-
采用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理系统研究了B2-和B19'-NiTi合金所有低指数表面的表面能、表面结构稳定性、表面电子结构等性质. 计算结果表明两种NiTi合金所有低指数表面的原子弛豫主要集中在表面2—3个原子层, 且以Ti原子为终止原子表面构型的原子振荡最为剧烈, Ni和Ti原子共同终止表面构型的原子振荡最小; 价电荷密度沿着表面构型向真空层方向快速衰减; 表面能计算结果显示其与配位数成反相关. B2-和B19'-NiTi合金的非密排且非化学计量比表面的表面能取决于Ti的化学势, 表面能数值较高; 而密排面的表面构型符合化学计量比, 其表面能较低, 表现出卓越的化学稳定性; 其中以B2-NiTi(101)密排面的表面稳定性最优.NiTi shape memory alloy has been widely used in industrial and biological fields due to its excellent mechanical properties, unique shape memory effect and superelasticity. In this paper, the atomic relaxation, thermodynamic energy, structural stability, electronic structures and other properties of all low-index surfaces of B2- and B19'-NiTi alloys are systematically studied by using the first principles calculations based on density functional theory. The calculated results show that the atomic relaxations on all low-index surfaces of both B2- and B19'-NiTi alloys are mainly concentrated in 2−3 atomic layers on the surface, which means that the surface effect is mainly confined in two or three layers on the surface configuration. In addition, the atomic relaxation of Ti-terminated surface is most remarkable, and followed by Ni-terminated surface, while the atomic relaxation of Ni&Ti-terminated surface is insignificant. Furthermore, the valence charge density decays rapidly from the surface configuration to the vacuum layer. The calculation results of surface energy show that surface energy is inversely related to the coordinate number, and surface stability increases with the coordination number increasing. For B2- and B19'-NiTi, the surface energy of non-dense and non-stoichiometric surface depend on the chemical potential of Ti, and the surface energy is high. Therefore, the stabilities of these surfaces change with the chemical potential of Ti increasing. However, the surface energy values of dense surface configurations with stoichiometric ratio for B2-NiTi (101) and B19'-NiTi (010) are 1.81 J/m2 and 1.93 J/m2, respectively, which are both lower than those for other non-dense surfaces in the most Ti chemical potentials range, showing excellent structural stability. Moreover, the electron density analysis indicates that the dominant bonding for B2-NiTi (101) surface is the chained Ni-Ti-Ni metallic bond, the distribution of electrons and the distance between Ni and Ti atoms on the B2-NiTi (101) surface are more uniform and smaller, respectively, than those for B19'-NiTi (010) surface. In summary, the B2-NiTi (101) surface shows the high stability.
-
Keywords:
- first-principles /
- stability /
- surface energy /
- electronic property
[1] 马蕾, 王旭, 尚家香 2014 63 233103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma L, Wang X, Shang J X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 233103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 吴红丽, 赵新青, 宫声凯 2010 59 515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu H L, Zhao X Q, Gong S K 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wagner M F X, Windl W 2008 Acta. Mater. 56 6232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Huang X Y, Bungaro C, Godlevsky V, Rabe K M 2001 Phys. Rev. B 65 014108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Fukuda T, Kakeshita T, Houjoh H, Shiraishi S, Saburi T 1999 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 273−275 166
[6] 贾堤, 董治中, 于申军, 刘文西 1998 原子与分子 15 421
Jia D, Dong Z Z, Yu S J, Liu W X 1998 J. Atom. Mol. Phys. Sin. 15 421
[7] 姜振益, 李盛涛 2006 55 6032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang Z Y, Li S T 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 6032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hua Y J, Liu X, Meng C G, Yang D Z 2003 J. Wuhan. Univ. Technol. 18 6
[9] 朱建新, 李永华, 孟繁玲, 刘常升, 郑伟涛, 王煜明 2008 57 7204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu J X, Li Y H, Meng F L, Liu C S, Zheng W T, Wang Y M 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 7204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 单迪, 何鑫玉, 方长青, 邵晖 2015 材料导报A: 综述篇 29 28
Shan D, He X Y, Fang C Q, Shao H 2015 Mater. Rev. A 29 28
[11] 尹大宇, 朱锦宇, 段永宏, 李矛, 韩建业, 朱庆生 2011 华南国防医学杂志 25 52
Yin D Y, Zhu J Y, Duan Y H, Li M, Han J Y, Zhu Q S 2011 Milit. Medi. J. Sou. China 25 52
[12] 孔祥确, 金学军, 刘剑楠 2016 功能材料 47 1007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kong X Q, Jin X J, Liu J N 2016 Func. Mater. 47 1007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 邵明增, 崔春娟, 杨洪波 2018 材料导报A: 综述篇 32 1181
Shao M Z, Cui C J, Yang H B 2018 Mater. Rev. A 32 1181
[14] 杨贤金, 朱胜利, 崔振铎, 姚康德 2001 功能材料 32 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X J, Zhu S L, Cui Z D, Yao K D 2001 Func. Mater. 32 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Qiu D L, Wang A P, Yin Y S 2010 Appl. Surf. Sci. 257 1774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li Y F, Tang S L, Gao Y M, Ma S Q, Zheng Q L, Cheng Y H 2017 Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 31 1750161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nigussa K N, Støvneng J A 2011 Comput. Phys. Commun. 182 1979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Vishnu K G, Strachan A 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 014114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Sandoval L, Haskins J B, Lawson J W 2018 Acta Mater. 154 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fischer T H, Almlof J 1992 J. Phys. Chem. 96 9768
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li G F, Zheng H Z, Shu X Y, Peng P 2016 Met. Mater. Int. 22 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Pfetzing-Micklich J, Somsen C, Dlouhy A, Begau C, Hartmaier A, Wagner M F X, Eggeler G 2013 Acta Mater. 61 602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Mercier O, Melton K N, Gremaud G, Häji J 1980 J. Appl. Phys. 51 1833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Hatcher N, Kontsevoi O Y, Freeman A J 2009 Phys. Rev. B 80 144203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sestak P, Cerny M, Pokluda J 2008 Strength. Mater. 40 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sedlak P, Frost M, Kruisova A, Hirmanova K, Heller L, Sittner P 2014 J.Mater. Eng. Perf. 23 2591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zeng Z Y, Hu C E, Cai L C, Chen X R, Jing F Q 2010 Physica B 405 3665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fiorentini V, Methfessel M 1996 J. Phys-Condens. Mat. 8 6525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Lazzeri M, Vittadini A, Selloni A 2001 Phys. Rev. B 63 155409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
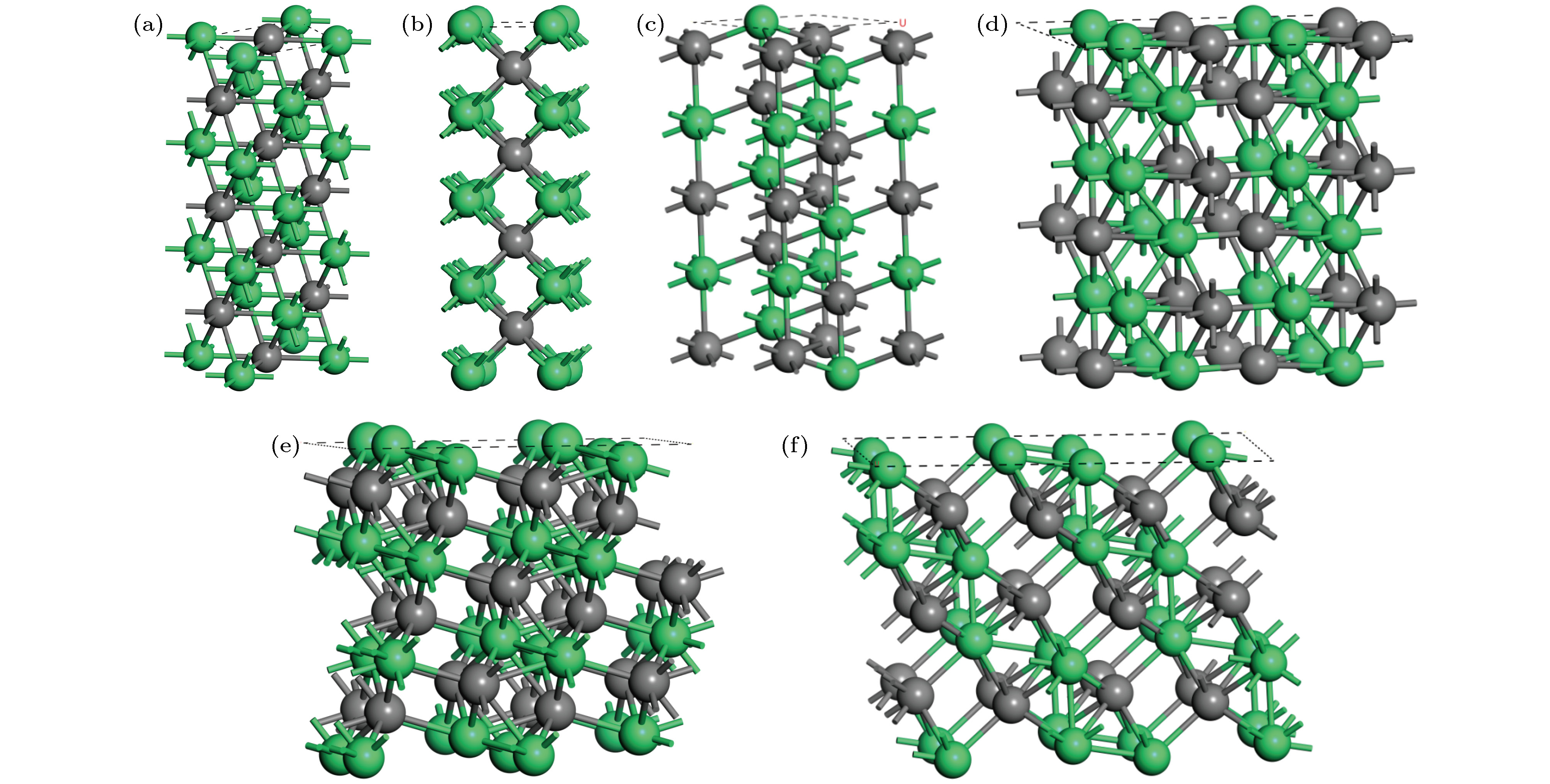
图 1 NiTi合金的低指数表面原子构型 (a) B2-NiTi(101)_NiTi; (b) B2-NiTi_Ni; (100); (c) B2-NiTi(111)_Ni; (d) B19’-NiTi(010)_NiTi; (e) B19'-NiTi(001)_Ni; (f) B19'-NiTi(110)_Ni; 绿色球和黑色球分别代表Ni, Ti原子
Fig. 1. Atomic low-index surface configurations of NiTi alloy: (a) B2-NiTi(101)_NiTi; (b) B2-NiTi(100)_Ni; (c) B2-NiTi(111)_Ni; (d) B19’-NiTi(010)_NiTi; (e) B19'-NiTi(001)_Ni; (f) B19'-NiTi(110)_Ni.
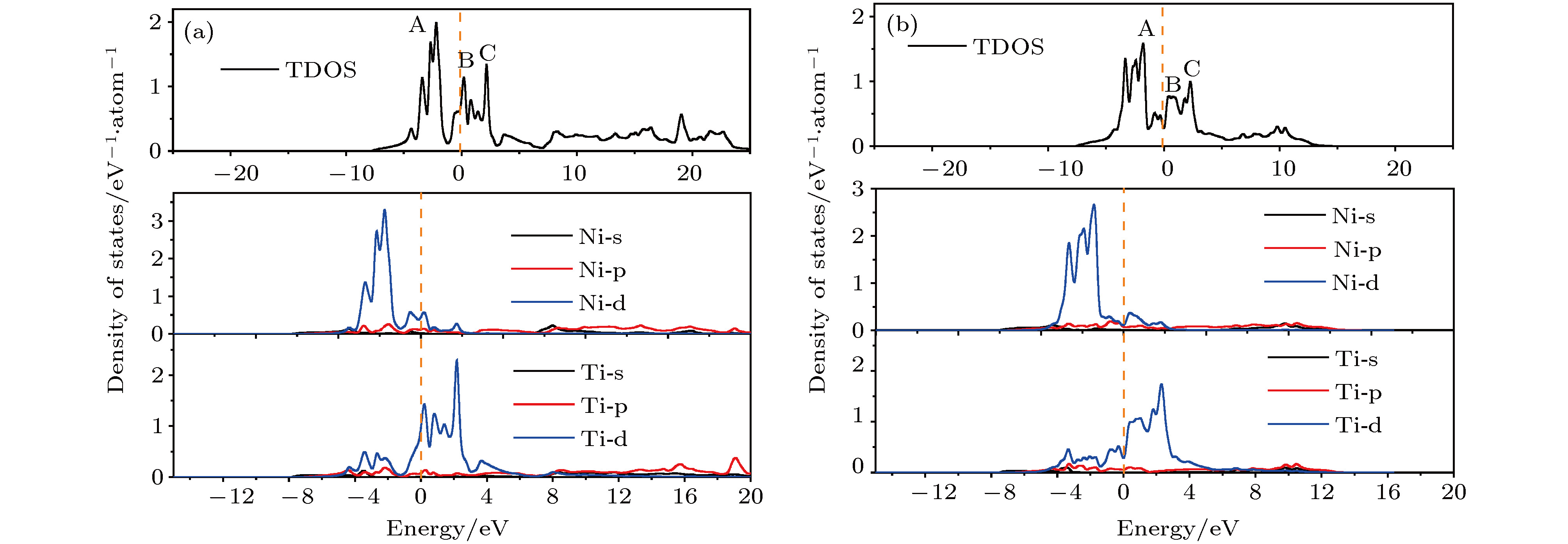
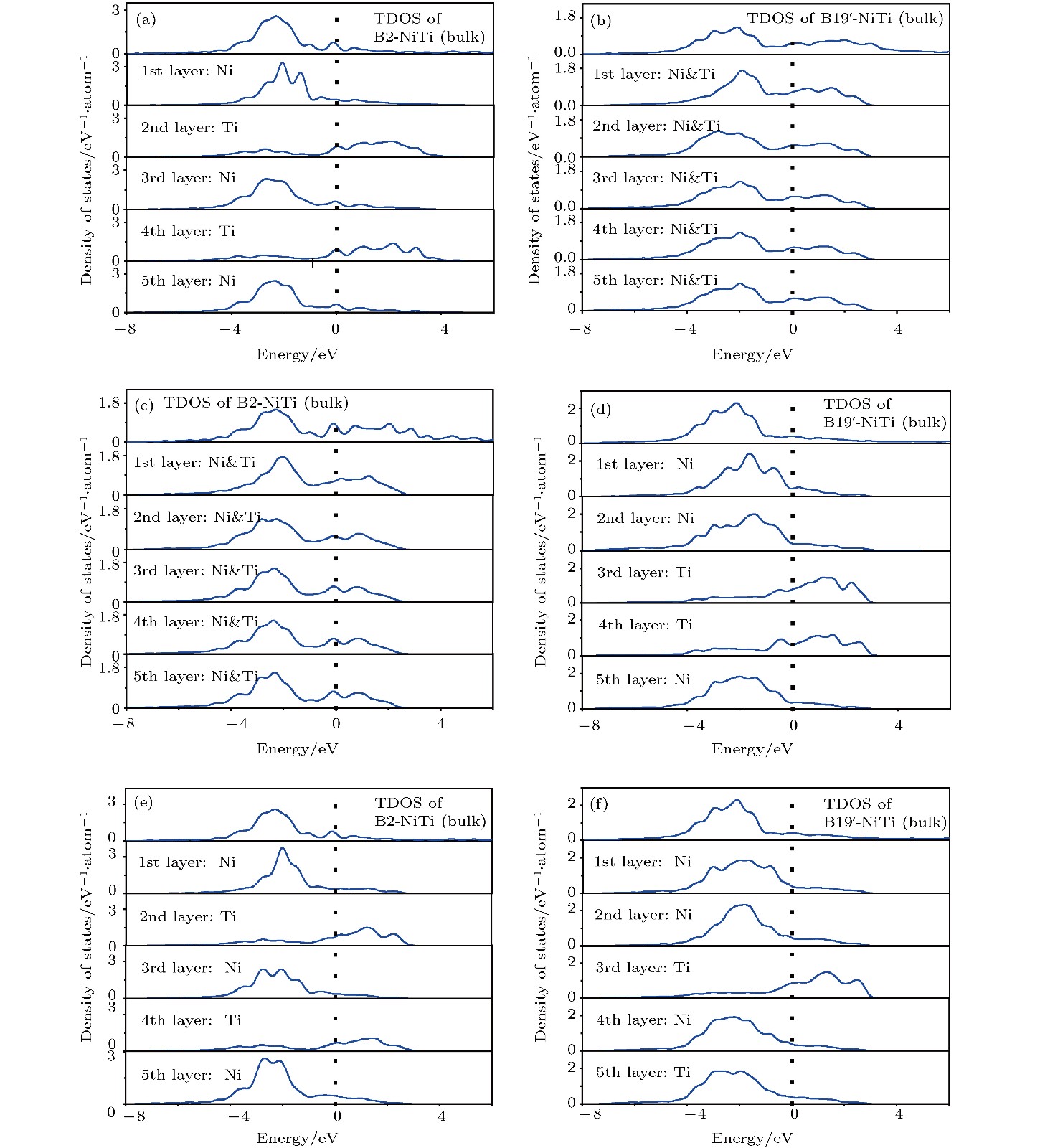
图 6 B2-和B19'-NiTi体相总DOS和表面构型层投影DOS曲线 (a) B2-NiTi (100)_Ni; (b) B19'-NiTi (010)_NiTi; (c) B2-NiTi (101)_NiTi; (d) B19'-NiTi (101)_Ni; (e) B2-NiTi (111)_Ni; (f) B19'-NiTi (111)_Ni
Fig. 6. Total DOS of B2 and B19'-NiTi body phase and surface configurations layer projected DOS curves: (a) B2-NiTi (100)_Ni; (b) B19'-NiTi (010)_NiTi; (c) B2-NiTi (101)_NiTi; (d) B19'-NiTi (101)_Ni; (e) B2-NiTi (111)_Ni; (f) B19'-NiTi (111)_Ni.
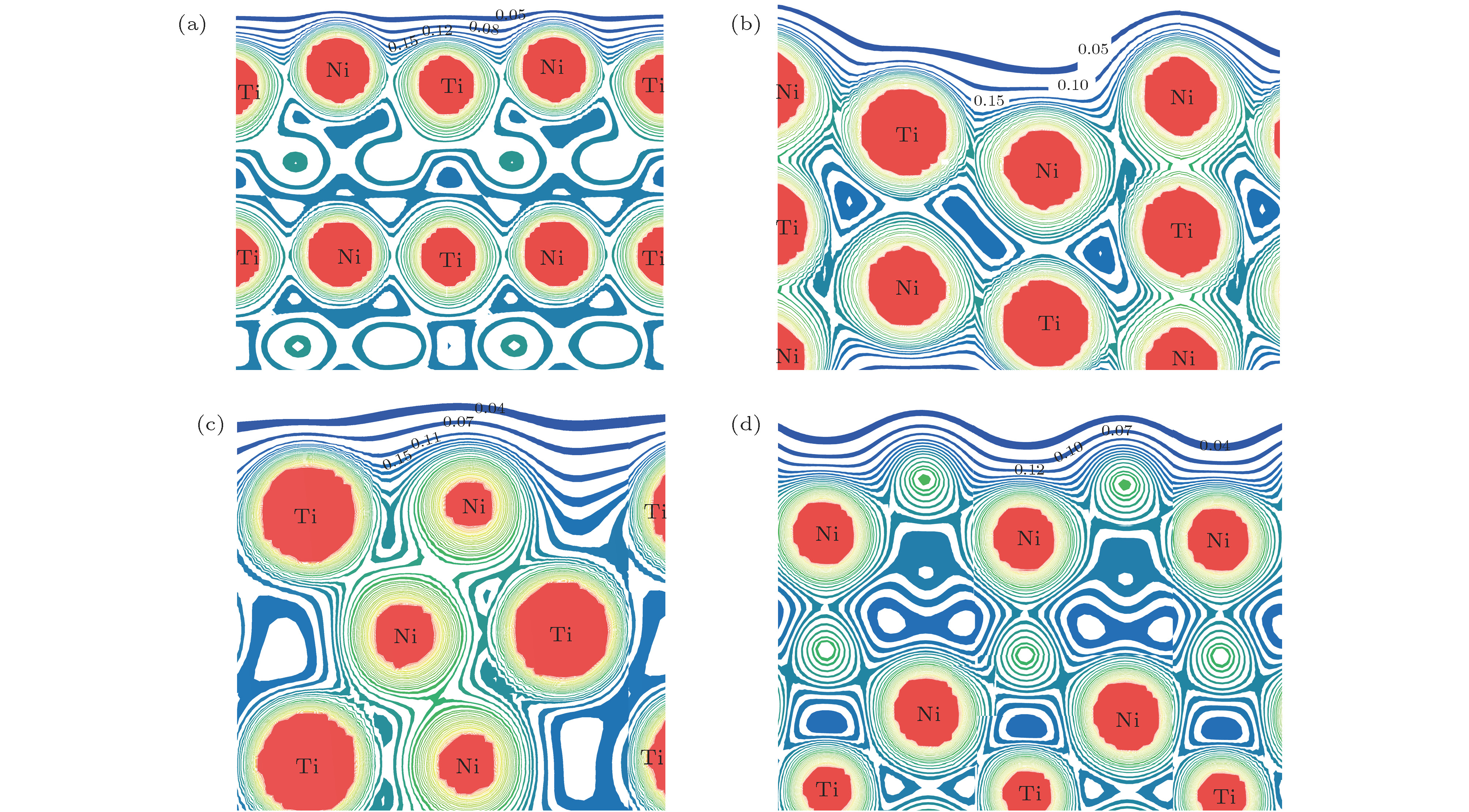
图 7 B2-和B19'-NiTi表面构型总电子密度分布 (a) B2-NiTi (101)_NiTi; (b) B2-NiTi (111)_Ni; (c) B19'-NiTi (010)_NiTi; (d) B19'-NiTi (101)_Ni
Fig. 7. Total electron density distribution of B2- and B19'-NiTi surface configurations: (a) B2-NiTi (101)_NiTi; (b) B2-NiTi (111)_Ni; (c) B19'-NiTi (010)_NiTi; (d) B19'-NiTi (101)_Ni.
表 1 NiTi合金的晶格常数、密度、剪切模量、体模量及生成焓
Table 1. Calculated cell parameters, density, shear modulus, bulk modulus and formation enthalpy.
Compounds a/Å b/Å c/Å V/Å3 G/MPa B/MPa ${\Delta _{\rm{r}}}H$/eV·atom–1 B2-NiTi 3.015 (3.033a, 3.016b, 3.01c) — — 27.402 (27.901a, 27.434b, 27.27c) 69.0 (73d) 155.5 (142.3a, 150.0b, 142e) –0.374 (–0.35f) B19'-NiTi 4.646 (4.685g, 4.813h, 4.631i) 4.108 (4.035g, 4.121h, 4.10i) 2.898 (2.941g, 3.007h, 2.885i) 55.705 (55.080g, 58.610h, 54.84i) 26.2 (23j) 148.9 (147k, 158f) –0.328 注: a, b, d, g, h, j, k为理论参考值, Ref.[21-22,23,3,26,27-28]; c, 实验参考值, Inorganic Crystal Structure Database (ICSD) #105413; e, 实验参考值Ref.[24]; f, 实验参考值, Ref.[25]; i, 实验参考值, ICSD #240195. 表 2 B2-NiTi表面原子层位移相对体相间距的变化率随切片厚度的变化 (%)
Table 2. Relaxations of B2-NiTi surfaces with different terminations and slab thickness given in terms of the change of interlayer spacing in percent of the bulk spacing (%).
Surface Termination Interlayer Slab thickness 3 5 7 9 11 (101) Ni, Ti ${\varDelta _{12}}$ –9.67 –10.42 –9.99 –9.88 –9.91 ${\varDelta _{23}}$ –0.19 1.18 1.99 1.78 ${\varDelta _{34}}$ –0.83 –0.65 –0.47 ${\varDelta _{45}}$ 0.43 1.15 ${\varDelta _{56}}$ 0.57 (100) Ni ${\varDelta _{12}}$ –1.77 –8.13 –8.89 –8.78 –8.93 ${\varDelta _{23}}$ 3.85 3.48 2.79 2.76 ${\varDelta _{34}}$ –0.72 –0.41 0.17 ${\varDelta _{45}}$ 1.11 –0.37 ${\varDelta _{56}}$ 2.18 Ti ${\varDelta _{12}}$ –2.24 –21.68 –17.08 –15.16 –16.68 ${\varDelta _{23}}$ 15.42 12.14 7.11 10.78 ${\varDelta _{34}}$ 0.01 4.03 2.82 ${\varDelta _{45}}$ –5.72 –1.93 ${\varDelta _{56}}$ 1.53 -
[1] 马蕾, 王旭, 尚家香 2014 63 233103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma L, Wang X, Shang J X 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 233103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 吴红丽, 赵新青, 宫声凯 2010 59 515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu H L, Zhao X Q, Gong S K 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wagner M F X, Windl W 2008 Acta. Mater. 56 6232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Huang X Y, Bungaro C, Godlevsky V, Rabe K M 2001 Phys. Rev. B 65 014108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Fukuda T, Kakeshita T, Houjoh H, Shiraishi S, Saburi T 1999 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 273−275 166
[6] 贾堤, 董治中, 于申军, 刘文西 1998 原子与分子 15 421
Jia D, Dong Z Z, Yu S J, Liu W X 1998 J. Atom. Mol. Phys. Sin. 15 421
[7] 姜振益, 李盛涛 2006 55 6032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang Z Y, Li S T 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 6032
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hua Y J, Liu X, Meng C G, Yang D Z 2003 J. Wuhan. Univ. Technol. 18 6
[9] 朱建新, 李永华, 孟繁玲, 刘常升, 郑伟涛, 王煜明 2008 57 7204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu J X, Li Y H, Meng F L, Liu C S, Zheng W T, Wang Y M 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 7204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 单迪, 何鑫玉, 方长青, 邵晖 2015 材料导报A: 综述篇 29 28
Shan D, He X Y, Fang C Q, Shao H 2015 Mater. Rev. A 29 28
[11] 尹大宇, 朱锦宇, 段永宏, 李矛, 韩建业, 朱庆生 2011 华南国防医学杂志 25 52
Yin D Y, Zhu J Y, Duan Y H, Li M, Han J Y, Zhu Q S 2011 Milit. Medi. J. Sou. China 25 52
[12] 孔祥确, 金学军, 刘剑楠 2016 功能材料 47 1007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kong X Q, Jin X J, Liu J N 2016 Func. Mater. 47 1007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 邵明增, 崔春娟, 杨洪波 2018 材料导报A: 综述篇 32 1181
Shao M Z, Cui C J, Yang H B 2018 Mater. Rev. A 32 1181
[14] 杨贤金, 朱胜利, 崔振铎, 姚康德 2001 功能材料 32 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang X J, Zhu S L, Cui Z D, Yao K D 2001 Func. Mater. 32 154
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Qiu D L, Wang A P, Yin Y S 2010 Appl. Surf. Sci. 257 1774
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li Y F, Tang S L, Gao Y M, Ma S Q, Zheng Q L, Cheng Y H 2017 Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 31 1750161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Nigussa K N, Støvneng J A 2011 Comput. Phys. Commun. 182 1979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Vishnu K G, Strachan A 2012 Phys. Rev. B 85 014114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Sandoval L, Haskins J B, Lawson J W 2018 Acta Mater. 154 182
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fischer T H, Almlof J 1992 J. Phys. Chem. 96 9768
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li G F, Zheng H Z, Shu X Y, Peng P 2016 Met. Mater. Int. 22 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Pfetzing-Micklich J, Somsen C, Dlouhy A, Begau C, Hartmaier A, Wagner M F X, Eggeler G 2013 Acta Mater. 61 602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Mercier O, Melton K N, Gremaud G, Häji J 1980 J. Appl. Phys. 51 1833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Hatcher N, Kontsevoi O Y, Freeman A J 2009 Phys. Rev. B 80 144203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sestak P, Cerny M, Pokluda J 2008 Strength. Mater. 40 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sedlak P, Frost M, Kruisova A, Hirmanova K, Heller L, Sittner P 2014 J.Mater. Eng. Perf. 23 2591
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zeng Z Y, Hu C E, Cai L C, Chen X R, Jing F Q 2010 Physica B 405 3665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Fiorentini V, Methfessel M 1996 J. Phys-Condens. Mat. 8 6525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Lazzeri M, Vittadini A, Selloni A 2001 Phys. Rev. B 63 155409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 13538
- PDF下载量: 184
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: