved performance.
-
Keywords:
- antimicrobial peptide /
- cell membrane /
- single-molecule tracking /
- molecular dynamics simulations /
- single molecular kinetics
[1] Fox J L 2013 Nat. Biotechnol. 31 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lu X M, Liu J J, Gou L, Li J L, Yuan B, Yang K, Ma Y 2019 Adv. Healthc. Mater. 8 1801521
[3] Wimley W C 2010 ACS Chem. Biol. 5 905
[4] Sancho-Vaello E, Zeth K 2015 Fut. Microbiol. 10 1103
[5] Hong J J, Lu X M, Deng Z X, Xiao S F, Yuan B, Yang K 2019 Molecules 24 1775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Huang H W 2000 Biochemistry 39 8348
[7] Lee M T, Sun T L, Hung W C, Huang H W 2013 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110 14243
[8] Liu J J, Xiao S F, Li J L, Yuan B, Yang K, Ma Y Q 2018 Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1860 2234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Mishra A, Lai G H, Schmidt N W, Sun V Z, Rodriguez A R, Tong R, Tang L, Cheng J J, Deming T J, Kamei D T, Wong G C L 2011 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 16883
[10] Huang H W, Chen F Y, Lee M T 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 198304
[11] Rzepiela A J, Sengupta D, Goga N, Marrink S J 2010 Faraday Discuss. 144 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Deng Z X, Li J L, Yuan B, Yang K 2019 Commun. Theor. Phys. 71 887
[13] 陆乃彦, 元冰, 杨恺 2013 62 178701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu N Y, Yuan B, Yang K 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 178701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 梁燚然, 梁清 2019 68 028701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang Y R, Liang Q 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 028701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Barkai E, Garini Y, Metzler R 2012 Phys. Today 65 29
[16] Ge F, Xue J F, Wang Z H, Xiong B, He Y 2019 Sci. China Chem. 62 1072
[17] He W, Song H, Su Y, Geng L, Ackerson B J, Peng H B, Tong P 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] JelgerHR, Siewert J M, 2008 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 45
[19] Newcomb C J, Sur S, Lee S S, Yu J M, Zhou Y, Snead M L, Stupp S I 2016 Nano Lett. 16 3042
[20] Lozano M M, Hovis J S, Moss Ⅲ F R, Boxer S G 2016 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 9996
[21] Shishina A K, Kovrigina E A, Galiakhmetov A R, Rathore R, Kovrigin E L 2018 Biochemistry 57 872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Huang H W 2006 Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1758 1292
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Dumonteil E, Majumdar SN, Rosso A, Zoia A, 2013 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Shen R, Guo WL 2009 Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1788 1024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Leonov D V, Dzuba S A, Surovtsev N V 2019 RSC Adv. 9 34451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Goodchild J A, Walsh D L, Connell S D 2019 Langmuir 35 15352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 A3 包裹钙黄绿素的巨单层囊泡在浓度为 (a) 0.5和 (b) 5.0 µg/mL蜂毒肽溶液中的荧光共聚焦显微照片, 包括绿色 (钙黄绿素) 通道、红色 (脂分子) 通道和复合通道. 右图为对应的蜂毒肽作用方式的卡通图, 包括膜表面吸附和跨膜插入
Figure A3. Confocal images of calcein-encapsulated GUVs exposed to melittin at 0.5 or 5.0 µg/mL. The images were taken in the green (calcein), red (lipid) and overlaid channels. Cartoons on the right refer to the corresponding action states of peptides, including surface adsorption and transmembrane insertion
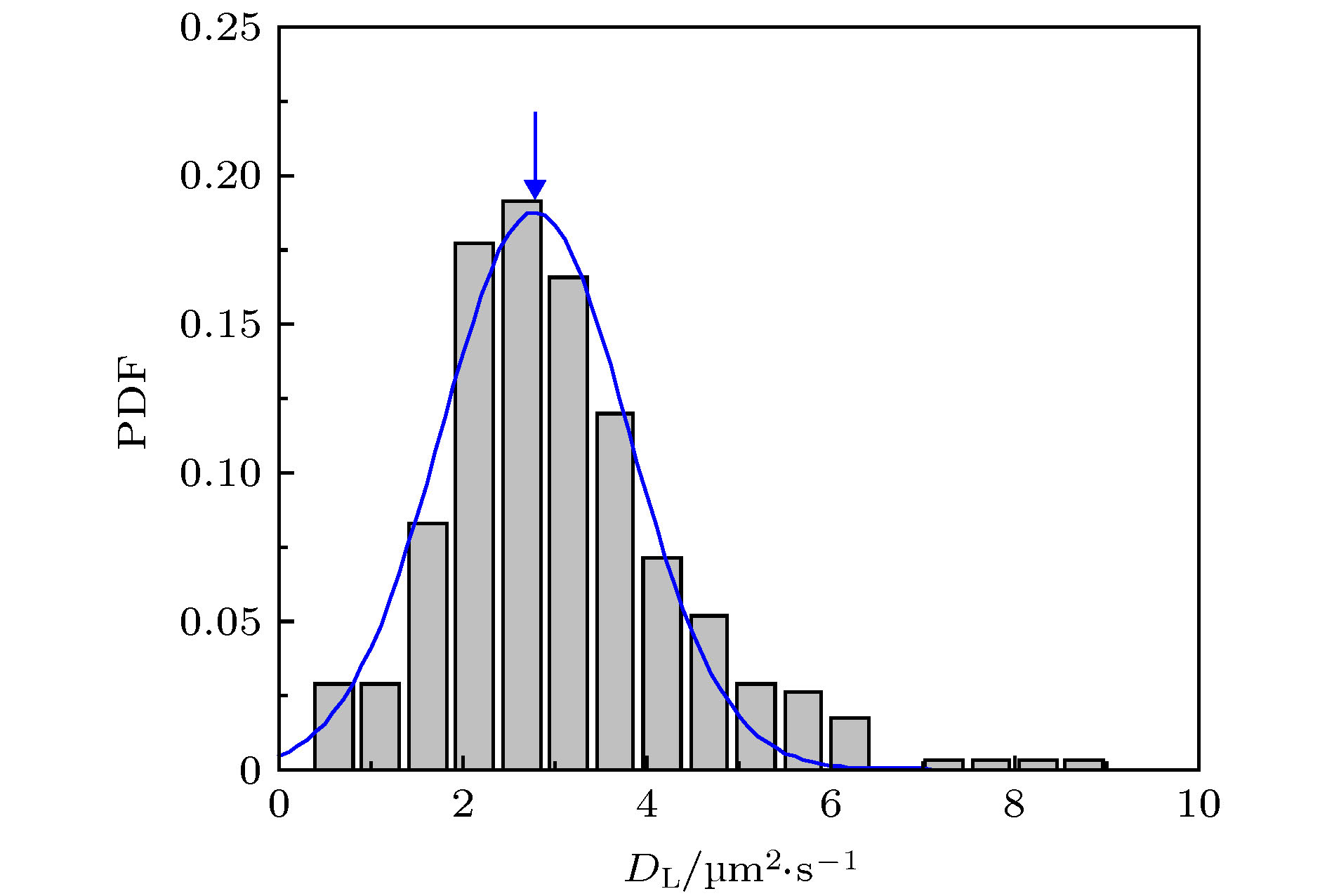
图 1 蜂毒肽作用下脂质分子在脂膜上的运动情况 (a) 荧光显微镜照片, 部分脂分子的运动轨迹以彩色线标注; (b) 典型的脂质分子运动轨迹, 采集时间皆为3 s, 部分移动范围较小的轨迹以蓝色箭头标注; (c) 典型的脂质分子时间平均均方位移分布. 蜂毒肽浓度为0.5 µg/mL
Figure 1. Diffusion of lipids on a DOPC/DPPC membrane under the action of melittin at 0.5 µg/mL: (a) Microscopy image with some trajectories marked in colors; (b) typical lipid trajectories in 3 s; Some of the immobile ones are marked with blue arrows; (c) representative time-averaged MSD of lipids.
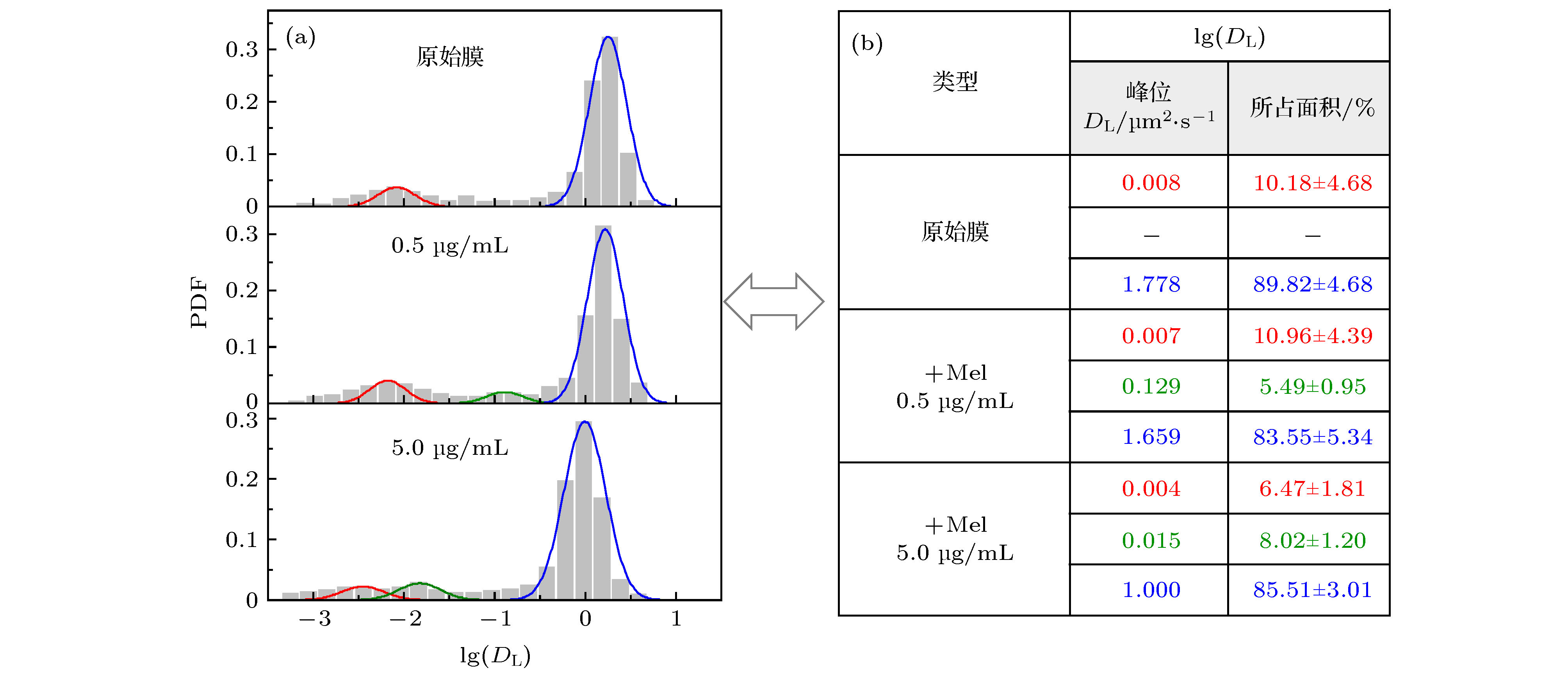
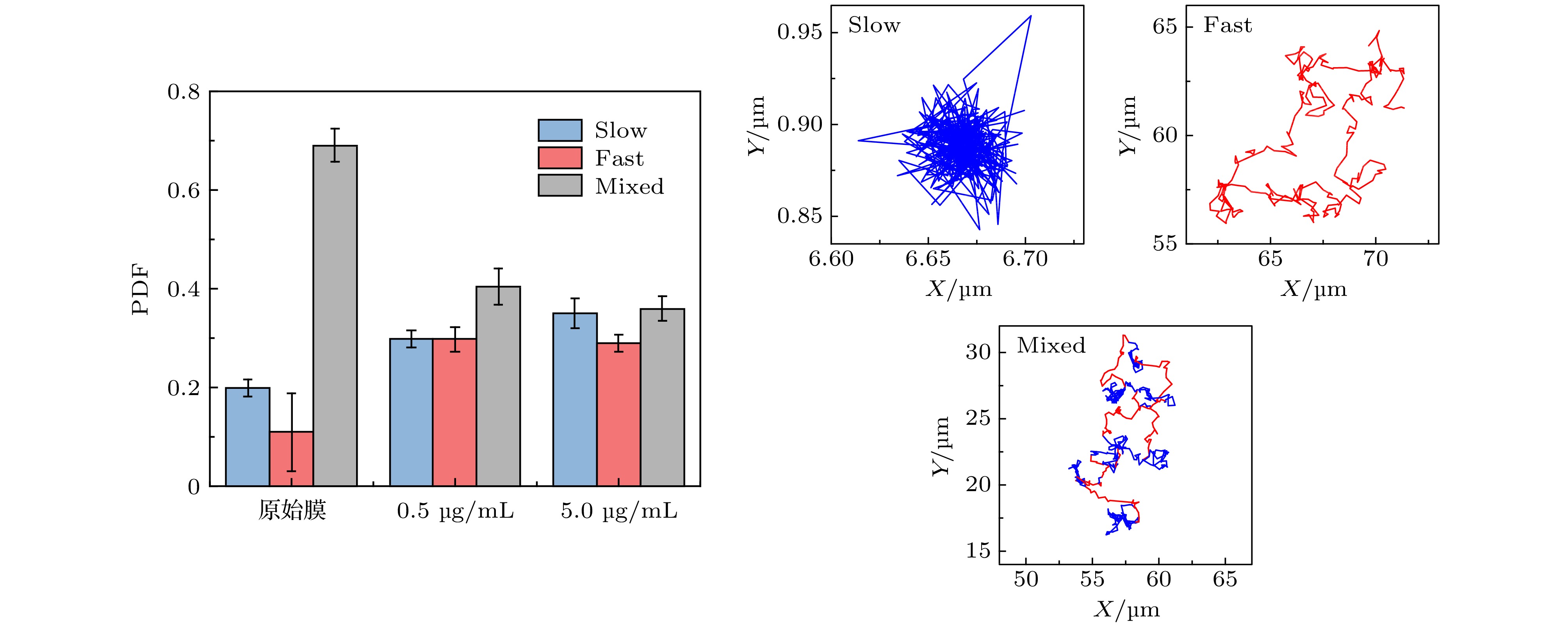
图 2 不同浓度蜂毒肽作用下脂分子扩散系数的分布 (a) 脂质扩散系数分布柱状图及拟合曲线; (b) 相应的拟合峰中心位置和在 (a) 图中所占面积比例, 显示为拟合曲线面积比例(± 与原始柱状图面积比例之间的误差). 三个体系对应的实验样本数分别为657 (原始膜体系), 427 (蜂毒肽浓度0.5 µg/mL)和507 (蜂毒肽浓度5.0 µg/mL)
Figure 2. PDF distribution of lipid diffusion coefficients (DL) of membrane with different melittin concentrations: (a) Histograms andfittings of the PDF; (b) corresponding peak locations and area proportionsin (a). Sample numbers are 657 (pristine membrane), 427 (with Mel at 0.5 µg/mL) and 507 (with Mel at 5.0 µg/mL), respectively.
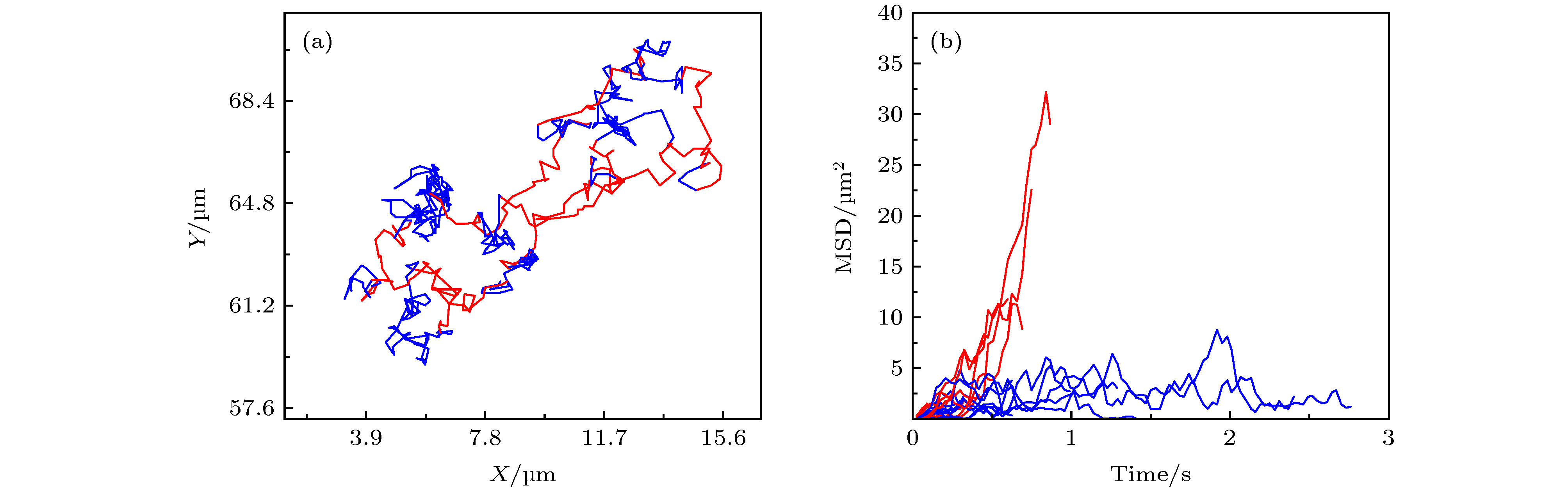
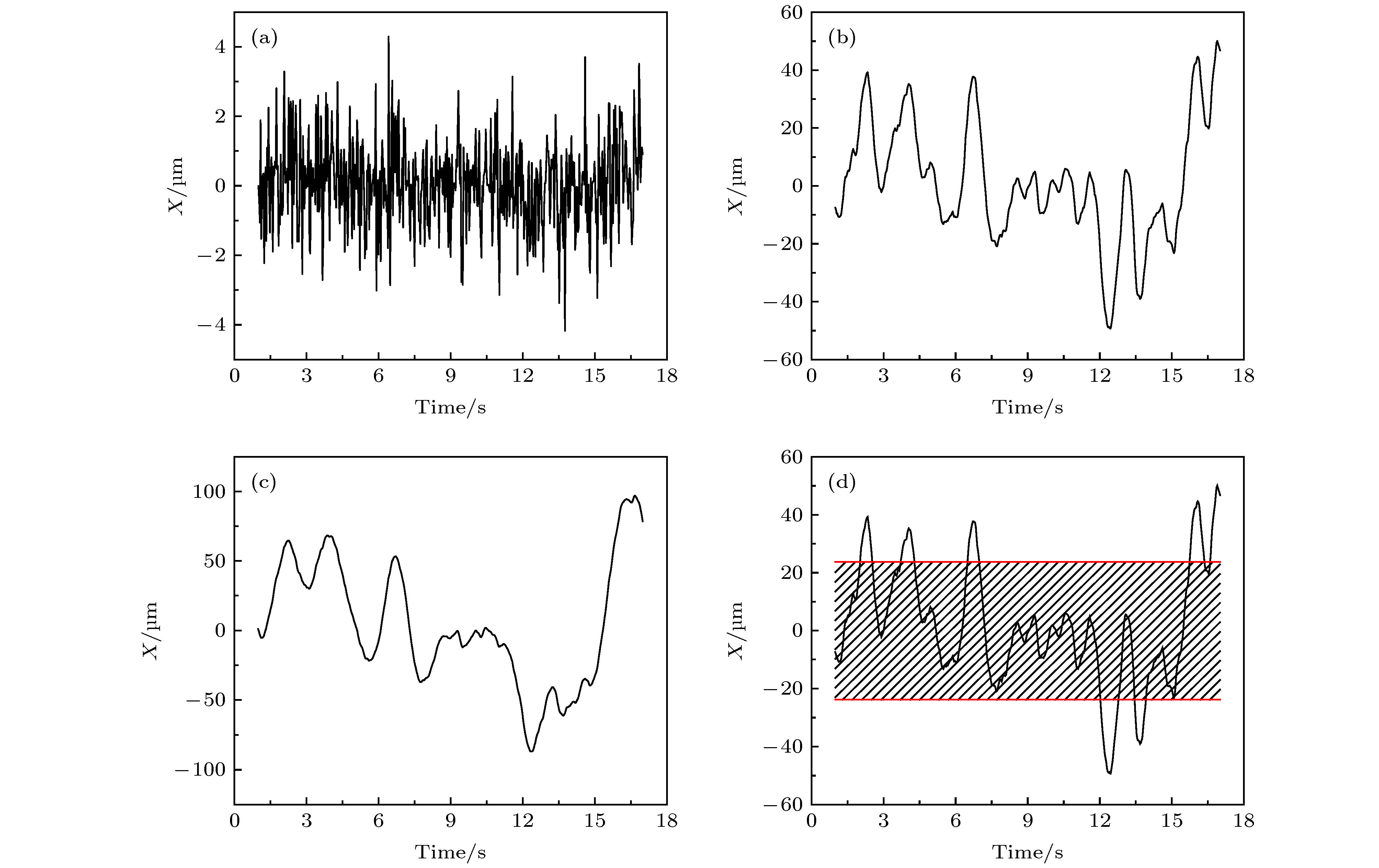
图 A7 (a) 第32阶系数小波变换区分后的轨迹曲线, 红色和蓝色分别对应轨迹中运动较快和较慢的阶段;(b) 与图 (a) 中红色、蓝色阶段相对应的MSD分布
Figure A7. (a) Trajectory discriminated by wavelet using the 32 th scale coefficient, whose red part refers to the “fast” motion type and blue part refers to the “slow” motion type;(b)the corresponding MSD distributions of the red and blue parts.
图 4 蜂毒肽对脂膜相分离行为的干扰 (a) 蜂毒肽与相分离脂膜相互作用过程的分子动力学模拟截图.上图是俯视图, 下图是侧视图. 红色对应蜂毒肽, 蓝色代表DPPC脂分子头基, 绿色为DUPC脂分子头基. 侧视图中脂质尾链未显示; (b) 吸附或插膜状态下多肽与周围脂质分子的相互作用细节. 颜色同 (a). 此外, 多肽周围的部分脂分子尾链以黄色棒表示, 远离多肽的脂质分子仅显示头部 (灰色); (c)相边界长度(L) 在蜂毒肽加入前后随时间的变化. 图(a) 中的时间点对应标记于图(c) 中. 插图为多肽作用下单个脂分子扩散MSD的等值分布图, 其中以红色圆圈标出多肽位置 P/L = 12/512
Figure 4. Interaction between melittin and a phase-separated bilayer: (a) Snapshots showing the melittin-inducedporeformation process. Top: top view, bottom: side view. Red: melittin, blue: DPPC headgroup, green: DUPC headgroup. For clarity, lipid tails are not shown; (b) interaction details between Mel (red) and the surrounding lipids. Color codes are the same as in (a), with tails of the surrounding lipids in yellow, and heads of lipids away from the peptides in grey; (c) time evolution of phase boundary length (L) before and after the addition of melittin at P/L = 12/512. The time points of (a) are marked correspondingly in (c).
表 B1 实验样本数
Table B1. Number of samples in different experimental conditions
原始膜 0.5 µg/mL 5.0 µg/mL 657 427 507 表 B2 基于三次独立实验结果的秩和检验置信度分析
Table B2. Confidence analysis using rank sum test based on three independently repeated experiments
体系 实验次数 p h 原始膜 1&2 0.95 0 1&3 0.60 0 0.5 µg/mL 1&2 0.84 0 1&3 0.62 0 5.0 µg/mL 1&2 0.97 0 1&3 0.63 0 表 B3 脂分子扩散系数PDF分布的方差分析
Table B3. Variance analysis of the DL distribution in different conditions.
原始膜 0.5 µg/mL 5.0 µg/mL 均值/µm2·s–1 1.277 1.316 0.661 方差 0.899 0.924 0.483 标准差 0.948 0.961 0.695 -
[1] Fox J L 2013 Nat. Biotechnol. 31 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lu X M, Liu J J, Gou L, Li J L, Yuan B, Yang K, Ma Y 2019 Adv. Healthc. Mater. 8 1801521
[3] Wimley W C 2010 ACS Chem. Biol. 5 905
[4] Sancho-Vaello E, Zeth K 2015 Fut. Microbiol. 10 1103
[5] Hong J J, Lu X M, Deng Z X, Xiao S F, Yuan B, Yang K 2019 Molecules 24 1775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Huang H W 2000 Biochemistry 39 8348
[7] Lee M T, Sun T L, Hung W C, Huang H W 2013 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110 14243
[8] Liu J J, Xiao S F, Li J L, Yuan B, Yang K, Ma Y Q 2018 Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1860 2234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Mishra A, Lai G H, Schmidt N W, Sun V Z, Rodriguez A R, Tong R, Tang L, Cheng J J, Deming T J, Kamei D T, Wong G C L 2011 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 16883
[10] Huang H W, Chen F Y, Lee M T 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 198304
[11] Rzepiela A J, Sengupta D, Goga N, Marrink S J 2010 Faraday Discuss. 144 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Deng Z X, Li J L, Yuan B, Yang K 2019 Commun. Theor. Phys. 71 887
[13] 陆乃彦, 元冰, 杨恺 2013 62 178701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu N Y, Yuan B, Yang K 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 178701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 梁燚然, 梁清 2019 68 028701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang Y R, Liang Q 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 028701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Barkai E, Garini Y, Metzler R 2012 Phys. Today 65 29
[16] Ge F, Xue J F, Wang Z H, Xiong B, He Y 2019 Sci. China Chem. 62 1072
[17] He W, Song H, Su Y, Geng L, Ackerson B J, Peng H B, Tong P 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] JelgerHR, Siewert J M, 2008 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 45
[19] Newcomb C J, Sur S, Lee S S, Yu J M, Zhou Y, Snead M L, Stupp S I 2016 Nano Lett. 16 3042
[20] Lozano M M, Hovis J S, Moss Ⅲ F R, Boxer S G 2016 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 9996
[21] Shishina A K, Kovrigina E A, Galiakhmetov A R, Rathore R, Kovrigin E L 2018 Biochemistry 57 872
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Huang H W 2006 Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1758 1292
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Dumonteil E, Majumdar SN, Rosso A, Zoia A, 2013 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110 11
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Shen R, Guo WL 2009 Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1788 1024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Leonov D V, Dzuba S A, Surovtsev N V 2019 RSC Adv. 9 34451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Goodchild J A, Walsh D L, Connell S D 2019 Langmuir 35 15352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 11530
- PDF Downloads: 117
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: