-
In recent years, the discovery of the transverse spin of acoustic wave in a structural acoustic field and acoustic structural surface wave has expanded our knowledge of the basic characteristics of acoustic waves and opened up new avenues for their manipulation. On the structured surface, however, the distribution of acoustic surface waves often presents a uniform distribution, which restricts the local modification of acoustic spin angular momentum and particle manipulation capabilities. In this study, we develop some acoustic waveguides with gradients that are flat, up-convex, and down-concave in order to manipulate the lateral spin distributions of acoustic surface waves. We verify the direction-locking near-field acoustic spin-momentum, explore the pressure field distribution and the spin angular momentum density distribution of a spin acoustic source excited in each of the three gradient structures, and we also show how to manipulate the spin intensity distributions of acoustic surface waves in the gradient waveguides through theoretical analysis and numerical simulation. The numerical calculation results show that when the acoustic surface wave is excited by a clockwise rotating spin source and propagates along the left side of the waveguide, the spin angular momentum density is positive on the upper surface of the structured waveguide and negative on the lower surface. The spin angular momentum distribution and the direction of propagation of acoustic wave are entirely changed when the spin source is rotated counterclockwise. Specifically, an unequal distribution of acoustic spin angular momentum is produced by the upper convex-type waveguide and bottom concave-type waveguide when we convert the flat-type acoustic structure waveguide into a gradient-type waveguide. According to the computation results, the down-concave type waveguide exhibits a stronger density of acoustic spin angular momentum at the end and the acoustic surface waves gather at the end of the constructed waveguide. On the other hand, the waveguide collects acoustic waves close to the structure center when it is an up-convex structural waveguide. The findings can open up new avenues for manipulating particles using acoustic waves, by providing a means for controlling the acoustic spin angular momentum density and improving our understanding of symmetry in acoustic near-field physics.
-
Keywords:
- acoustic metamaterials /
- acoustic spin angular momentum /
- unidirectional sound propagation /
- gradient acoustic waveguides
[1] Belinfante F J 1939 Physica 6 7
[2] Ohanian H C 1986 Am. J. Phys. 54 6
[3] Belinfante F J 1940 Physica 7 5
[4] Andrews D L, Babiker M 2012 The Angular Momentum of Light (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
[5] Bliokh K Y, Bekshaev A Y, Nori F 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 3300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bekshaev A Y, Bliokh K Y, Nori F 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 011039
[7] Aiello A, Banzer P, Neugebauer M, Leuchs G 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 12
[8] Rodriguez-Fortuño F J, Marino G, Ginzburg P, O’Connor D, Martinez A, Wurtz G A, Zayats A V 2013 Science 2013 340 6130
[9] Petersen J, Volz J, Rauschenbeutel A 2014 Science 346 6205
[10] Bliokh K Y, Smirnova D, Nori F Q 2015 Science 348 6242
[11] Bliokh K Y, Nori F 2015 Phys. Rep. 592 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lodahl P, Mahmoodian S, Stobbe S, Rauschenbeutel A, Schneeweiss P, Volz J, Pichler H, Zoller P 2017 Nature 541 7638
[13] Shomroni I, Rosenblum S, Lovsky Y, Bechler O, Guendelman G, Dayan B 2014 Science 345 6199
[14] Sollner I, Mahmoodian S, Hansen S L, Midolo L, Javadi A, Kiršanskė G, Pregnolato T, El-Ella H, Lee E H, Song J D, Stobbe S, Lodahl P 2015 Nat. Nanotechnol. 10 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Rosenblum S, Bechler O, Shomroni I, Lovsky Y, Guendelman G, Dayan B 2016 Nat. Photonics 10 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Scheucher M, Hilico A, Will E, Volz J, Rauschenbeutel A 2016 Science 354 6319
[17] Crocker M J 1998 Handbook of Acoustics (New York: Wiley
[18] Long Y, Ren J, Chen H 2018 PNAS 115 40
[19] Shi C Z, Zhao R K, Long Y, Yang S, Wang Y, Chen H, Ren J, Zhang X 2019 NSR 6 4
[20] Bliokh K Y, Nori F 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 020301
[21] Long Y, Ge H, Zhang D M, Xu X Y, Ren J, Lu M H, Bao M, Chen H, Chen Y F 2020 NSR 7 6
[22] Hu P, Wu H W, Sun W J, Zhou N, Chen X, Yang Y Q, Sheng Z Q 2023 Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 022201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sun W J, Wu H W, Hu P, Zhou N, Chen X, Yang Y Q, Sheng Z Q 2023 Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 202201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Bliokh K Y, Nori F 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 174310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Long Y, Zhang D M, Yang C W, Ge J M, Chen H, Ren J 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 4716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Weiner M, Ni X, Alu A, Khanikaev A B 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 6332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Cselyuszka N, Sečujski M, Engheta N, Crnojević-Bengin V 2016 New J. Phys. 18 103006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhu J, Chen Y Y, Zhu X F, Garcia-Vidal F J, Yin X B, Zhang W L, Zhang X 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 1728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Jia H, Lu M H, Ni X, Bao M, Li X D 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 124504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ooi K, Okada T , Tanaka K 2011 Phys. Rev. B 84 115405
[31] Xie P X, Sheng Z Q, Huang Z X, Hu P, Wu H W 2023 Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 222202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Long Y, Yang C W, Chen H, Ren J 2023 Phys. Rev. Appl. 19 064053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a) 平整型一维结构声学波导示意图; (b) 不同波导宽度$ {\mathrm{W}} $色散关系曲线; (c)声学表面波沿波导前后向传输比随频率变化的曲线图; (d) 顺时针旋转的自旋声源定向激发声学表面波沿波导向左传播, $ W=10\;{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{m}} $, 频率$ f=0.93\;{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (e) 声学表面波的声学自旋角动量密度分布; (f)声学表面波沿波导向左传播的声压强度变化曲线图; (g) 逆时针旋转的自旋声源定向激发声学表面波沿波导向右传播; (h)声学表面波的声学自旋角动量密度分布; (i)声学表面波沿波导向右传播的声压强度分布曲线图
Figure 1. (a) Schematic diagram of the flat one-dimensional structured acoustic waveguide; (b) dispersion relation curves for different waveguide widths $ {{W}} $; (c) plotting of the forward-backward transmission ratio fluctuation with frequency of acoustic surface wave propagation along the waveguide; (d) directional excitation of acoustic surface waves along the waveguide propagating to the left by a clockwise rotating spin acoustic sources, $ W=10\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{m}} $, $ f=0.93\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (e) density distribution of the acoustic spin angular momentum of the acoustic surface waves; (f) variation of the acoustic pressure strength along the waveguide for the directionally excited leftward propagation of an acoustic surface wave; (g) directional excitation of acoustic surface waves along the waveguide propagating to the left by the counterclockwise rotating spin acoustic sources; (h) acoustic spin angular momentum density distribution of acoustic surface waves; (i) plot illustrates the variation in sound pressure intensity for the rightward propagation of the acoustic surface waves along the waveguide.
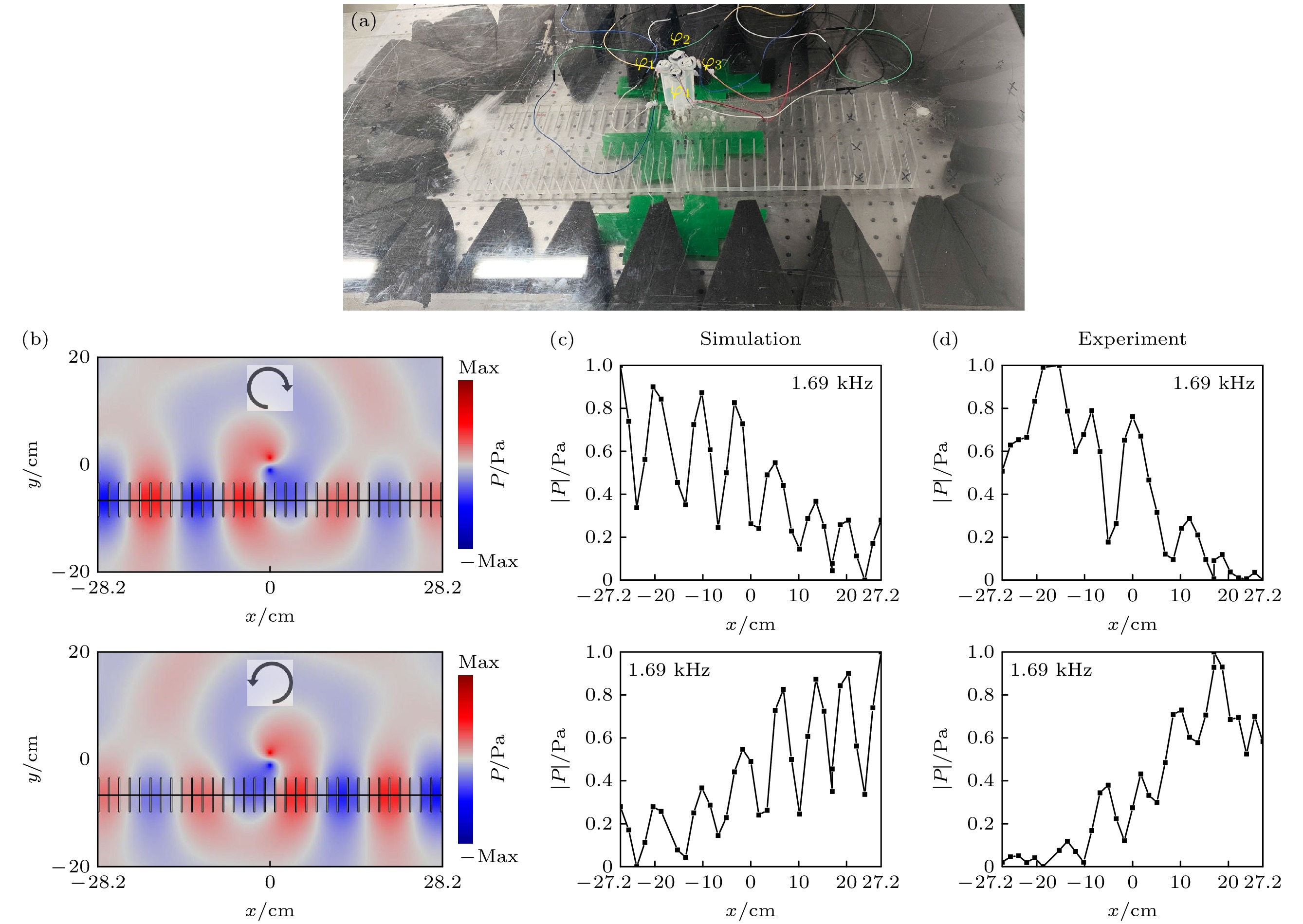
图 2 (a) 实验装置; (b) 顺时针与逆时针旋转的自旋声源定向激发声学表面波沿波导定向传播, 频率$ f=1.69\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (c) 仿真, 声学表面波沿波导传播的声压强度变化; (d) 实验, 声学表面波沿波导传播的声压强度变化
Figure 2. (a) Experimental setup; (b) directional excitation of acoustic surface waves along waveguides by clockwise and counterclockwise rotating spin acoustic sources, $ f=1.69\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (c) simulation, acoustic pressure intensity variation of acoustic surface waves propagating along a waveguide; (d) experiment, acoustic pressure intensity variation of acoustic surface waves propagating along a waveguide.
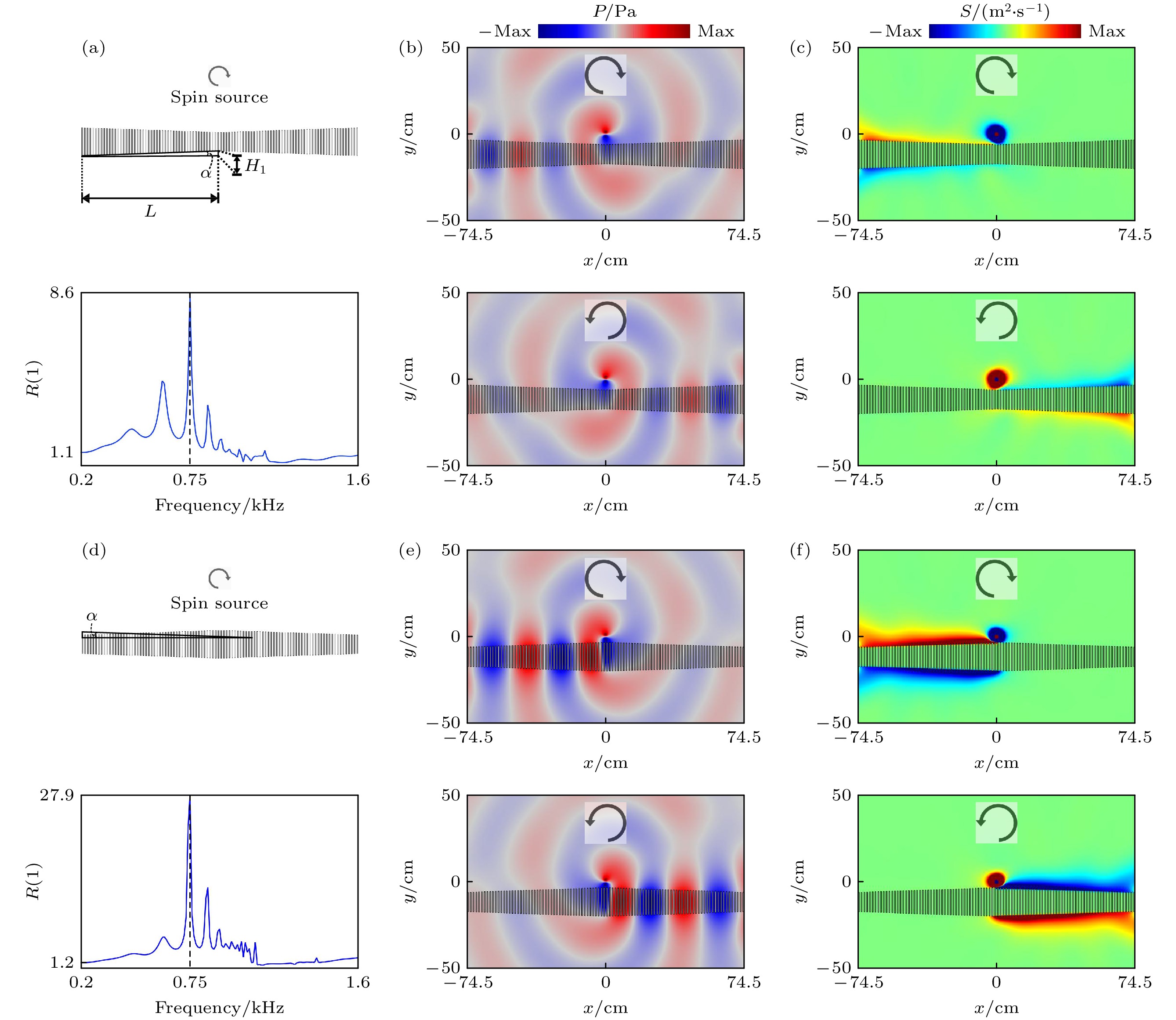
图 3 (a) 下凹型一维结构声学波导示意图和声学表面波沿波导前后向传输比随频率变化的曲线图; (b) 顺时针与逆时针旋转的自旋声源定向激发声学表面波沿波导定向传播, 频率$ f=0.75\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (c) 下凹型波导上的自旋角动量密度分布; (d) 上凸型一维结构声学波导示意图和声学表面波沿波导前后向传输比随频率变化的曲线图; (e) 顺时针与逆时针旋转的自旋声源定向激发声学表面波沿波导定向传播, $ f=0.75\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (f) 上凸型波导上的自旋角动量密度分布
Figure 3. (a) Schematic diagram of an acoustic waveguide with a concave one-dimensional structure and the variation of the forward-to-backward transmission ratio of an acoustic surface wave along the waveguide as a function of frequency; (b) directional excitation of acoustic surface waves along waveguides by clockwise and counterclockwise rotating spin acoustic sources, $ f=0.75\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (c) spin angular momentum density distribution on the concave waveguide; (d) schematic diagram of an up-convex one-dimensional structured acoustic waveguide and the variation of the forward-backward transmission ratio of acoustic surface waves along the waveguide with frequency; (e) directional excitation of acoustic surface waves along waveguides by clockwise and counterclockwise rotating spin acoustic sources, $ f=0.75\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (f) spin angular momentum density distribution on the upper convex waveguide.
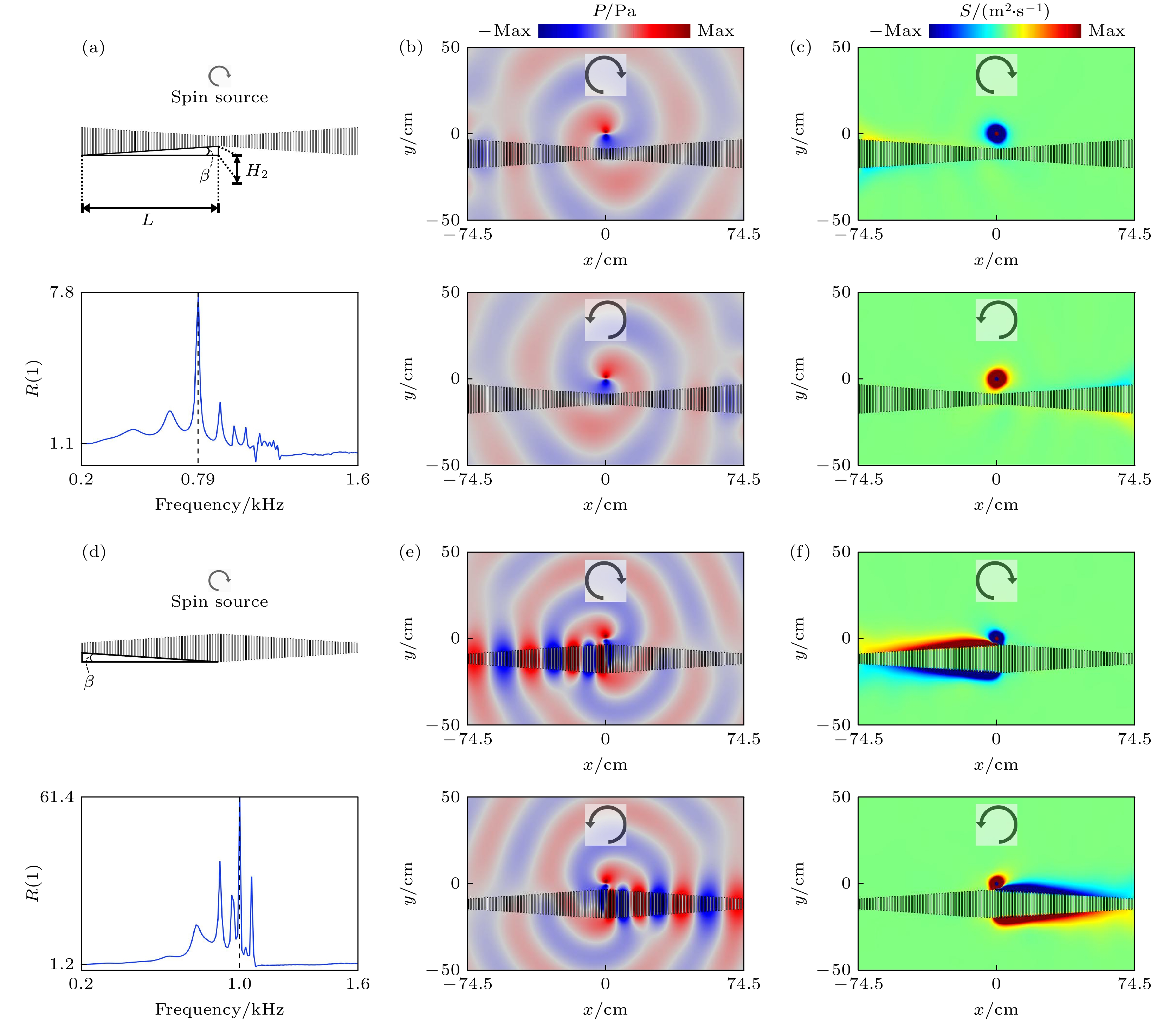
图 4 (a)下凹型一维结构声学波导示意图和声学表面波沿波导前后向传输比随频率变化的曲线图; (b) 顺时针与逆时针旋转的自旋声源定向激发声学表面波沿波导定向传播, 频率$ f=0.79\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (c) 下凹型波导上的自旋角动量密度分布; (d) 上凸型一维结构声学波导示意图和声学表面波沿波导前后向传输比随频率变化的曲线图; (e) 顺时针与逆时针旋转的自旋声源定向激发声学表面波沿波导定向传播, $ f=1.0\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (f) 上凸型波导上的自旋角动量密度分布
Figure 4. (a) Schematic diagram of an acoustic waveguide with a concave one-dimensional structure and the variation of the forward-to-backward transmission ratio of an acoustic surface wave along the waveguide as a function of frequency; (b) directional propagation of acoustic surface waves along the waveguide directionally excited by the clockwise and counterclockwise rotating spin acoustic sources, $ f=0.79\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (c) spin angular momentum density distribution on the concave waveguide; (d) schematic diagram of an up-convex one-dimensional structured acoustic waveguide and the variation of the forward-backward transmission ratio of acoustic surface waves along the waveguide with frequency; (e) directional propagation of acoustic surface waves along the waveguide directionally excited by the clockwise and counterclockwise rotating spin acoustic sources, $ f=1.0\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (f) spin angular momentum density distribution on the upper convex waveguide.
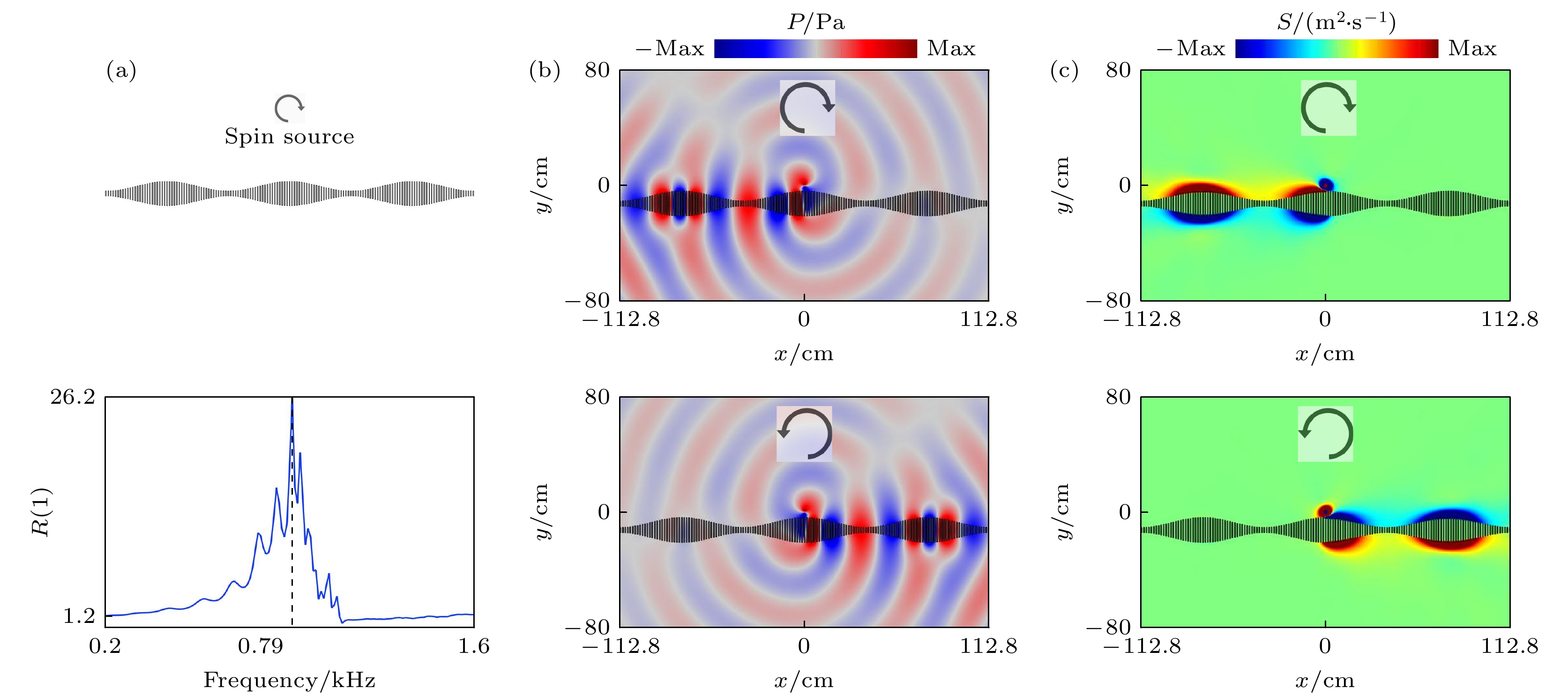
图 5 (a) 以波峰为对称中心的一维结构声学波导示意图和声学表面波沿波导前后向传输比随频率变化的曲线图; (b) 顺时针与逆时针旋转的自旋声源定向激发声学表面波沿波导定向传播, $ f=0.91\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (c) 以波峰为对称中心的波导上的自旋角动量密度分布
Figure 5. (a) Schematic diagram of a one-dimensional structured acoustic waveguide with the wave crest as the center of symmetry and the variation of the forward-backward transmission ratio of acoustic surface waves along the waveguide as a function of frequency; (b) directional excitation of acoustic surface waves propagating along the waveguide by the clockwise and counterclockwise rotating spin acoustic sources, $ f=0.91\;{\mathrm{ }}{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{z}} $; (c) density distribution of spin angular momentum on the waveguide with the crest as the center of symmetry.
-
[1] Belinfante F J 1939 Physica 6 7
[2] Ohanian H C 1986 Am. J. Phys. 54 6
[3] Belinfante F J 1940 Physica 7 5
[4] Andrews D L, Babiker M 2012 The Angular Momentum of Light (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
[5] Bliokh K Y, Bekshaev A Y, Nori F 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 3300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Bekshaev A Y, Bliokh K Y, Nori F 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 011039
[7] Aiello A, Banzer P, Neugebauer M, Leuchs G 2015 Nat. Photonics 9 12
[8] Rodriguez-Fortuño F J, Marino G, Ginzburg P, O’Connor D, Martinez A, Wurtz G A, Zayats A V 2013 Science 2013 340 6130
[9] Petersen J, Volz J, Rauschenbeutel A 2014 Science 346 6205
[10] Bliokh K Y, Smirnova D, Nori F Q 2015 Science 348 6242
[11] Bliokh K Y, Nori F 2015 Phys. Rep. 592 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Lodahl P, Mahmoodian S, Stobbe S, Rauschenbeutel A, Schneeweiss P, Volz J, Pichler H, Zoller P 2017 Nature 541 7638
[13] Shomroni I, Rosenblum S, Lovsky Y, Bechler O, Guendelman G, Dayan B 2014 Science 345 6199
[14] Sollner I, Mahmoodian S, Hansen S L, Midolo L, Javadi A, Kiršanskė G, Pregnolato T, El-Ella H, Lee E H, Song J D, Stobbe S, Lodahl P 2015 Nat. Nanotechnol. 10 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Rosenblum S, Bechler O, Shomroni I, Lovsky Y, Guendelman G, Dayan B 2016 Nat. Photonics 10 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Scheucher M, Hilico A, Will E, Volz J, Rauschenbeutel A 2016 Science 354 6319
[17] Crocker M J 1998 Handbook of Acoustics (New York: Wiley
[18] Long Y, Ren J, Chen H 2018 PNAS 115 40
[19] Shi C Z, Zhao R K, Long Y, Yang S, Wang Y, Chen H, Ren J, Zhang X 2019 NSR 6 4
[20] Bliokh K Y, Nori F 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 020301
[21] Long Y, Ge H, Zhang D M, Xu X Y, Ren J, Lu M H, Bao M, Chen H, Chen Y F 2020 NSR 7 6
[22] Hu P, Wu H W, Sun W J, Zhou N, Chen X, Yang Y Q, Sheng Z Q 2023 Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 022201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sun W J, Wu H W, Hu P, Zhou N, Chen X, Yang Y Q, Sheng Z Q 2023 Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 202201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Bliokh K Y, Nori F 2019 Phys. Rev. B 99 174310
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Long Y, Zhang D M, Yang C W, Ge J M, Chen H, Ren J 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 4716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Weiner M, Ni X, Alu A, Khanikaev A B 2022 Nat. Commun. 13 6332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Cselyuszka N, Sečujski M, Engheta N, Crnojević-Bengin V 2016 New J. Phys. 18 103006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhu J, Chen Y Y, Zhu X F, Garcia-Vidal F J, Yin X B, Zhang W L, Zhang X 2013 Sci. Rep. 3 1728
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Jia H, Lu M H, Ni X, Bao M, Li X D 2014 J. Appl. Phys. 116 124504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ooi K, Okada T , Tanaka K 2011 Phys. Rev. B 84 115405
[31] Xie P X, Sheng Z Q, Huang Z X, Hu P, Wu H W 2023 Appl. Phys. Lett. 122 222202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Long Y, Yang C W, Chen H, Ren J 2023 Phys. Rev. Appl. 19 064053
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3809
- PDF Downloads: 235
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: