-
Channel proteins act as precise molecular regulators of transmembrane transport, a fundamental process essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis. These proteins dynamically modulate their functional states through conformational changes, forming the structural basis for complex physiological processes such as signal transduction and energy metabolism. Single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy and single-channel patch-clamp electrophysiology represent two cornerstone techniques in modern biophysics: the former enables molecular-resolution analysis of structural dynamics, while the latter provides direct functional characterization of ion channel activity. Despite their complementary capabilities, integrating these techniques to simultaneously monitor protein conformational dynamics and functional states remains technically challenging, primarily due to the strong autofluorescence background inherent to single-molecule imaging in cellular environments. To address this limitation, we developed a spatially selective optical excitation system capable of localized illumination. By integrating tunable optical modules, we generated a dynamically adjustable excitation field on living cell membranes, achieving precise spatial registration between the excitation volume and the patch-clamp recording site. This system achieved submicron-scale alignment between the excitation zone and the micropipette contact area, enabling simultaneous electrophysiological recording and background-suppressed fluorescence detection within the patched membrane domain. Experimental validation demonstrated the system’s ability to perform single-molecule fluorescence imaging and trajectory analysis within designated observation areas, with imaging resolution inversely correlated with the size of the illuminated region. Optimized optical design allowed for precise excitation targeting while minimizing background illumination, resulting in high signal-to-noise ratio single-molecule imaging with significantly reduced photodamage. Integration with cell-attached patch-clamp configurations established a dual-modality platform for synchronized acquisition of single-molecule fluorescence images and single-channel recordings. Validation using mechanosensitive mPiezo1 channels confirmed the system’s compatibility with single-channel recordings, demonstrating that optical imaging induces no detectable interference with electrophysiological signal acquisition. This methodology overcomes longstanding challenges in the concurrent application of single-molecule imaging and electrophysiological techniques in live-cell environments. It establishes a novel experimental framework for investigating structure-function relationships in channel proteins and membrane-associated molecular machines through spatially coordinated optoelectronic measurements on live-cell membranes, with broad applicability in molecular biophysics and studies of transmembrane transport mechanisms.
-
Keywords:
- channel proteins /
- live-cell dynamic imaging /
- single-molecule fluorescence imaging /
- cell-attached recording /
- single-molecule tracking
-
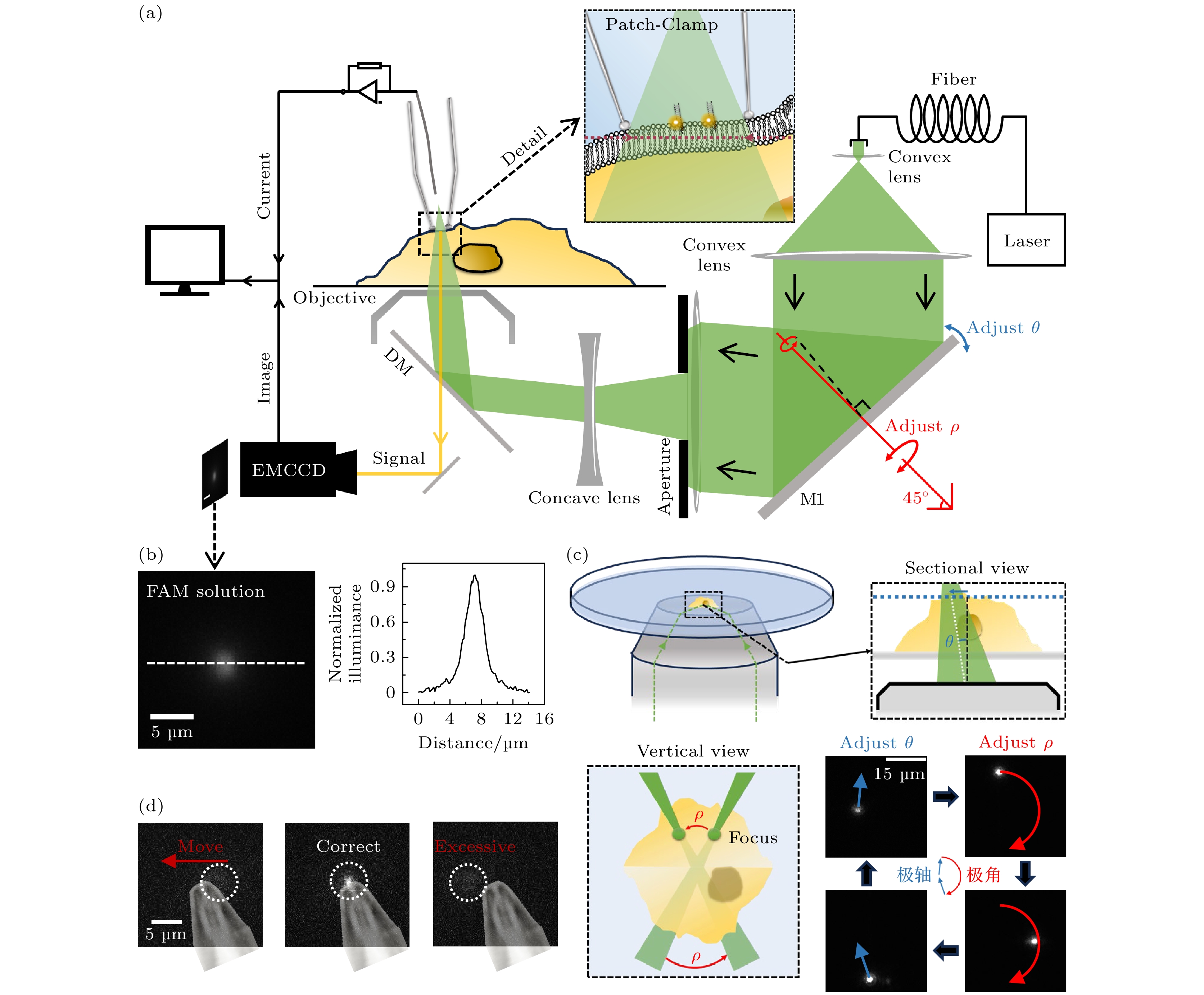
图 1 细胞膜上表面单分子荧光成像方法 (a) 细胞膜上表面单分子荧光成像光路图, 其中θ与ρ为光路中反射镜M1调整聚焦光斑的实际参数, M1沿着固定轴(红色轴)的旋转能够对ρ进行调整; (b) 在羧基荧光素(CF)溶液中单分子成像光斑图像以及白线截面的归一化强度分布; (c) 在羧基荧光素溶液中, 聚焦光斑位置通过反射镜M1的参数调节示意图与实际效果(右下), 其中虚线框图分别为侧剖面视图(右上)与正上方俯视图(左下); (d) 聚焦成像光斑通过调整位置实现与针尖匹配, 其中针尖图像为贴图标记, 白色虚线框指示了聚焦光斑位置
Figure 1. Cell membrane surface single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique: (a) Optical setup diagram for single-molecule fluorescence imaging on the upper leaflet of the cell membrane, in this diagram, θ and ρ represent the actual parameters adjusted by mirror M1 to focus the light spot, rotation of mirror M1 along the fixed axis (red-marked axis) enables precise control over the ρ parameter; (b) normalized intensity distribution of single-molecule imaging spot images and white reference line cross-section in carboxyfluorescein (CF) solution; (c) schematic diagram of focused laser spot position adjustment via mirror M1 parameters (bottom right) in CF solution, with experimental validation (bottom right). Dashed-line boxes denote: (top right) side cross-sectional view and (bottom left) top-down view; (d) alignment of the focused imaging laser spot with a probe tip via positional adjustment, where the tip image is overlaid as a reference marker, and white dashed boxes denote the focal spot location.
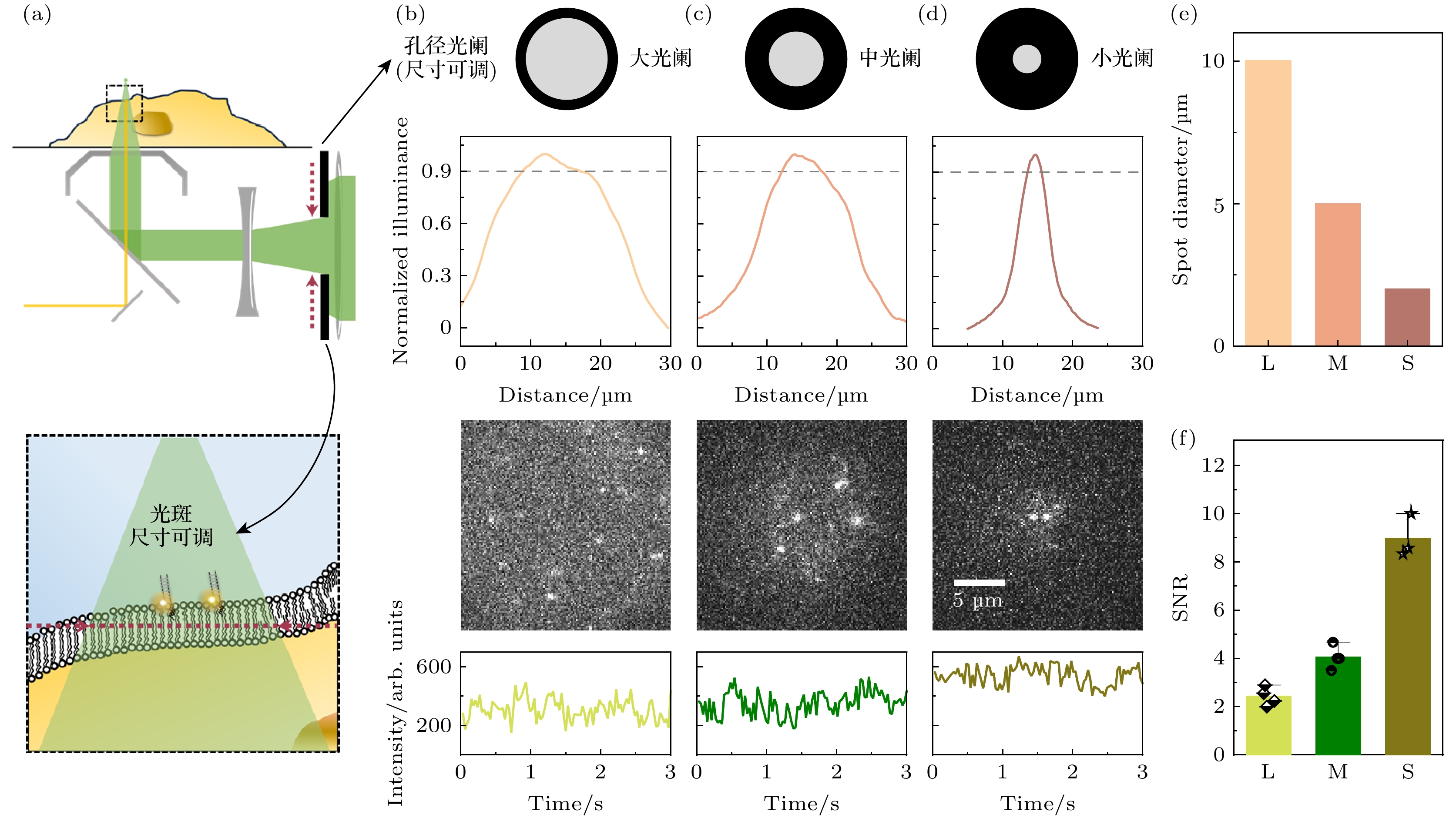
图 2 细胞膜上表面单分子荧光成像 (a) 扩大成像范围光路原理示意图, 上半图中黑色虚线框放大为下半图, 下半图中的红色虚线指代物镜的前焦面; (b)—(d) 可调光阑孔径变化可以影响成像光斑的尺寸和信噪水平; (e) 不同孔径的光阑所产生的成像光斑直径; (f) 不同孔径的光阑下单分子自由扩散信号的信噪比(SNR)
Figure 2. Single-molecule fluorescence imaging of the upper leaflet of the cell membrane: (a) Schematic diagram of expanded imaging field optical path design, the black dashed box in the upper panel is zoomed in as the lower panel, where the red dashed line indicates the front focal plane of the objective lens; (b)–(d) adjustment of the adjustable aperture diameter influences both the imaging spot size and the SNR; (e) variation in imaging spot diameter with aperture size; (f) SNR of single-molecule free diffusion signals under varying aperture diameters.
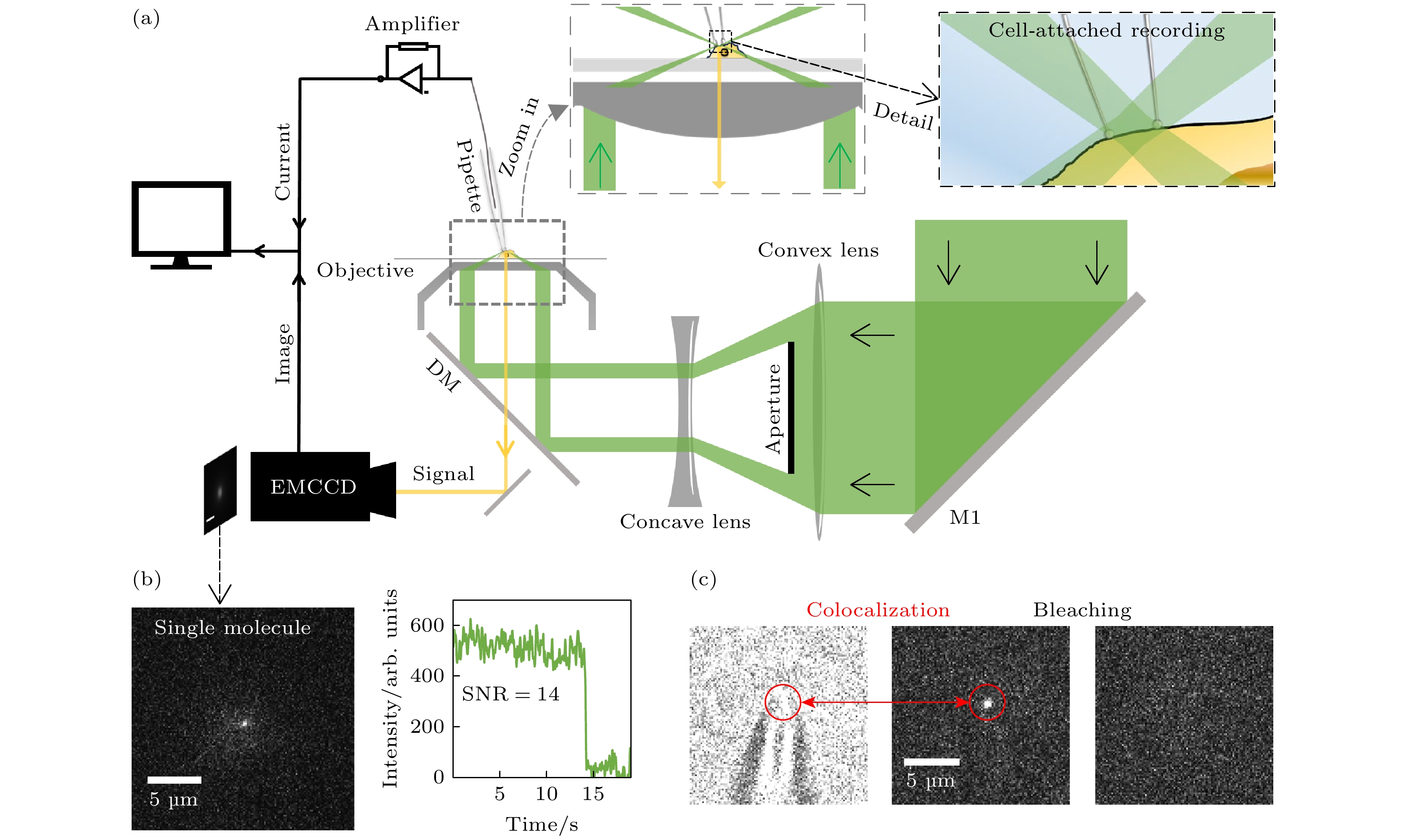
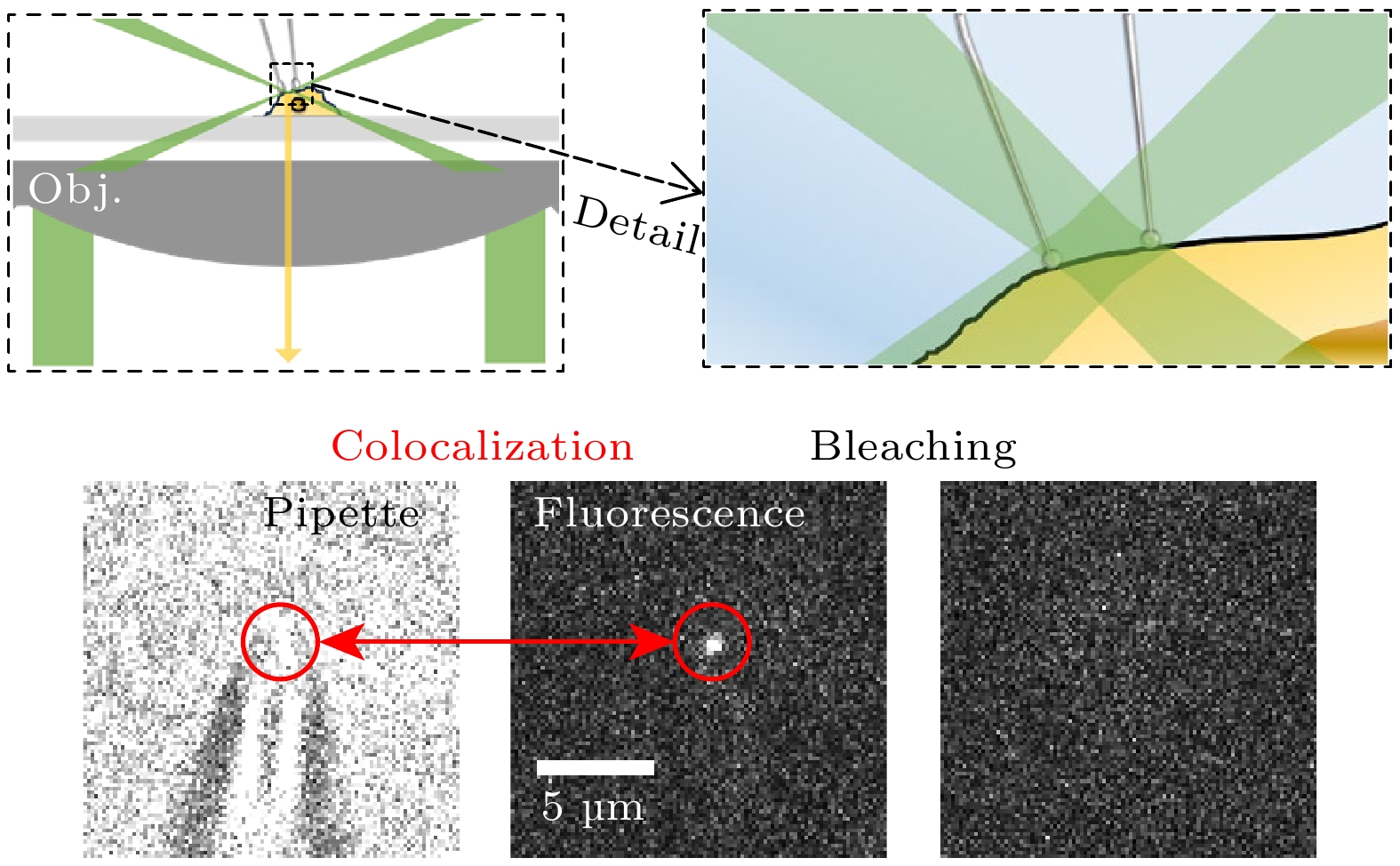
图 3 荧光膜片钳联用装置设置 (a) 荧光膜片钳联用装置示意图; (b) 在聚焦光斑处实现单分子荧光成像的实例以及其数据展示; (c) 针尖与针尖荧光信号共定位以及针尖荧光信号的漂白
Figure 3. Fluorescence-patch-clamp system configuration: (a) Schematic diagram of fluorescence-patch-clamp system; (b) examples of single-molecule fluorescence imaging at focused laser spots and corresponding data; (c) colocalization of the probe tip and its fluorescence signal, along with photobleaching of the tip fluorescence.
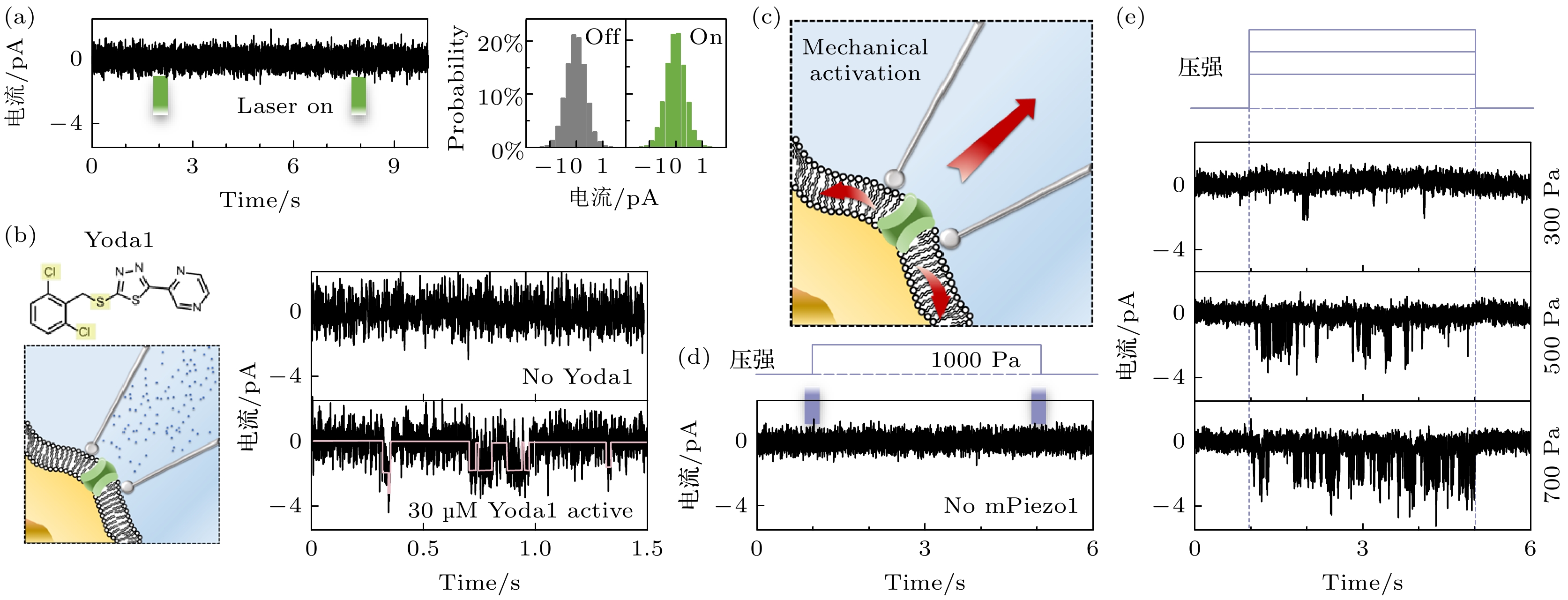
图 4 荧光膜片钳联用装置中膜片钳系统的性能 (a) 聚焦光斑对单通道记录不产生影响, 以及对应的统计图; (b) 使用Yoda1激活mPiezo1示意图以及mPiezo1的单通道信号; (c) 通过改变压强, 使细胞膜上产生机械应力以激活mPiezo1; (d) 在未转染mPiezo1的细胞上进行压力变化测试; (e) 在转染了mPiezo1的HEK293细胞上施加不同的压力变化以不同程度地激活钳制区域的mPiezo1
Figure 4. Performance evaluation of the patch-clamp system in fluorescence-patch-clamp system: (a) The focused laser spot has no measurable impact on single-channel electrophysiological recordings, as demonstrated by statistical analysis; (b) schematic of mpiezo1 activation using yoda1 and single channel signaling of mPiezo1; (c) by changing the pressure, mechanical stress is generated on the cell membrane to activate mPiezo1; (d) pressure change tests on cells not transfected with mPiezo1; (e) application of differential mechanical pressure to mPiezo1-transfected HEK293 cells to induce region-specific activation of mPiezo1.
-
[1] Jiang D, Banh R, El-Din T M G, Tonggu L, Lenaeus M J, Pomes R, Zheng N, Catterall W A 2021 Cell 184 5151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yang X Z, Lin C, Chen X D, Li S Q, Li X M, Xiao B L 2022 Nature 604 377
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jentsch T J, Pusch M 2018 Physiol. Rev. 98 1493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cui Y N, Yu M, Yao X M, Xing J J, Lin J X, Li X J 2018 Mol. Plant 11 1315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Weiss S 2000 Nat. Struct. Biol. 7 724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Smiley R D, Hammes G G 2006 Chem. Rev. 106 3080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Drapeau P, Ali D W, Buss R R, Saint-Amant L 1999 J. Neurosci. Methods 88 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Neher E, Sakmann B 1976 Nature 260 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hamill O P, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth F J 1981 Pflug. Arch. Euro. J. Phys. 391 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Mann S A, Heide J, Knott T, Airini R, Epureanu F B, Deftu A F, Deftu A T, Radu B M, Amuzescu B 2019 J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 100 1065990
[11] Mason M J, Simpson A K, Mahaut-Smith M P, Robinson H P C 2005 Biophys. J. 88 739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Alcami P, Franconville R, Llano I, Marty A 2012 J. Neurosci. 32 3118
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Maki B A, Cummings K A, Paganelli M A, Murthy S E, Popescu G K 2014 J Vis Exp. 88 e51629
[14] Ludewig U, Pusch M, Jentsch T J 1997 Biophys. J. 73 789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vazetdinova A, Valiullina-Rakhmatullina F, Rozov A, Evstifeev A, Khazipov R, Nasretdinov A 2022 Front. Mol. Neurosci. 15 979479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bykova E A, Zhang X D, Chen T Y, Zheng J 2006 Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13 1115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Alford R, Ogawa M, Hassan M, Gandjbakhche A H, Choyke P L, Kobayashi H 2010 Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 5 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yildiz A, Forkey J N, McKinney S A, Ha T, Goldman Y E, Selvin P R 2003 Science 300 2061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gill J K, Shaw G S 2024 Chembiochem 25 e202400193
[20] 贾棋, 樊秦凯, 侯文清, 杨晨光, 王利邦, 王浩, 徐春华, 李明, 陆颖 2021 70 158701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia Q, Fan Q K, Hou W Q, Yang C G, Wang L B, Wang H, Xu C H, Li M, Lu Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 158701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 陈泽, 马建兵, 黄星榞, 贾棋, 徐春华, 张慧东, 陆颖 2018 67 118201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Z, Ma J B, Huang X Y, Jia Q, Xu C H, Zhang H D, Lu Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 118201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li Y, Qian Z Y, Ma L, Hu S X, Nong D G, Xu C H, Ye F F, Lu Y, Wei G H, Li M 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 12906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 樊秦凯, 杨晨光, 胡书新, 徐春华, 李明, 陆颖 2023 72 147801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan Q K, Yang C G, Hu S X, Xu C H, Li M, Lu Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 147801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Hou W Q, Ma D F, He X L, Han W J, Ma J B, Wang H, Xu C H, Xie R P, Fan Q H, Ye F F, Hu S X, Li M, Lu Y 2021 Nano Lett. 21 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 马东飞, 侯文清, 徐春华, 赵春雨, 马建兵, 黄星榞, 贾棋, 马璐, 刘聪, 李明, 陆颖 2020 69 038701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma D F, Hou W Q, Xu C H, Zhao C Y, Ma J B, Huang X Y, Jia Q, Ma L, Liu C, Li M, Lu Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 038701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhou L, He R, Fang P N, Li M Q, Yu H S, Wang Q M, Yu Y, Wang F B, Zhang Y, Chen A D, Peng N F, Lin Y, Zhang R, Trilling M, Broering R, Lu M J, Zhu Y, Liu S 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Levring J, Terry D S, Kilic Z, Fitzgerald G, Blanchard S, Chen J 2023 Nature 616 606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Tokunaga M, Imamoto N, Sakata-Sogawa K 2008 Nature Methods 5 159
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Sasmal D K, Yadav R, Lu H P 2016 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 8789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Sasmal D K, Lu H P 2014 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 12998
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Hilgemann D W, Lu C C 1998 Ion Channels, Pt B 293 267
[32] Couey J J, Ryan D P, Glover J T, Dreixler J C, Young J B, Houamed K M 2002 Neurosci. Lett. 329 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Lee C H, Wallace D C, Burke P J 2024 Mitochondrial communications 2 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Icha J, Weber M, Waters J C, Norden C 2017 Bioessays 39 1700003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Syeda R, Xu J, Dubin A E, Coste B, Mathur J, Truc H, Matzen J, Lao J, Tully D C, Engels I H, Petrassi H M, Schumacher A M, Montal M, Bandell M, Patapoutian A 2015 Elife 4 e07369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Yang Z, Zhou S H, Zhang Q Y, Song Z C, Liu W W, Sun Y, Wang M W, Fu X L, Zhu K K, Guan Y, Qi J Y, Wang X H, Sun Y N, Lu Y, Ping Y Q, Xi Y T, Teng Z X, Xu L, Xiao P, Xu Z G, Xiong W, Qin W, Yang W, Yi F, Chai R J, Yu X, Sun J P 2025 Cell Res. 35 243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Metrics
- Abstract views: 309
- PDF Downloads: 6
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: