-
Multi-cavitation bubble system can easily produce cavitation clouds with various structure types, including ring-like cavitation structures. Nonetheless, the evolutionary behavior of the structure and the physical mechanism of its formation are less investigated. In this work, high-speed photography and image analysis techniques are used to study the evolution of ring-like cavitation bubble aggregation structure in an ultrasonic cleaning tank with a frequency of 40 kHz. The ring-like structure usually appears near the pressure nodule, and its radius is less than a one-eighth wavelength. The structure involves establishment, stability and disappearance during an envelope wave period, and its morphology is stable. The ring-like cavitation structure exists as a bubble transport phenomenon, and the formed small bubble clusters flow to the outside of the ring and become discrete cavitation bubbles, or the bubble nuclei rejoin the cycle of bubble transport in the main accumulation area of the bubble. The size of the ring structure and the bubble accumulation area oscillate slightly, and there exists the whole structure rotation phenomenon, which depends on the interaction of the main sound field and the secondary radiation field with the bubbles. Furthermore, in this work, a mathematical model of two bubbles is used to investigate the physical mechanism behind the formation of a ring. It is found that the sound field is a key factor in ring formation. The ring chain model is used to analyze the structural stability by taking into account the time delay caused by the secondary acoustic radiation of the bubble. The numerical results show that the equivalent potential energy distribution of a ring bubble chain with a one-eighth wavelength in radius can stabilize each bubble in the potential well, and the radial distribution presents a ring-like barrier structure. The higher the sound pressure, the greater the equivalent potential, and the more the bubbles are clustered. The higher the driving sound field, the more complete the ring chain structure is. However, high sound pressure may cause the agglomeration of bubbles with high number density to disintegrate the stability of the ring aggregation of bubbles and evolve into other types of bubble aggregation structures. The theoretical results are in good consistence with the experimental phenomena.
-
Keywords:
- ultrasonic cavitation /
- ring-like bubble structure /
- equivalent potential energy /
- stability
[1] 陈伟中 2014 声空化物理 (北京: 科技出版社) 第140页
Chen W Z 2014 Acoustic Cavitation Physics (Beijing: Science press) p140
[2] Behnia S, Jafari A, Soltanpoor W, Jahanbakhsh O 2009 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 41 818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chahine G L, Kapahi A, Choi J K, Hsiao C T 2016 Ultrason. Sonochem. 29 528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang Y, Wu W H, Wang J Y, Zhai W 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 244303 [张颖, 吴文华, 王建元, 翟薇 2022 71 244303]
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Wu W H, Wang J Y, Zhai W 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 244303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mettin R 2005 Mod. Trends Appl. Res. Signpost 1
[6] Mettin R, Luther S, Ohl C D, Lauterborn W 1999 Ultrason. Sonochem. 6 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lauterborn W, Kurz T, Mettin R, Ohl C D 1999 Adv. Chem. Phys. 110 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hatanaka S I, Yasui K, Kozuka T, Tuziuti T, Mitome H 2002 Ultrasonics 40 655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fatjó G G A, Torres Pérez A, Hadfield M 2010 Ultrason. Sonochem. 17 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yamashita T, Ando K 2019 Ultrason. Sonochem. 52 268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Alloul M, Dollet B, Stephan O, Bossy E, Quilliet C, Marmottant P 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett 129 134501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang A M, Li S M, Cui P, Li S, Liu Y L 2023 Phys. Fluids 35 033323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang A M, Li S M, Cui P, Li S, Liu Y L 2023 Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 13 100438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu P F, Bai L X, Lin W J, Yan J C 2017 Ultrason. Sonochem. 38 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 白立新, 吴鹏飞, 李超, 邓京军, 曾志杰 2018 应用声学 37 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai L X, Wu P F, Li C, Deng J J, Zeng Z J 2018 Appl. Acoust. 37 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李凡, 张先梅, 田华, 胡静, 陈时, 王成会, 郭建中, 莫润阳 2022 71 084303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li F, Zhang X M, Tian H, Hu J, Chen S, Wang C H, Guo J Z, Mo R Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 084303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bai L C, Sun J G, Gao Y D, Xu W L, Zeng Z J, Ma Y H, Bai L X 2021 Ultrason. Sonochem. 74 105577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 白立春, 孙劲光, 高艳东 2021 70 054701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai L C, Sun J G, Gao Y D 2021 Acta Phys. Sin 70 054701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 许龙, 汪尧 2023 72 024303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L, Wang Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 024303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang L L, Chen W Z, Shen Y, Wu Y R, Zhao G Y, Kou S Y 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 044303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu W H, Yang P F, Zhai W, Wei B B 2019 Chin. Phys. Lett. 36 084302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Avvaru B, Pandit A B 2009 Ultrason. Sonochem. 16 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 李希胜 王绍纯 2014 自动检测技术 (北京: 冶金工业出版社) 第226页
Li X S, Wang S Z 2014 Automatic Measurement Technique (Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press) p226
[24] Li F, Zhang X M, Tian H, Hu J, Chen S, Mo R Y, Wang C H, Guo J Z 2022 Ultrason. Sonochem. 87 106057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li F, Huang C Y, Zhang X M, Wang C H, Guo J Z, Lin S Y, Shen Z Z, Tian H 2023 Ultrasonics 132 106992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Li F, Huang C Y, Zhang X M, Wang C H, Hu J, Chen S, Tian H, Shen Z Z, Guo J Z, Lin S Y 2023 Ultrason. Sonochem. 98 106500
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] An Y 2011 Phys. Rev. E 83 066313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang W J, An Y 2013 Phy. Rev. E 87 053023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Mettin R, Ohl C D, Lauterborn W 1999 Ultrasonics 524 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 沈壮志 2015 64 124702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen Z Z 2015 Acta Phys. Sin 64 124702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
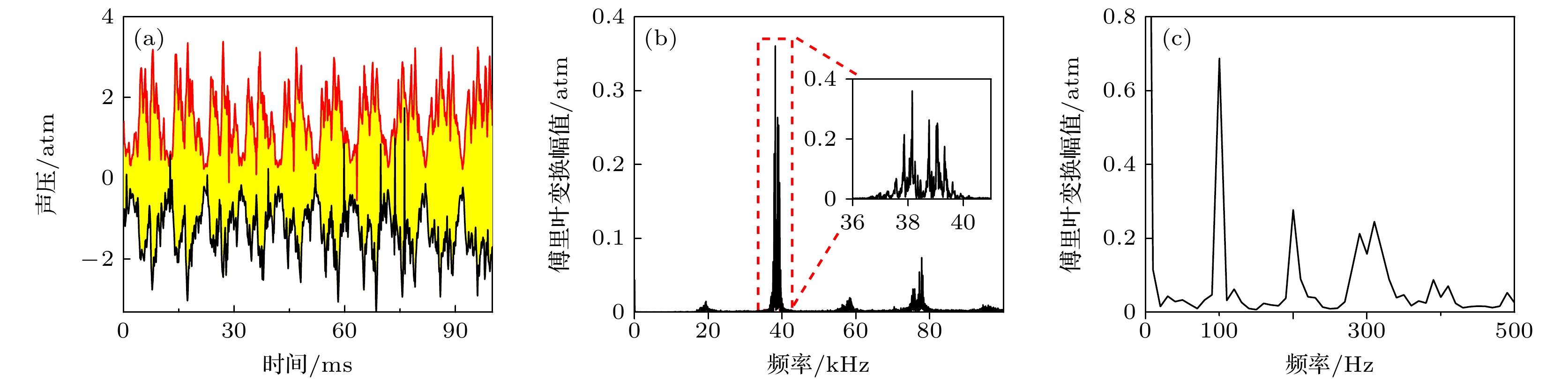
图 2 液体的空化信号 (a) 波形图(红色和黑色曲线分别为空化场信号的上下包络线); (b) 空化信号幅度谱; (c) 空化信号上包络线的幅度谱
Figure 2. Cavitation signal of liquid: (a) Waveform diagram (the red and black curves are the upper and lower envelope lines of the cavitation field signal, respectively); (b) amplitude spectrum of cavitation signal; (c) amplitude spectrum of envelope on cavitation signal.
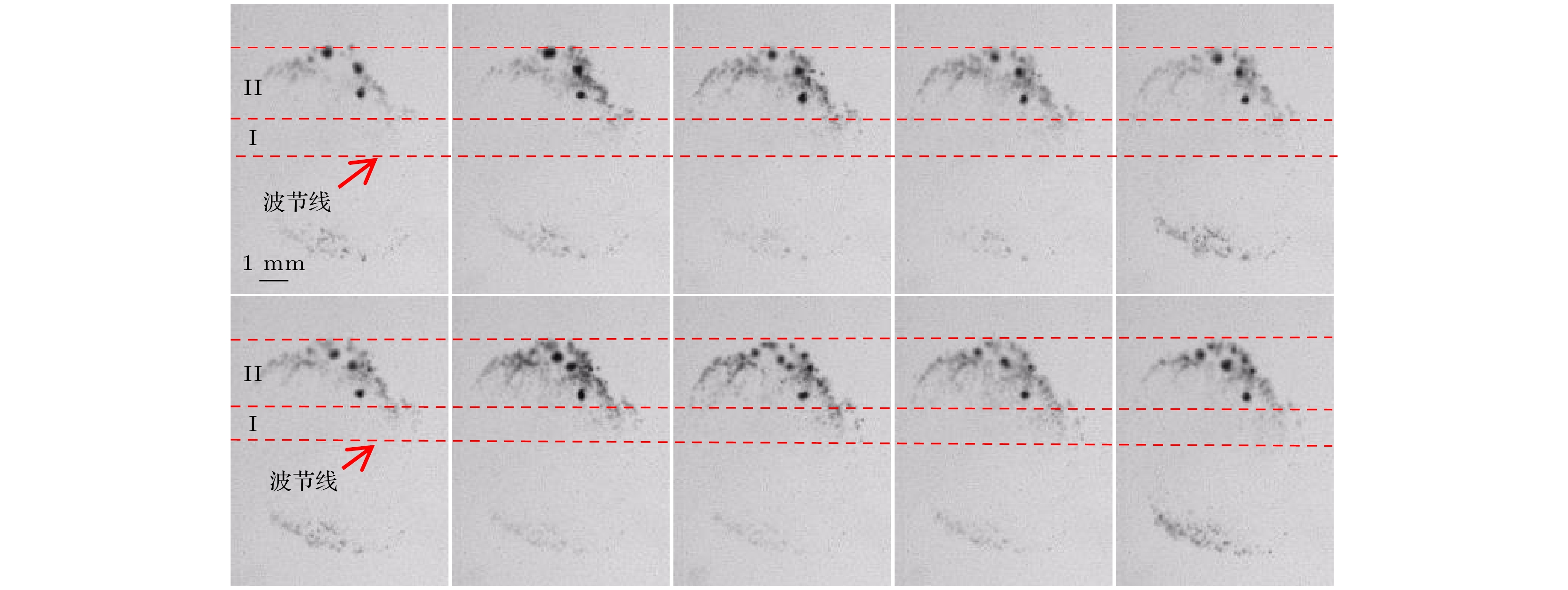
图 3 环状空化结构演化时间序列(代表帧选自补充材料视频1(//m.suprmerch.com/article/doi/10.7498/aps.73.20231956)), 图中红色虚线用于区分上环状结构分布的不同区域形貌
Figure 3. Ring-like cavitation structure evolution time series (representative frame selected from supplementary video 1 (//m.suprmerch.com/article/doi/10.7498/aps.73.20231956)), the red dotted line in the figure is used to distinguish the topography of different regions of the upper ring-like structure distribution.
图 4 包络波周期对环形结构演化行为的影响(虚线椭圆用于标注气泡聚集区, 实线圆圈用于标注气泡聚集区内的小泡团, 代表帧选自补充材料视频1 (//m.suprmerch.com/article/doi/10.7498/aps.73.20231956))
Figure 4. Influence of envelope wave period on evolution behavior of ring structure (the dotted ellipse is used to mark the bubble aggregation area, and the solid circle is used to mark the bubble clusters in the bubble aggregation area, representative frame selected from Supplementary Video 1 (//m.suprmerch.com/article/doi/10.7498/aps.73.20231956)).
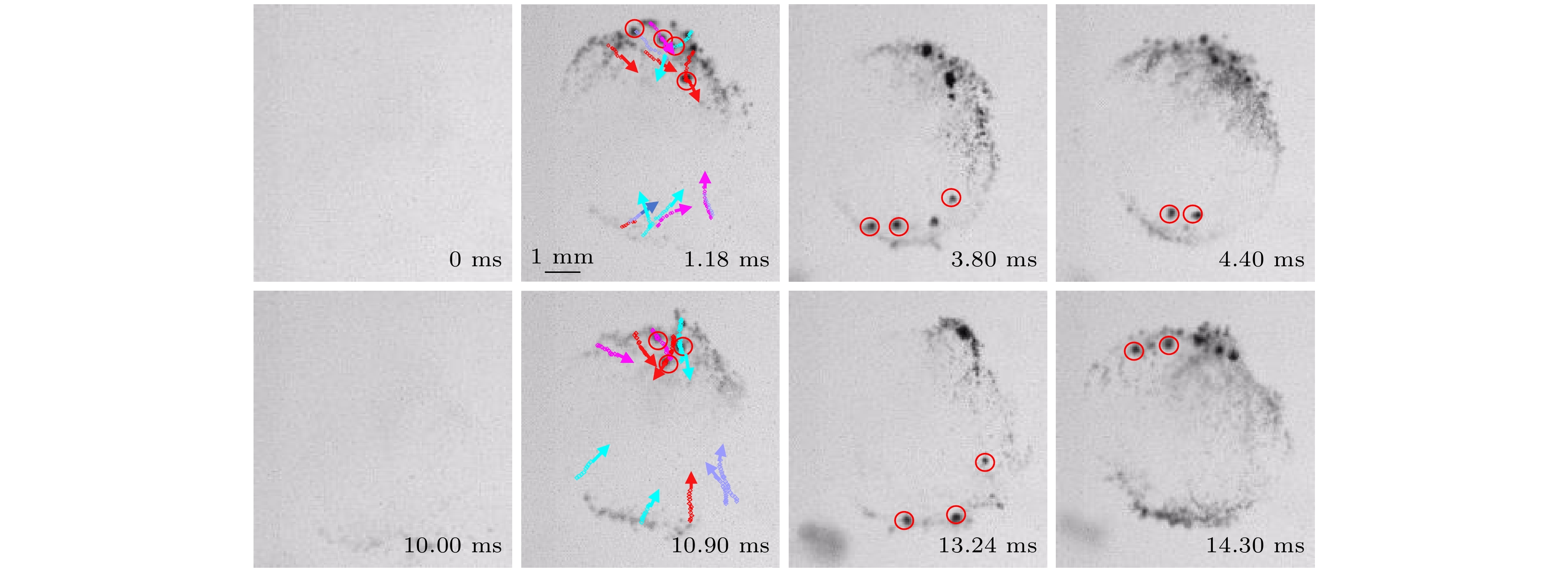
图 5 小气泡团在环状空化结构中的运动轨迹追踪(代表帧选自补充材料视频1 (//m.suprmerch.com/article/doi/10.7498/aps.73.20231956)), 红色圆圈标注被追踪的小泡团, 其他带箭头的标志线代表各气泡团的运动方向和轨迹
Figure 5. Trajectory tracking of small bubble clusters in ring-like cavitation structures (representative frame selected from Supplementary Video 1 (//m.suprmerch.com/article/doi/10.7498/aps.73.20231956)). The red circle marks the tracked bubble clusters, and other marked lines with arrows represent the movement direction and trajectory of each bubble cluster.
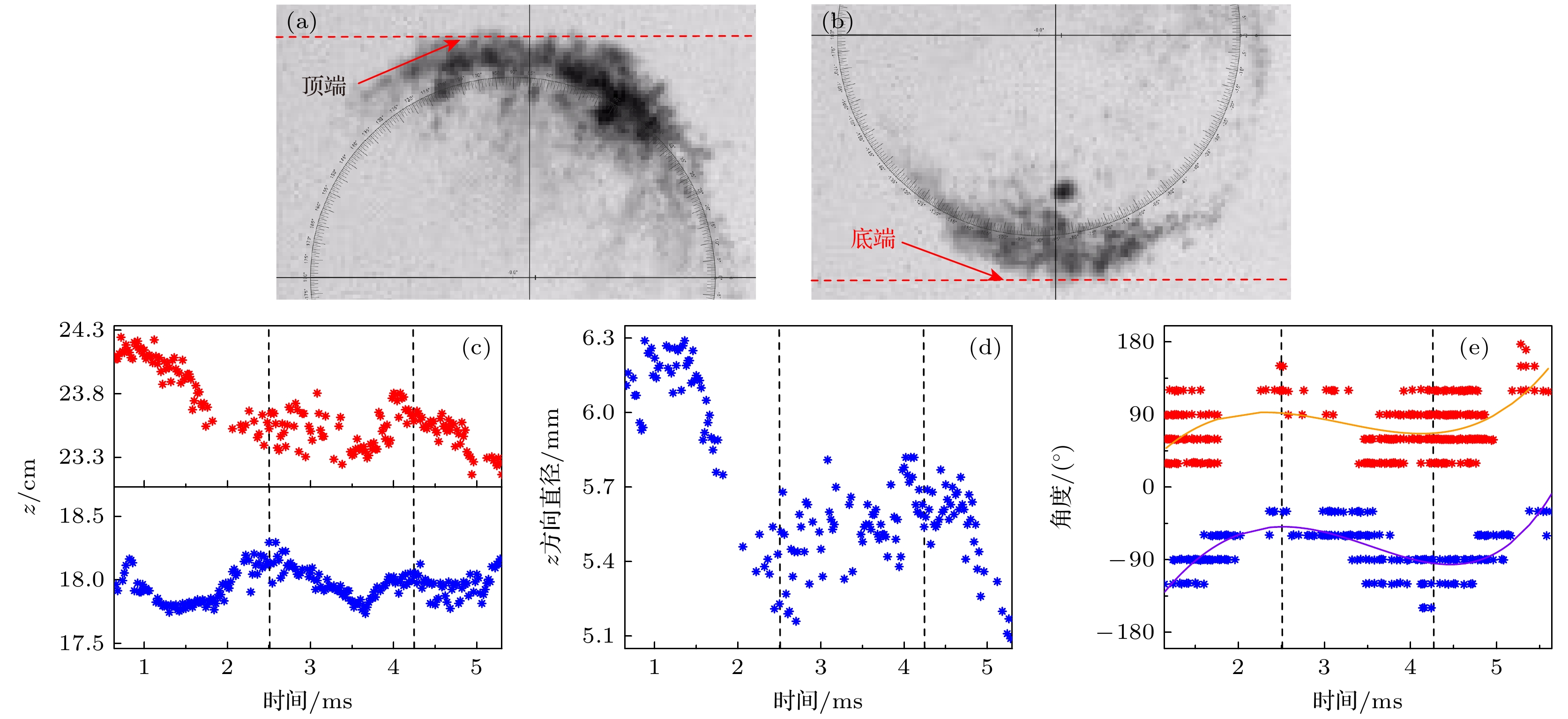
图 6 环状空化结构的演化规律, 追踪时间段为补充材料视频1 (//m.suprmerch.com/article/doi/10.7498/aps.73.20231956)的前6 ms (a), (b)环状结构气泡追踪示意图; (c)环状结构弧形顶端和底端位置变化; (d)结构直径变化(左右垂直虚线用于标注直径相对稳定变化时间段); (e)小泡团聚集位置所在的环结构角度分布
Figure 6. The evolution law of the ring-like cavitation structure and the tracking period are in the first 6 ms of Supplementary Video 1 (//m.suprmerch.com/article/doi/10.7498/aps.73.20231956): (a), (b) Schematic diagram of ring-like structure bubble tracking; (c) changes in the position of the top and bottom of the arc of the ring structure; (d) changes in structural diameter (the left and right vertical dashed lines are used to mark the period of relatively stable change in diameter.); (e) angle distribution of a ring-like structure where small bubble clusters gather.
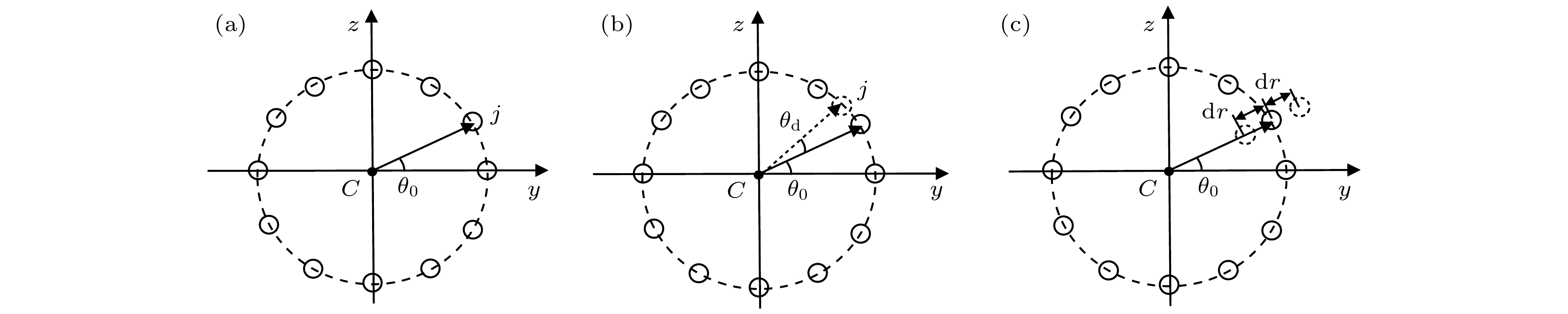
图 8 环形气泡链的结构示意图 (a)气泡在环形气泡链上的分布示意图; (b)计算等效势能θ方向分布的示意图; (c)计算等效势能径向分布的示意图
Figure 8. Structural diagram of the ring bubble chain: (a) Distribution diagram of the bubble on the ring bubble chain; (b) schematic diagram for calculating the distribution of the equivalent potential in the direction of θ; (c) schematic diagram for calculating the radial distribution of the equivalent potential.
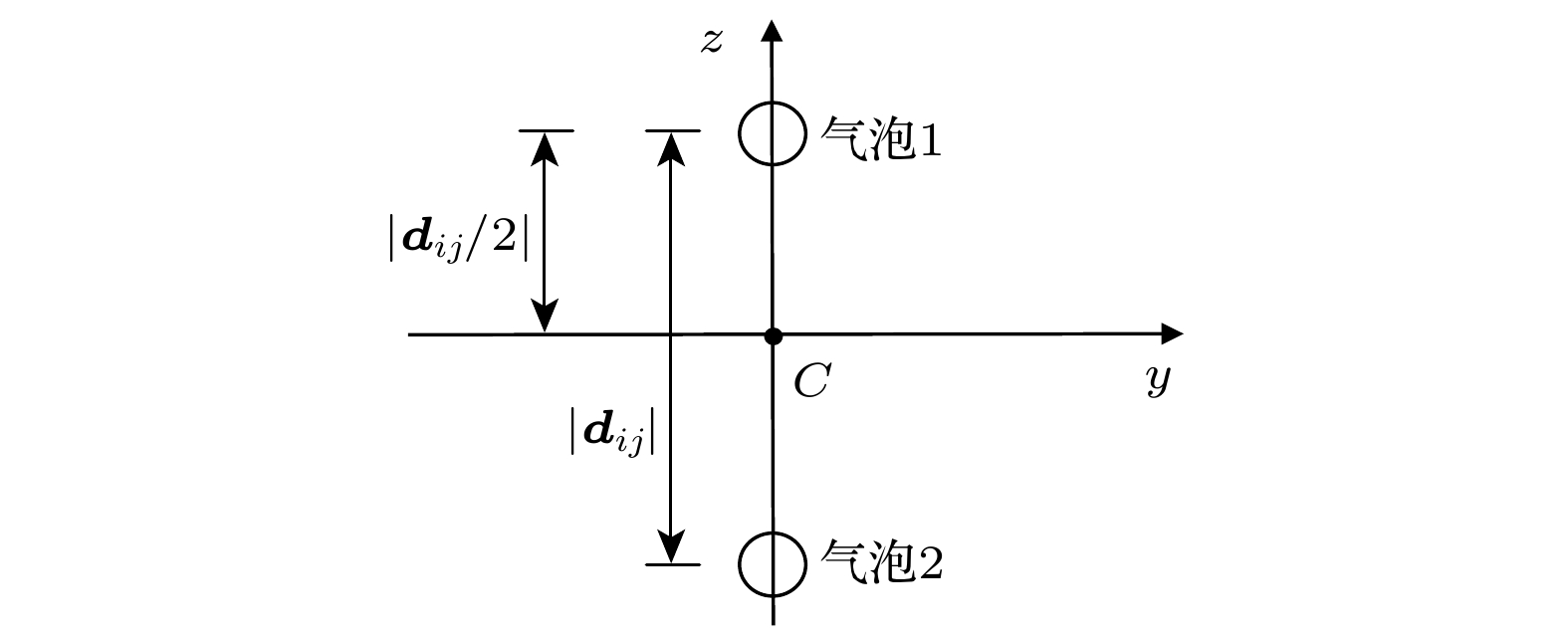
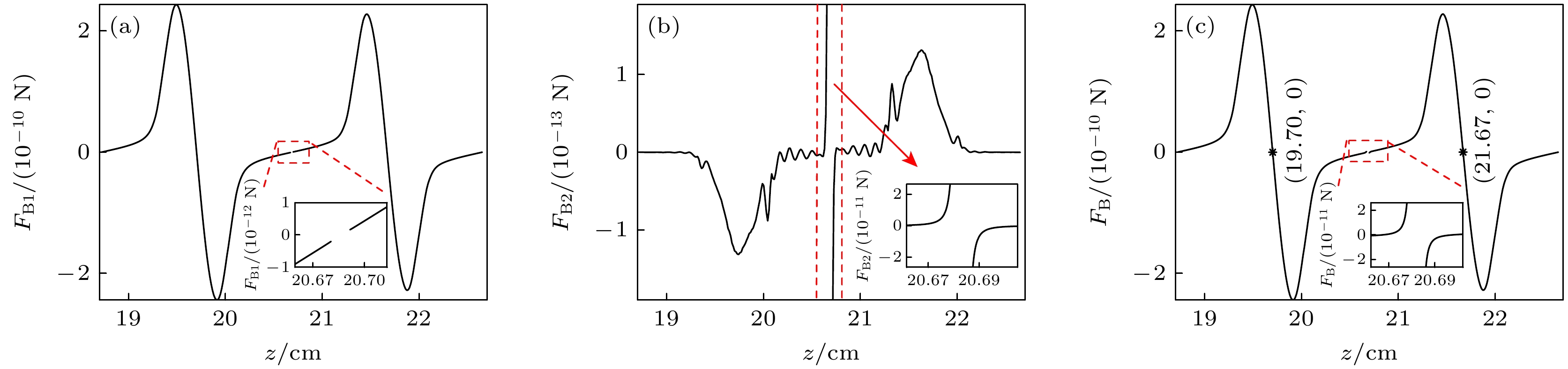
图 9 波节两侧对称耦合双泡在驻波场中的受力情况 (a) 所受的主Bjerknes力; (b)次Bjerknes力; (c)主Bjerknes力与次Bjerknes力的合力
Figure 9. The force of a symmetrically coupled double bubble on both sides of the node in a standing wave field: (a) The primary Bjerknes force; (b) the secondary Bjerknes force; (c) the resultant of the primary Bjerknes force and the secondary Bjerknes force.
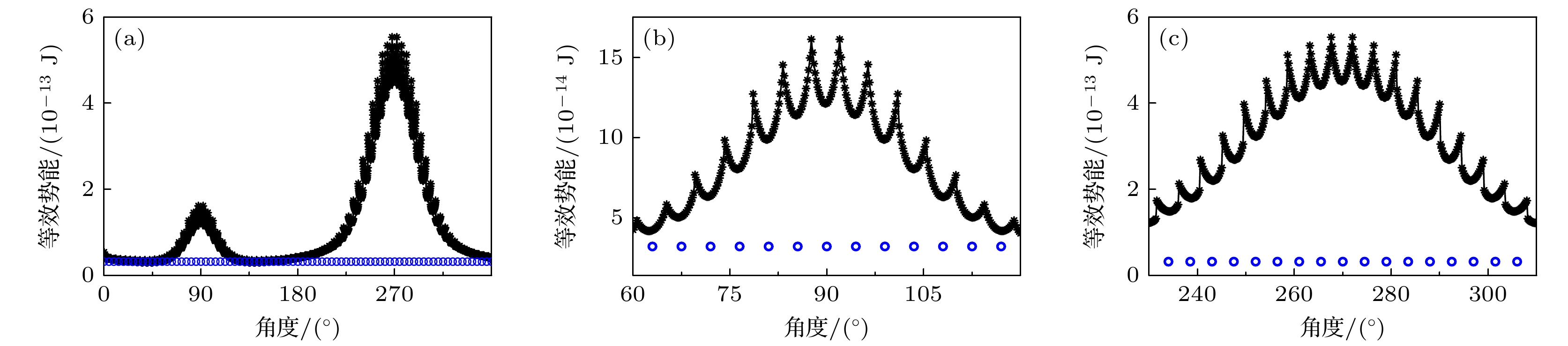
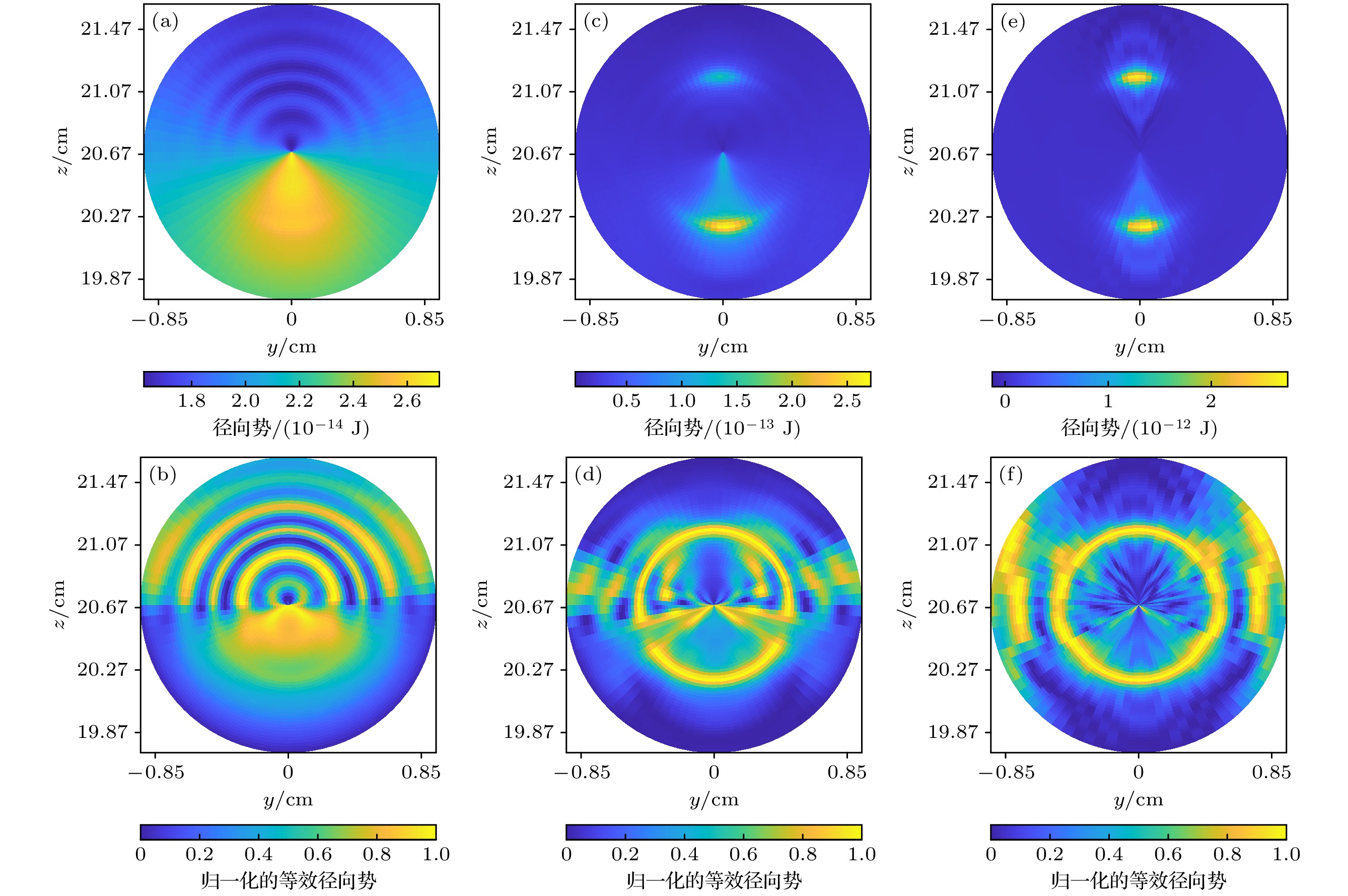
图 11 环形气泡链上等效势的径向分布 (a), (b), (c) 等效势的径向分布; (d), (e), (f)归一化等效势的径向分布; (a), (d) pA = 0.217 atm; (b), (e) pA = 0.655 atm; (c), (f) pA = 0.755 atm
Figure 11. The radial distribution of the equivalent potential on the ring bubble chain: (a), (b), (c) The radial distribution of the equivalent potential; (d), (e), (f) the radial distribution of the normalized equivalent potential; (a), (d) pA = 0.217 atm; (b), (e) pA = 0.655 atm; (c), (f) pA = 0.755 atm.
-
[1] 陈伟中 2014 声空化物理 (北京: 科技出版社) 第140页
Chen W Z 2014 Acoustic Cavitation Physics (Beijing: Science press) p140
[2] Behnia S, Jafari A, Soltanpoor W, Jahanbakhsh O 2009 Chaos Soliton. Fract. 41 818
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chahine G L, Kapahi A, Choi J K, Hsiao C T 2016 Ultrason. Sonochem. 29 528
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhang Y, Wu W H, Wang J Y, Zhai W 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 244303 [张颖, 吴文华, 王建元, 翟薇 2022 71 244303]
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Wu W H, Wang J Y, Zhai W 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 244303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Mettin R 2005 Mod. Trends Appl. Res. Signpost 1
[6] Mettin R, Luther S, Ohl C D, Lauterborn W 1999 Ultrason. Sonochem. 6 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Lauterborn W, Kurz T, Mettin R, Ohl C D 1999 Adv. Chem. Phys. 110 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hatanaka S I, Yasui K, Kozuka T, Tuziuti T, Mitome H 2002 Ultrasonics 40 655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Fatjó G G A, Torres Pérez A, Hadfield M 2010 Ultrason. Sonochem. 17 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yamashita T, Ando K 2019 Ultrason. Sonochem. 52 268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Alloul M, Dollet B, Stephan O, Bossy E, Quilliet C, Marmottant P 2022 Phys. Rev. Lett 129 134501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang A M, Li S M, Cui P, Li S, Liu Y L 2023 Phys. Fluids 35 033323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang A M, Li S M, Cui P, Li S, Liu Y L 2023 Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 13 100438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu P F, Bai L X, Lin W J, Yan J C 2017 Ultrason. Sonochem. 38 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 白立新, 吴鹏飞, 李超, 邓京军, 曾志杰 2018 应用声学 37 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai L X, Wu P F, Li C, Deng J J, Zeng Z J 2018 Appl. Acoust. 37 614
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李凡, 张先梅, 田华, 胡静, 陈时, 王成会, 郭建中, 莫润阳 2022 71 084303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li F, Zhang X M, Tian H, Hu J, Chen S, Wang C H, Guo J Z, Mo R Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 084303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bai L C, Sun J G, Gao Y D, Xu W L, Zeng Z J, Ma Y H, Bai L X 2021 Ultrason. Sonochem. 74 105577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 白立春, 孙劲光, 高艳东 2021 70 054701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bai L C, Sun J G, Gao Y D 2021 Acta Phys. Sin 70 054701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 许龙, 汪尧 2023 72 024303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L, Wang Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 024303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang L L, Chen W Z, Shen Y, Wu Y R, Zhao G Y, Kou S Y 2022 Chin. Phys. B 31 044303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu W H, Yang P F, Zhai W, Wei B B 2019 Chin. Phys. Lett. 36 084302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Avvaru B, Pandit A B 2009 Ultrason. Sonochem. 16 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 李希胜 王绍纯 2014 自动检测技术 (北京: 冶金工业出版社) 第226页
Li X S, Wang S Z 2014 Automatic Measurement Technique (Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press) p226
[24] Li F, Zhang X M, Tian H, Hu J, Chen S, Mo R Y, Wang C H, Guo J Z 2022 Ultrason. Sonochem. 87 106057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Li F, Huang C Y, Zhang X M, Wang C H, Guo J Z, Lin S Y, Shen Z Z, Tian H 2023 Ultrasonics 132 106992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Li F, Huang C Y, Zhang X M, Wang C H, Hu J, Chen S, Tian H, Shen Z Z, Guo J Z, Lin S Y 2023 Ultrason. Sonochem. 98 106500
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] An Y 2011 Phys. Rev. E 83 066313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Zhang W J, An Y 2013 Phy. Rev. E 87 053023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Mettin R, Ohl C D, Lauterborn W 1999 Ultrasonics 524 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 沈壮志 2015 64 124702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen Z Z 2015 Acta Phys. Sin 64 124702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
 8-20231956-Suppl video1.mp4
8-20231956-Suppl video1.mp4
 8-20231956-Suppl video2.mp4
8-20231956-Suppl video2.mp4
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 3421
- PDF Downloads: 59
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: