-
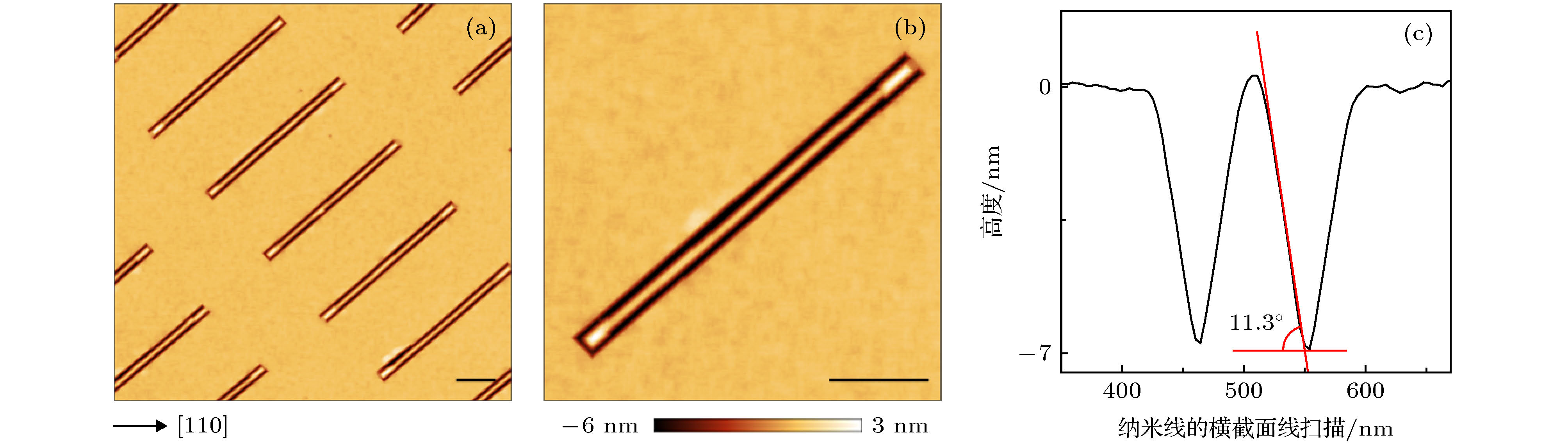
Controllable growth of nanowires is a prerequisite for addressability and scalability of nanowire quantum devices. By combining top-down nanofabrication and bottom-up self-assembly, site-controlled GeSi nanowires with two (105) facets can be grown on Si (001) substrate with pre-patterned trenches. Trenches along the [100] or [010] crystallographic direction with 60 nm in width and 6 nm in height are fabricated on Si substrate by electron beam lithography and reactive ion etching. Subsequently, a 60-nm-thick Si buffer layer is grown at 330–400 ℃ on the patterned substrate to improve the surface quality. The facets at the tip of the trenches transform into (11n) after depositing the Si buffer layer. Self-organized GeSi nanowires form inside the trenches by depositing the 6-nm-thick Si67Ge33 film at 450 ℃ followed by 1 h annealing at 510 ℃. The GeSi nanowires are (105)-faceted with an average height of approximately 7 nm. Furthermore, we systematically study the influence of annealing temperature, Ge concentration and pattern period on the formation of site-controllable GeSi nanowire on a patterned Si (001) substrate. The GeSi nanowires can be formed only inside the trenches within a specific annealing temperature ranging from 500 ℃ to 520 ℃. It is also discovered that GeSi nanowires are very sensitive to Ge concentration, as they cannot form at lower Ge concentration due to a large nucleation energy barrier. In contrast, high Ge concentration will lead to the discontinuity of nanowires caused by higher atomic diffusion barrier. The generated GeSi nanowires in the trenches exhibit similar dimensions at different pattern periods, which indicates that the growth process is thermodynamically determined. Overall, we realize the controllable growth of the GeSi nanowires, while the length of nanowires can reach the millimeter even centimeter scales, replying on the patterned trench length. The above results offer a controllable growth method of the Ge nanowires, which could potentially lead to the scalability of the Ge quantum devices on Si substrates.
-
Keywords:
- molecular beam epitaxy /
- qubit /
- patterned substrate /
- GeSi nanowires
[1] Loss D, diVincenzo D P 1998 Phys. Rev. A 57 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Petta J R, Johnson A C, Taylor J M, Laird E A, Yacoby A, Lukin M D, Marcus C M, Hanson M P, Gossard A C 2005 Science 309 2180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nowack K C, Koppens F H L, Nazarov Y V, Vandersypen L M K 2007 Science 318 1430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Elzerman J M, Hanson R, Greidanus J S, Willems van Beveren L H, de Franceschi S, Vandersypen L M K, Tarucha S, Kouwenhoven L P 2003 Phys. Rev. B 67 161308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bluhm H, Foletti S, Neder I, Rudner M, Mahalu D, Umansky V, Yacoby A 2011 Nat. Phys. 7 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang J Y, Huang S Y, Huang G Y, Pan D, Zhao J H, Xu H Q 2017 Nano Lett. 17 4158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Koppens F, Buizert C, Tielrooij K J, Vink I T, Nowack K C, Meunier T, Kouwenhoven L P, Vandersypen L 2006 Nature 442 766
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hanson R, Kouwenhoven L P, Petta J R, Tarucha S, Vandersypen L M K 2007 Rev. Mod. Phys. 79 1217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Khaetskii A V, Loss D, Glazman L 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 186802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhong Z, Fang Y, Lu W, Lieber C M 2005 Nano Lett. 5 1143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Katsaros G, Spathis P, Stoffel M, Fournel F, Mongillo M, Bouchiat V, Lefloch F, Rastelli A, Schmidt O G, de Franceschi S 2010 Nat. Nanotech. 5 458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hu Y J, Churchill H O H, Reilly D J, Xiang J, Lieber C M, Marcus C M 2007 Nat. Nanotech. 2 622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Higginbotham A P, Larsen T W, Yao J, Yan H, Lieber C M, Marcus C M, Kuemmeth F 2014 Nano Lett. 14 3582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li S X, Li Y, Gao F, Xu G, Li H O, Cao G, Xiao M, Wang T, Zhang J J, Guo G P 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 133105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kloeffel C, Trif M, Loss D 2011 Phys. Rev. B 84 195314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Maier F, Klinovaja J, Loss D 2014 Phys. Rev. B 90 195421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Watzinger H, Kukučka J, Vukušić L, Gao F, Wang T, Schäffler F, Zhang J J, Katsaros G 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 3902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] de Vries F K, Shen J, Skolasinski R J, Nowak M P, Varjas D, Wang L, Wimmer M, Ridderbos J, Zwanenburg F A, Li A, Koelling S, Verheijen M A, Bakkers E P A M, Kouwenhoven L P 2018 Nano Lett. 18 6483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li W D, Wu W, Williams R S 2012 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 30 06F304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wagner R S, Ellis W C 1964 Appl. Phys. Lett. 4 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lauhon L J, Gudiksen M S, Wang D, Lieber C M 2002 Nature 420 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang J J, Katsaros G, Montalenti F, Scopece D, Rezaev R O, Mickel C, Rellinghaus B, Miglio L, de Franceschi S, Rastelli A, Schmidt O G 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 085502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li Y, Li S X, Gao F, Li H O, Xu G, Wang K, Liu D, Cao G, Xiao M, Wang T, Zhang J J, Guo G C, Guo G P 2018 Nano Lett. 18 2091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xu G, Li Y, Gao F, Li H O, Liu H, Wang K, Cao G, Xiao M, Wang T, Zhang J J, Guo G C, Guo G P 2019 arXiv: 1905.01586v1
[25] Zhang J J, Stoffel M, Rastelli A, Schmidt O G, Jovanović V, Nanver L K, Bauer G 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 173115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhong Z Y, Halilovic A, Fromherz T, Schäffler F, Bauera G 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 4779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen G, Springholz G, Jantsch W, Schäffler F 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 043103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Du L, Scopece D, Springholz G, Schäffler F, Chen G 2014 Phys. Rev. B 90 075308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kern W, Puotinen D A 1970 RCA Review 31 187
[30] Eaglesham D J, White A E, Feldman L C, Moriya N, Jacobson D C 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 1643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Gai Z, Yang W S, Sakurai T, Zhao R G 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 13009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhong Z, Schwinger W, Schäffler F, Bauer G, Vastola G, Montalenti F, Miglio L 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 176102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Vastola G, Grydlik M, Brehm M, Fromherz T, Bauer G, Boioli F, Miglio L, Montalenti F 2011 Phys. Rev. B. 84 155415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Hu H, Gao H J, Liu F 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 216102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhang J J, Rastelli A, Schmidt O G, Scopece D, Miglio L, Montalenti F 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 083109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen G, Sanduijav B, Matei D, Springholz G, Scopece D, Beck M J, Montalenti F, Miglio L 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 055503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Jesson D E, Chen K M, Pennycook S J, Thundat T, Warmack R J 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 1330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Tersoff J, leGoues F K 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 3570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Shu D J, Liu F, Gong X G 2001 Phys. Rev. B 64 245410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Huang L, Liu F, Gong X G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 155320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
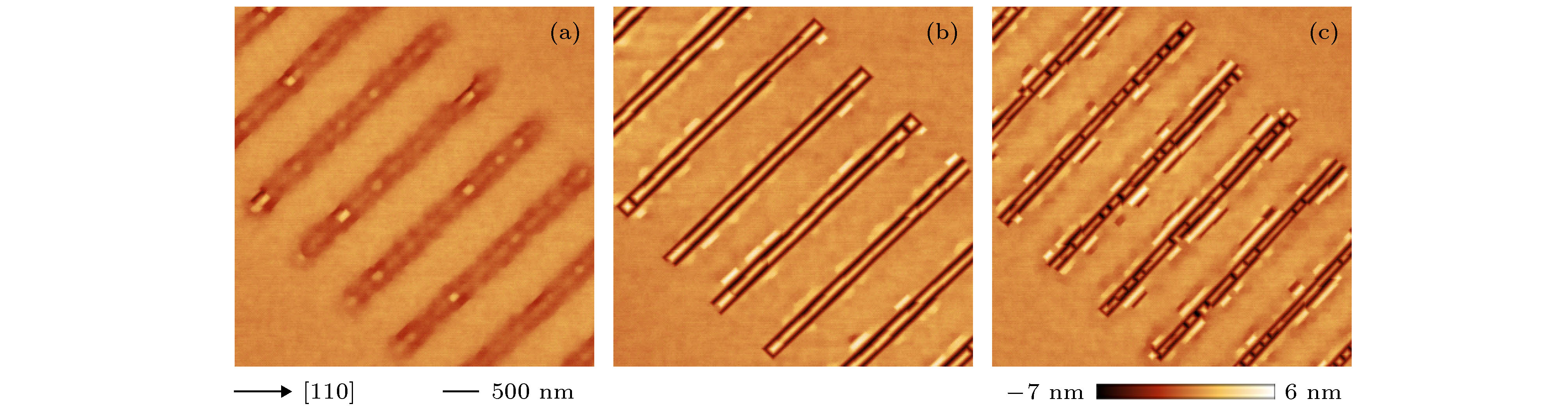
图 3 在硅凹槽结构图形衬底上沉积4 nm的Si67G33薄膜, 然后在不同温度退火后得到的样品表面AFM图 (a) 450 ℃; (b) 500 ℃; (c) 510 ℃; (d) 520 ℃; (e) 530 ℃; (f) 550 ℃
Figure 3. AFM images of the trench-patterned samples with 4 nm Si67Ge33 film after 1 h annealing at different temperatures: (a) 450 ℃; (b) 500 ℃; (c) 510 ℃; (d) 520 ℃; (e) 530 ℃; (f) 550 ℃.
-
[1] Loss D, diVincenzo D P 1998 Phys. Rev. A 57 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Petta J R, Johnson A C, Taylor J M, Laird E A, Yacoby A, Lukin M D, Marcus C M, Hanson M P, Gossard A C 2005 Science 309 2180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nowack K C, Koppens F H L, Nazarov Y V, Vandersypen L M K 2007 Science 318 1430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Elzerman J M, Hanson R, Greidanus J S, Willems van Beveren L H, de Franceschi S, Vandersypen L M K, Tarucha S, Kouwenhoven L P 2003 Phys. Rev. B 67 161308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Bluhm H, Foletti S, Neder I, Rudner M, Mahalu D, Umansky V, Yacoby A 2011 Nat. Phys. 7 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang J Y, Huang S Y, Huang G Y, Pan D, Zhao J H, Xu H Q 2017 Nano Lett. 17 4158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Koppens F, Buizert C, Tielrooij K J, Vink I T, Nowack K C, Meunier T, Kouwenhoven L P, Vandersypen L 2006 Nature 442 766
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hanson R, Kouwenhoven L P, Petta J R, Tarucha S, Vandersypen L M K 2007 Rev. Mod. Phys. 79 1217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Khaetskii A V, Loss D, Glazman L 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 186802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhong Z, Fang Y, Lu W, Lieber C M 2005 Nano Lett. 5 1143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Katsaros G, Spathis P, Stoffel M, Fournel F, Mongillo M, Bouchiat V, Lefloch F, Rastelli A, Schmidt O G, de Franceschi S 2010 Nat. Nanotech. 5 458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hu Y J, Churchill H O H, Reilly D J, Xiang J, Lieber C M, Marcus C M 2007 Nat. Nanotech. 2 622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Higginbotham A P, Larsen T W, Yao J, Yan H, Lieber C M, Marcus C M, Kuemmeth F 2014 Nano Lett. 14 3582
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Li S X, Li Y, Gao F, Xu G, Li H O, Cao G, Xiao M, Wang T, Zhang J J, Guo G P 2017 Appl. Phys. Lett. 110 133105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kloeffel C, Trif M, Loss D 2011 Phys. Rev. B 84 195314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Maier F, Klinovaja J, Loss D 2014 Phys. Rev. B 90 195421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Watzinger H, Kukučka J, Vukušić L, Gao F, Wang T, Schäffler F, Zhang J J, Katsaros G 2018 Nat. Commun. 9 3902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] de Vries F K, Shen J, Skolasinski R J, Nowak M P, Varjas D, Wang L, Wimmer M, Ridderbos J, Zwanenburg F A, Li A, Koelling S, Verheijen M A, Bakkers E P A M, Kouwenhoven L P 2018 Nano Lett. 18 6483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li W D, Wu W, Williams R S 2012 J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 30 06F304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wagner R S, Ellis W C 1964 Appl. Phys. Lett. 4 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lauhon L J, Gudiksen M S, Wang D, Lieber C M 2002 Nature 420 57
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhang J J, Katsaros G, Montalenti F, Scopece D, Rezaev R O, Mickel C, Rellinghaus B, Miglio L, de Franceschi S, Rastelli A, Schmidt O G 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 085502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li Y, Li S X, Gao F, Li H O, Xu G, Wang K, Liu D, Cao G, Xiao M, Wang T, Zhang J J, Guo G C, Guo G P 2018 Nano Lett. 18 2091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Xu G, Li Y, Gao F, Li H O, Liu H, Wang K, Cao G, Xiao M, Wang T, Zhang J J, Guo G C, Guo G P 2019 arXiv: 1905.01586v1
[25] Zhang J J, Stoffel M, Rastelli A, Schmidt O G, Jovanović V, Nanver L K, Bauer G 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 173115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhong Z Y, Halilovic A, Fromherz T, Schäffler F, Bauera G 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 4779
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen G, Springholz G, Jantsch W, Schäffler F 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 043103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Du L, Scopece D, Springholz G, Schäffler F, Chen G 2014 Phys. Rev. B 90 075308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kern W, Puotinen D A 1970 RCA Review 31 187
[30] Eaglesham D J, White A E, Feldman L C, Moriya N, Jacobson D C 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 1643
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Gai Z, Yang W S, Sakurai T, Zhao R G 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 13009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhong Z, Schwinger W, Schäffler F, Bauer G, Vastola G, Montalenti F, Miglio L 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 176102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Vastola G, Grydlik M, Brehm M, Fromherz T, Bauer G, Boioli F, Miglio L, Montalenti F 2011 Phys. Rev. B. 84 155415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Hu H, Gao H J, Liu F 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 216102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhang J J, Rastelli A, Schmidt O G, Scopece D, Miglio L, Montalenti F 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 083109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Chen G, Sanduijav B, Matei D, Springholz G, Scopece D, Beck M J, Montalenti F, Miglio L 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 055503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Jesson D E, Chen K M, Pennycook S J, Thundat T, Warmack R J 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 1330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Tersoff J, leGoues F K 1994 Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 3570
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Shu D J, Liu F, Gong X G 2001 Phys. Rev. B 64 245410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Huang L, Liu F, Gong X G 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 155320
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 14330
- PDF Downloads: 169
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: