-
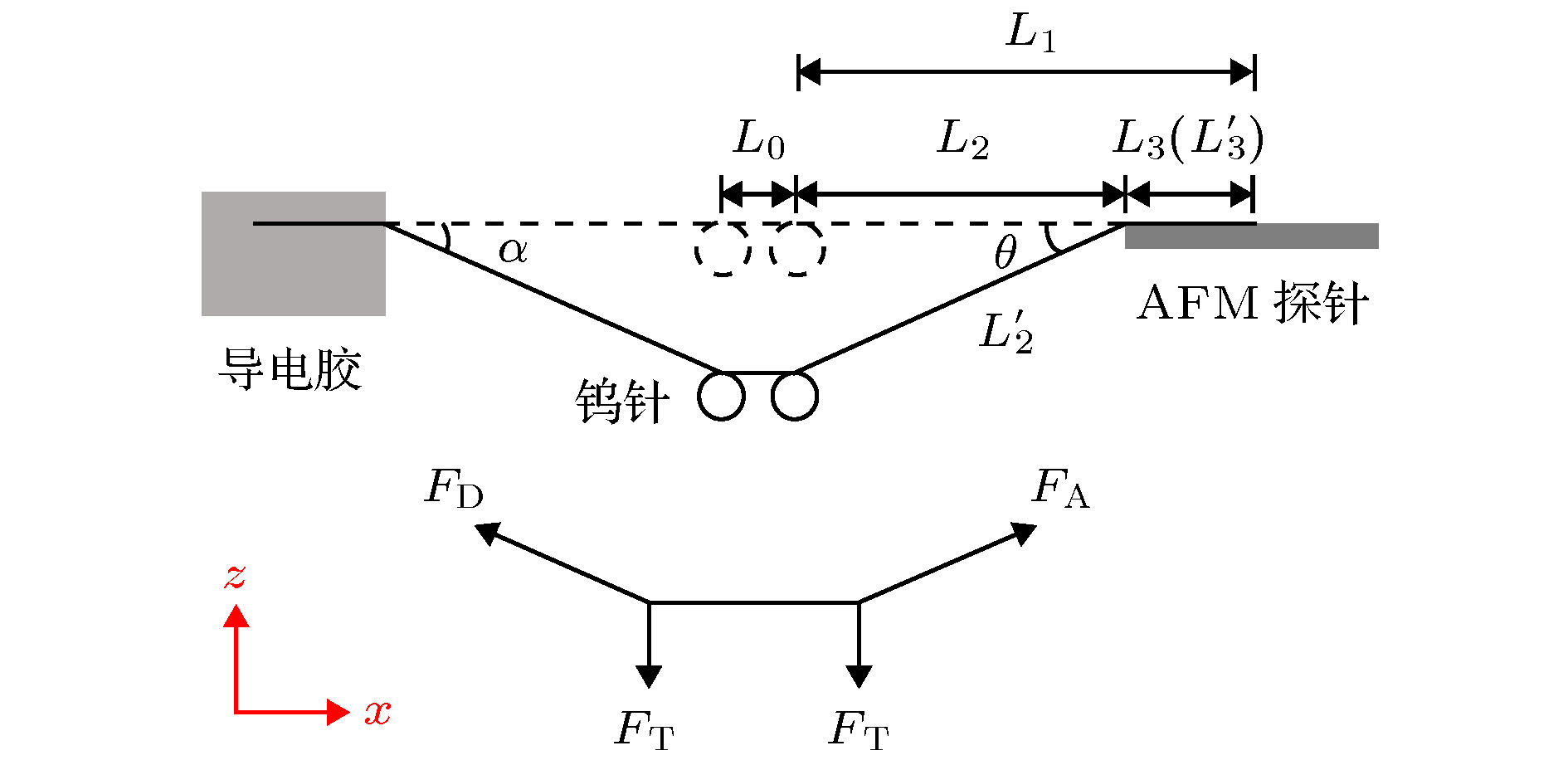
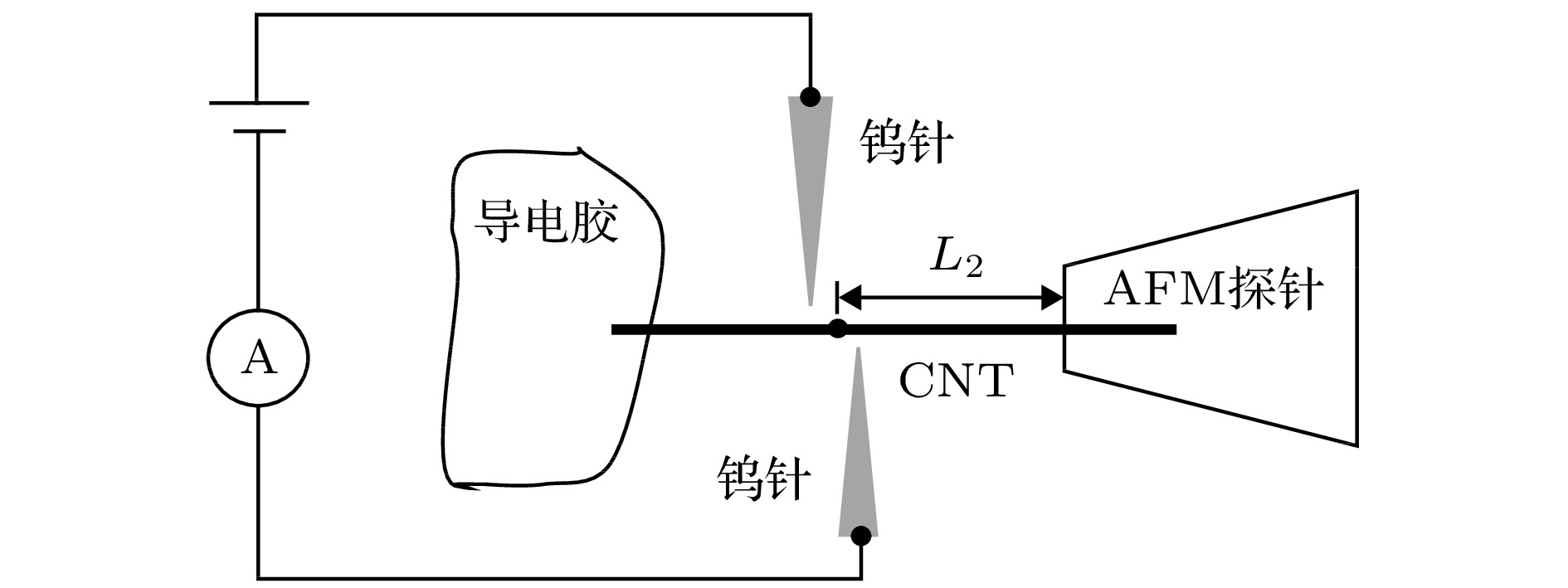
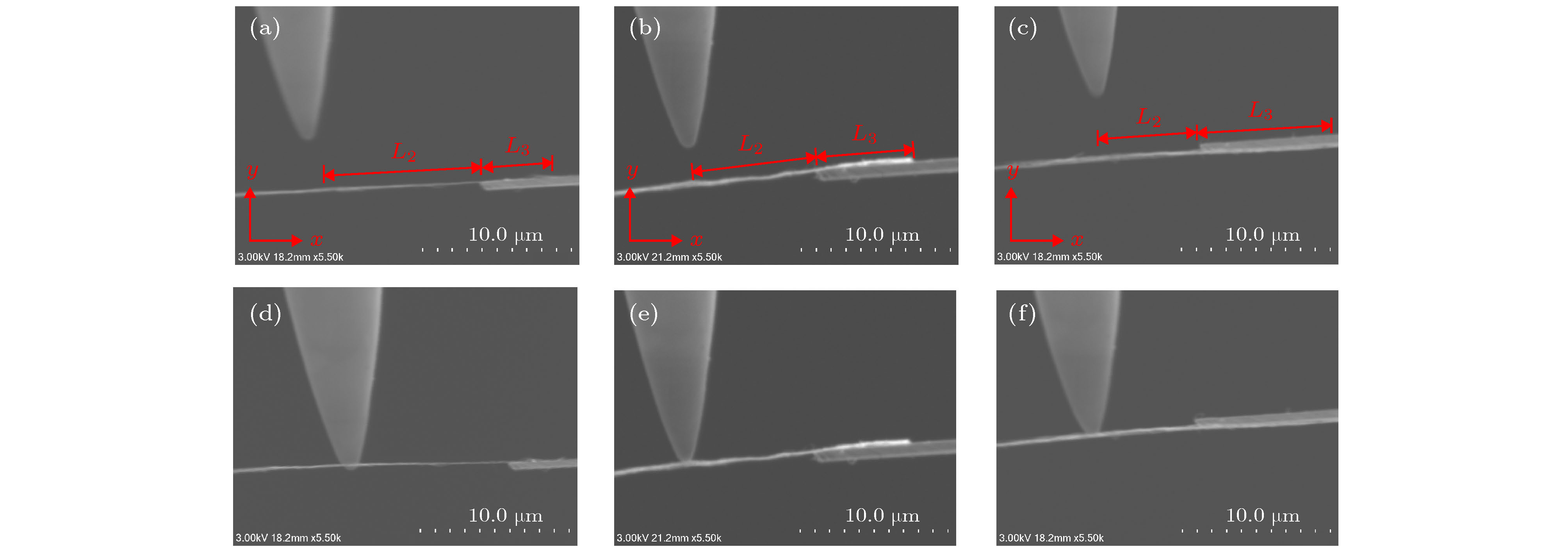
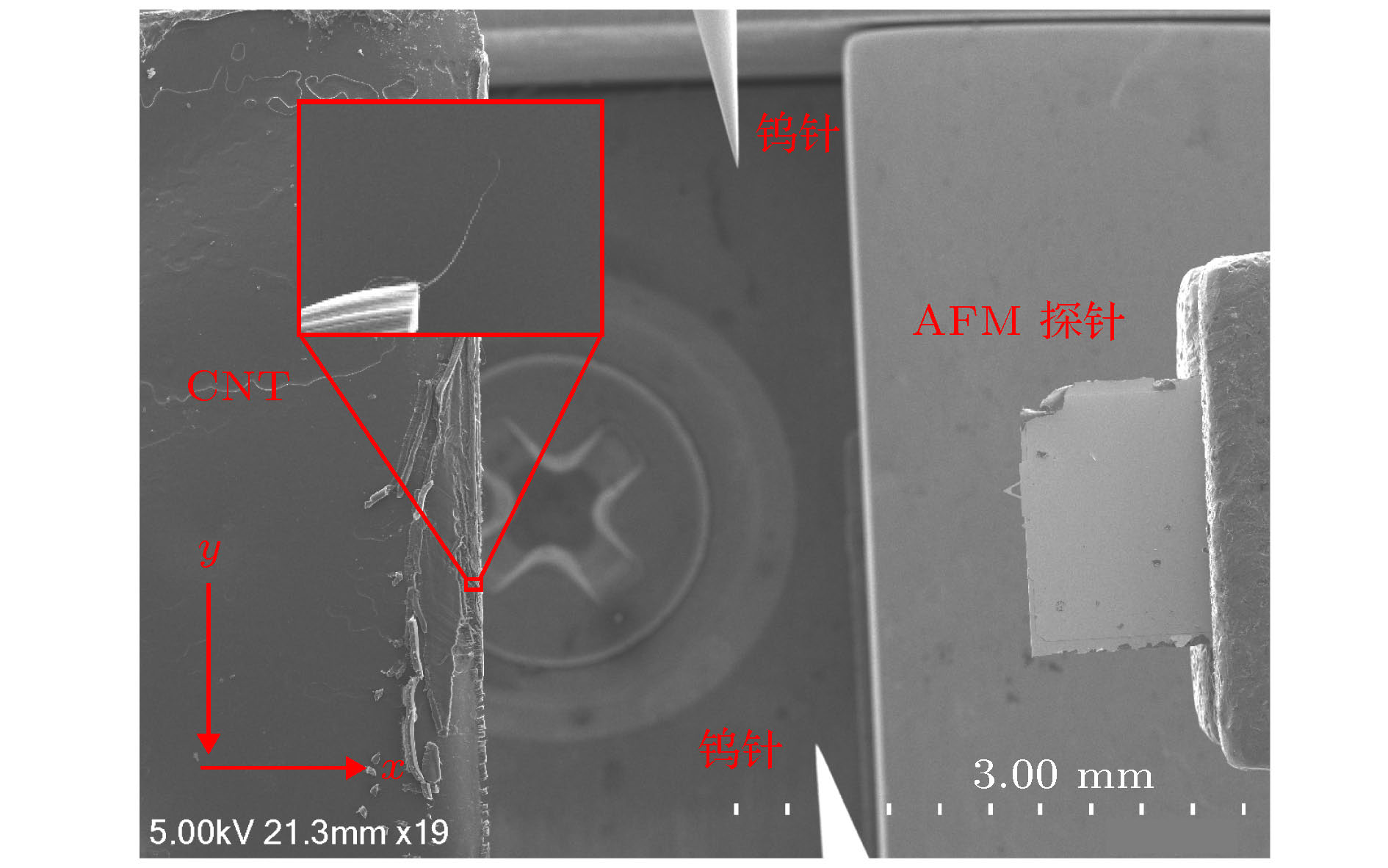
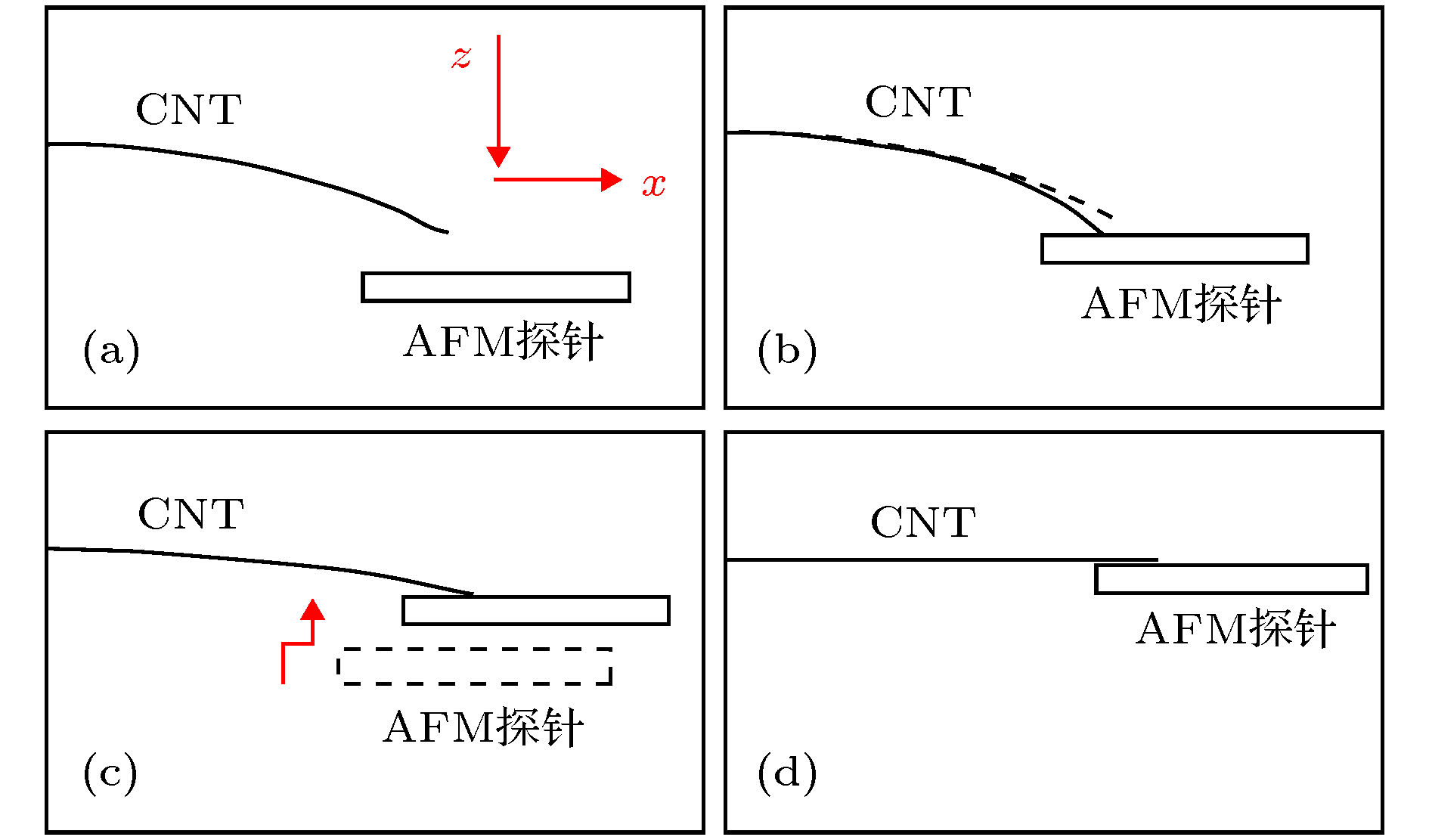
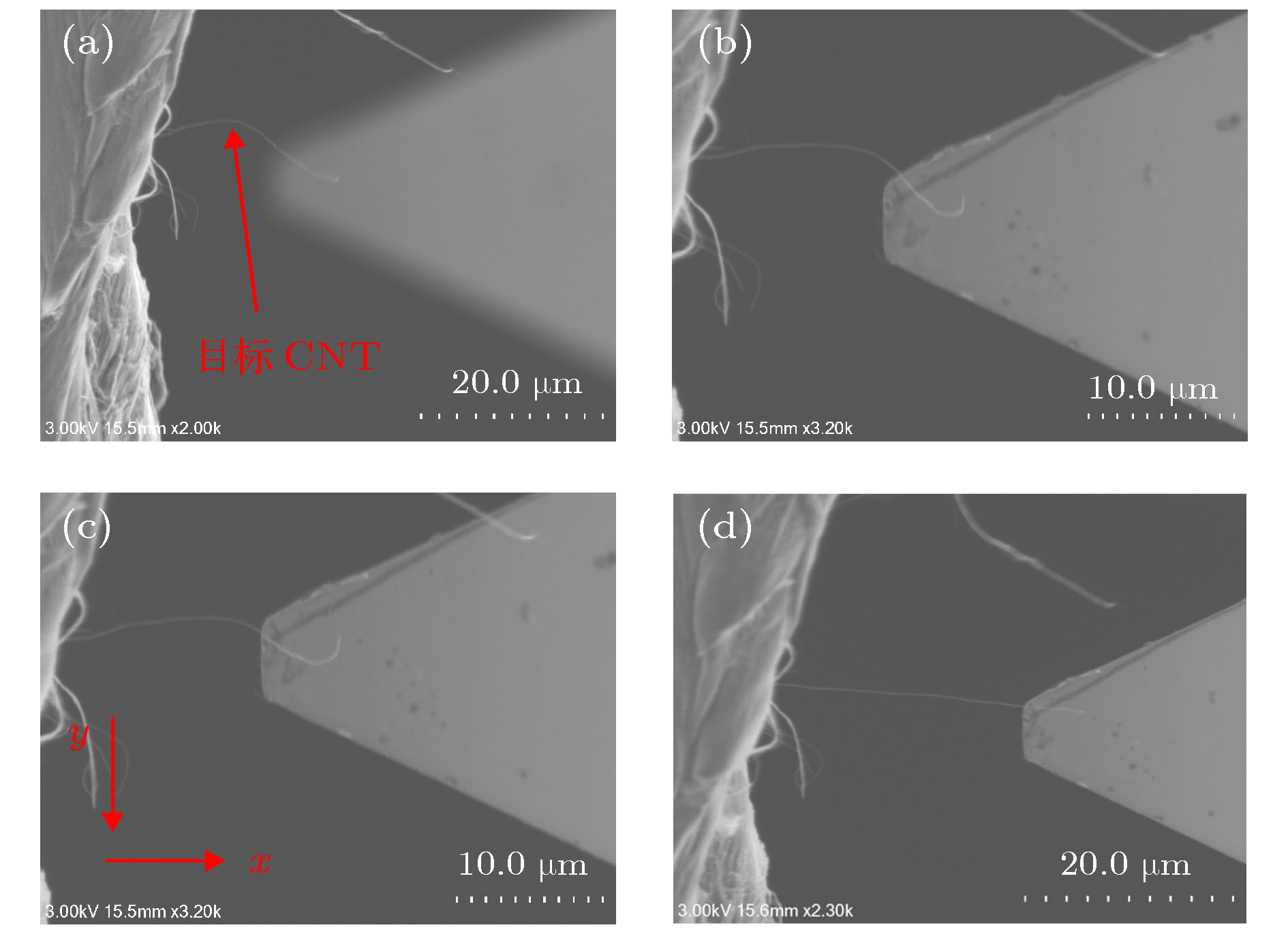
In this paper, a length-controllable picking-up method of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is proposed and the electrical performance data utilized for the conductivity analysis of CNT are also obtained. The micro-nano-operation system inside scanning electron microscope (SEM) is composed of 4 manipulation units each with 3 degrees of freedom, which is driven by piezoelectric ceramics and flexure hinges. In this micro manipulation system, an atomic force microscope (AFM) probe is used as the end effector to adjust the spatial pose of the CNT based on van der Waals force and two tungsten needles are used to cut the CNT from the target length and to measure the I-V characteristic data simultaneously. At first, the AFM probe is moved in the z direction to approach to the CNT until the end of the CNT is adsorbed onto the surface of the AFM probe. And then the AFM probe moves alternately in the x and z direction in order to stretch the CNT into a horizontal straight line, only in this way can the length of the CNT be measured accurately and can the cutting position be determined. Two tungsten needles cleaned by using hydrofluoric acid to remove the oxide layer are controlled to contact both sides of the cutting position on CNT and connected to the TECK 2280S power supply through the electric cabinet to apply a gradually increasing DC voltage, and the current in the circuit is measured and recorded by the TECK DMM7510 until the current abruptly changes to zero which indicates that the CNT between the tungsten needles has been cut off. The stress of the CNT in contact with the tungsten needles and the AFM probe are analyzed. The modeling of van der Waals force between AFM probe and CNT which can influence the pick-up length error caused by the deformation of CNT under the force of tungsten needles is completed. It is found that the contact length of them and the pick-up length error decrease while the van der Waals force between the AFM probe and CNT increases. The circuit models for contact between the tungsten needles and three operating objects, such as semiconducting CNT, metallic CNT and CNT bundle, are also established. In addition, the I-V characteristic equations of circuit model which can be used to fit the I-V data are derived separately. The CNT pick-up experiment is carried out and the results demonstrate that the proposed picking method can control the length of CNT effectively, but the conductivity of CNT can also be judged by fitting the I-V obtained experiment data through the derived I-V characteristic equations.
-
Keywords:
- carbon nanotubes /
- pose adjustment /
- length control /
- conductivity analysis
[1] Iijima S 1991 Nature 354 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Brady G J, Way A J, Safron N S, Evensen H T, Gopalan P, Arnold M S 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1601240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen B Y, Zhang P P, Ding L, Han J, Qiu S, Li Q W, Zhang Z Y, Peng L M 2016 Nano Lett. 16 5120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Franklin A D, Luisier M, Han S J, Tulevski G, Breslin C M, Gignac L, Lundstrom M S, Haensch W 2012 Nano Lett. 12 758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lee C S, Pop E, Franklin A D, Haensch W, Wong H S P 2015 IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 62 3061
[6] Lundstrom M S, Antoniadis D A 2014 IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 61 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘兴辉, 赵宏亮, 李天宇, 张仁, 李松杰, 葛春华 2013 62 147308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X H, Zhao H L, Li T Y, Zhang R, Li S J, Ge C H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 147308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 刘红, 印海建, 夏树宁 2009 58 8489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H, Yin H J, Xia S N 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 8489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Qiu C G, Zhang Z Y, Xiao M M, Yang Y J, Zhong D L, Peng L M 2017 Science 355 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang S C, Kang L X, Wang X, Tong L M, Yang L W, Wang Z Q, Qi K, Deng S B, Li Q W, Bai X D, Ding F, Zhang J 2017 Nature 543 234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Collins P G, Arnold M S, Avouris P 2001 Science 292 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tulevski G S, Franklin A D, Afzali A 2013 ACS Nano 7 2971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Fukuda T, Arai F, Dong L X 2003 Proc. IEEE 91 1803
[14] Wei X L, Chen Q, Liu Y, Peng L M 2007 Nanotechnology 18 185503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Eichhorn V, Fatikow S, Wortmann T, Stolle C, Edeler C, Jasper D, Sardan O, Bøggild P, Boetsch G, Canales C, Clavel R 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Kobe, Japan, May 12−17, 2009 p1826
[16] Eichhorn V, Fatikow S, Wich T, Dahmen C, Sievers T, Andersen K N, Carlson K, Bøggild P 2008 J. Micro-Nano Mechatron. 4 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang Z, Chen T, Wang Y Q, Sun L N, Fukuda T 2016 Micro Nano Lett. 11 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ding H Y, Shi C Y, Ma L, Yang Z, Wang M Y, Wang Y Q, Chen T, Sun L N, Fukuda T 2018 Sensors 18 1137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shi Q, Yang Z, Guo Y N, Wang H P, Sun L N, Huang Q, Fukuda T 2017 IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 22 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] An L, Friedrich C R 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 272 169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yu N, Nakajima M, Shi Q, Yang Z, Wang H P, Sun L N, Huang Q, Fukuda T 2017 Scanning 2017 5910734
[22] Yu N, SHI Q, Nakajima M, Wang H P, Yang Z, Sun L N, Huang Q, Fukuda T 2017 J. Micromech. Microeng. 27 105007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li J, He Y J, Han Y M, Liu K, Wang J P, Li Q Q, Fan S S, Jiang K L 2012 Nano Lett. 12 4095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li D Q, Wei Y, Zhang J, Wang J T, Lin Y H, Liu P, Fan S S, Jiang K L 2017 Nano Res. 10 1896
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Venema L C, Wildöer J W G, Temminck H L J T, Dekker C 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yang L, Greenfeld I, Wagner H D 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1500969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 杨权, 马立, 杨斌, 丁汇洋, 陈涛, 杨湛, 孙立宁, 福田敏男 2018 67 136801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Q, Ma L, Yang B, Ding H Y, Chen T, Yang Z, Sun L N, Fukuda T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 136801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lan C, Strsungsitthisunti P, Amama P B, Fisher T, Xu X 2008 Nanotechnology 19 125703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang Z Y, Jin C H, Liang X L, Chen Q, Peng L M 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 073102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang Z Y, Yao K, Liu Y, Jin C H, Liang X L, Chen Q, Peng L M 2007 Adv. Funct. Mater. 17 2478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yu N, Nakajima M, Shi Q, Takeuchi M, Yang Z, Huang Q, Fukuda T 2015 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII) Nagoya, Japan, December 11−13, 2015 p956
-
表 1 微纳操作单元性能参数
Table 1. Performance parameters of micro-nano operating unit.
性能参数 取值 粗定位 运动范围/mm $10 \times 10 \times 5$ 最大运动速度/mm·s–1 > 3 最小运动步长/nm < 100 精定位 运动范围/μm $20$ 最大运动速度/μm·s–1 $ > 45$ 开环控制分辨率/nm 0.1 闭环控制分辨率/nm 1 精度/nm 5 -
[1] Iijima S 1991 Nature 354 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Brady G J, Way A J, Safron N S, Evensen H T, Gopalan P, Arnold M S 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1601240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen B Y, Zhang P P, Ding L, Han J, Qiu S, Li Q W, Zhang Z Y, Peng L M 2016 Nano Lett. 16 5120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Franklin A D, Luisier M, Han S J, Tulevski G, Breslin C M, Gignac L, Lundstrom M S, Haensch W 2012 Nano Lett. 12 758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lee C S, Pop E, Franklin A D, Haensch W, Wong H S P 2015 IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 62 3061
[6] Lundstrom M S, Antoniadis D A 2014 IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 61 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 刘兴辉, 赵宏亮, 李天宇, 张仁, 李松杰, 葛春华 2013 62 147308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu X H, Zhao H L, Li T Y, Zhang R, Li S J, Ge C H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 147308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 刘红, 印海建, 夏树宁 2009 58 8489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H, Yin H J, Xia S N 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 8489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Qiu C G, Zhang Z Y, Xiao M M, Yang Y J, Zhong D L, Peng L M 2017 Science 355 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhang S C, Kang L X, Wang X, Tong L M, Yang L W, Wang Z Q, Qi K, Deng S B, Li Q W, Bai X D, Ding F, Zhang J 2017 Nature 543 234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Collins P G, Arnold M S, Avouris P 2001 Science 292 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tulevski G S, Franklin A D, Afzali A 2013 ACS Nano 7 2971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Fukuda T, Arai F, Dong L X 2003 Proc. IEEE 91 1803
[14] Wei X L, Chen Q, Liu Y, Peng L M 2007 Nanotechnology 18 185503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Eichhorn V, Fatikow S, Wortmann T, Stolle C, Edeler C, Jasper D, Sardan O, Bøggild P, Boetsch G, Canales C, Clavel R 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Kobe, Japan, May 12−17, 2009 p1826
[16] Eichhorn V, Fatikow S, Wich T, Dahmen C, Sievers T, Andersen K N, Carlson K, Bøggild P 2008 J. Micro-Nano Mechatron. 4 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yang Z, Chen T, Wang Y Q, Sun L N, Fukuda T 2016 Micro Nano Lett. 11 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ding H Y, Shi C Y, Ma L, Yang Z, Wang M Y, Wang Y Q, Chen T, Sun L N, Fukuda T 2018 Sensors 18 1137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Shi Q, Yang Z, Guo Y N, Wang H P, Sun L N, Huang Q, Fukuda T 2017 IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 22 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] An L, Friedrich C R 2012 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 272 169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yu N, Nakajima M, Shi Q, Yang Z, Wang H P, Sun L N, Huang Q, Fukuda T 2017 Scanning 2017 5910734
[22] Yu N, SHI Q, Nakajima M, Wang H P, Yang Z, Sun L N, Huang Q, Fukuda T 2017 J. Micromech. Microeng. 27 105007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li J, He Y J, Han Y M, Liu K, Wang J P, Li Q Q, Fan S S, Jiang K L 2012 Nano Lett. 12 4095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li D Q, Wei Y, Zhang J, Wang J T, Lin Y H, Liu P, Fan S S, Jiang K L 2017 Nano Res. 10 1896
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Venema L C, Wildöer J W G, Temminck H L J T, Dekker C 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yang L, Greenfeld I, Wagner H D 2016 Sci. Adv. 2 e1500969
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] 杨权, 马立, 杨斌, 丁汇洋, 陈涛, 杨湛, 孙立宁, 福田敏男 2018 67 136801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Q, Ma L, Yang B, Ding H Y, Chen T, Yang Z, Sun L N, Fukuda T 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 136801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lan C, Strsungsitthisunti P, Amama P B, Fisher T, Xu X 2008 Nanotechnology 19 125703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang Z Y, Jin C H, Liang X L, Chen Q, Peng L M 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 073102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhang Z Y, Yao K, Liu Y, Jin C H, Liang X L, Chen Q, Peng L M 2007 Adv. Funct. Mater. 17 2478
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Yu N, Nakajima M, Shi Q, Takeuchi M, Yang Z, Huang Q, Fukuda T 2015 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII) Nagoya, Japan, December 11−13, 2015 p956
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9374
- PDF Downloads: 89
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: