-
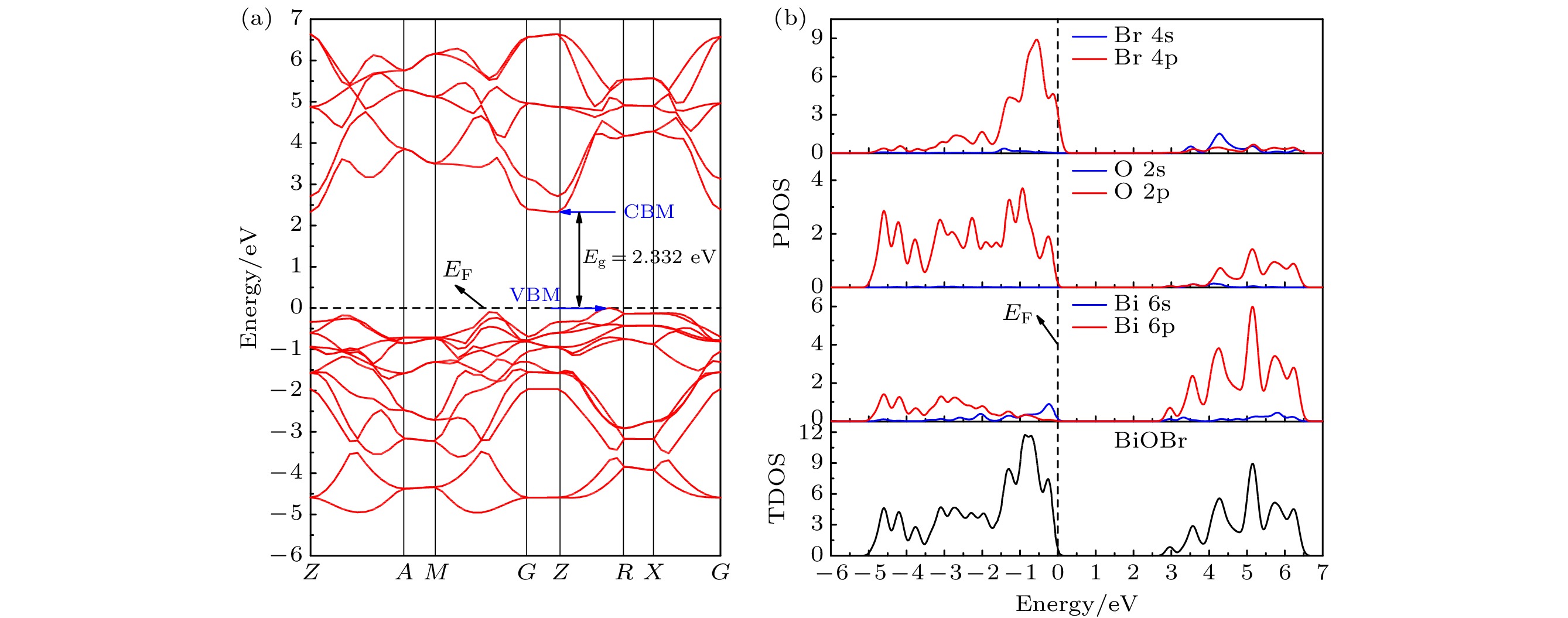
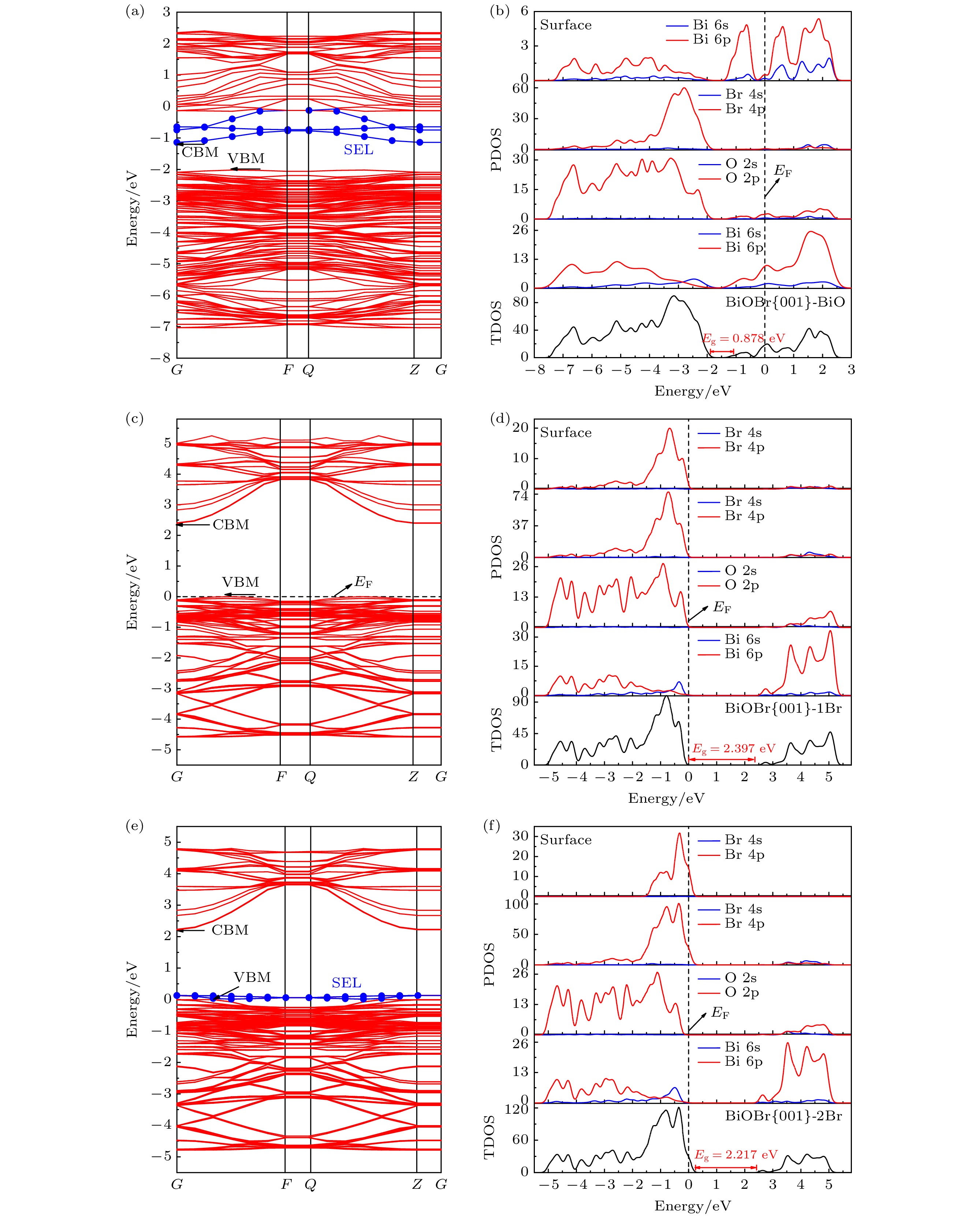
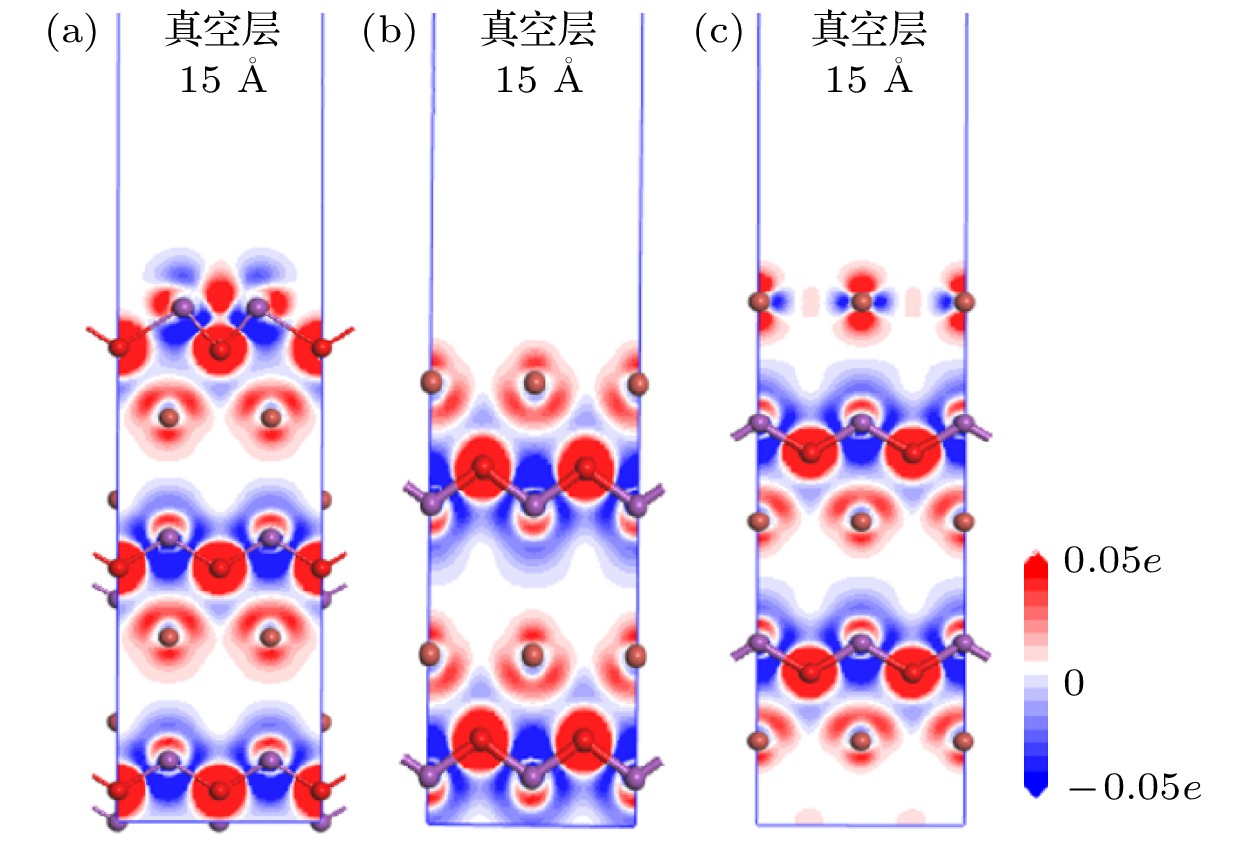
基于密度泛函理论(density functional theory, DFT)的第一性原理方法研究了暴露不同原子终端的BiOBr{001}表面以及单原子Pt吸附于BiOBr{001}-BiO不同位置的几何构型、电子结构、光学性质和电荷转移. 计算结果表明: BiOBr{001}面BiO终端暴露可诱导产生表面态且价带和导带能级向低能方向移动, 光氧化性增强, 尤其导带下方出现的表面态能级有助于光生电子-空穴对的分离和迁移, 光吸收显著增强, 且BiOBr{001}面BiO终端的功函数远低于贵金属Pt, 有利于电荷定向转移. 其次, 单原子Pt吸附于BiOBr{001}-BiO为基底的表面, 在禁带中间诱导产生杂质能级, Pt吸附于穴位时吸附能最小, 光响应能力最好且电荷转移量最大, 吸附于顶位和桥位时, 形成开放性的贫电子区域, 因此可预测穴位为Pt原子的吸附位点, 预示其良好的降解有机污染物效果, Pt吸附于BiOBr{001}-BiO的顶位和桥位, 具有潜在的CO2还原或固氮等领域应用.
-
关键词:
- 第一性原理 /
- BiOBr{001}面 /
- 单原子Pt /
- 电子性质 /
- 吸附位点
In this work, the geometrical configuration, electronic structure, optical properties and charge transfer behavior of BiOBr{001} surface with three different atomic exposure terminations (-BiO, -1Br and -2Br) and single-atom Pt at different adsorption positions on the BiOBr{001}-BiO surface (top, bridge and hollow site) are calculated by the first-principles calculation method based on density functional theory (DFT). More emphasis is placed on the research of the relative rule between single-atom Pt and BiOBr{001} surface. The calculation results show that the BiOBr{001}-BiO system exhibits the appearance of surface energy levels and the shift towards the lower energy for valence band and conduction band, enhancing the photocatalytic oxidation performance, especially, the existence of surface energy levels below the conduction band will contribute to the separation and migration of electron-hole pairs and the significant improvement of photo-response capability. Besides, the work function of BiOBr{001}-BiO system is much lower than one of noble metal Pt, which is beneficial to the directional transfer of photogenerated charge. Therefore, the BiOBr{001}-BiO system should be selected as an ideal substrate for interaction with the noble metal Pt. Furthermore, single-atom Pt is adsorbed at different positions of BiOBr{001}-BiO surface, with induced impurity energy levels in the forbidden band, achieving the smallest adsorption energy, the best photo-response capability. Particularly, the transferred charge number is the largest value (–0.920e) when Pt atom is adsorbed on a hollow site. However, the open electron-poor region will be formed when Pt atom is adsorbed at the top and bridge sites of BiOBr{001}-BiO surface. What is more, our findings should provide the excellent theoretical guidance for achieving the photocatalytic CO2 reduction and nitrogen fixation on the BiOBr{001} surface to build up the top and bridge sites as the adsorption sites of Pt atom. The adsorption sites of Pt atoms are located at the hollow sites of BiOBr{001} surface, which should obtain the high photocatalytic oxidizing activity of degrading organic pollutants. Finally, our work can not only present the basic data for the optimized local electronic structure and photocatalytic application for noble metal decorated BiOBr-based materials, but also provide a kind of research strategy for further exploring and designing efficient noble metal decorated BiOX-based or other semiconductor-based photocatalyst systems.-
Keywords:
- first-principles /
- BiOBr{001} surface /
- single-atom Pt /
- electronic properties /
- adsorption sites
[1] Li X B, Xiong J, Gao X M, Ma J, Huang J T 2019 J. Hazard. Mater. 387 121690
[2] Li J Y, Dong X A, Sun Y J, Cen W L, Dong F 2018 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 226 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Huo Y N, Zhang J, Miao M, Jin Y 2012 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 111-112 334
[4] Gao Q, Wu X, Zhu R 2020 Constr. Build. Mater. 257 119569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yang Y, Zhang C, Lai C, Zeng G M, Huang D L, Cheng M, Wang J J, Chen F, Zhou C Y, Xiong W P 2018 Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 254 76
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li T, Zhang X C, Zhang C M, Li R, Liu J X, Lv R, Zhang H, Han P D, Fan C M, Zheng Z F 2019 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21 868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ye L Q, Su Y R, Jin X L, Xie H Q, Zhang C 2014 Environ. Sci.: Nano 1 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bai S, Li X, Kong Q, Long R, Wang C, Jiang J, Xiong Y 2015 Adv. Mater. 27 3444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu B R, Li J, Liu L, Li Y D, Guo S H, Gao Y Q, Li N, Ge L 2019 Chin. J. Catal. 40 713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y, Wang Y, Li W, Yang Q, Hou Q, Wei L, Liu L, Huang F, Ju M 2017 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 210 352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Qiao B, Wang A, Yang X, Allard L F, Jiang Z, Cui Y, Liu J, Li J, Zhang T 2011 Nat. Chem. 3 634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wan J, Chen W, Jia C, Zheng L, Dong J, Zheng X, Wang Y, Yan W, Chen C, Peng Q, Wang D, Li Y 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1705369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li X, Bi W, Zhang L, Tao S, Chu W, Zhang Q, Luo Y, Wu C, Xie Y 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 2427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nie L, Mei D H, Xiong H F, Peng B, Ren Z B, Hernandez X I P, Delariva A, Wang M, Engelhard M H, Kovarik L 2017 Science 358 1419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shi Y, Zhao C, Wei H, Guo J, Liang S, Wang A, Zhang T, Liu J, Ma T 2014 Adv. Mater. 26 8147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang H B, Liu G G, Shi L, Ye J H 2018 Adv. Energy Mater. 8 1701343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu H, Fang Z, Su Y, Suo Y, Huang S, Zhang Y, Ding K 2018 Chem. Asian. J. 13 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang X C, Li G Q, Fan C M, Ding G Y, Wang Y W, Han P D 2014 Comput. Mater. Sci. 95 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li H, Shang J, Ai Z, Zhang L 2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 6393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Pfrommer B G, Cote M, Louie S G, Cohen M L 1997 J. Comput. Phys. 131 233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Vanderbilt D 1990 Phys. Rev. B 41 7892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao Z Y, Dai W W 2014 Inorg. Chem. 53 13001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] T T, C Z B, Jia J C, Bei C, Guo Y J 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 433 1175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huang W L, Zhu Q S 2009 J. Comput. Chem. 30 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Bhachu D S, Moniz S J A, Sathasivam S, Scanlon D O, Walsh A, Bawaked S M, Mokhtar M, Obaid A Y, Parkin I P, Tang J, Carmalt C J 2016 Chem. Sci. 7 4832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ye L Q, Jin X L, Liu C, Ding C H, Xie H Q, Chu K H, Wong P K 2016 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 187 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Guo J Q, Liao X, Lee M H, Hyett G, Huang C C, Hewak D W, Mailis S, Zhou W, Jiang Z 2019 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 243 502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang X C, Guo T Y, Wang X W, Wang Y W, Fan C M, Zhang H 2014 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 150-151 486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu L P, Zhuang Z B, Xie T, Wang Y G, Li J, Peng Q, Li Y D 2009 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 16423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhao K, Zhang L, Wang J, Li Q, He W, Yin J J 2013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 15750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kong T, Wei X M, Zhu G Q, Huang Y H 2017 J. Mater. Sci. 52 5686
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhang H J, Liu L, Zhou Z 2012 RSC Adv. 2 9224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ma Z Y, Li P H, Ye L Q, Wang L, Xie H Q, Zhou Y 2018 Catal. Sci. Technol. 8 5129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhang Z, Wang Y F, Zhang X C, Zhang C M, Wang Y W, Zhang H, Fan C M 2018 Chem. Pap. –Chem. Zvesti 72 2413
[36] Guo W, Qin Q, Geng L, Wang D, Guo Y, Yang Y 2016 J. Hazard. Mater. 308 374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wu D P, Wang R, Yang C, An Y P, Lu H, Wang H J, Cao K, Gao Z Y, Zhang W C, Xu F, Jiang K 2019 J.Colloid Interface Sci. 556 111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
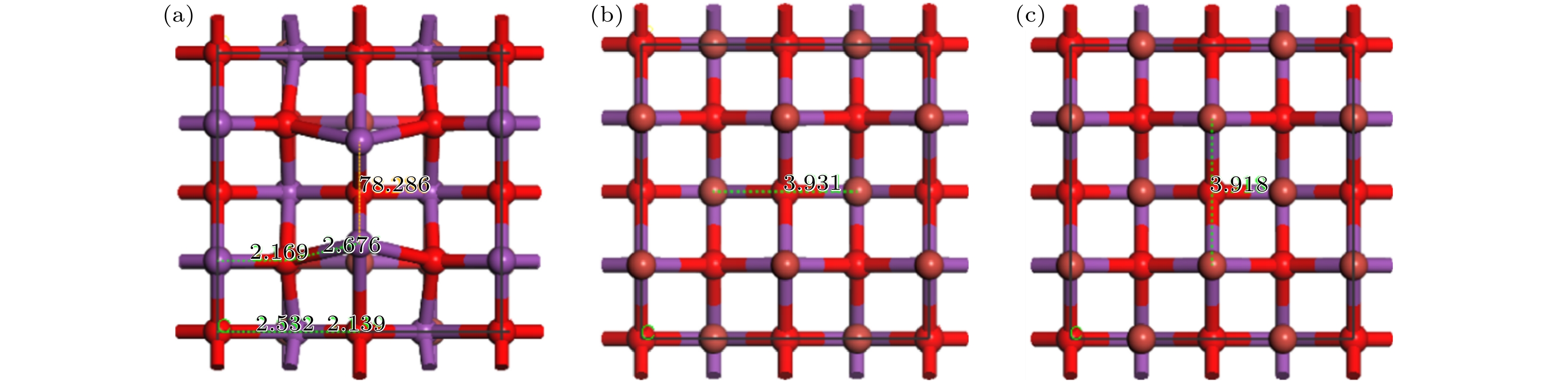
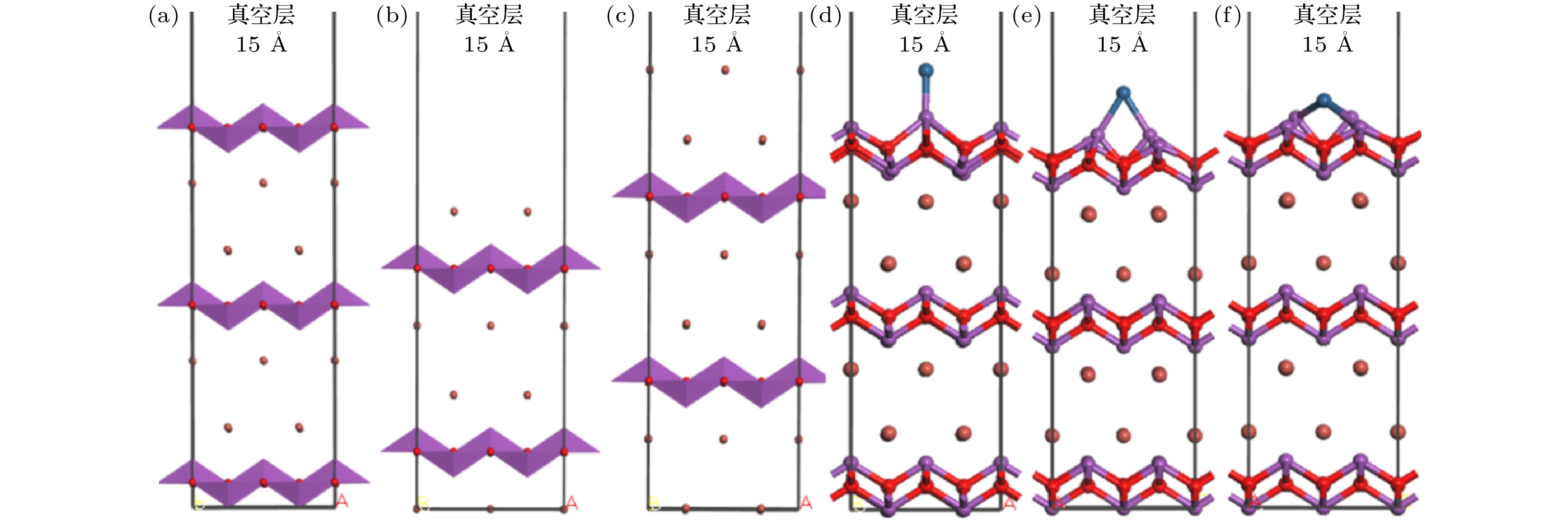
图 1 不同原子暴露终端BiOBr{001}面及单原子Pt吸附于BiOBr{001}-BiO不同位置的晶体结构模型 (a) -BiO; (b) -1Br; (c) -2Br; (d) TPt; (e) BPt; (f) HPt
Fig. 1. The crystal structure model of BiOBr{001} surface with different atom exposure terminations and single atom Pt adsorbed on different positions of BiOBr{001}-BiO: (a) -BiO; (b) -1Br; (c) -2Br; (d) TPt; (e) BPt; (f) HPt.
表 1 不同原子暴露终端BiOBr{001}面的表面能和电子性质计算结果
Table 1. The calculation results of the surface energy and electronic properties of the BiOBr{001} surface with different atom exposure terminations.
Surface Esurf/(J·m–2) Erel/(J·m–2) Esurf /(J·m–2) [16] W/eV VBM CBM Eg/eV SEL {001}-BiO 2.244 –0.137 2.2—2.4 2.576 G –2.020 G-F –1.142 0.878 –1.142—0.126 {001}-1Br 0.005 –0.002 –0.2—0.3 7.203 G-F 0 G 2.397 2.397 –3.825—0 {001}-2Br 2.142 –0.025 2.2—2.5 7.566 G-F 0 G 2.217 2.217 0.011—0.128 表 2 单原子Pt在BiOBr{001}-BiO面不同吸附位置的吸附能、功函数和电子性质的计算结果
Table 2. The calculation results of the adsorption energy, work function, and electronic properties of single-atom Pt at different adsorption positions on BiOBr{001}-BiO surface.
Sites Eads /(J·m–2) Pt-Bi length/Å VBM CBM Eg/eV Pt 5d states SEL T –5.189 2.612 G-F –2.379 G –0.745 1.634 –2.307— –1.497 –0.745—0.063 B –5.427 2.568 F –2.045 G –0.741 1.634 –1.688 — –1.609 –0.741—0.517 H –6.087 2.831 G F –2.101 G –0.746 1.356 –2.051 — –1.777 –0.746—-0.013 表 3 Pt/BiOBr{001}-BiO体系的功函数W和Mulliken电荷变化值 ∆Q
Table 3. Work function W and Mulliken charge change value ∆Q of Pt/BiOBr{001}-BiO.
Systems Pt BiOBr{001}-BiO TPt/BiOBr{001}-BiO BPt/BiOBr{001}-BiO HPt/BiOBr{001}-BiO Work function /eV 5.650 2.576 3.300 3.254 3.001 Pt Mulliken charge ∆Q /e — — –0.810 –0.860 –0.920 -
[1] Li X B, Xiong J, Gao X M, Ma J, Huang J T 2019 J. Hazard. Mater. 387 121690
[2] Li J Y, Dong X A, Sun Y J, Cen W L, Dong F 2018 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 226 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Huo Y N, Zhang J, Miao M, Jin Y 2012 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 111-112 334
[4] Gao Q, Wu X, Zhu R 2020 Constr. Build. Mater. 257 119569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yang Y, Zhang C, Lai C, Zeng G M, Huang D L, Cheng M, Wang J J, Chen F, Zhou C Y, Xiong W P 2018 Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 254 76
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li T, Zhang X C, Zhang C M, Li R, Liu J X, Lv R, Zhang H, Han P D, Fan C M, Zheng Z F 2019 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21 868
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ye L Q, Su Y R, Jin X L, Xie H Q, Zhang C 2014 Environ. Sci.: Nano 1 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bai S, Li X, Kong Q, Long R, Wang C, Jiang J, Xiong Y 2015 Adv. Mater. 27 3444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu B R, Li J, Liu L, Li Y D, Guo S H, Gao Y Q, Li N, Ge L 2019 Chin. J. Catal. 40 713
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y, Wang Y, Li W, Yang Q, Hou Q, Wei L, Liu L, Huang F, Ju M 2017 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 210 352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Qiao B, Wang A, Yang X, Allard L F, Jiang Z, Cui Y, Liu J, Li J, Zhang T 2011 Nat. Chem. 3 634
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wan J, Chen W, Jia C, Zheng L, Dong J, Zheng X, Wang Y, Yan W, Chen C, Peng Q, Wang D, Li Y 2018 Adv. Mater. 30 1705369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li X, Bi W, Zhang L, Tao S, Chu W, Zhang Q, Luo Y, Wu C, Xie Y 2016 Adv. Mater. 28 2427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nie L, Mei D H, Xiong H F, Peng B, Ren Z B, Hernandez X I P, Delariva A, Wang M, Engelhard M H, Kovarik L 2017 Science 358 1419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Shi Y, Zhao C, Wei H, Guo J, Liang S, Wang A, Zhang T, Liu J, Ma T 2014 Adv. Mater. 26 8147
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhang H B, Liu G G, Shi L, Ye J H 2018 Adv. Energy Mater. 8 1701343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu H, Fang Z, Su Y, Suo Y, Huang S, Zhang Y, Ding K 2018 Chem. Asian. J. 13 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang X C, Li G Q, Fan C M, Ding G Y, Wang Y W, Han P D 2014 Comput. Mater. Sci. 95 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li H, Shang J, Ai Z, Zhang L 2015 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 6393
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Pfrommer B G, Cote M, Louie S G, Cohen M L 1997 J. Comput. Phys. 131 233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Vanderbilt D 1990 Phys. Rev. B 41 7892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao Z Y, Dai W W 2014 Inorg. Chem. 53 13001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] T T, C Z B, Jia J C, Bei C, Guo Y J 2018 Appl. Surf. Sci. 433 1175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Huang W L, Zhu Q S 2009 J. Comput. Chem. 30 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Bhachu D S, Moniz S J A, Sathasivam S, Scanlon D O, Walsh A, Bawaked S M, Mokhtar M, Obaid A Y, Parkin I P, Tang J, Carmalt C J 2016 Chem. Sci. 7 4832
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Ye L Q, Jin X L, Liu C, Ding C H, Xie H Q, Chu K H, Wong P K 2016 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 187 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Guo J Q, Liao X, Lee M H, Hyett G, Huang C C, Hewak D W, Mailis S, Zhou W, Jiang Z 2019 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 243 502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang X C, Guo T Y, Wang X W, Wang Y W, Fan C M, Zhang H 2014 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 150-151 486
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu L P, Zhuang Z B, Xie T, Wang Y G, Li J, Peng Q, Li Y D 2009 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 16423
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Zhao K, Zhang L, Wang J, Li Q, He W, Yin J J 2013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 15750
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Kong T, Wei X M, Zhu G Q, Huang Y H 2017 J. Mater. Sci. 52 5686
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhang H J, Liu L, Zhou Z 2012 RSC Adv. 2 9224
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Ma Z Y, Li P H, Ye L Q, Wang L, Xie H Q, Zhou Y 2018 Catal. Sci. Technol. 8 5129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhang Z, Wang Y F, Zhang X C, Zhang C M, Wang Y W, Zhang H, Fan C M 2018 Chem. Pap. –Chem. Zvesti 72 2413
[36] Guo W, Qin Q, Geng L, Wang D, Guo Y, Yang Y 2016 J. Hazard. Mater. 308 374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wu D P, Wang R, Yang C, An Y P, Lu H, Wang H J, Cao K, Gao Z Y, Zhang W C, Xu F, Jiang K 2019 J.Colloid Interface Sci. 556 111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 9414
- PDF下载量: 250
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: