-
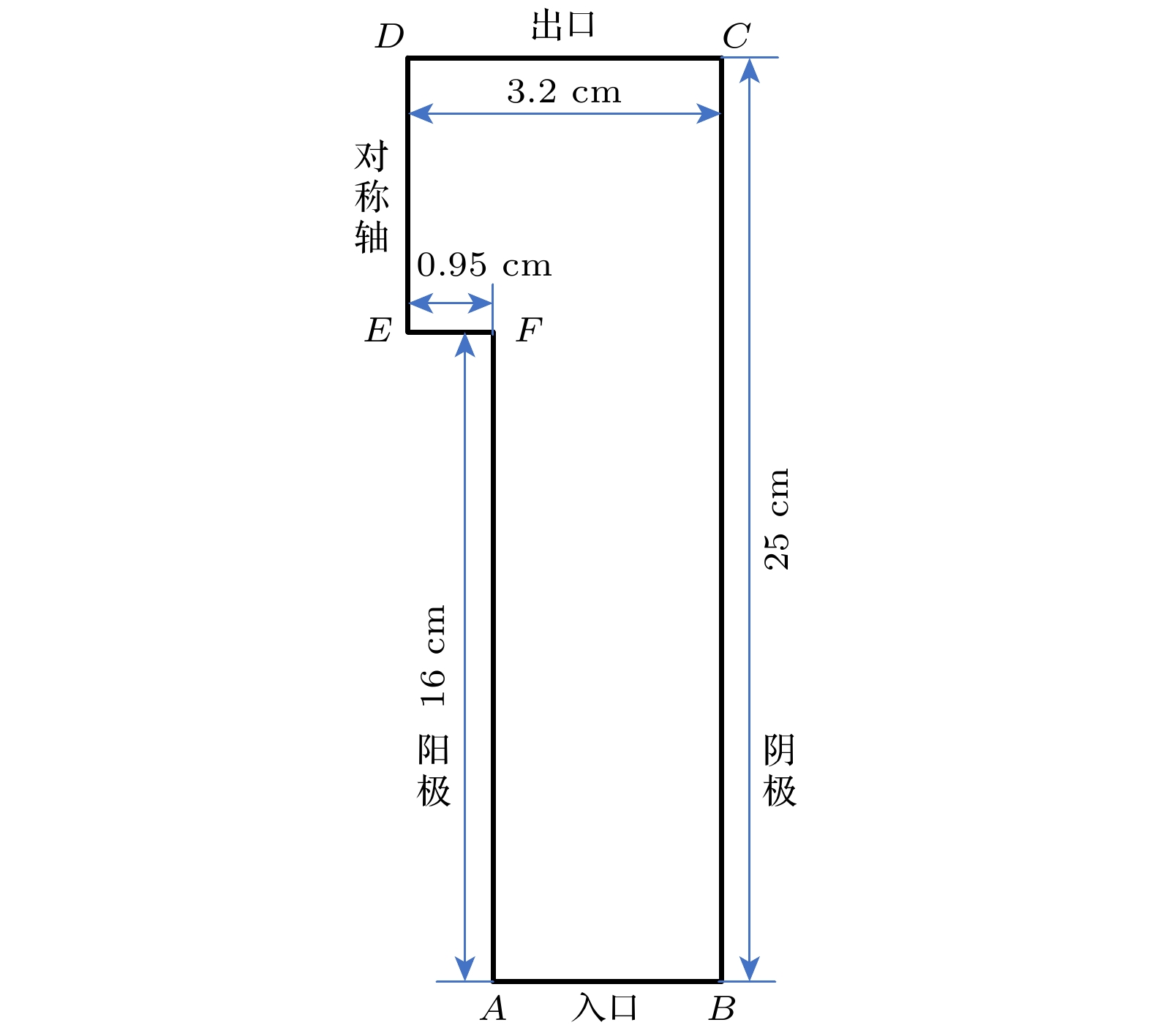
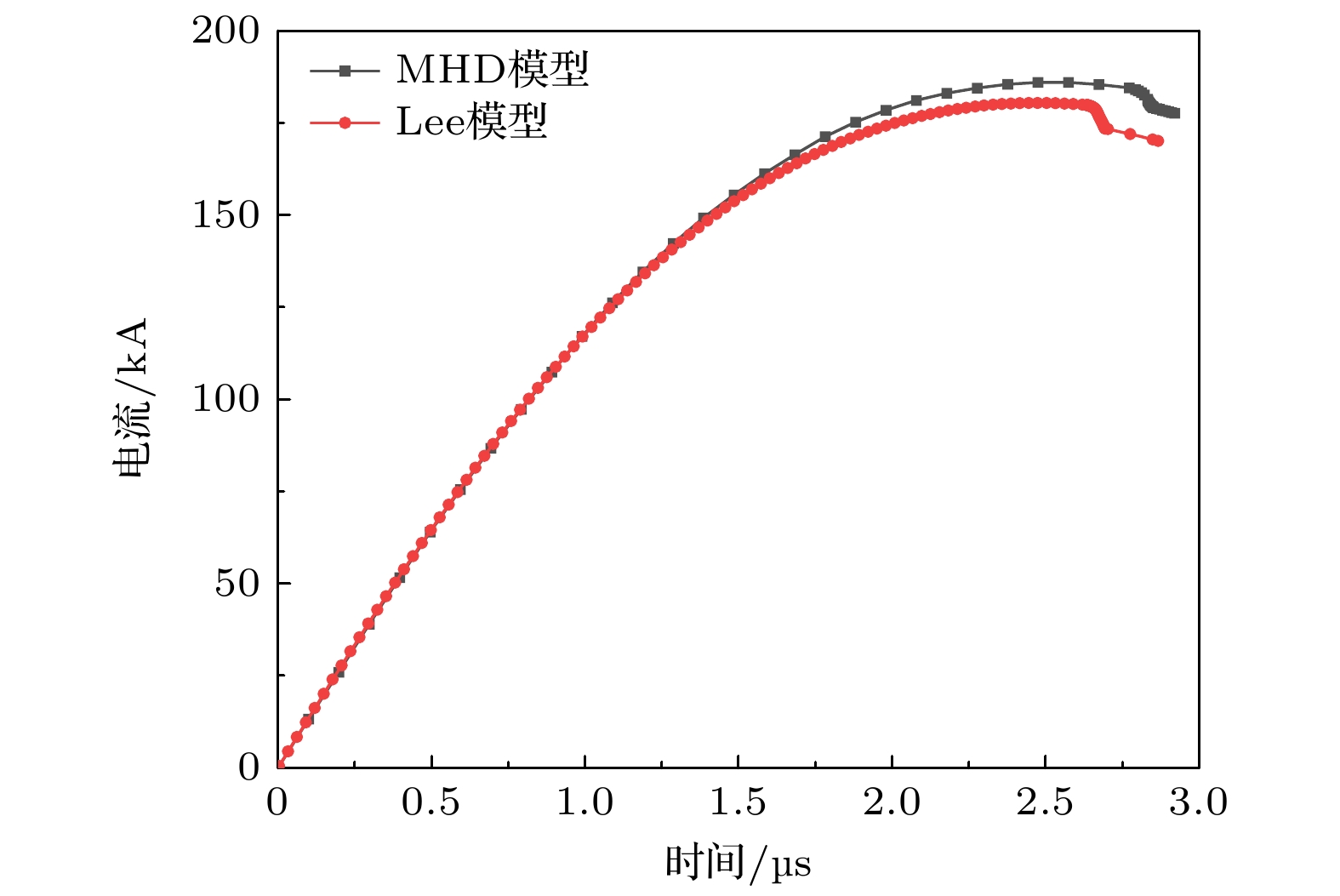
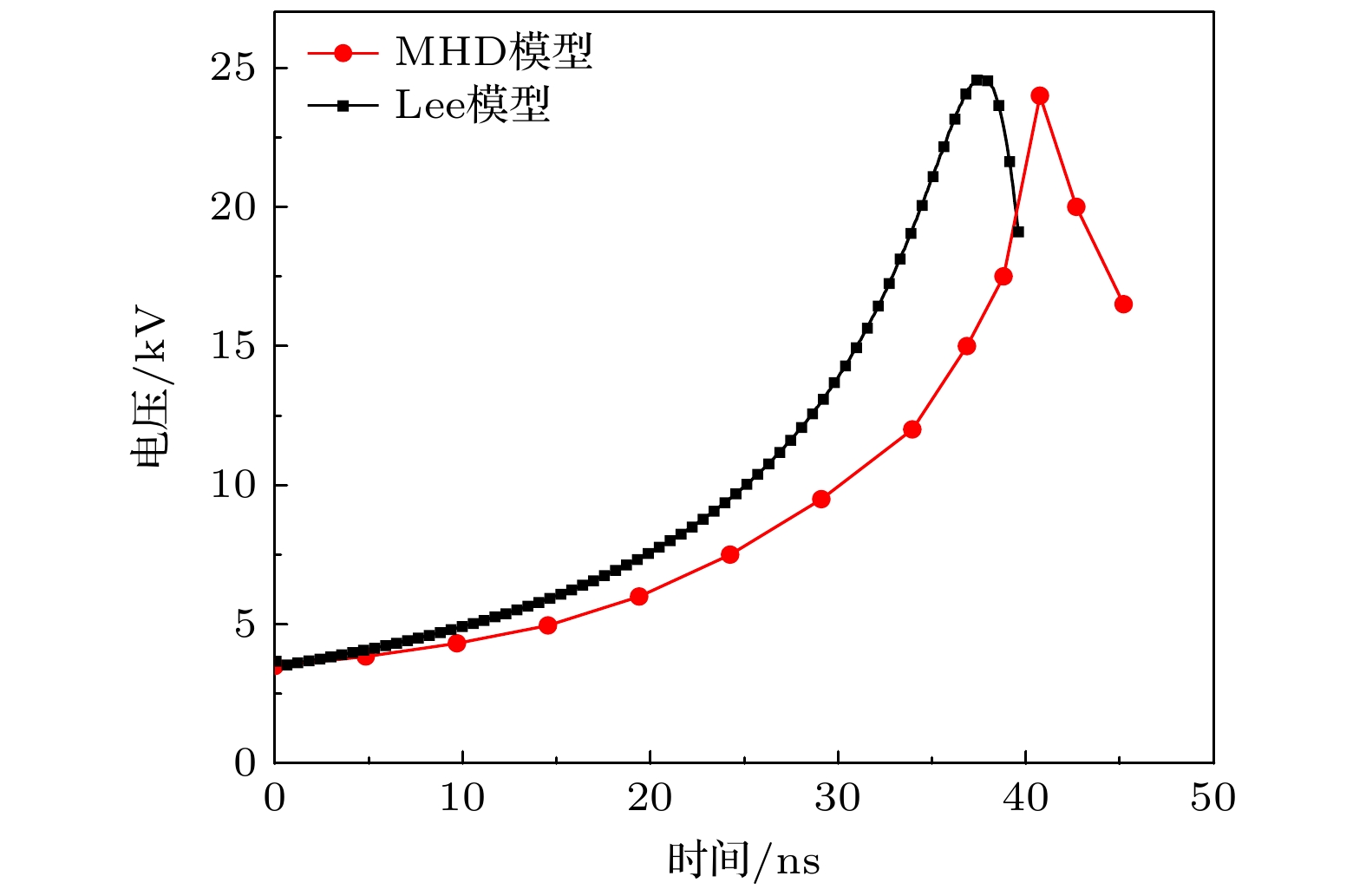
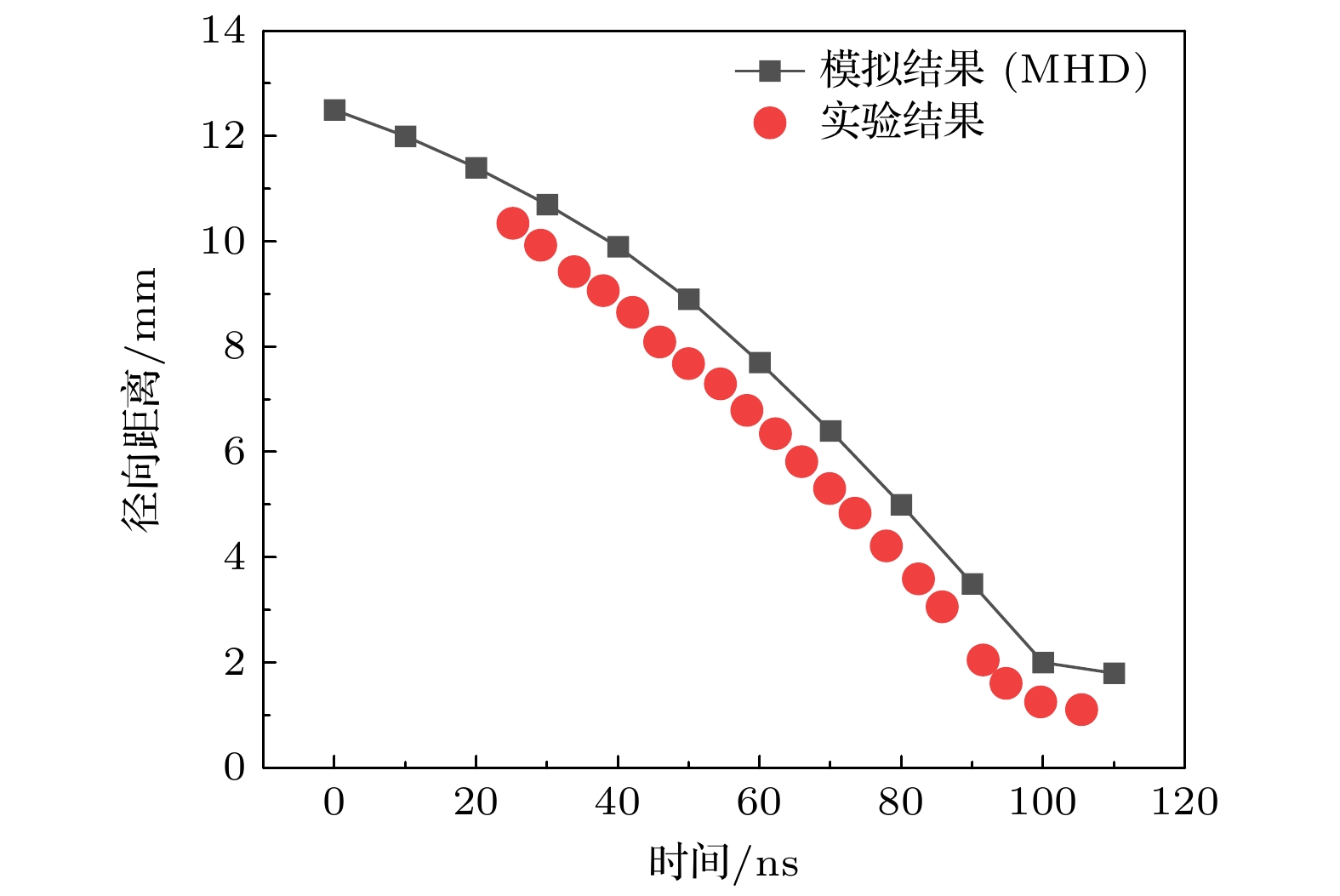
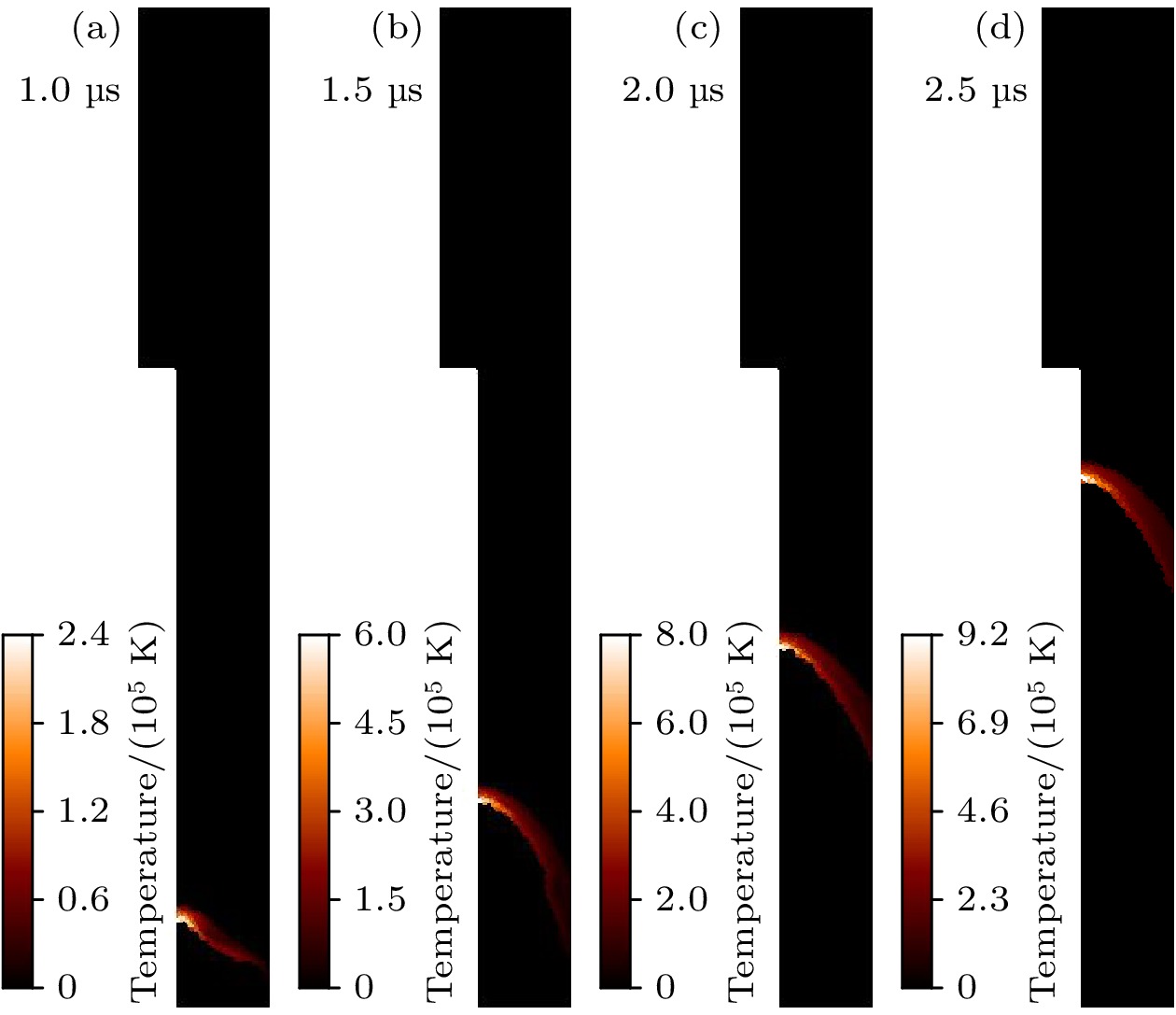
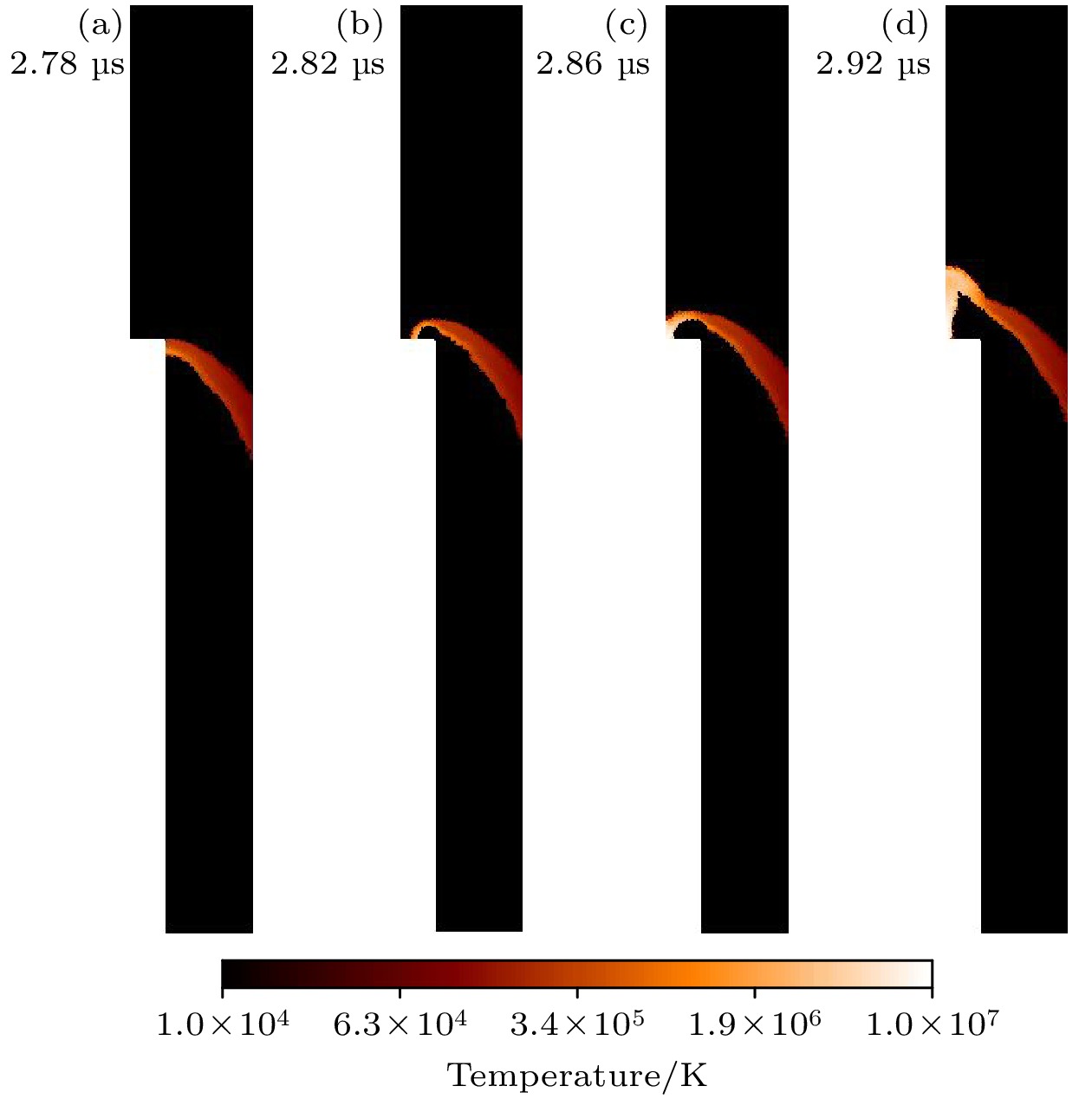
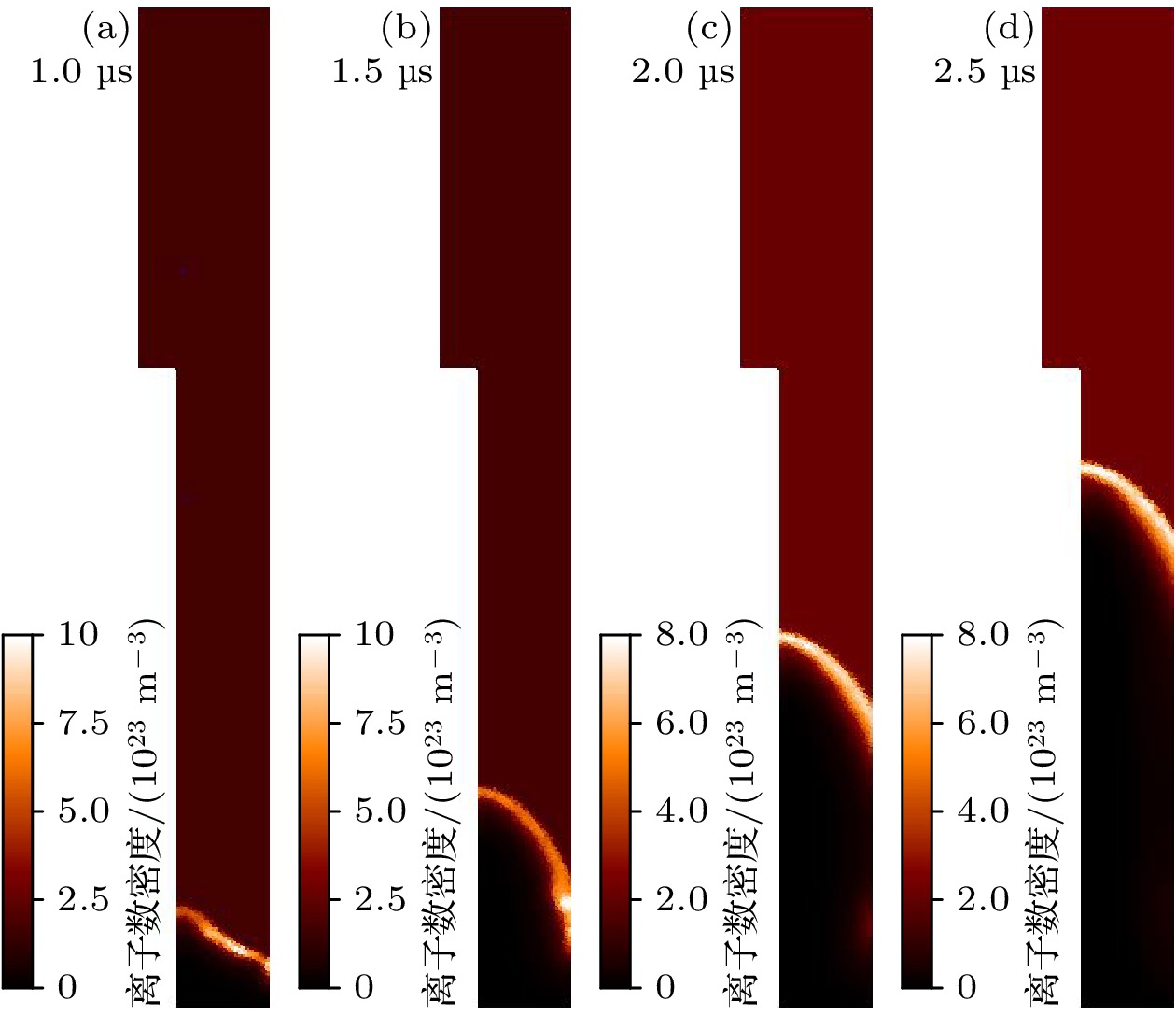
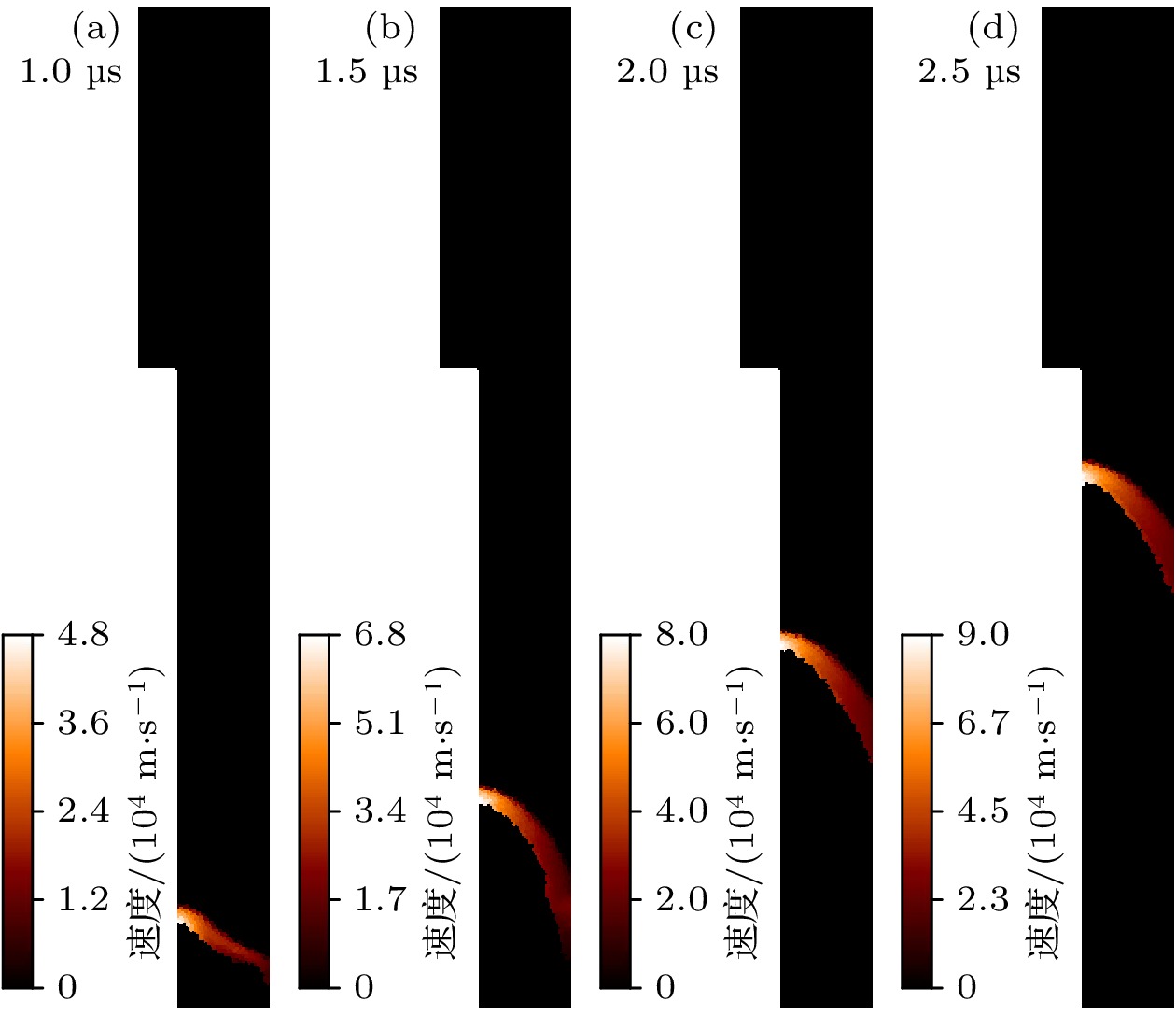
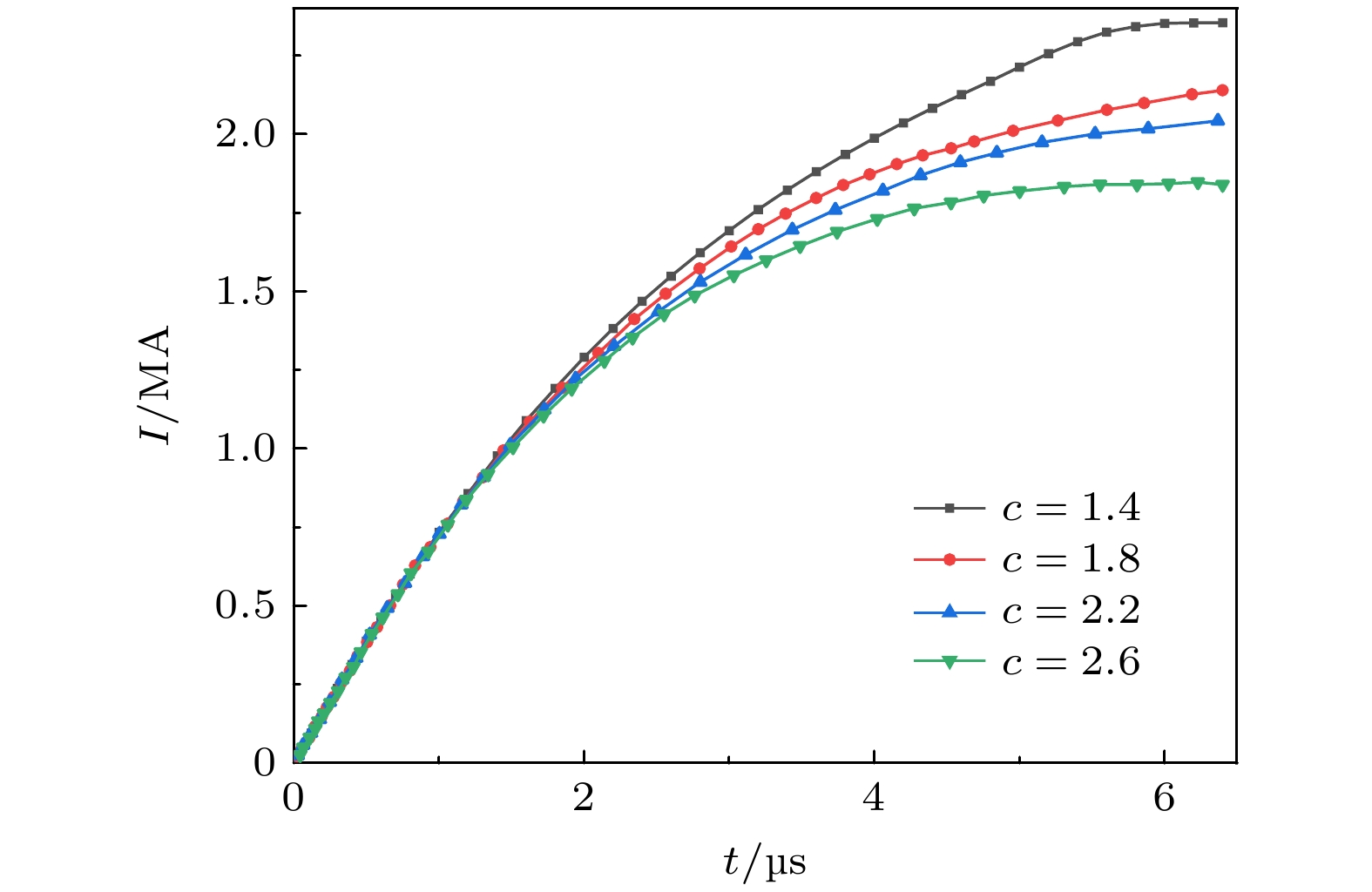
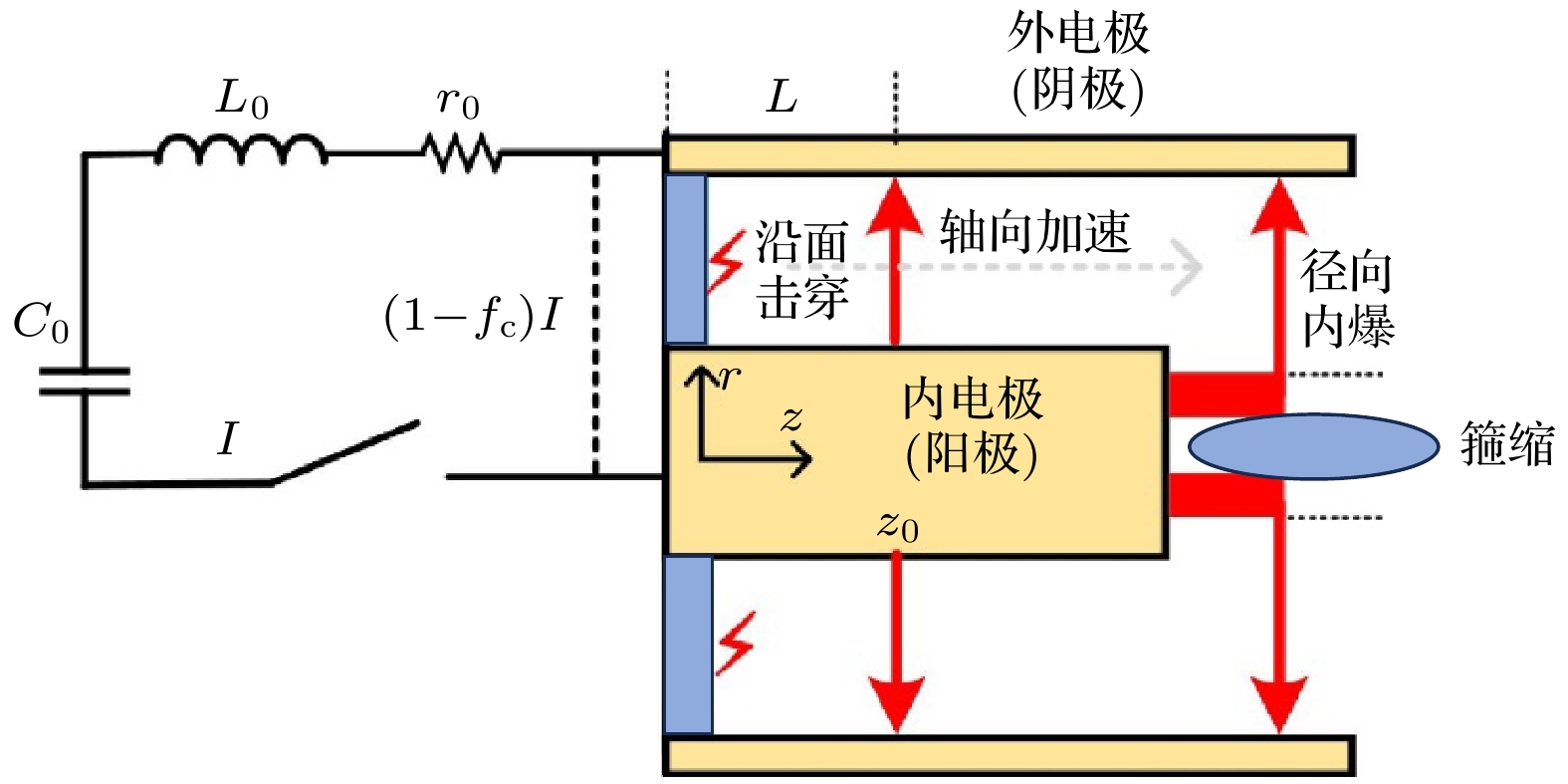
Dense plasma focus (DPF) device is a pulsed high current discharge device, which is widely used in particle accelerator, controlled nuclear fusion, space propulsion, and pulsed neutron source. However, existing models for DPF dynamics, including semi-empirical snowplow approximations and particle-in-cell (PIC) methods, face limitations in balancing computational efficiency and comprehensive physical descriptions. In contrast, magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) models can comprehensively analyze the macroscopic phenomena (e.g. sheath motion, current distribution, fluid instabilities) and the influence of parameters (e.g. electrode geometry, gas pressure, and driving current waveforms) on DPF performance. Although MHD cannot self-consistently resolve kinetic behaviors like high-energy particle beams or neutron production during pinch phases, it remains highly valuable for investigating macroscopic DPF physics when quantitative neutron yield analysis is unnecessary. Therefore, a two-temperature MHD model coupled with an external RLC circuit is developed in this paper, which combines electron-ion thermal nonequilibrium, resistive effects, and plasma transport coefficients derived from Braginskii formulations. The model is rigorously validated based on experimental data from two benchmark DPF devices (UNU and UDMPF1), demonstrating high consistency in current waveform, voltage profile, and radial implosion trajectory. The research shows that the DPF plasma sheath is continuously accelerated along the axial direction under the action of the Lorentz force. When it moves to the end of the inner electrode, due to Z-pinch effect, the plasma sheath bends radially inward and is further compressed onto the axis of symmetry, finally forming a high-temperature and high-density plasma region in front of the inner electrode end, the so-called plasma focus. For the UNU device, simulations reveal distinct plasma evolution phases. One is the axial acceleration (0–2.5 μs), where the current sheath reaches a speed of up to 90 km/s under the dominance of Lorentz force, with ion temperatures rising from 1 eV to 100 eV, and the other is the radial implosion (2.78–2.90 μs), during which plasma density increases by an order of magnitude (reaching to ~1024 m–3) and ion temperature surges to ~1 keV through magnetically driven compression. Further studies also find that for large DPF devices, with the inductance reduced and the capacitance increased, the circuit current is easily saturated. However, increasing the circuit voltage has a more significant effect on the increase of current. This paper shows that for large DPF devices, the ratio of anode radius to cathode radius needs to be as small as possible, which can increase the peak current and pinch current of DPF while keeping other parameters unchanged.
-
Keywords:
- dense plasma focus /
- magnetohydrodynamic simulation /
- plasma acceleration /
- pinch
[1] Filippov N, Filippova T, Vinogradov V 1962 Nucl. Fusion 2 577
[2] Mather J 1964 Phys. Fluids 7 S28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Khan I, Jabbar S, Hussain T 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 268 2228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Khan K, Ahmad R, Hussain T 2022 Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 177 892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Rawat R 2015 J. Phys. Conf. Ser 591 012021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Soto L 2005 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 A361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tang V, Adams M, Rusnak B 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Temple B, Barnouin O, Miley G H 1991 Fusion Sci. Technol. 19 846
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Thomas R, Yang Y, Miley G 2005 AIP Conf. Proc. 746 536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Auluck S 2023 Phys. Plasmas 30 043109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gribkov V, Latyshev S, Miklaszewski R 2010 Phys. Scr. 81 035502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Verma R, Roshan M, Malik F 2008 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 17 045020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lerner E J, Hassan S M, Karamitsos Z I, Fritsch R 2023 J. Fusion Energy 42 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bennett N, Blasco M, Breeding K, et al. 2016 Source and Diagnostic Development for a Neutron Diagnosed Subcritical Experiment North Las Vegas, NV (United States
[15] Bennett N, Blasco M, Constantino D 2016 Dense Plasma Focus Experimental Results and Plans for NDSE North Las Vegas, NV (United States
[16] Krishnan M 2012 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40 3189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bernard A, Coudevilie A, Jolas A 1975 Phys. Fluids 18 180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sadowski M, Herold H, Schmidt H 1984 Phys. Lett. A 105 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Decker G, Kies W, Nadolny R 1996 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 5 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Brzosko J S, Robouch B, Klobukowska J 1987 Fusion Sci. Technol. 12 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gribkov V, Bienkowska B, Borowiecki M, Dubrovsky A V, Ivanova-Stanik I, Karpinski L, Miklaszewski R A, Paduch M, Scholz M, Tomaszewski K 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 1977
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 浓密等离子体焦点研究小组 1975 24 309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dense Plasma Focus Group 1975 Acta Phys. Sin. 24 309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 吕铭方, 韩旻, 杨津基, 王新新 1996 清华大学学报 5 36
Lv M F, Han Y, Yang J J, Wang X X 1996 Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 5 36
[24] 王新新, 韩旻, 王志文, 刘坤 1999 中国科学 29 76
Wang X X, Han Y, Wang Z W, Liu K 1999 Sci. China 29 76
[25] 张贵新, 罗承沐, 王新新等 2002 高电压技术 28 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G X, Luo C M, Wang X X 2002 High Volt. Eng. 28 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 韩旻, 罗承沐, 王克超 1995 强激光与粒子束 7 461
Han Y, Luo C M, Wang K C 1995 High Power Laser Part. Beams 7 461
[27] 龙继东, 陈林, 丰树平 2019 高能量密度物理 2 42
Long J D, Chen L, Feng S P, 2019 High Energy Dens. Phys. 2 42
[28] 陈林, 丰树平, 高顺受 2004 中国科学 34 458
Chen L, Feng S P, Gao S S 2004 Sci. China 34 458
[29] 李名加, 范娟, 章法强 2018 强激光与粒子束 30 129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M J, Fan J, Zhang F Q 2018 High Power Laser Part. Beams 30 129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 郭洪生, 杨高照, 朱学彬 2012 核电子学与探测技术 32 880
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo H S, Yang G Z, Zhu X B 2012 Nucl. Electron. Detection Tech. 32 880
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Xi H, Liang C, Zhang F 2021 J. Instrum. 16 P12021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 谈效华, 戴晶怡, 米伦, 黄华国, 谢超美, 周明贵 2004 第三届北京核学会核应用技术学术交流会
Tan X H, Dai J Y, Mi L, Huang H G, Xie C M, Zhou M G 2004 The 3rd Beijing Nuclear Society Nuclear Application Technology Academic Exchange meeting
[33] Haines M 2011 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 53 093001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Auluck S, Kunes P, Paduch M, Sadowski M J, Krauz V I, Lee S, Soto L, Scholz M, Miklaszewski R, Schmidt H, Blagoev A, Samuelli M, Seng Y S, Springham S V, Talebitaher A, Pavez C, Akel M, Yap S L, Verma R, Kolacek, Keat P L C, Rawat R S, Abdou A, Zhang G X, Laas T 2021 Plasma 4 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Hart P J 1962 Phys. Fluids 5 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Lee S 2014 J. Fusion Energy 33 319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Potter D 1971 Phys. Fluids 14 1911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Garanin S F, Mamyshev V I 2008 Plasma Phys. Rep. 34 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Meehan B T, Niederhau H 2016 JDMS 13 153
[40] Schmidt A, Tang V, Welch D 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 205003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Schmidt A, Link A, Welch D 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 102703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Angus J, Link A, Schmid A 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 010701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] 刘全 2002 博士学位论文(北京: 中国工程物理研究院研究生院)
Liu Q 2002, Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Graduate School of China Academy of Engineering Physics
[44] Braginskii S 1965 Rev. Plasma Phys. 1 205
[45] Lim L H, Yap S, Lim L K, Lee M C, Poh H S, Ma J, Yap S S, Lee S 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 092702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Filippov N, Filippova T, Vinogradov V 1962 Nucl. Fusion 2 577
[2] Mather J 1964 Phys. Fluids 7 S28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Khan I, Jabbar S, Hussain T 2010 Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 268 2228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Khan K, Ahmad R, Hussain T 2022 Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 177 892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Rawat R 2015 J. Phys. Conf. Ser 591 012021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Soto L 2005 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 47 A361
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Tang V, Adams M, Rusnak B 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Temple B, Barnouin O, Miley G H 1991 Fusion Sci. Technol. 19 846
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Thomas R, Yang Y, Miley G 2005 AIP Conf. Proc. 746 536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Auluck S 2023 Phys. Plasmas 30 043109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gribkov V, Latyshev S, Miklaszewski R 2010 Phys. Scr. 81 035502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Verma R, Roshan M, Malik F 2008 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 17 045020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lerner E J, Hassan S M, Karamitsos Z I, Fritsch R 2023 J. Fusion Energy 42 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bennett N, Blasco M, Breeding K, et al. 2016 Source and Diagnostic Development for a Neutron Diagnosed Subcritical Experiment North Las Vegas, NV (United States
[15] Bennett N, Blasco M, Constantino D 2016 Dense Plasma Focus Experimental Results and Plans for NDSE North Las Vegas, NV (United States
[16] Krishnan M 2012 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40 3189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bernard A, Coudevilie A, Jolas A 1975 Phys. Fluids 18 180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sadowski M, Herold H, Schmidt H 1984 Phys. Lett. A 105 117
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Decker G, Kies W, Nadolny R 1996 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 5 112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Brzosko J S, Robouch B, Klobukowska J 1987 Fusion Sci. Technol. 12 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Gribkov V, Bienkowska B, Borowiecki M, Dubrovsky A V, Ivanova-Stanik I, Karpinski L, Miklaszewski R A, Paduch M, Scholz M, Tomaszewski K 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 1977
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 浓密等离子体焦点研究小组 1975 24 309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dense Plasma Focus Group 1975 Acta Phys. Sin. 24 309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 吕铭方, 韩旻, 杨津基, 王新新 1996 清华大学学报 5 36
Lv M F, Han Y, Yang J J, Wang X X 1996 Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 5 36
[24] 王新新, 韩旻, 王志文, 刘坤 1999 中国科学 29 76
Wang X X, Han Y, Wang Z W, Liu K 1999 Sci. China 29 76
[25] 张贵新, 罗承沐, 王新新等 2002 高电压技术 28 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G X, Luo C M, Wang X X 2002 High Volt. Eng. 28 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 韩旻, 罗承沐, 王克超 1995 强激光与粒子束 7 461
Han Y, Luo C M, Wang K C 1995 High Power Laser Part. Beams 7 461
[27] 龙继东, 陈林, 丰树平 2019 高能量密度物理 2 42
Long J D, Chen L, Feng S P, 2019 High Energy Dens. Phys. 2 42
[28] 陈林, 丰树平, 高顺受 2004 中国科学 34 458
Chen L, Feng S P, Gao S S 2004 Sci. China 34 458
[29] 李名加, 范娟, 章法强 2018 强激光与粒子束 30 129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li M J, Fan J, Zhang F Q 2018 High Power Laser Part. Beams 30 129
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 郭洪生, 杨高照, 朱学彬 2012 核电子学与探测技术 32 880
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo H S, Yang G Z, Zhu X B 2012 Nucl. Electron. Detection Tech. 32 880
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Xi H, Liang C, Zhang F 2021 J. Instrum. 16 P12021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 谈效华, 戴晶怡, 米伦, 黄华国, 谢超美, 周明贵 2004 第三届北京核学会核应用技术学术交流会
Tan X H, Dai J Y, Mi L, Huang H G, Xie C M, Zhou M G 2004 The 3rd Beijing Nuclear Society Nuclear Application Technology Academic Exchange meeting
[33] Haines M 2011 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 53 093001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Auluck S, Kunes P, Paduch M, Sadowski M J, Krauz V I, Lee S, Soto L, Scholz M, Miklaszewski R, Schmidt H, Blagoev A, Samuelli M, Seng Y S, Springham S V, Talebitaher A, Pavez C, Akel M, Yap S L, Verma R, Kolacek, Keat P L C, Rawat R S, Abdou A, Zhang G X, Laas T 2021 Plasma 4 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Hart P J 1962 Phys. Fluids 5 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Lee S 2014 J. Fusion Energy 33 319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Potter D 1971 Phys. Fluids 14 1911
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Garanin S F, Mamyshev V I 2008 Plasma Phys. Rep. 34 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Meehan B T, Niederhau H 2016 JDMS 13 153
[40] Schmidt A, Tang V, Welch D 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 205003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Schmidt A, Link A, Welch D 2014 Phys. Plasmas 21 102703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Angus J, Link A, Schmid A 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 010701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] 刘全 2002 博士学位论文(北京: 中国工程物理研究院研究生院)
Liu Q 2002, Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Graduate School of China Academy of Engineering Physics
[44] Braginskii S 1965 Rev. Plasma Phys. 1 205
[45] Lim L H, Yap S, Lim L K, Lee M C, Poh H S, Ma J, Yap S S, Lee S 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 092702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 745
- PDF Downloads: 29
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: