-
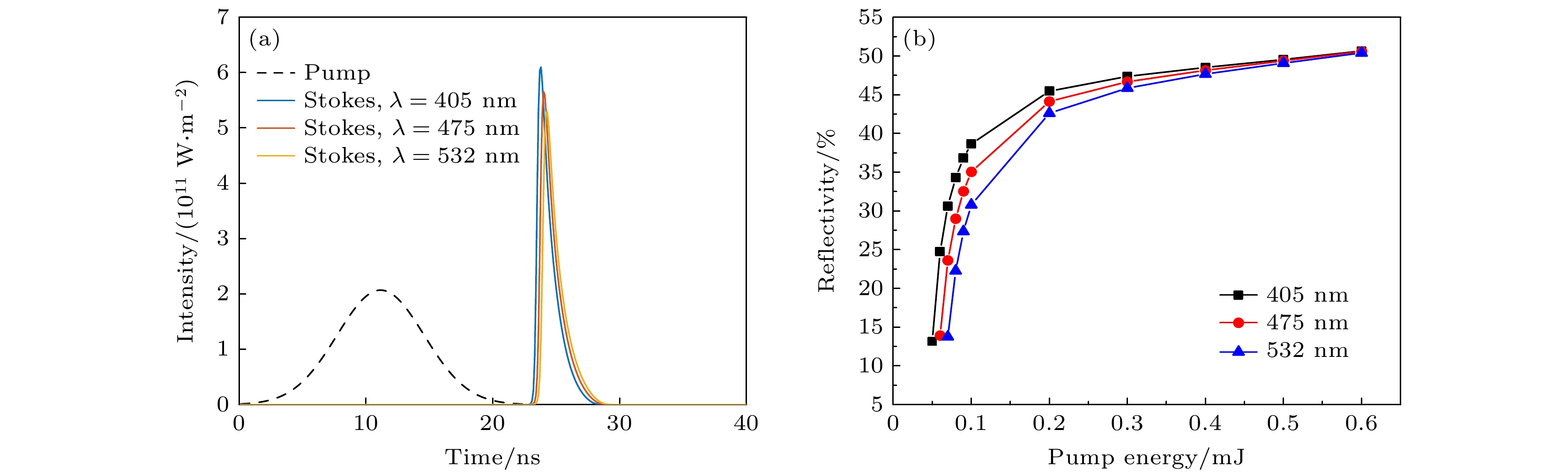
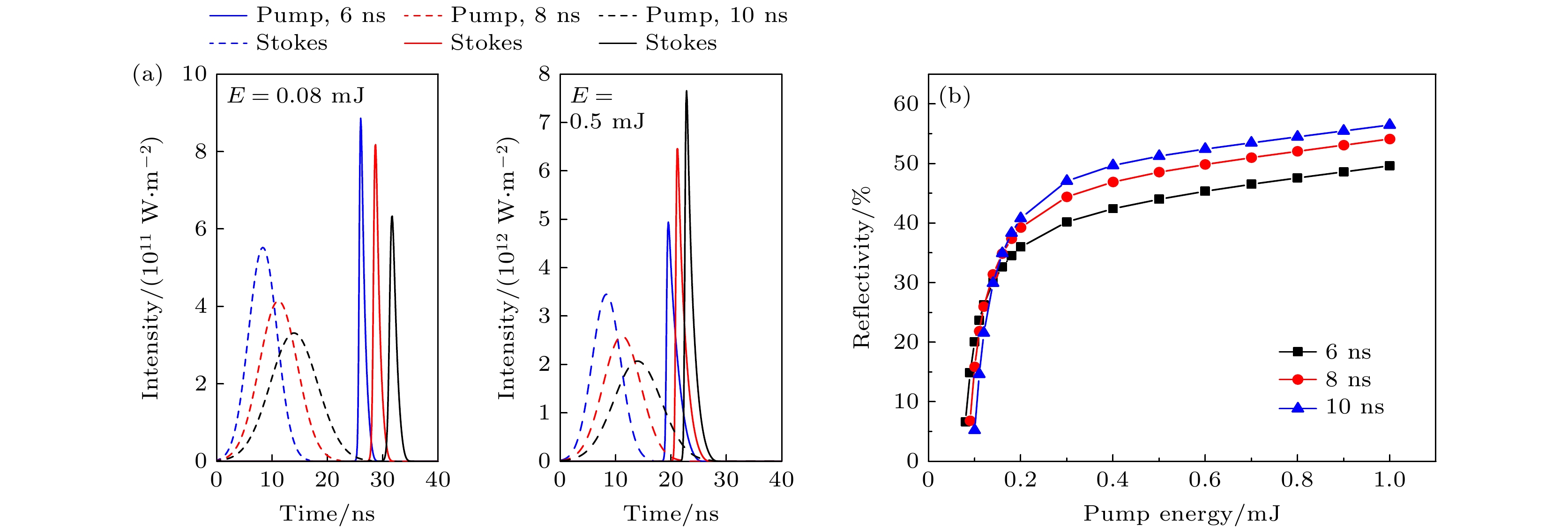
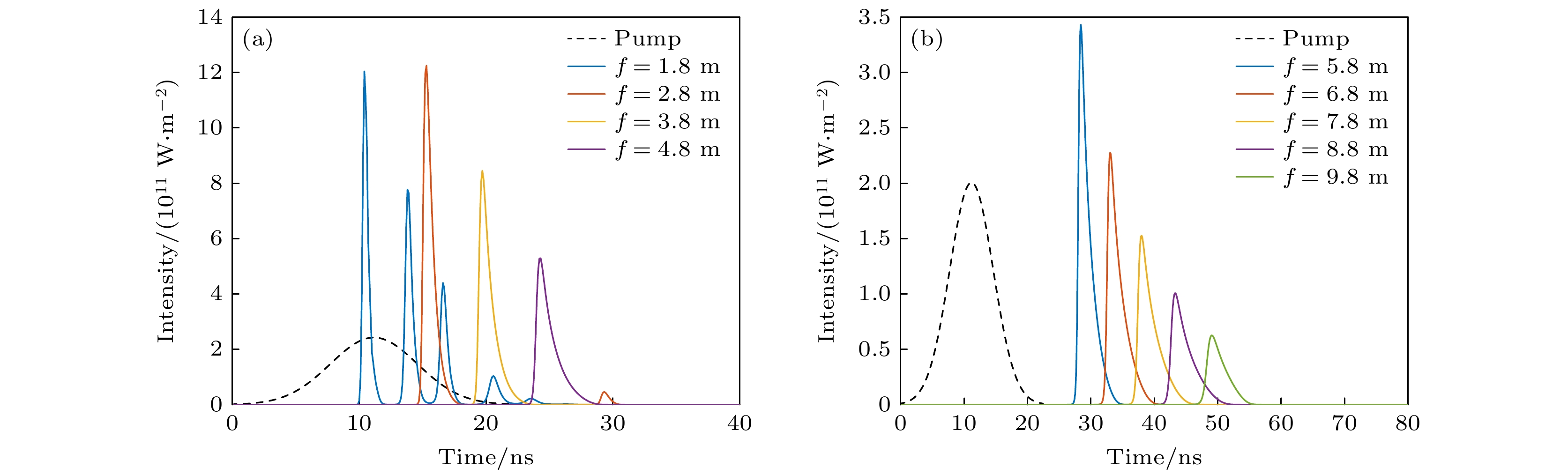
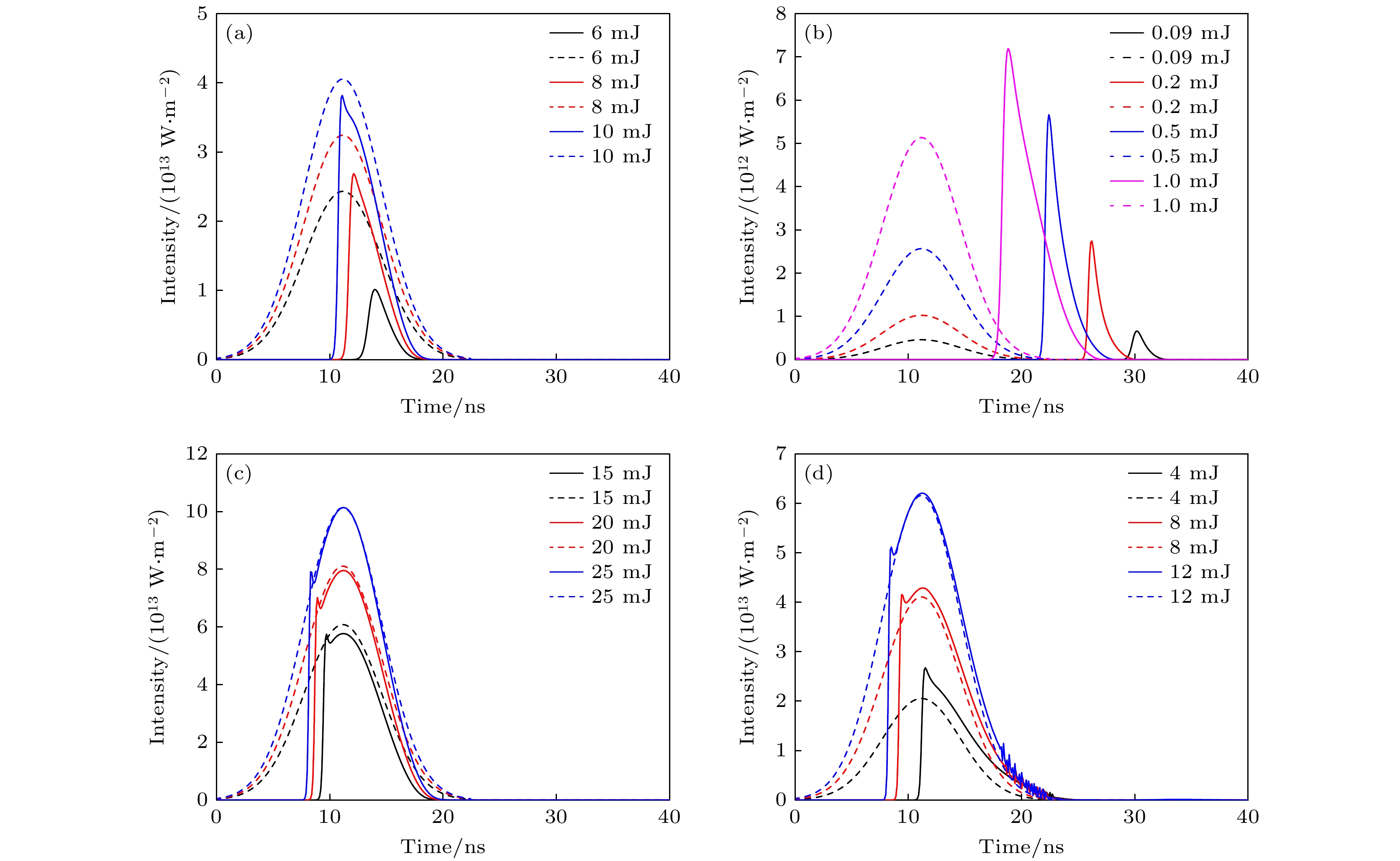
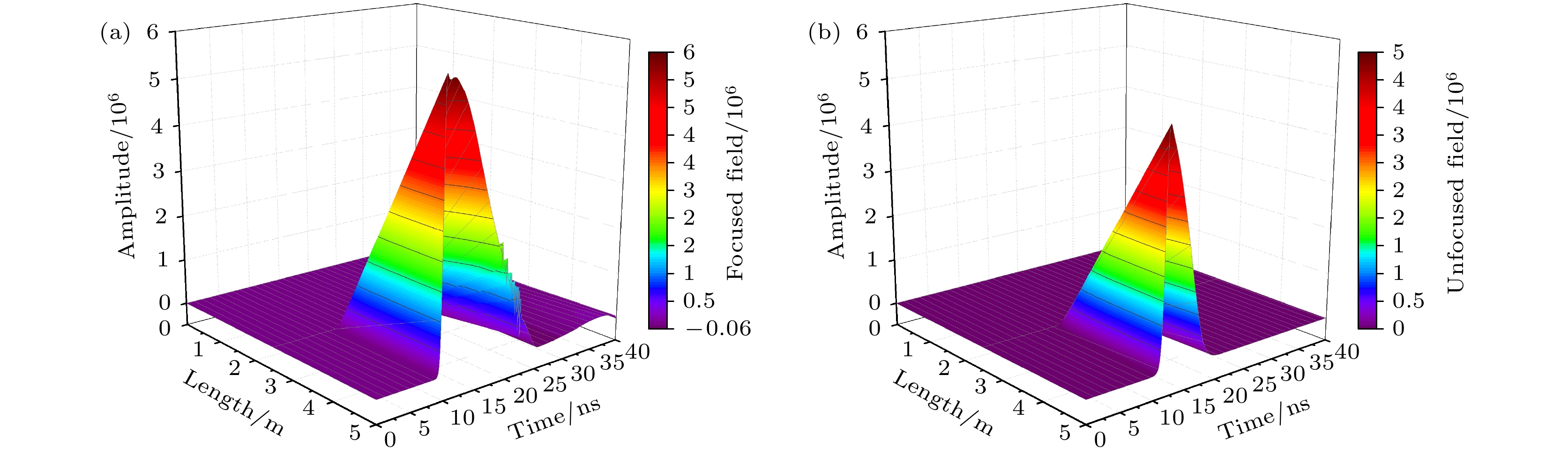
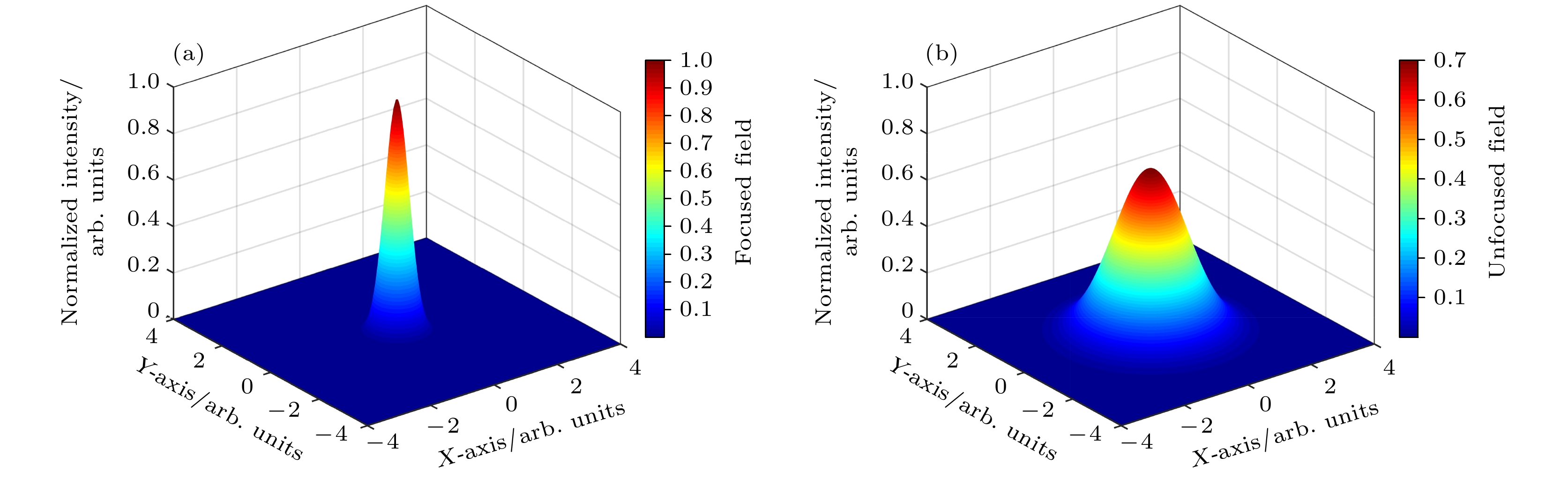
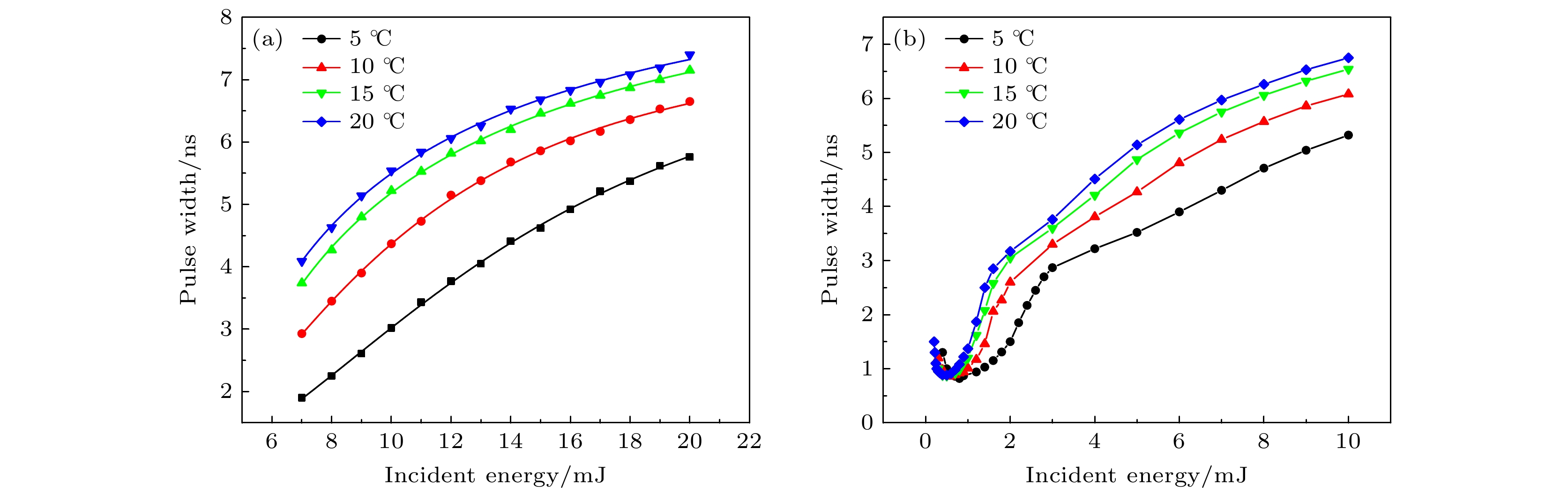
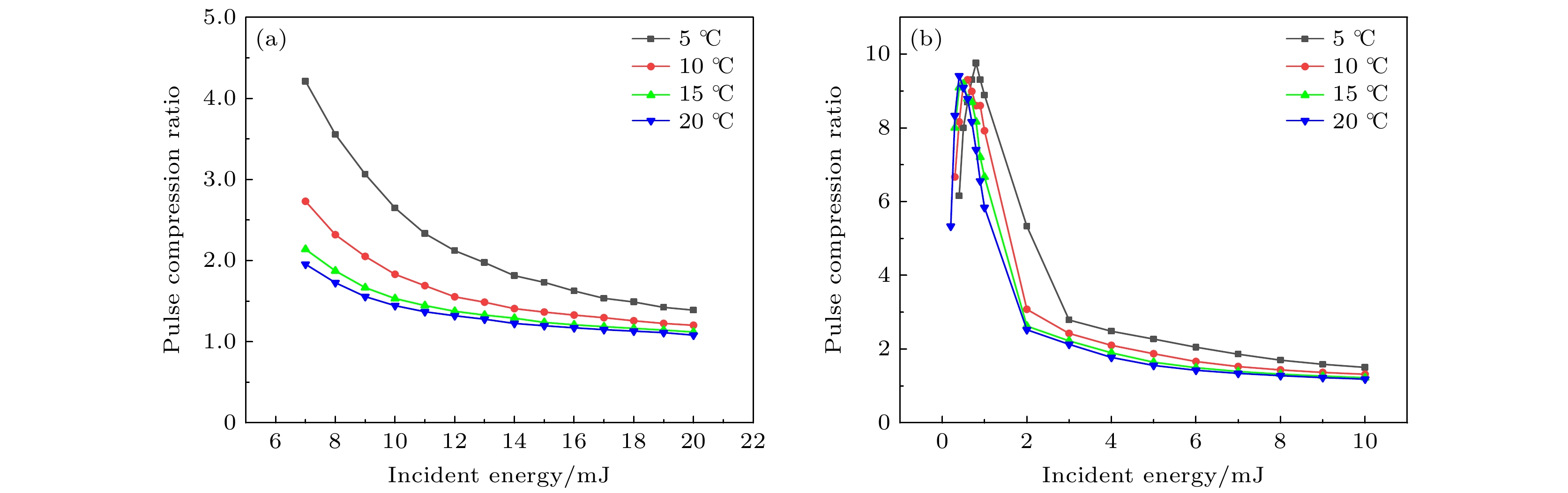
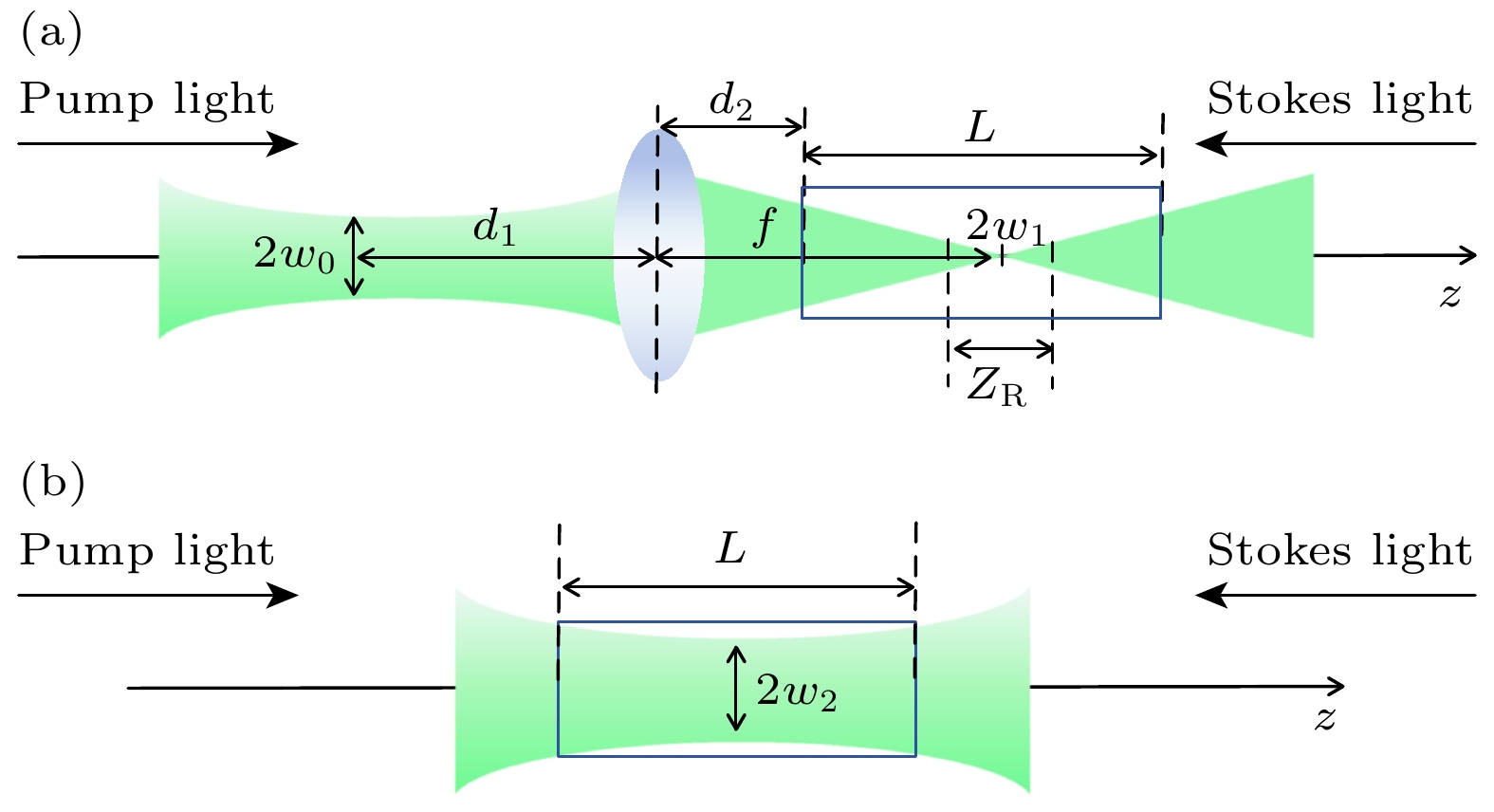
Stimulated Brillouin scattering lidar (SBS-LiDAR) technology possesses significant advantages such as high resolution, high signal-to-noise ratio, and strong anti-interference capacity, making it highly promising for simultaneous measurements of temperature, salinity, and sound velocity in seawater. Stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) is a nonlinear dynamic process characterized by temporal variations in its occurrence location, peak intensity, and spectral shape. Through numerical simulations of Stokes pulse, the conditions for SBS generation can be quantitatively determined, thereby establishing a theoretical foundation for optimizing lidar systems and enhancing their detection capabilities. Existing studies on Stokes pulses typically focus on specific experimental configurations under varying parameters, including medium properties, pump laser characteristics, and ambient environmental factors. There are still significant discrepancies in reported conclusions regarding the relationship between incident energy levels and pulse width variations, particularly in water-based environments where systematic research on the Stokes scattering pulse characteristics is clearly insufficient. In this study, a distributed noise model is used to theoretically simulate and analyze the time-domain signals of SBS in water at different laser wavelengths, pulse widths, and focal lengths. The characteristics of Stokes pulses generated by focused and non-focused configurations are investigated. The results indicate that under the same conditions, shorter incident wavelength produces significantly higher peak power of Stokes scattering light. The Stokes scattering light exhibits significant energy-dependent behavior: at low input energy, short pulse generates stronger scattering signal due to enhanced nonlinear interaction efficiency, while at high input energy, longer pulse exhibits excellent performance by maintaining temporal coherence. The larger focal length results in lower peak power but better pulse fidelity. As the incident energy increases, the pulse width of Stokes scattering light in the non-focused configuration exhibits a continuous increase. In contrast, for the focused configuration, the pulse width initially decreases and then increases, exhibiting an optimal compression value influenced by temperature and energy. At lower temperatures, the Stokes pulse width exhibits excellent compression performance near the threshold energy. Therefore, reducing secondary peak interference and suppressing spectral broadening are critical technical challenges that must be systematically addressed for short-range SBS-Lidar applications. In low-temperature detection scenarios, dynamic attenuation control becomes essential to prevent thermal stress-induced damage to photodetectors. These findings are of great significance in enhancing the performance of SBS-LiDAR system.
-
Keywords:
- stimulated Brillouin scattering /
- lidar /
- distributed noise model /
- time-domain pulse waveform
[1] Shen Y R 1984 The Principles of Nonlinear Optics (New York: Wiley
[2] Eliasson B, Senior A, Rietveld M, Phelps A D R, Cairns R A, Ronald K, Speirs D C, Trines R M G M, McCrea I, Bamford R, Mendonça J T, Bingham R 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 6209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhao Y, Lei A, Kang N, Li F, Li X, Liu H, Lin Z, Yin H, Xu Y, Yi Y, Xu Z 2024 Phys. Rev. E 110 065206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gonzalez-Herraez M, Song K Y, Thévenaz L 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 081113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wei W, Yi L L, Jaouèn Y, Morvan M, Weisheng H 2015 Opto-Electronics and Communications Conference (OECC) Shanghai, China June 28–July 2, 2015 p1
[6] Ballmann C W, Thompson J V, Traverso A J, Meng Z, Scully M O, Yakovlev V V 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 18139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ballmann C W, Meng Z, Traverso A J, Scully M O, Yakovlev V V 2017 Optica 4 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Shi J, Ouyang M, Gong W, Li S, Liu D 2008 Appl. Phys. B 90 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shi J, Xu J, Guo Y, Luo N, Li S, He X 2021 Phys. Rev. Appl 15 054024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xu N, Liu Z, Zhang X, Xu Y, Luo N, Li S, Xu J, He X, Shi J 2021 Opt. Express 29 36442
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Shi J, Xu N, Luo N, Li S, Xu J, He X 2022 Opt. Express 30 16419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Maier M, Rother W, Kaiser W 1967 Appl. Phys. Lett. 10 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hon D T 1981 Opt. Lett. 5 516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Eichler H J, Menzel R, Sander R, Smandek B 1992 Opt. Commun. 89 260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 徐德 2008 硕士学位论文 (杭州: 浙江大学)
Xu D 2008 M. S. Thesis ( Hangzhou: Zhejiang University
[16] 刘照虹 2018 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Liu Z H 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[17] 哈斯乌力吉, 吕志伟, 滕云鹏, 刘述杰, 李强, 何伟明 2007 56 878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hasi W L J, Lv Z W, Teng Y P, Liu S J, Li Q, He W M 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 郭少锋, 陆启生, 李强, 程湘爱, 邓少永, 曾学文 2004 强激光与粒子束 16 1106
Guo S F, Lu Q S, Li Q, Cheng X A, Deng S Y, Zeng X W 2004 High Power Laser Part. Beams 16 1106
[19] 邓少永, 郭少锋, 陆启生, 程湘爱 2005 54 3164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng S Y, Guo S F, Lu Q S, Cheng X A 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 3164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] He X, Tang Y, Shi J, Liu J, Cheng W, Mo X 2012 J. Mod. Opt. 59 1410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 龚华平, 吕志伟, 林殿阳, 刘松江 2007 56 5263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong H P, Lü Z W, Lin D Y, Liu S J 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 5263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu L, Bai Z, Chen Y, Jin D, Fan R, Qi Y, Ding J, Yan B, Wang Y, Lu Z 2022 Opt. Commun 515 128205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Boyd R W, Rzaewski K, Narum P 1990 Phys. Rev. A 42 5514
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Levent S 2014 Electromagnetic Modeling and Simulation (IEEE) (New York: Wiley-IEEE Press) pp407–513
[25] Schiemann S, Ubachs W, Hogervorst W 1997 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 33 358
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shi J, Tang Y, Wei H, Zhang L, Zhang D, Shi J, Gong W, He X, Yang K, Liu D 2012 Appl. Phys. B 108 717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Feng C, Xu X, Diels J C 2017 Opt. Express 25 12421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hirschberg J G, Byrne J D, Wouters A W, Boynton G C 1984 Appl. Opt. 23 2624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Millard R C, Seaver G 1990 Deep Sea Res. Part A 37 1909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Roquet F, Madec G, McDougall T J, Barker P M 2015 Ocean Modell. 90 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Damzen M J, Vlad V, Babin V, Mocofanescu A 2003 Stimulated Brillouin Scattering: Fundamentals and Applications (London: Institute of Physics Publishing) pp1–190
-
表 1 数值模拟参数设置
Table 1. Parameter setting for numerical simulation.
参数 数值 参数 数值 波长/nm 532 增益系数/(cm·GW–1) 3.8 脉宽/ns 8 折射率 1.333 光斑尺寸/mm 2.5 声子寿命/ps 200 介质池长/m 5 衰减系数/m–1 0.06 -
[1] Shen Y R 1984 The Principles of Nonlinear Optics (New York: Wiley
[2] Eliasson B, Senior A, Rietveld M, Phelps A D R, Cairns R A, Ronald K, Speirs D C, Trines R M G M, McCrea I, Bamford R, Mendonça J T, Bingham R 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 6209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhao Y, Lei A, Kang N, Li F, Li X, Liu H, Lin Z, Yin H, Xu Y, Yi Y, Xu Z 2024 Phys. Rev. E 110 065206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gonzalez-Herraez M, Song K Y, Thévenaz L 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 081113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wei W, Yi L L, Jaouèn Y, Morvan M, Weisheng H 2015 Opto-Electronics and Communications Conference (OECC) Shanghai, China June 28–July 2, 2015 p1
[6] Ballmann C W, Thompson J V, Traverso A J, Meng Z, Scully M O, Yakovlev V V 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 18139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ballmann C W, Meng Z, Traverso A J, Scully M O, Yakovlev V V 2017 Optica 4 124
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Shi J, Ouyang M, Gong W, Li S, Liu D 2008 Appl. Phys. B 90 569
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shi J, Xu J, Guo Y, Luo N, Li S, He X 2021 Phys. Rev. Appl 15 054024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xu N, Liu Z, Zhang X, Xu Y, Luo N, Li S, Xu J, He X, Shi J 2021 Opt. Express 29 36442
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Shi J, Xu N, Luo N, Li S, Xu J, He X 2022 Opt. Express 30 16419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Maier M, Rother W, Kaiser W 1967 Appl. Phys. Lett. 10 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hon D T 1981 Opt. Lett. 5 516
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Eichler H J, Menzel R, Sander R, Smandek B 1992 Opt. Commun. 89 260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 徐德 2008 硕士学位论文 (杭州: 浙江大学)
Xu D 2008 M. S. Thesis ( Hangzhou: Zhejiang University
[16] 刘照虹 2018 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Liu Z H 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[17] 哈斯乌力吉, 吕志伟, 滕云鹏, 刘述杰, 李强, 何伟明 2007 56 878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hasi W L J, Lv Z W, Teng Y P, Liu S J, Li Q, He W M 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 878
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 郭少锋, 陆启生, 李强, 程湘爱, 邓少永, 曾学文 2004 强激光与粒子束 16 1106
Guo S F, Lu Q S, Li Q, Cheng X A, Deng S Y, Zeng X W 2004 High Power Laser Part. Beams 16 1106
[19] 邓少永, 郭少锋, 陆启生, 程湘爱 2005 54 3164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Deng S Y, Guo S F, Lu Q S, Cheng X A 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 3164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] He X, Tang Y, Shi J, Liu J, Cheng W, Mo X 2012 J. Mod. Opt. 59 1410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 龚华平, 吕志伟, 林殿阳, 刘松江 2007 56 5263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong H P, Lü Z W, Lin D Y, Liu S J 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 5263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhu L, Bai Z, Chen Y, Jin D, Fan R, Qi Y, Ding J, Yan B, Wang Y, Lu Z 2022 Opt. Commun 515 128205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Boyd R W, Rzaewski K, Narum P 1990 Phys. Rev. A 42 5514
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Levent S 2014 Electromagnetic Modeling and Simulation (IEEE) (New York: Wiley-IEEE Press) pp407–513
[25] Schiemann S, Ubachs W, Hogervorst W 1997 IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 33 358
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shi J, Tang Y, Wei H, Zhang L, Zhang D, Shi J, Gong W, He X, Yang K, Liu D 2012 Appl. Phys. B 108 717
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Feng C, Xu X, Diels J C 2017 Opt. Express 25 12421
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Hirschberg J G, Byrne J D, Wouters A W, Boynton G C 1984 Appl. Opt. 23 2624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Millard R C, Seaver G 1990 Deep Sea Res. Part A 37 1909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Roquet F, Madec G, McDougall T J, Barker P M 2015 Ocean Modell. 90 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Damzen M J, Vlad V, Babin V, Mocofanescu A 2003 Stimulated Brillouin Scattering: Fundamentals and Applications (London: Institute of Physics Publishing) pp1–190
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 897
- PDF Downloads: 39
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: