-
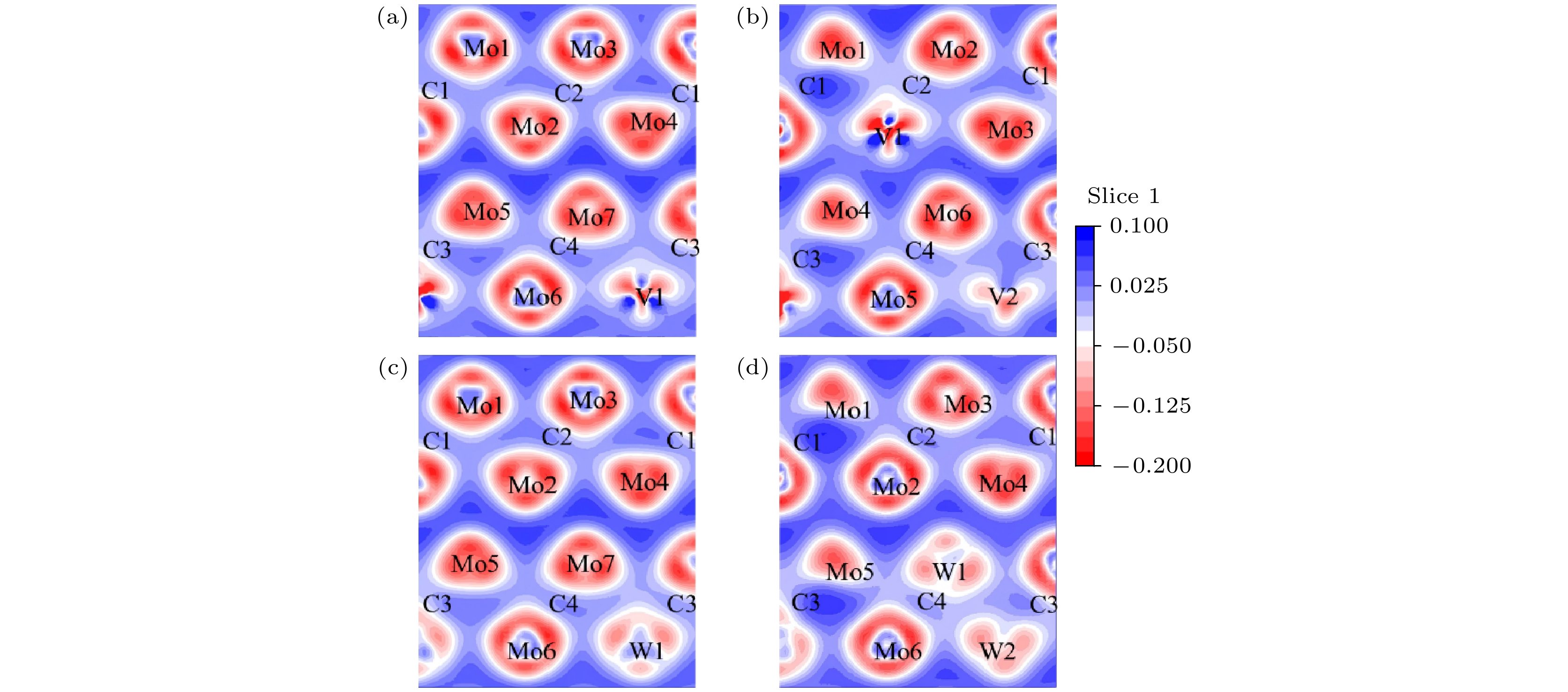
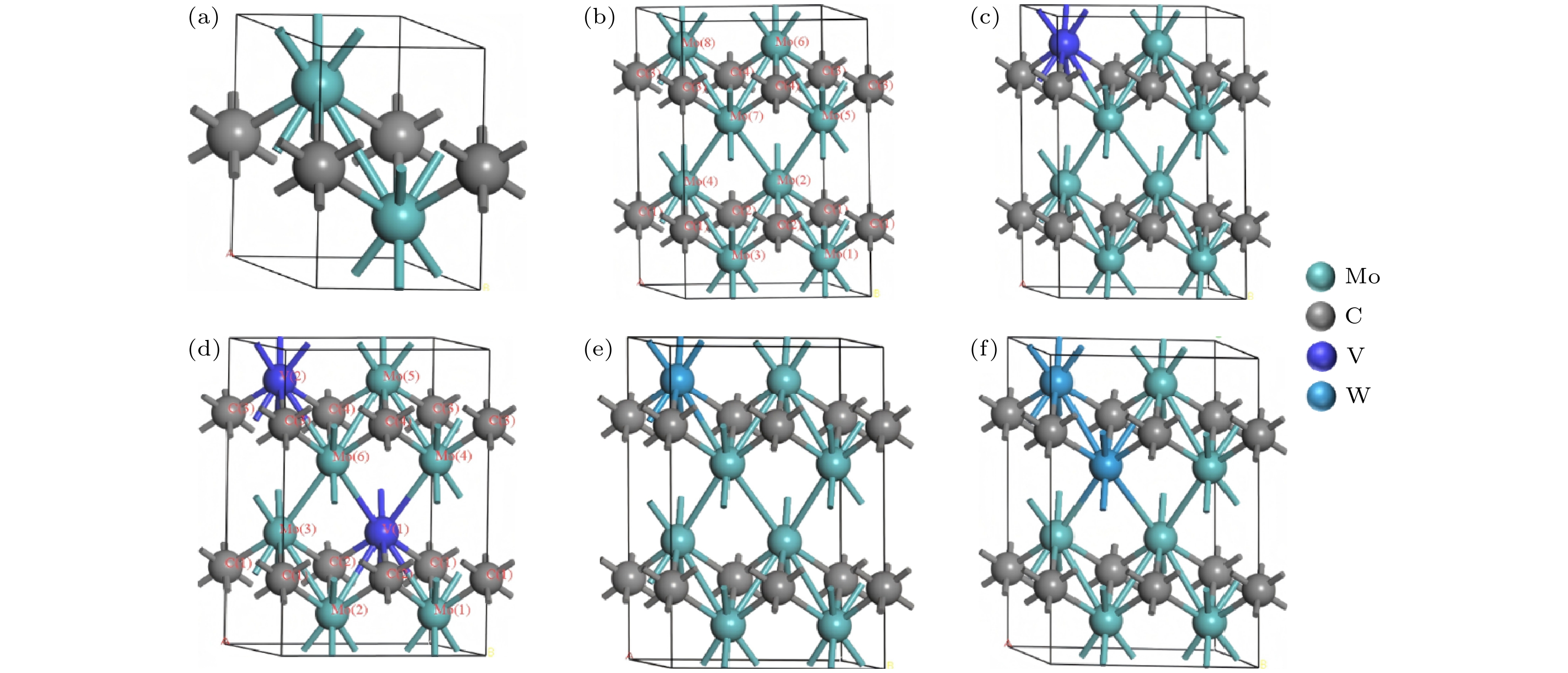
Secondary hardening ultra-high-strength steel is widely utilized in aerospace and other advanced engineering, with the nanoscale M2C precipitates serving as the primary strengthening factor. Mo plays a crucial role in the forming of Mo2C secondary hardening phase, which can form composite M2C precipitates with elements such as Cr, V, and W, thereby modifying the composition and properties of Mo2C. To investigate the effects of V and W doping on Mo2C, first-principles calculations are used to analyze the formation enthalpy, electronic structure, and mechanical properties of the doped systems. The CASTEP module is utilized in this study, with the Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) functional adopted in the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) framework. The results indicate that V doping reduces the lattice parameters and the formation enthalpy, thereby enhancing structural stability. In contrast, W doping increases the lattice parameters and lowers the formation enthalpy but leads the structural stability to decrease. In terms of mechanical properties, V doping reduces toughness while increasing hardness, whereas W doping improves the strength-toughness balance by mitigating the rate of hardness reduction. Covalent bonds are formed within the system, with V and W doping changing their characteristics: compared with the C—Mo bond, the C—V bond exhibits weaker covalency, while the C—W bond displays stronger covalency. Additionally, V doping enhances the stability of Mo—C bonds, whereas W doping reduces their stability. Charge population analysis reveals that metal atoms (Mo, V, and W) act as electron donors, while carbon atoms act as electron acceptors.
-
Keywords:
- first-principles /
- M2C /
- elastic properties /
- electronic structure
[1] Dahl J M, Novotny P M 1999 Adv. Mater. Processes. 155 23
[2] Speich G R, Leslie W C 1972 Metall. Trans. 3 1043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Garrison W M, Maloney J L 2005 Mater. Sci. Eng. , A 403 299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 吴迪 2016 博士学位论文 (秦皇岛: 燕山大学)
Wu D 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University
[5] 李阿妮, 厉勇, 王春旭, 刘宪民 2007 钢铁 42 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li A N, Li Y, Wang C X, Liu X M 2007 Iron Steel 42 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王春旭, 张鹏杰, 高远航, 厉勇, 韩顺, 刘少尊 2020 金属热处理 45 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C X, Zhang P J, Gao Y H, Li Y, Han S, Liu S Z 2020 Heat Treat. Met. 45 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kwon H 1991 Metall. Trans. A 22 1119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kwon H, Lee K B, Yang H R, Lee J B, Kim Y S 1997 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28 775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lee K B, Yang H R, Kwon H 2001 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32 1862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lee K B, Yang H R, Kwon H 2001 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32 1659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Speich G R, Dabkowski D S, Porter L F 1973 Metall. Trans. 4 303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu X T, Zhou X L, Yang M S 2023 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34 961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu H L, Zhu J C, Lai Z H, Zhao R D, He D 2009 Scr. Mater. 60 949
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang X R, Yan M F 2009 J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 24 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X R, Yan M F, Chen H T 2009 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 25 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu Y Z, Jiang Y H, Zhou R, Liu X F, Feng J 2015 Ceram. Int. 41 5239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Vanderbilt D 1990 Phys. Rev. B. 41 7892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Guo J, Feng Y L, Tang C, Wang L, Qing X L, Yang Q X, Ren X J 2022 Materials 15 4719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Abderrahim F Z, Faraoun H I, Ouahrani T 2012 Physica B 407 3833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Luo Y, Cheng C, Chen H J, Liu K, Zhou X L 2019 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 31 405703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Peng M J, Wang R F, Wu Y J, Yang A C, Duan Y H 2022 Vacuum 196 110715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao R D, Wu F F, Liu X, Zhu J C, Zhao Z F 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 681 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu M M, Wen L, Tang B Y, Peng L M, Ding W J 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 506 412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Jang J H, Lee C H, Heo Y U, Suh D W 2012 Acta Mater. 60 208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yan M, Zhang H, Gong C, Zhang M, Gao Q 2025 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 196 112374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Boucetta S, Zegrar F 2013 J. Magnes. Alloys 1 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gao X P, Jiang Y H, Zhou R, Feng J 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 587 819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 李士明, 张启富, 邱肖盼, 张子月, 仲海峰 2022 材料保护 55 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S M, Zhang Q F, Qiu X P, Zhang Z Y, Zhong H F 2022 Mater. Prot. 55 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Chen X Q, Niu H, Li D, Li Y 2011 Intermetallics 19 1275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Tian Y J, Xu B, Zhao Z S 2012 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 33 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Teter D M 1998 MRS Bull. 23 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Haines J, Leger J M, Bocquillon G 2001 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 31 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 卢彩彬, 李新梅 2021 科学技术与工程 21 10646
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu C B, Li X M 2021 Sci. Techno. Eng. 21 10646
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Li Y F, Gao Y M, Fan Z J, Xiao B, Yue Q W, Min T, Ma S Q 2010 Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 405 1011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
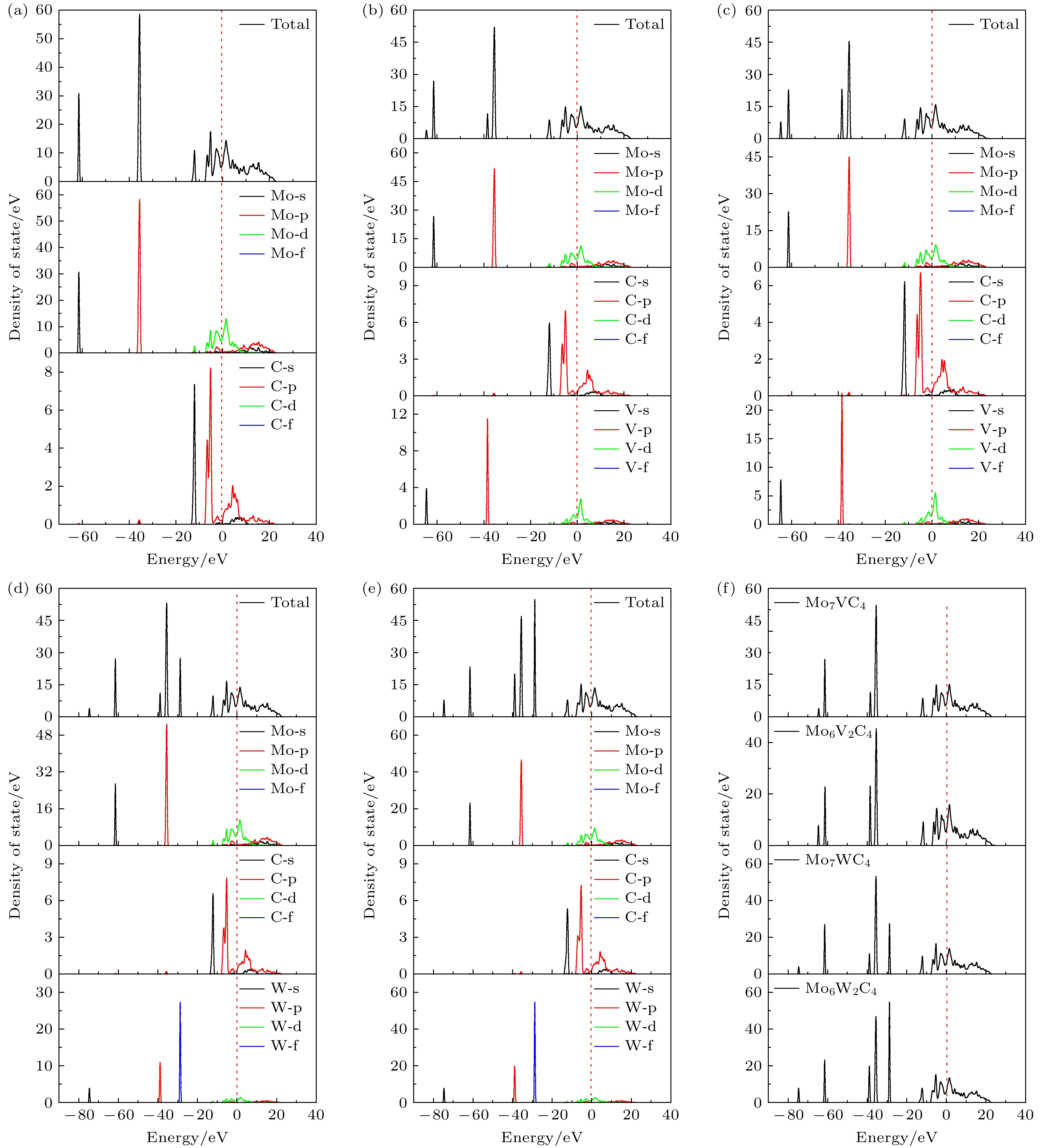
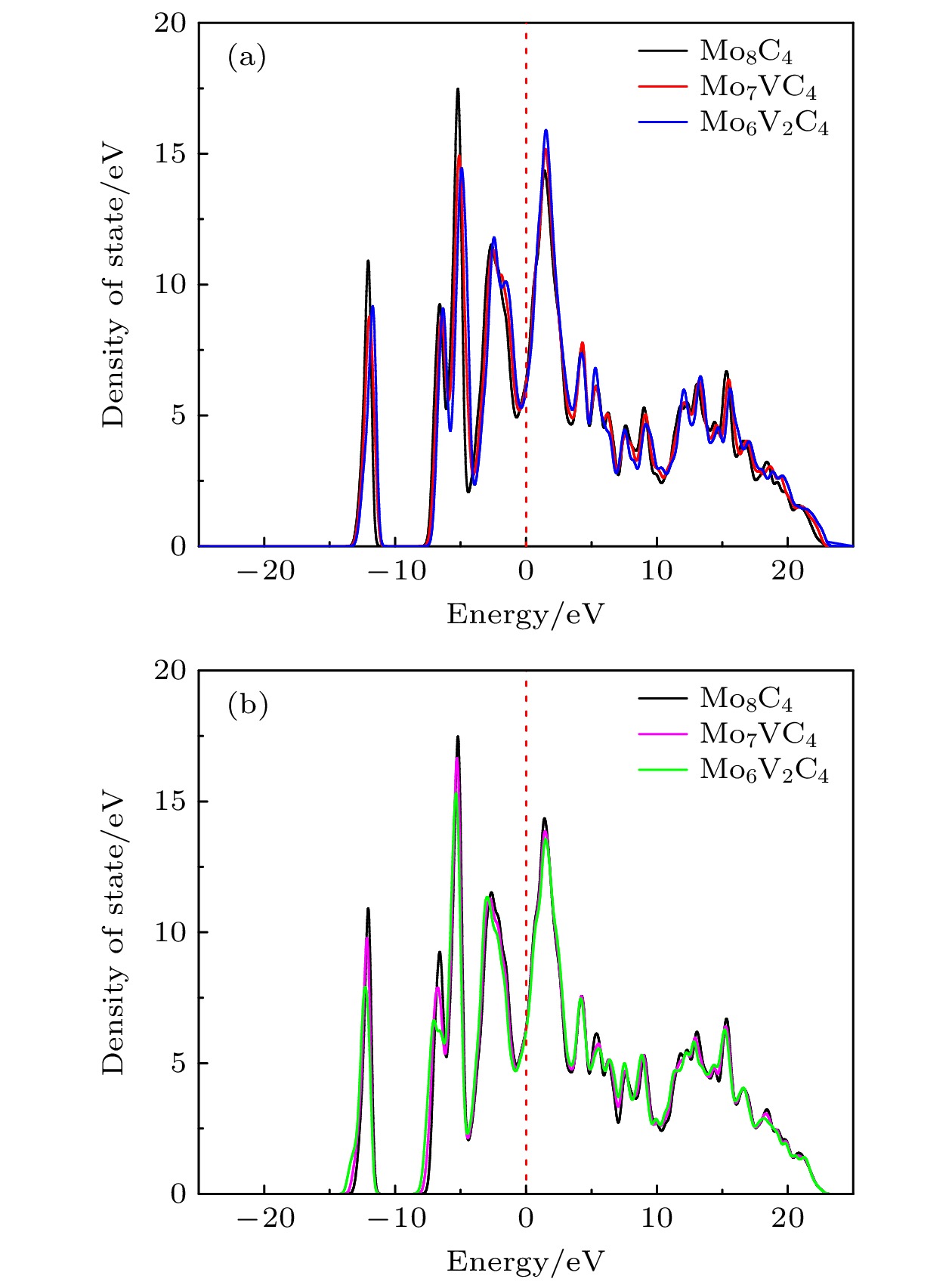
图 3 5种构型的态密度及各原子分波态密度图 (a) Mo8C4; (b) Mo7VC4; (c) Mo6V2C4; (d) Mo7WC4; (e) Mo6W2C4. (f) 4种掺杂构型的总态密度图
Figure 3. Density of states for five configurations and the partial density of states for each atom: (a) Mo8C4; (b) Mo7VC4; (c) Mo6V2C4; (d) Mo7WC4; (e) Mo6W2C4. (f) Total density of states for four doped configurations.
表 1 V, W掺杂前后的晶格参数a, b, c, V以及α, β, γ
Table 1. Lattice parameters a, b, c, volume V, and angles α, β, γ before and after doping with V and W.
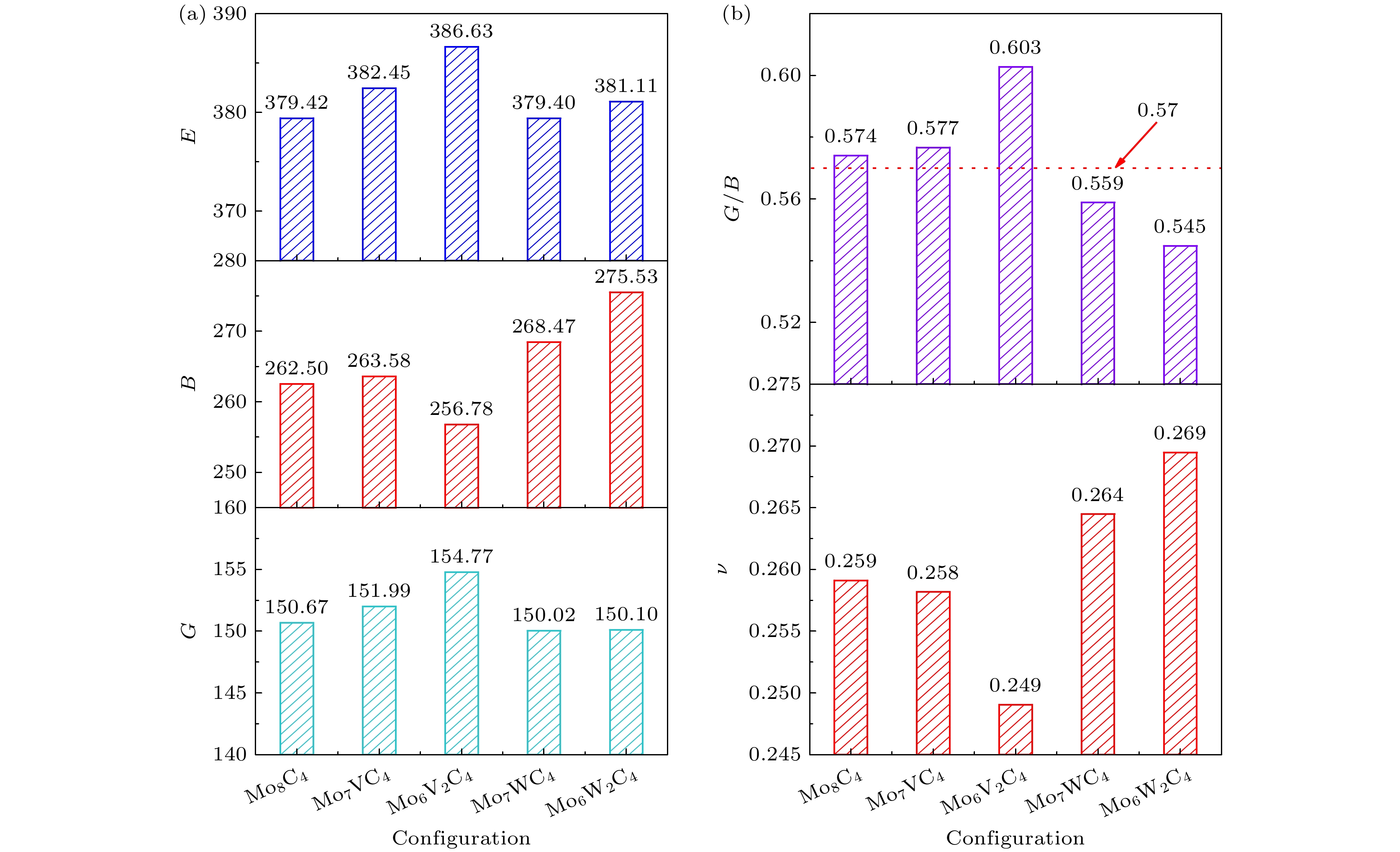
Configuration a/Å b/Å c/Å V/Å α β γ Volume expansion rate/% Mo2C 3.059 3.059 4.665 37.794 90.00 90.00 120.00 — (Mo4C2)[12] 3.056 3.056 9.331 75.476 — — — — (Mo2C)[13] 3.054 3.054 4.652 37.58 — — — — (Mo2C)[15] 3.051 3.051 4.624 37.3114 — — — — Mo8C4 6.108 3.054 9.346 150.996 90.06 89.98 120.00 — Mo7VC4 6.083 3.041 9.282 148.737 90.04 90.02 119.98 –1.50% Mo6V2C4 6.051 3.026 9.215 146.201 89.84 90.34 119.96 –3.18% Mo7WC4 6.109 3.055 9.350 151.139 90.07 89.96 119.99 0.09% Mo6W2C4 6.112 3.054 9.355 151.272 90.09 89.97 119.98 0.18% (V2C)[20] 3.045 3.045 4.409 35.4 — — — — (V2C)[21] 2.89 — — — — — — — (W2C)[20] 3.19 3.19 4.626 40.77 — — — — (W2C)[20] 3.060 3.060 4.703 — — — — — 表 2 不同构型的形成焓
Table 2. Enthalpy of formation for different configurations.
Configuration ΔH/(eV·atom–1) Mo8C4 –0.131 (Mo2C)[13] –0.113 Mo7VC4 –0.192 Mo6V2C4 –0.264 Mo7WC4 –0.121 Mo6W2C4 –0.111 表 3 不同构型的单晶弹性常数
Table 3. Single crystal elastic constants of different configurations.
Configuration C11/GPa C12/GPa C13/GPa C33/GPa C44/GPa C66/GPa Mo8C4 475.26 119.88 180.55 451.77 137.69 178.17 Mo7VC4 481.10 117.69 177.65 466.54 134.82 178.91 Mo6V2C4 473.96 119.00 166.23 461.58 141.35 176.42 Mo7WC4 478.11 125.91 187.67 459.93 137.32 177.95 Mo6W2C4 483.65 131.41 196.03 468.71 137.92 178.09 表 4 不同构型的维氏硬度HV, Hardness (Tian)和硬度H
Table 4. Vickers hardness (HV), hardness (Tian), and hardness (H) of different configurations.
Configuration HV/GPa Hardness/GPa H/GPa Mo8C4 16.64 16.57 42.79 Mo7VC4 16.84 17.46 43.00 Mo6V2C4 18.12 18.13 41.71 Mo7WC4 15.98 16.00 43.92 Mo6W2C4 15.43 15.59 45.25 表 5 不同构型的弹性各向异性指数(AU, AB, AG)
Table 5. Elastic anisotropy indices (AU, AB, AG) of different configurations.
Configuration BV/GPa GV/GPa BR/GPa GR/GPa AU AB/% AG/% Mo8C4 262.69 152.04 262.30 149.30 0.0931 0.0753 0.9073 Mo7VC4 263.86 153.98 263.30 149.99 0.1352 0.1059 1.3137 Mo6V2C4 256.93 155.90 256.62 153.64 0.0750 0.0617 0.7319 Mo7WC4 268.74 151.14 268.20 148.90 0.0773 0.1017 0.7471 Mo6W2C4 275.88 151.23 275.17 148.98 0.0779 0.1295 0.7472 表 6 不同构型的键布居
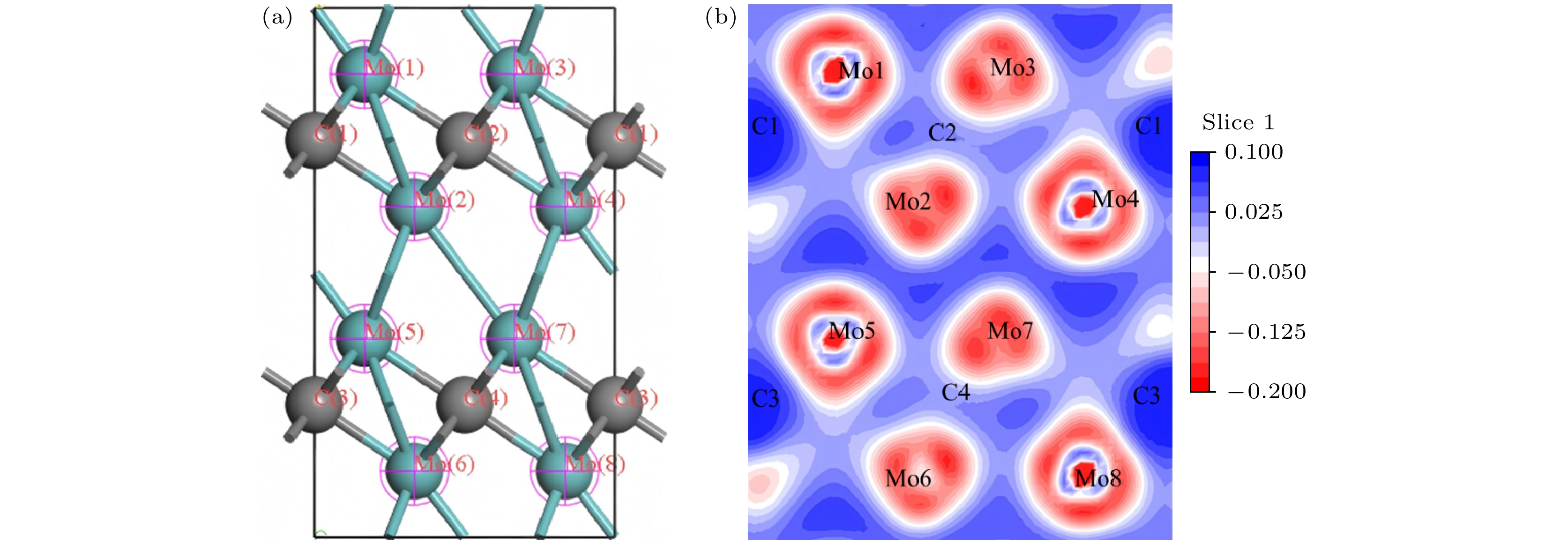
Table 6. Different configurations of bond population.
Configuration Bond Number Population Length/Å Mo8C4 C—Mo 8 0.67 2.1141 C—Mo 8 0.28 2.1143 C—Mo[15] — — 2.118[15] Mo7VC4 C—Mo 7 0.69 2.1116 C—Mo 7 0.28 2.1131 C4—V1 1 0.17 2.0367 C3—V1 1 0.60 2.0380 Mo6V2C4 C—Mo 6 0.73 2.1057 C—Mo 6 0.28 2.1076 C—V 2 0.59 2.0420 C—V 2 0.17 2.0675 Mo7WC4 C—Mo 7 0.66 2.1152 C—Mo 7 0.27 2.1164 C4—W1 1 0.34 2.1173 C3—W1 1 0.79 2.1233 Mo6W2C4 C—Mo 6 0.65 2.1162 C—Mo 6 0.26 2.1187 C—W 2 0.31 2.1210 C—W 2 0.76 2.1238 表 7 Mo8C4的电荷布居
Table 7. Charge distribution of Mo8C4.
Configuration Atom s p d f Total electron/e Muliken charge/e Mo8C4 Mo 2.20 6.64 4.86 0.00 13.70 0.30 C 1.44 3.16 0.00 0.00 4.60 –0.60 表 9 W掺杂Mo8C4的电荷布居
Table 9. Charge distribution of W-doped Mo8C4.
Configuration Atom Total electron/e Muliken charge/e Configuration Atom Total electron/e Muliken charge/e Mo7WC4 Mo1 13.70 0.29 Mo6W2C4 Mo1 13.70 0.30 Mo2 13.70 0.31 Mo2 13.70 0.30 Mo3 13.70 0.29 Mo3 13.72 0.29 Mo4 13.70 0.30 Mo4 13.72 0.29 Mo5 13.70 0.30 Mo5 13.66 0.33 Mo6 13.68 0.32 Mo6 13.66 0.33 Mo7 13.66 0.33 W1 27.70 0.29 W1 27.84 0.27 W2 27.70 0.29 C1 4.60 –0.60 C1 4.60 –0.60 C2 4.60 –0.60 C2 4.60 –0.60 C3 4.62 –0.61 C3 4.62 –0.62 C4 4.60 –0.61 C4 4.62 –0.62 表 8 V掺杂Mo8C4的电荷布居
Table 8. Charge distribution of V-doped Mo8C4.
Configuration Atom Total electron/e Muliken charge/e Configuration Atom Total electron/e Muliken charge/e Mo7VC4 Mo1 13.76 0.24 Mo6V2C4 Mo1 13.80 0.20 Mo2 13.70 0.30 Mo2 13.80 0.20 Mo3 13.76 0.24 Mo3 13.80 0.21 Mo4 13.72 0.29 Mo4 13.80 0.20 Mo5 13.74 0.26 Mo5 13.80 0.21 Mo6 13.78 0.22 Mo6 13.80 0.20 Mo7 13.76 0.25 V1 12.38 0.62 V1 12.38 0.63 V2 12.38 0.62 C1 4.60 –0.60 C1 4.62 –0.61 C2 4.60 –0.60 C2 4.62 –0.61 C3 4.62 –0.62 C3 4.62 –0.62 C4 4.62 –0.61 C4 4.62 –0.61 -
[1] Dahl J M, Novotny P M 1999 Adv. Mater. Processes. 155 23
[2] Speich G R, Leslie W C 1972 Metall. Trans. 3 1043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Garrison W M, Maloney J L 2005 Mater. Sci. Eng. , A 403 299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 吴迪 2016 博士学位论文 (秦皇岛: 燕山大学)
Wu D 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University
[5] 李阿妮, 厉勇, 王春旭, 刘宪民 2007 钢铁 42 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li A N, Li Y, Wang C X, Liu X M 2007 Iron Steel 42 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王春旭, 张鹏杰, 高远航, 厉勇, 韩顺, 刘少尊 2020 金属热处理 45 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C X, Zhang P J, Gao Y H, Li Y, Han S, Liu S Z 2020 Heat Treat. Met. 45 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kwon H 1991 Metall. Trans. A 22 1119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kwon H, Lee K B, Yang H R, Lee J B, Kim Y S 1997 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28 775
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Lee K B, Yang H R, Kwon H 2001 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32 1862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Lee K B, Yang H R, Kwon H 2001 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32 1659
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Speich G R, Dabkowski D S, Porter L F 1973 Metall. Trans. 4 303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu X T, Zhou X L, Yang M S 2023 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34 961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Liu H L, Zhu J C, Lai Z H, Zhao R D, He D 2009 Scr. Mater. 60 949
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang X R, Yan M F 2009 J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 24 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X R, Yan M F, Chen H T 2009 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 25 419
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu Y Z, Jiang Y H, Zhou R, Liu X F, Feng J 2015 Ceram. Int. 41 5239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Vanderbilt D 1990 Phys. Rev. B. 41 7892
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Guo J, Feng Y L, Tang C, Wang L, Qing X L, Yang Q X, Ren X J 2022 Materials 15 4719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Abderrahim F Z, Faraoun H I, Ouahrani T 2012 Physica B 407 3833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Luo Y, Cheng C, Chen H J, Liu K, Zhou X L 2019 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 31 405703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Peng M J, Wang R F, Wu Y J, Yang A C, Duan Y H 2022 Vacuum 196 110715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao R D, Wu F F, Liu X, Zhu J C, Zhao Z F 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 681 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu M M, Wen L, Tang B Y, Peng L M, Ding W J 2010 J. Alloys Compd. 506 412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Jang J H, Lee C H, Heo Y U, Suh D W 2012 Acta Mater. 60 208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Yan M, Zhang H, Gong C, Zhang M, Gao Q 2025 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 196 112374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Boucetta S, Zegrar F 2013 J. Magnes. Alloys 1 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gao X P, Jiang Y H, Zhou R, Feng J 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 587 819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 李士明, 张启富, 邱肖盼, 张子月, 仲海峰 2022 材料保护 55 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S M, Zhang Q F, Qiu X P, Zhang Z Y, Zhong H F 2022 Mater. Prot. 55 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Chen X Q, Niu H, Li D, Li Y 2011 Intermetallics 19 1275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Tian Y J, Xu B, Zhao Z S 2012 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 33 93
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Teter D M 1998 MRS Bull. 23 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Haines J, Leger J M, Bocquillon G 2001 Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 31 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 卢彩彬, 李新梅 2021 科学技术与工程 21 10646
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lu C B, Li X M 2021 Sci. Techno. Eng. 21 10646
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Li Y F, Gao Y M, Fan Z J, Xiao B, Yue Q W, Min T, Ma S Q 2010 Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 405 1011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 768
- PDF Downloads: 28
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: