-
Nonreciprocal electromagnetic wave transmission is essential for wireless communication, quantum computing, and radar systems, traditionally relying on breaking time-reversal symmetry through static magnetic fields or structural modifications, which face limitations in tunability and integration. Recent advancements in cavity magnonics, particularly the use of bound states in the continuum (BIC) and pump-induced magnon mode (PIM), have enhanced the nonreciprocal isolation and dynamic control of magnon dynamics. In this study, a novel method to achieve broadband-tunable microwave nonreciprocal isolation is presented by introducing multiple modulated pump signals, thereby extending traditional single-mode magnon-based nonreciprocal transmission to multi-channel and broadband regimes. The core method involves exciting multiple PIMs in a cavity magnonics system and strongly coupling them with BIC to generate hybrid modes with pronounced nonreciprocal characteristics. The experimental setup is comprised of a 1-millimeter-diameter yttrium iron garnet (YIG) sphere positioned at the node of a microwave resonator (central frequency: 2.92 GHz), with pump signals injected through a microwave patch antenna. By dynamically tuning the frequency, power, and number of pump signals, the precise control over the number of nonreciprocal isolation channels and their spectral positions is realized. Notably, the continuous tuning of the nonreciprocal bandwidth is achieved by increasing the number of pump signals from 2 to 5, expanding the isolation bandwidth from 6 MHz to 14 MHz. Furthermore, by tailoring the spectral distribution of pump signals, the system realizes flexible switching between bandpass and band-stop isolation states. Importantly, this method eliminates the need of static magnetic field adjustments or structural reconfiguration, relying solely on coherent microwave-photon interactions to modulate PIM-BIC coupling. Experimental results highlight two key physical outcomes: 1) Extending conventional single-mode magnonic nonreciprocal transmission to multi-channel and broadband-tunable regimes; 2) achieving microwave nonreciprocal control without the need of static magnetic field adjustments or structural reconfiguration. These advances establish a robust platform for designing reconfigurable multi-channel isolators and circulators, which can be directly applied to microwave communication systems, quantum information processing, and radar technologies.
[1] Yu Z F, Fan S H 2009 Nat. Photonics 3 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lira H, Yu Z F, Fan S H, Lipson M 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 033901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fang K, Yu Z F, Fan S H 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 153901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sounas D L, Alù A 2017 Nat. Photonics 11 774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kang M S, Butsch A, Russell P St J 2011 Nat. Photonics 5 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Manipatruni S, Robinson J T, Lipson M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 213903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Peng B, Özdemir Ş K, Lei F, Monifi F, Gianfreda M, Long G L, Fan S H, Nori F, Bender C M, Yang L 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Estep N A, Sounas D L, Soric J, Alù A 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Jalas D, Petrov A, Eich M, Freude W, Fan S H, Yu Z F, Baets R, Popović M, Melloni A, Joannopoulos J D, Vanwolleghem J D, Vanwolleghem M, Doerr C R, Renner D H 2013 Nat. Photonics 7 579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Reiskarimian N, Krishnaswamy H 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kord A, Sounas D L, Alù A 2017 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 66 911
[12] Abdo B, Sliwa K, Frunzio L, Devoret M 2013 Phys. Rev. X 3 031001
[13] Lecocq F, Ranzani L, Peterson G A, Cicak K, Simmonds R W, Teufel J D, Aumentado J 2017 Phys. Rev. Appl. 7 024028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chapman B J, Rosenthal E I, Kerckhoff J, Moores B A, Vale L R, Mates J A B, Hilton G C, Lalumière K, Blais A, Lehnert K W 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 041043
[15] Sliwa K M, Hatridge M, Narla A, Shankar S, Frunzio L, Schoelkopf R J, Devoret M H 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 041020
[16] Ranzani L, Aumentado J 2015 New J. Phys. 17 023024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kodera T, Sounas D L, Caloz C 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 031901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Caloz C, Alù A, Tretyakov S, Sounas D, Achouri K, Deck-Léger Z-L 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 047001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang Y P, Rao J W, Yang Y, Xu P C, Gui Y S, Yao B M, You J Q, Hu C M 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 127202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao Y T, Rao J W, Gui Y S, Wang Y P, Hu C M 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 14 014035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qian J, Rao J W, Gui Y S, Wang Y P, An Z H, Hu C M 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 031901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Rao J W, Yao B, Wang C Y, Zhang C, Yu T, Lu W 2023 Phys. Rev. Lett. 130 046705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen Z, Rao J, Zhao K X, Yang F, Wang C X, Yao B, Lu W 2024 Appl. Phys. Lett. 125 031901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
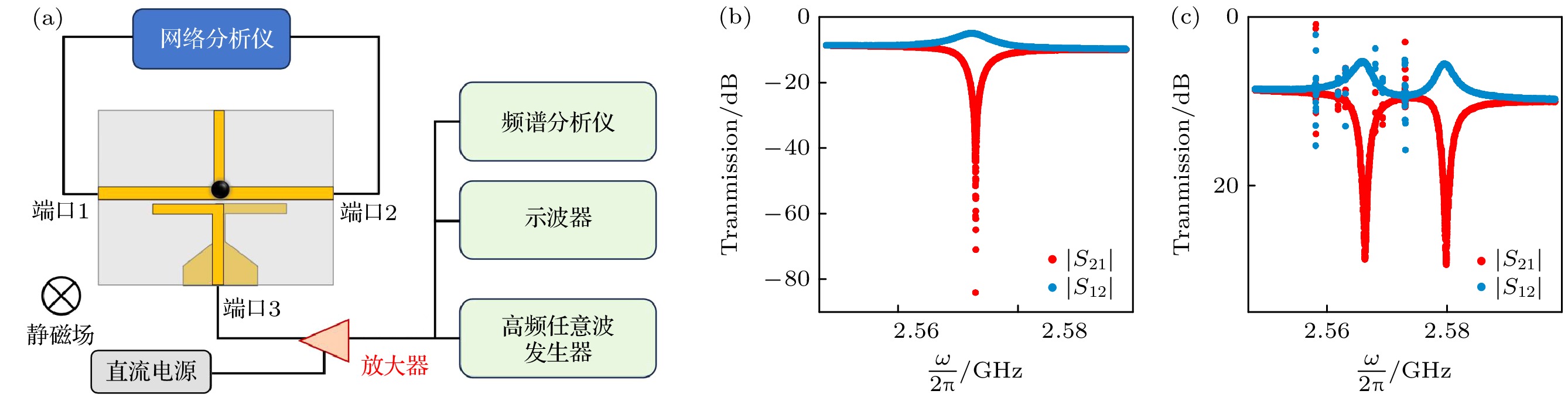
图 1 (a) 具有非互易特性的腔磁子系统实验装置图, 直径1 mm的YIG小球放置在微波谐振腔上, 通过VNA在1, 2端口测量其透射谱, 在3端口经由微波贴片天线送入泵浦信号; (b) 测量了系统在BIC条件下的|S21|和|S12|透射谱; (c) 在BIC频率(2.573 GHz)处输入一个功率为20 dBm的泵浦信号, 泵浦信号激发的PIM与BIC发生强耦合, 形成两个混合模式
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup for the cavity magnonic system with nonreciprocal characteristics, a 1-mm-diameter YIG sphere is placed at the node of a microwave resonator, the transmission spectra are measured between ports 1 and 2 using a vector network analyzer (VNA), while pump signals are injected into port 3 through a microwave patch antenna; (b) transmission spectra |S21| and |S12| of the system are measured under the BIC condition; (c) a pump signal with a power of 20 dBm is injected at the BIC frequency, exciting PIMs that strongly couple with the BIC, resulting in the formation of two hybrid modes.
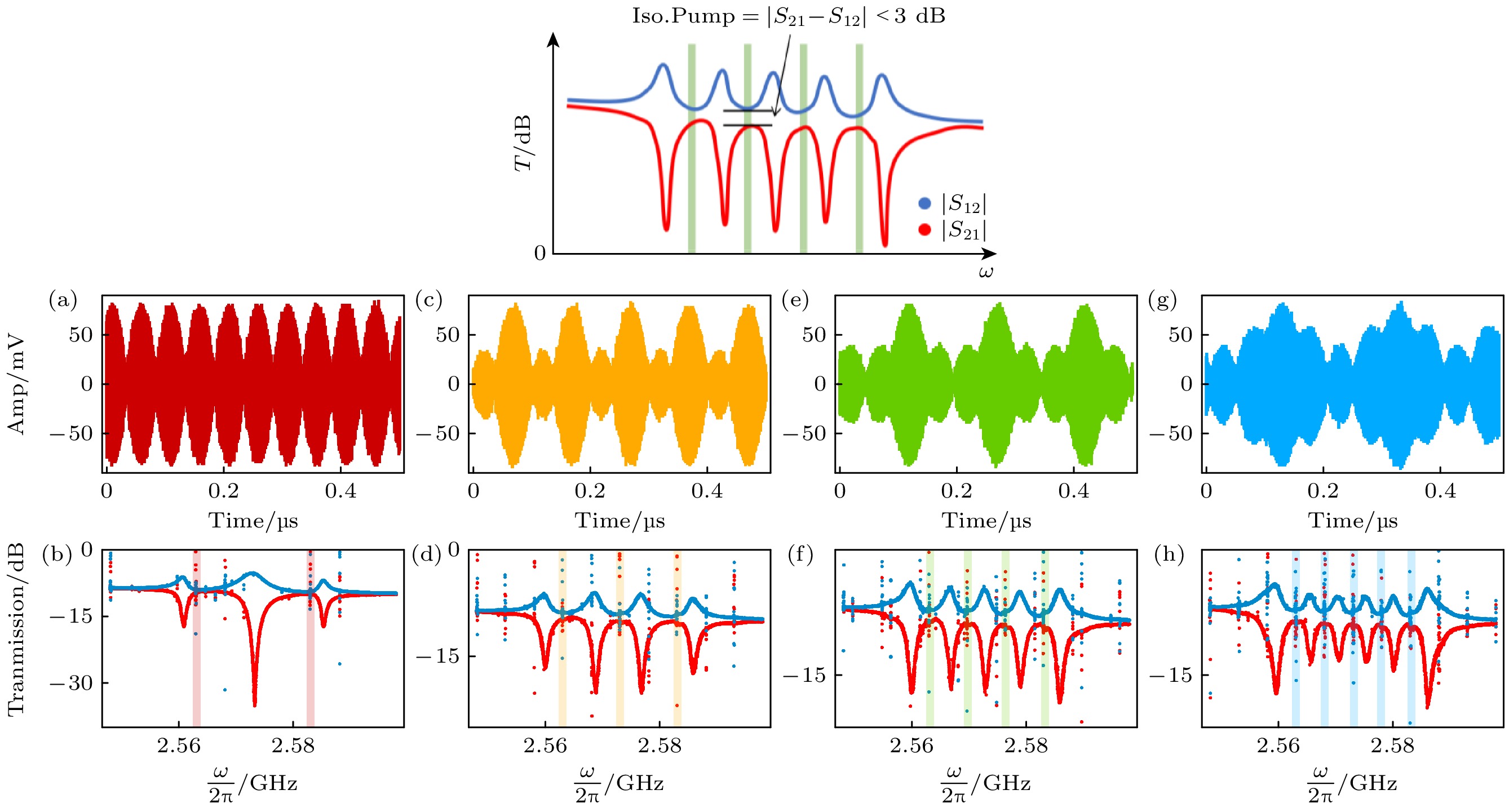
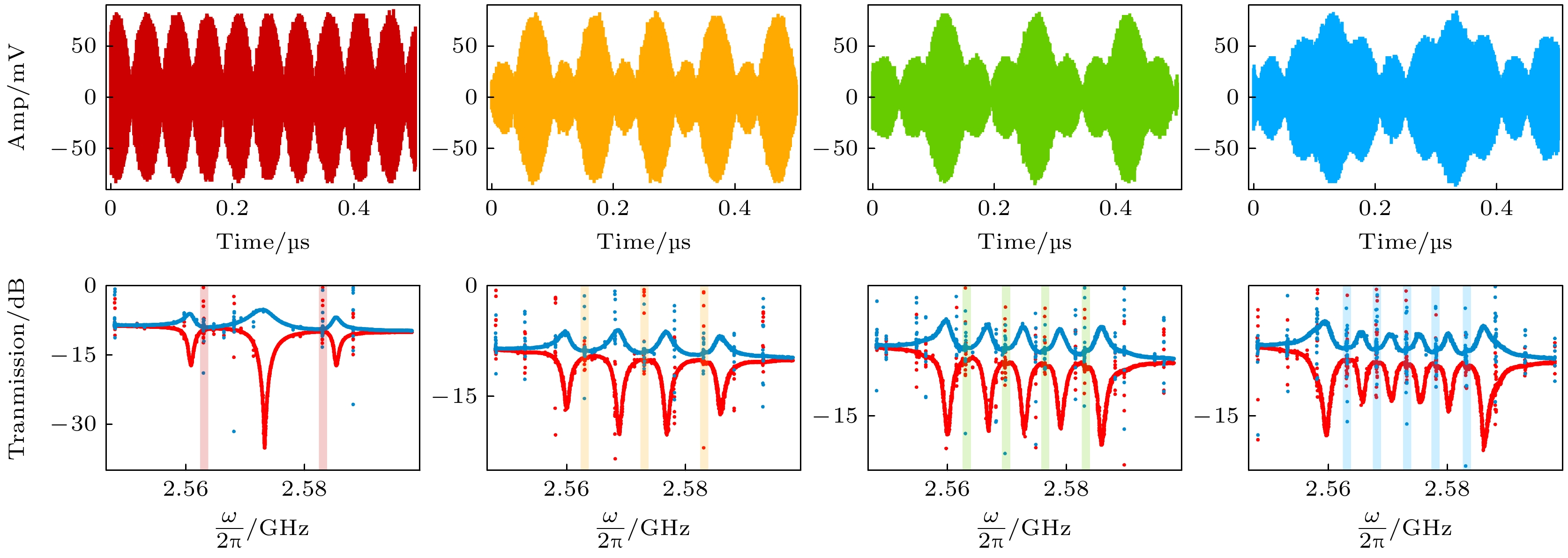
图 2 (a), (c), (e), (g)分别为输入的泵浦调制信号在时域上的波形(其主要频率分量, 在频域上20 MHz的带宽内输入2—5个均分带宽的泵浦信号, 在右侧列中用透明条带表示); (b), (d), (f), (h)展示了系统可以调制的不同通道数, 当输入相应的泵浦调制信号时, 在VNA上测量的|S21|和|S12|透射谱
Fig. 2. (a), (c), (e), (g) depict the time-domain waveforms of the input modulated pump signals, the main frequency components of these signals are distributed within a 20 MHz bandwidth in the frequency domain, with 2 to 5 evenly spaced pump signals injected, as indicated by the transparent bands on the right; (b), (d), (f), (h) illustrate the number of modulation channels achievable by the system. These results are obtained from the transmission spectra |S21| and |S12| measured on the VNA when the corresponding modulated pump signals are applied.
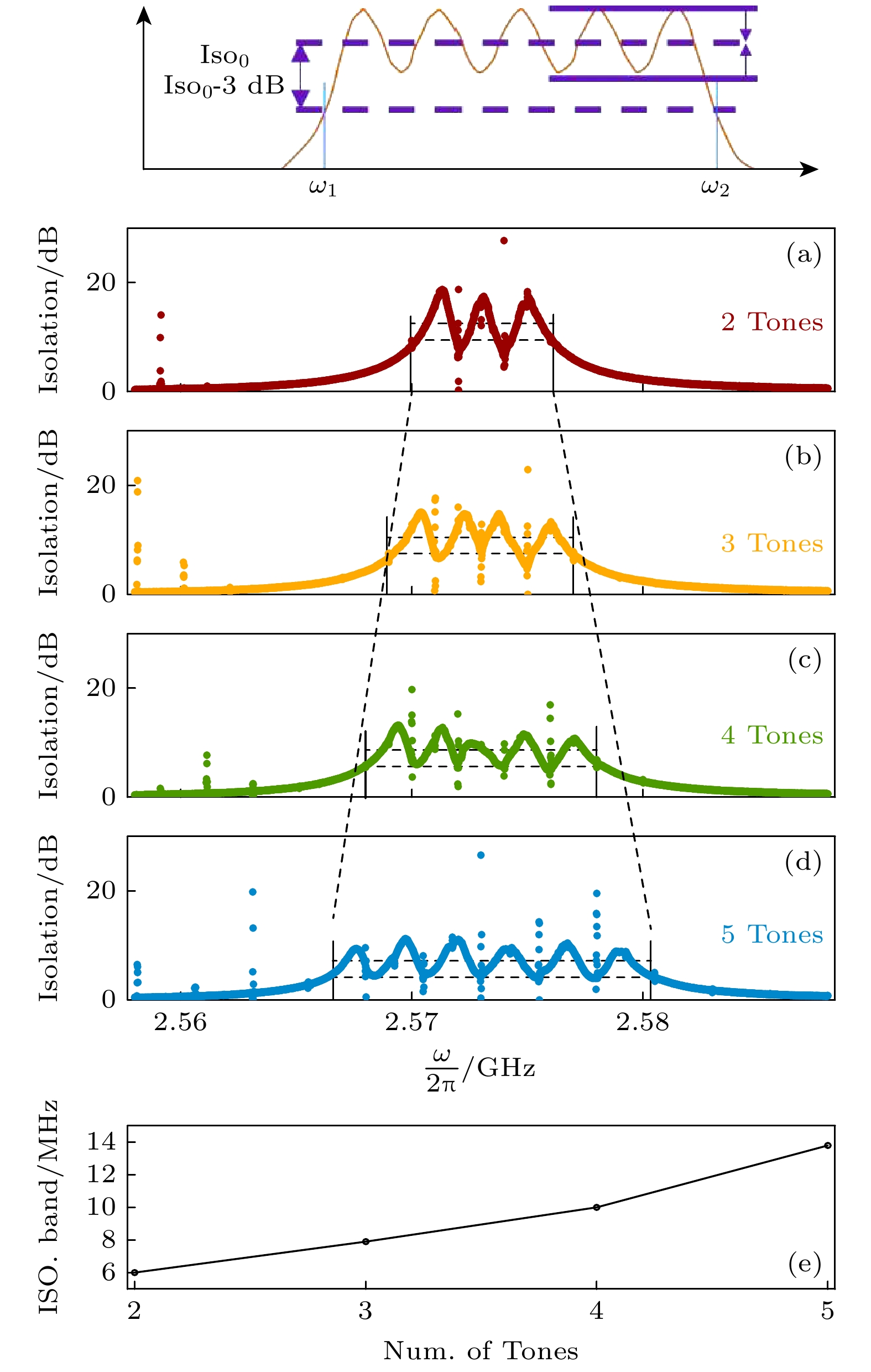
图 3 (a)—(d) 不同泵浦调制信号下的非互易隔离带, 横轴表示调制的非互易带的隔离区域, 纵轴是器件对微波信号的非互易隔离度; (e) 隔离带宽的大小随输入泵浦信号的数目连续变化, 横轴是输入泵浦信号的数目, 纵轴是非互易隔离带的隔离带宽
Fig. 3. (a)–(d) The nonreciprocal isolation bands under different modulated pump signals, the horizontal axis represents the isolation regions of the modulated nonreciprocal bands, while the vertical axis corresponds to the nonreciprocal isolation degree of the device for microwave signals; (e) the variation in isolation bandwidth as a function of the number of input pump signals, the horizontal axis indicates the number of input pump signals, and the vertical axis represents the isolation bandwidth of the nonreciprocal isolation bands.
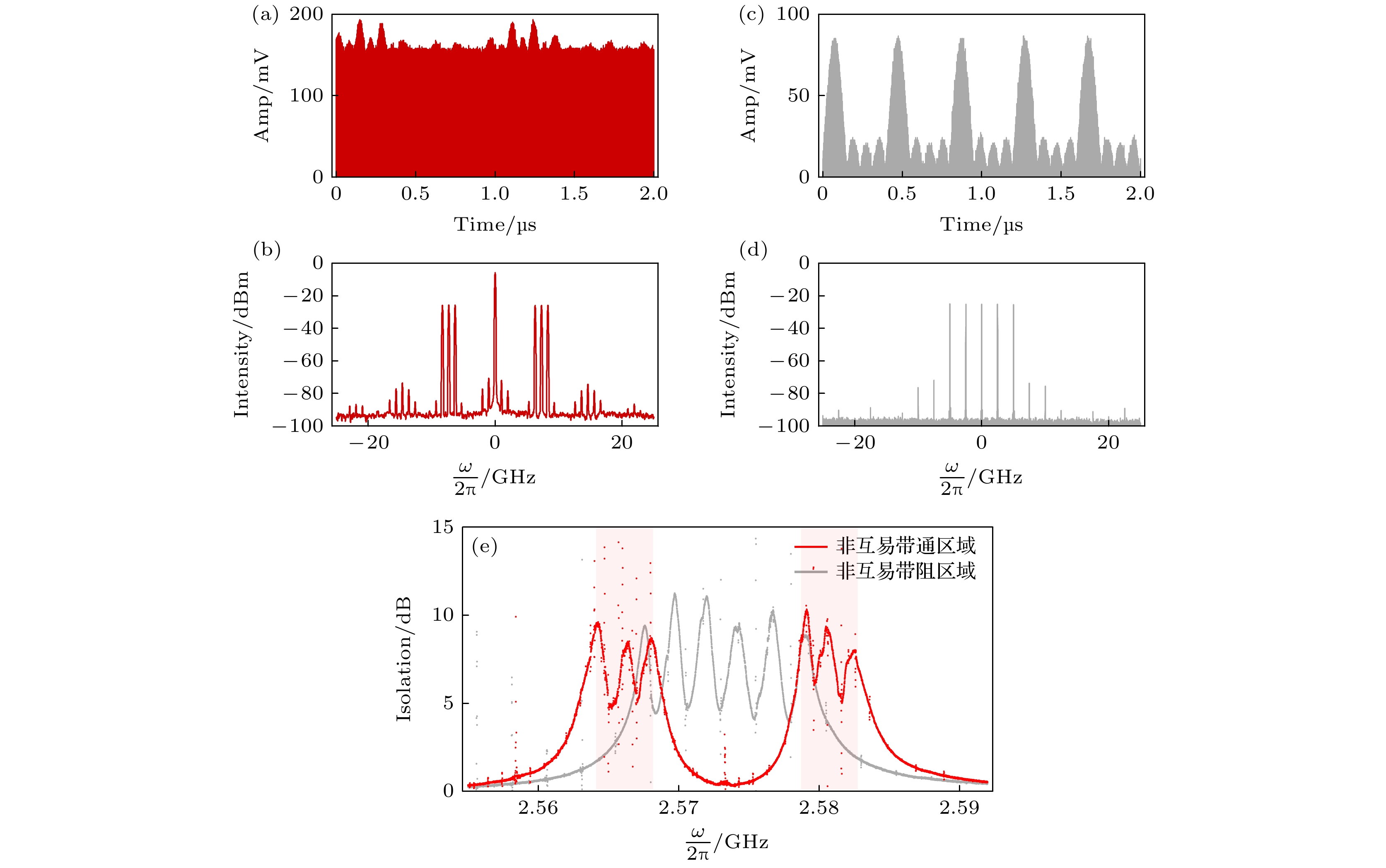
图 4 (a), (b) 测量的带通隔离器的输入泵浦信号的时域和频域图像; (c), (d) 测量的带阻隔离器的输入泵浦信号的时域和频域图像; (e)红色非互易带区域为带通区域, 灰色部分为带阻区域
Fig. 4. (a), (b) The time-domain and frequency-domain representations of the input pump signals for the band-pass isolator; (c), (d) the time-domain and frequency-domain representations of the input pump signals for the band-stop isolator; (e) the red nonreciprocal band corresponds to the band-pass region, while the gray area represents the band-stop region.
-
[1] Yu Z F, Fan S H 2009 Nat. Photonics 3 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lira H, Yu Z F, Fan S H, Lipson M 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 033901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Fang K, Yu Z F, Fan S H 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 153901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sounas D L, Alù A 2017 Nat. Photonics 11 774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kang M S, Butsch A, Russell P St J 2011 Nat. Photonics 5 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Manipatruni S, Robinson J T, Lipson M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 213903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Peng B, Özdemir Ş K, Lei F, Monifi F, Gianfreda M, Long G L, Fan S H, Nori F, Bender C M, Yang L 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Estep N A, Sounas D L, Soric J, Alù A 2014 Nat. Phys. 10 923
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Jalas D, Petrov A, Eich M, Freude W, Fan S H, Yu Z F, Baets R, Popović M, Melloni A, Joannopoulos J D, Vanwolleghem J D, Vanwolleghem M, Doerr C R, Renner D H 2013 Nat. Photonics 7 579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Reiskarimian N, Krishnaswamy H 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Kord A, Sounas D L, Alù A 2017 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 66 911
[12] Abdo B, Sliwa K, Frunzio L, Devoret M 2013 Phys. Rev. X 3 031001
[13] Lecocq F, Ranzani L, Peterson G A, Cicak K, Simmonds R W, Teufel J D, Aumentado J 2017 Phys. Rev. Appl. 7 024028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chapman B J, Rosenthal E I, Kerckhoff J, Moores B A, Vale L R, Mates J A B, Hilton G C, Lalumière K, Blais A, Lehnert K W 2017 Phys. Rev. X 7 041043
[15] Sliwa K M, Hatridge M, Narla A, Shankar S, Frunzio L, Schoelkopf R J, Devoret M H 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 041020
[16] Ranzani L, Aumentado J 2015 New J. Phys. 17 023024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kodera T, Sounas D L, Caloz C 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 031901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Caloz C, Alù A, Tretyakov S, Sounas D, Achouri K, Deck-Léger Z-L 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 047001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang Y P, Rao J W, Yang Y, Xu P C, Gui Y S, Yao B M, You J Q, Hu C M 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 127202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao Y T, Rao J W, Gui Y S, Wang Y P, Hu C M 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 14 014035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Qian J, Rao J W, Gui Y S, Wang Y P, An Z H, Hu C M 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 031901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Rao J W, Yao B, Wang C Y, Zhang C, Yu T, Lu W 2023 Phys. Rev. Lett. 130 046705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen Z, Rao J, Zhao K X, Yang F, Wang C X, Yao B, Lu W 2024 Appl. Phys. Lett. 125 031901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1752
- PDF下载量: 60
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: