-
Based on the multiple-vantage observations of STEREO, SOHO, wind and other spacecraft, the fast and wide coronal mass ejections (CME) during the 24th solar cycle from January 2010 to September 2014 are selected in this paper. Using the outputs of Richardson’s (2014) empirical model of solar energetic particle (SEP) intensity under different conditions, the effects of its associations such as CME, pre-CME, and type II radio bursts, on SEP intensity are analyzed, and the relationship between SEP event and these characteristics is also discussed. The main conclusions are as follows. 1) The presence or absence of pre-CME within 13 h before fast CME significantly improves the model prediction effect and has a significant influence on whether fast CME produces SEP event. Compared with the events without pre-CMEs, the events with pre-CMEs have a low proportion of false alarms (FR: 47.7% vs. 70%). However, the number of pre-CMEs does not improve the model output. 2) CMEs with type-II radio bursts have significantly lower FR to generate SEP events than fast CMEs without type-II radio bursts (42% vs. 68%). And selecting type-II radio bursts as a constraint will filter out some small/weak SEP events, the relationship between model predictions and observations especially for large SEP events (e.g. Ip ≥ 0.01 pfu/MeV) will stand out. Moreover, if the type-II radio enhancement is taken into account, FR can be further reduced to 29.4%, and the proportion of hits can be further increased (HR: 48.5%), and the model prediction is significantly improved. 3) The larger the start frequency of type II radio bursts, the smaller the end frequency is, and FR decreases slightly, but at the same time, a large number of SEP events are excluded by this condition, and the results show that the constraints on the start/end frequency of type-II radio bursts do not improve the model predictions distinctly. 4) If the sub-classification of type-II radio bursts is considered as the model constraint, the CMEs associated with multi-band type-II radio bursts have better model predictions than those with single-band events. For example, m-DH-km type-II radio bursts have lower FR (35.4%) and higher HR (48%), and the accuracy of empirical model is higher. In summary, we find that in addition to the velocity and angular width of CME, the associations of pre-CME, type II radio bursts and their enhancement, and multi-band sub-classification are the favorable conditions for CME to generate SEP events. The SEP intensities obtained by the empirical model have better consistency with the observations, and better predictions can be obtained. This investigation indicates that SEP events are more likely generated by fast and wide CMEs accompanied by pre-CMEs, multi-band type II radio bursts and their enhancements, which seem to serve as discriminative signal for SEP-rich and SEP-poor CMEs.
-
Keywords:
- solar energetic particle /
- coronal mass ejection /
- type II radio burst
[1] 王劲松, 吕建永 2010 空间天气学 第1版 (北京: 气象出版社) 第16—31页
Wang J S, Lü J Y 2010 Space Weather Science (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Meteorological Press) pp16–31
[2] Kahler S W 2001 J. Geophys. Res. 106 20947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Reams D V 1999 Space. Sci. Rev. 90 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cliver E W, Kahler S W 2004 Astrophys. J. 605 902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kahler S W 1992 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 30 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Gopalswamy N, Yashiro S, Krucker S, Stenborg G, Howard R A 2004 J. Geophys. Res. 109 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ding L G, Jiang Y, Zhao L, Li G 2013 Astrophys. J. 763 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cane H V, Von Rosenvinge T T, Cohen C M S, Mewaldt R A 2003 Geophys. Res. Lett. 30 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cane H V, Mewaldt R A, Cohen C M S, Von Rosenvinge T T 2006 J. Geophys. Res. 111 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Le G M, Zhang X F 2017 Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 17 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Le G M, Li C, Zhang X F 2017 Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 17 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y, Lyu D, Wu X H, Qin G 2022 Astrophys. J. 940 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Stewart R T, McCabe M K, Koomen M J, Hansen R T, Dulk G A 1974 Sol. Phys. 36 203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hundhausen A J, Holzer T E, Low B C 1987 J. Geophys. Res. 92 0148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vršnak B, Lulić S 2000 Sol. Phys. 196 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Vršnak B, Cliver E 2008 Sol. Phys. 253 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kahler S W 1982 J. Geophys. Res. 87 2439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cane H V, Erickson W C, Prestage N P 2002 J. Geophys. Res. 107 1315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wild J, McCready L 1950 Aust. J. Sci. Res. Ser. A: Phys. Sci. 3 387
[20] Cane H V, Stone R G, Fainberg J, Stewart R T, Steinberg J L, Hoang S 1981 Geophys. Res. Lett. 8 1285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Prakash O, Umapathy S, Shanmugaraju A, Vršnak B 2009 Sol. Phys. 258 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kahler S W 1996 Amer. Inst. Phys. 374 61
[23] Gopalswamy N, Aguilar-Rodriguez E, Yashiro S, Nunes S, Kaiser M L, Howard R A 2005 J. Geophys. Res. 110 07
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Winter L M, Ledbetter K 2015 Astrophys. J. 809 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kahler S W, Ling A G, Gopalswamy N 2019 Sol. Phys. 294 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 朱聪, 丁留贯, 周坤论, 钱天麒 2021 70 099601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu C, Ding L G, Zhou K L, Qian T Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 099601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Marqué C, Posner A, Klein K L 2006 Astrophys. J. 642 1222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gopalswamy N, Yashiro S, Akiyama S, Mäkelä P, Xie H, Kaiser M, Howard R, Bougeret J 2008 Ann. Geophys. 26 3033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kahler S W, Reames D V, Burkepile J T 2000 High Energy Solar Physics- Anticipating Hessi 206 468
[30] Shen C, Li G, Kong X, Hu J, Sun X D, Ding L, Chen Y, Wang Y M, Xia L 2013 Astrophys. J. 763 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ding L G, Li G, Dong L H, Jiang Y, Jian Y, Gu B 2014 J. Geophys. Res. 119 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Gopalswamy N, Yashiro S, Kaiser M L, Howard R A, Bougeret J L 2001 Astrophys. J. 548 L91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Ding L G, Wang Z W, Feng L, Li G, Jiang Y 2019 Res. Astron. Astrophys. 19 001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 周坤论, 丁留贯, 钱天麒, 朱聪, 王智伟, 封莉 2020 69 169601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou K L, Ding L G, Qian T Q, Zhu C, Wang Z W, Feng L 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 169601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Posner A 2007 Space Weather 5 05001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Richardson I G, Mays M L, Thompson B J 2018 Space Weather 16 1862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Falconer D, Barghouty A F, Khazanov I, Moore R 2011 Space Weather 9 04003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Papaioannou A, Anastasiadis A, Kouloumvakos A, Paassilta M, Vainio R, Valtonen E, Belov A V, Eroshenko E, Abunina M, Abunin A 2018 Sol. Phys. 293 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Laurenza M, Cliver E W, Hewitt J, Storini M, Ling A G, Balch C C, Kaiser M L 2009 Space Weather 7 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Balch C C 1999 Radiat. Meas. 30 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Bruno A, Richardson I G 2021 Sol. Phys. 296 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Garcia H A 2004 Space Weather 2 02002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Huang X, Wang H N, Li L P 2012 Res. Astron. Astrophys. 12 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Núñez M 2011 Space Weather 9 07003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Núñez M 2015 Space Weather 13 727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Núñez M, Santiago P, Malandraki O 2017 Space Weather 15 861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Núñez M 2018 J. Space Weather Space Clim. 8 A36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Richardson L G, von Rosenvinge T T, Cane H V, Christian E R, Cohen C M S, Labrador A W, Leske R A, Mewaldt R A, Wiedenbeck M E, Stone E C 2014 Sol. Phys. 289 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Torres J, Zhao L, Chan P K, Zhang M 2022 Space Weather 20 002797
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] 王智伟, 丁留贯, 周坤论, 乐贵明 2018 地球 61 3515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z W, Ding L G, Zhou K L, Le G M 2018 Chin. J. Geophys. 61 3515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Hanssen A W, Kuipers W J A 1965 Koninklijk Ned. Meteor. Instit. 81 2
-
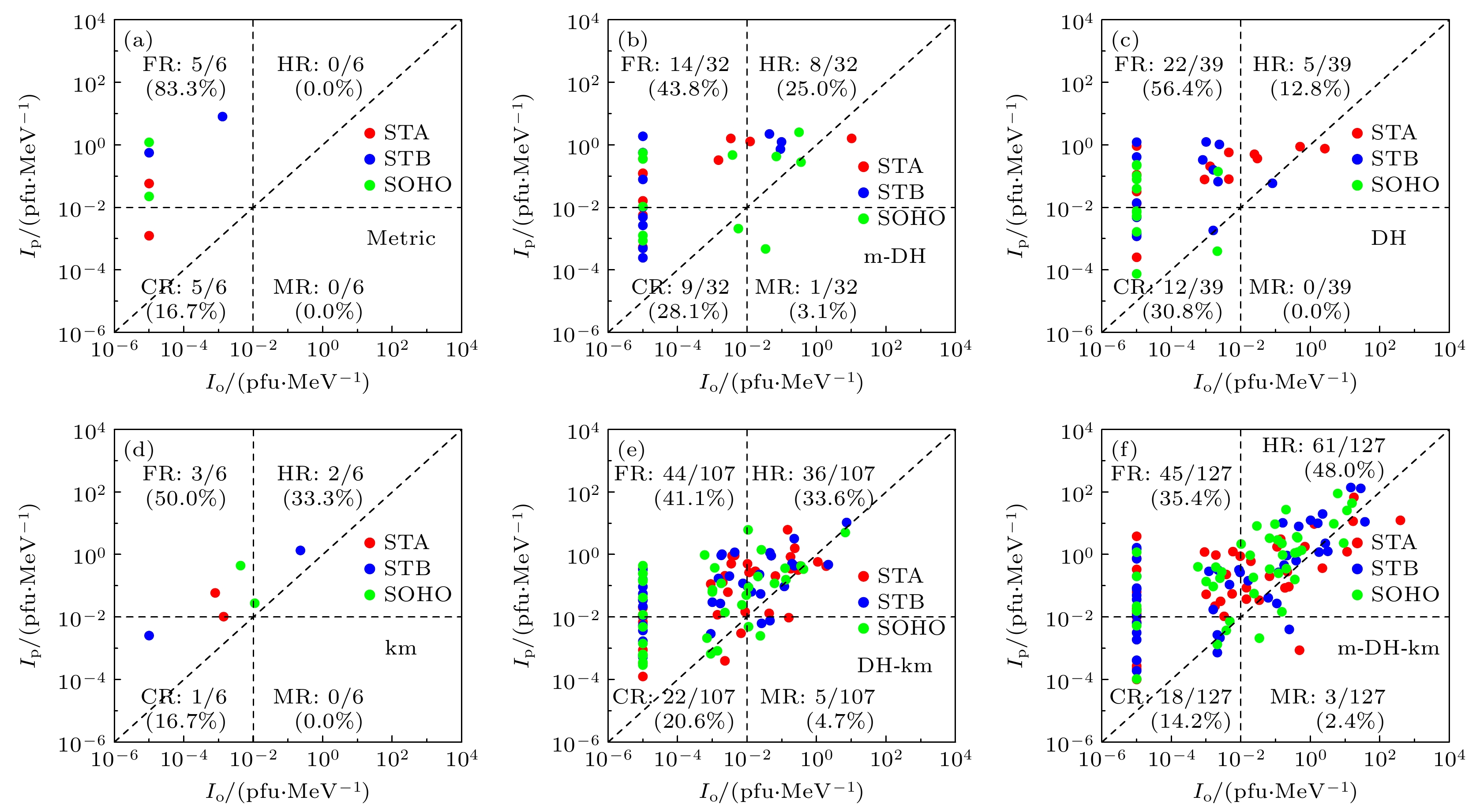
图 1 SEP强度预测值(Ip)与观测值(Io)对比, SEP事件阈值准线将事件样本分为四类
Figure 1. Predicted versus observed SEP peak intensities at SOHO or STEREO-A/B (STA/STB) spacecraft for the fast and wide CMEs with speed greater than 900 km/s and width greater than 60º in the study period. The quadrants defined by crosshairs set at equal predicted and observed intensity thresholds divide the events into hits, false alarms, correct rejections, and misses.
图 2 (a)不存在pre-CME时, SEP强度预测值与观测值关系; (b)存在pre-CME时, SEP强度预测值与观测值关系; (c)样本事件数量随pre-CME事件数量的变化(黑), HR, FR, CR和MR随pre-CME事件数量的变化(蓝、红、橙、紫)
Figure 2. Predicted versus observed SEP intensities for the fast and wide CMEs without (a) or with (b) pre-CMEs, and (c) the number of selected events (black) and percentages of HR (blue), FR (red), CR (yellow), and MR (purple) versus the number of pre-CMEs.
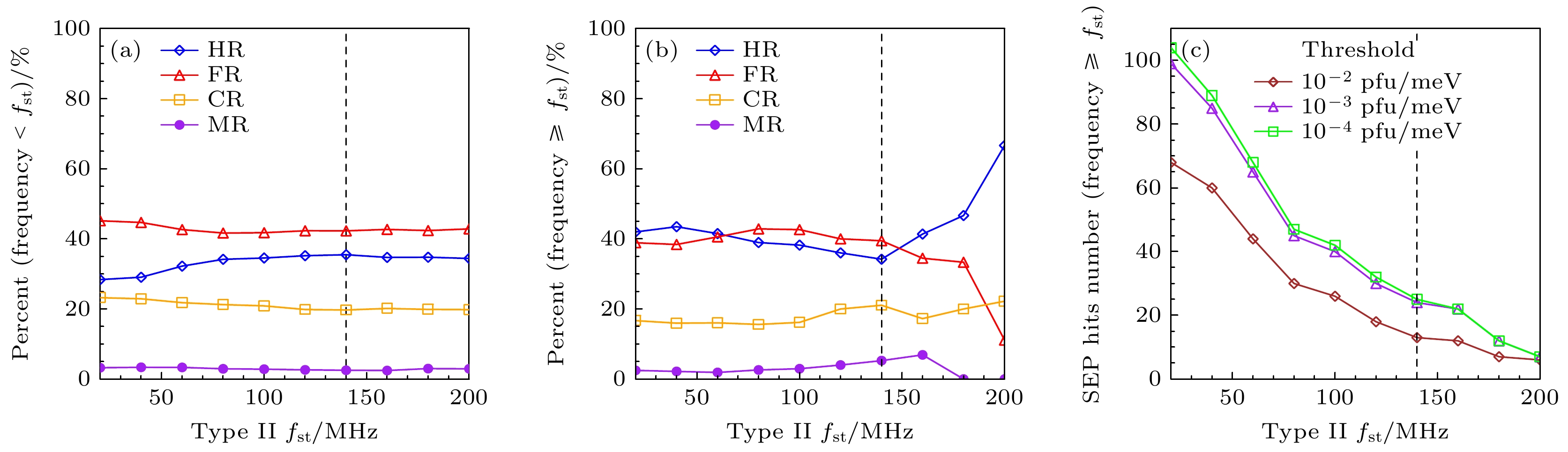
图 5 (a) 击中、误报、正确拒绝和漏报占比随II型射电暴起始频率上限阈值($ {f}_{{\mathrm{s}}{\mathrm{t}}} $)的变化; (b) HR, FR, CR, MR随起始频率下限阈值($ {f}_{{\mathrm{s}}{\mathrm{t}}} $)的变化; (c) 不同SEP事件强度阈值情况下, 击中事件数量随II型射电暴起始频率阈值条件的变化
Figure 5. (a) Fraction of hits, false alarms, correct rejections, and misses in all predictions versus the upper limit threshold ($ {f}_{{\mathrm{s}}{\mathrm{t}}} $) of the starting frequency of type II radio bursts; (b) similar to panel (a) but for the lower limit threshold $ {(f}_{{\mathrm{s}}{\mathrm{t}}}) $; (c) number of hit events among all the predictions in different thresholds of SEP intensity using the lower limit starting frequency threshold for type II radio bursts.
图 6 (a) 击中、误报、正确拒绝和漏报占比随II型射电暴结束频率上限阈值($ {f}_{{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{d}}} $)的变化; (b) HR, FR, CR, MR随下限阈值$ ({f}_{{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{d}}} $)的变化; (c) 不同SEP事件强度阈值情况下, 击中事件数量随II型射电暴结束频率阈值条件的变化
Figure 6. (a) Fraction of hits, false alarms, correct rejections, and misses in all predictions versus the upper limit threshold ($ {f}_{{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{d}}} $) of the ending frequency of type II radio bursts; (b) similar to panel (a) but for the lower limit threshold $ {(f}_{{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{d}}}) $; (c) number of hit events among all the predictions in different thresholds of SEP intensity using the lower limit ending frequency threshold for type II radio bursts.
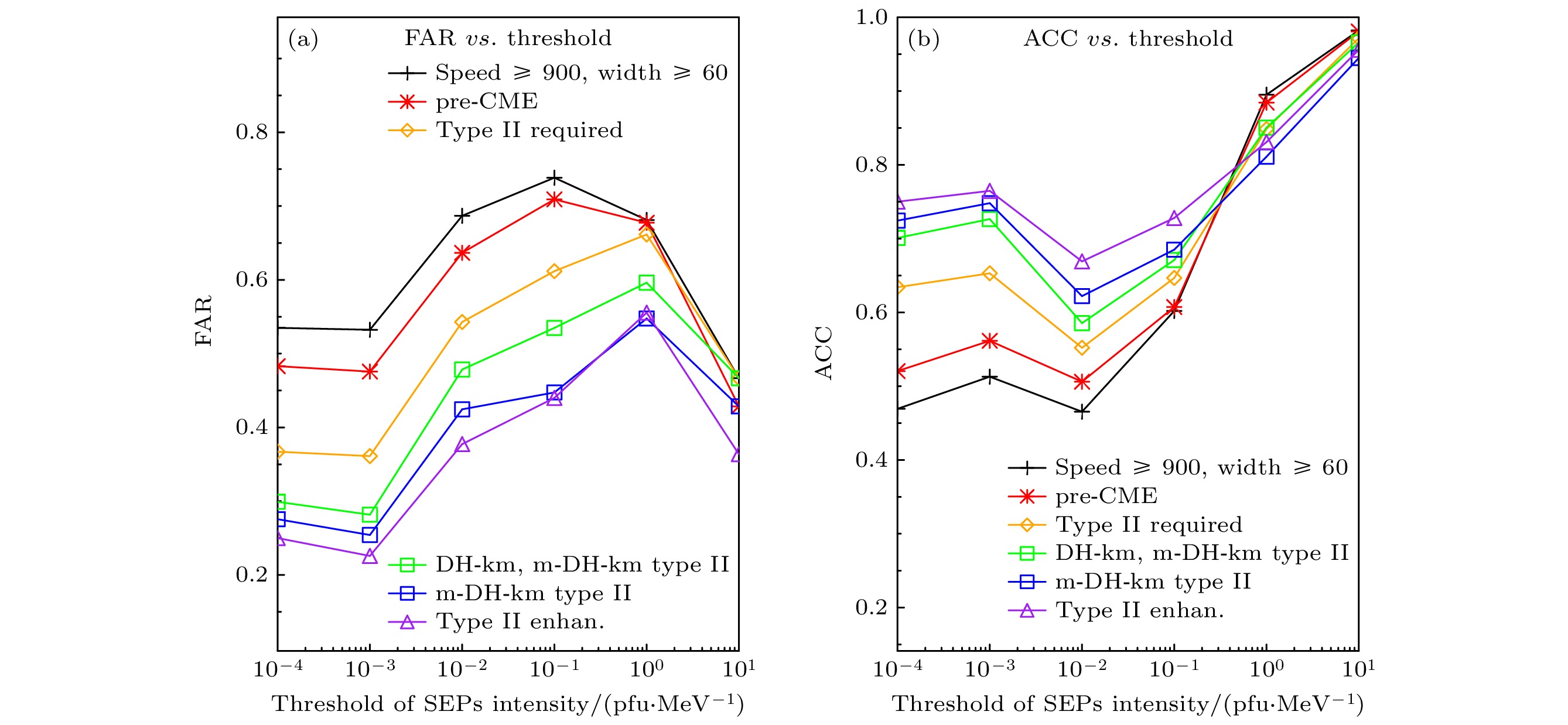
图 8 (a)误报率FAR和(b)准确率ACC随SEP事件峰值强度阈值设定值的变化. 黑色“+”表示CME速度≥900 km/s且角宽≥60°; 红色“*”表示存在pre-CME; 橙色菱形表示存在II型射电暴; 绿色正方形表示伴随DH-km或m-DH-km波段的II型射电暴, 即IP II型射电暴; 蓝色正方形表示伴随m-DH-km波段的II型射电暴; 紫色三角形表示伴随的II型射电暴存在射电增强
Figure 8. (a) False alarm ratio versus threshold of SEP peak intensity (0 is a perfect score), for different CME selections based on their associations. The curves are for CME with speed ≥ 900 km/s and angular width ≥ 60° (black crosses), pre-CME required (red asterisks), type II radio bursts required (orange diamonds), IP type II radio bursts (DH-km or m-DH-km) required (green squares), m-DH-km type II radio bursts required (blue squares); radio enhancement in type II radio bursts (purple triangles). (b) The accuracy (fraction of correct predictions) versus threshold (perfect score = 1).
表 1 不同SEP事件强度阈值情况下有/无II型射电暴伴随的SEP事件误报对比
Table 1. False alarms fraction of SEP predictions for CMEs with/without type II radio bursts at different SEP intensity thresholds.
强度阈值/
(pfu⋅MeV–1)无II型射电暴(188) 有II型射电暴(317) $ {10}^{-2} $ 68.1% 42.0% $ {10}^{-3} $ 71.8% 32.8% $ {10}^{-4} $ 80.9% 36.6% 表 2 不同类型II型射电暴条件下的模型输出结果
Table 2. Predicted results of SEPs associated with different classes of type II radio bursts.
II型射电
暴类型事件数量 数量
占比/%误报
占比/%击中
占比/%metric 6 1.9 83.3 0 DH 39 12.3 56.4 12.8 km 6 1.9 50 33.3 m-DH 32 10.1 43.8 25.0 DH-km 107 33.8 41.1 33.6 m-DH-km 127 40.1 35.4 48.0 表 3 当SEP阈值强度选为0.01 pfu/MeV时的模型输出结果和评价指标
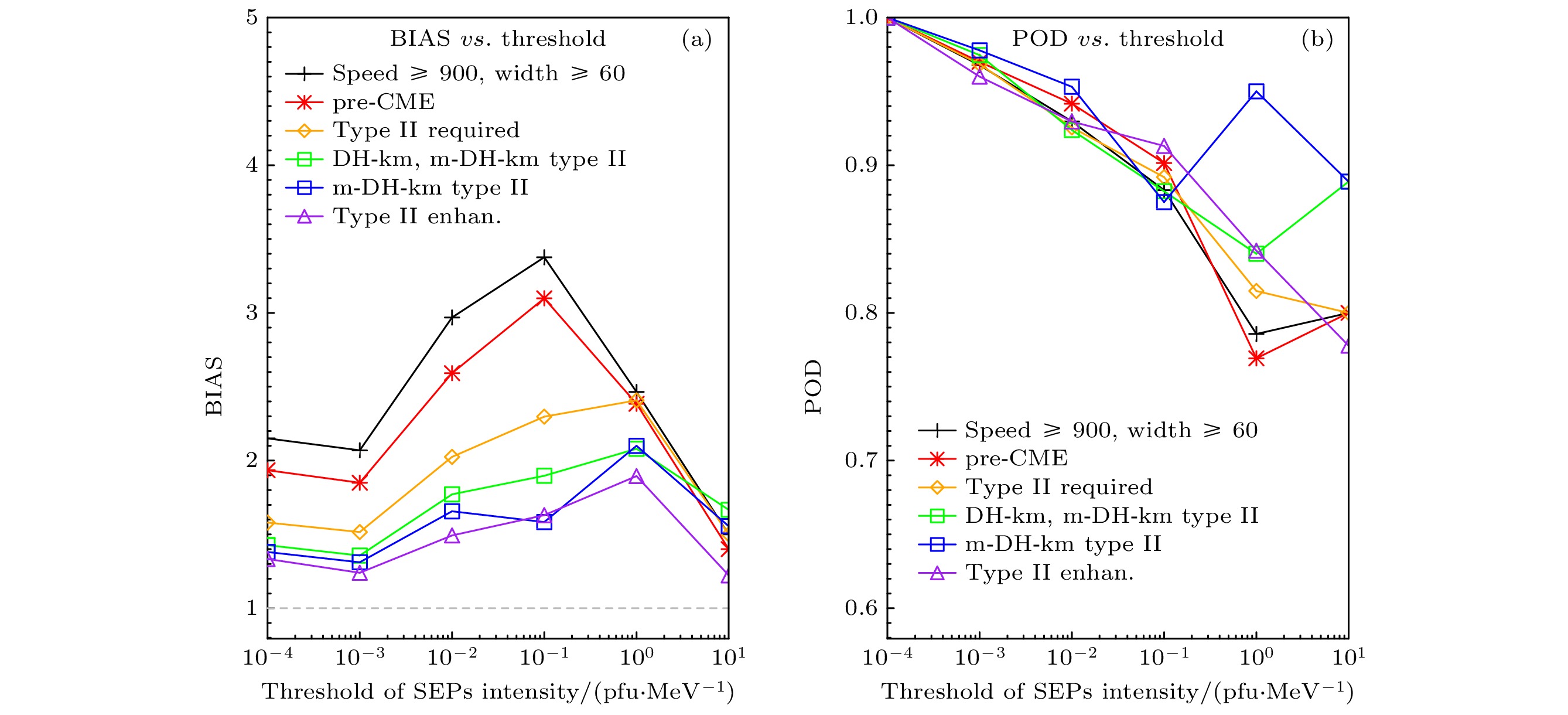
Table 3. Example of skill scores for SEP intensity threshold = 0.01 pfu/MeV.
条件 total Hits FA Cr Misses FAR POD BIAS POFD HK ACC 完美得分 0 1 1 0 1 1 CME速度≥900 km/s, 角宽≥60°(对照组) 505 119 261 116 9 0.69 0.93 2.97 0.69 0.24 0.47 无pre-CME 90 6 63 19 2 0.91 0.75 8.63 0.77 -0.02 0.28 有pre-CME 415 113 198 97 7 0.64 0.94 2.59 0.67 0.27 0.51 无II型射电暴 188 7 128 53 0 0.95 1.00 19.29 0.71 0.29 0.32 有II型射电暴 317 112 133 63 9 0.54 0.93 2.02 0.68 0.25 0.55 无射电增强 181 46 93 38 4 0.67 0.92 2.78 0.71 0.21 0.46 有射电增强 136 66 40 25 5 0.38 0.93 1.49 0.62 0.31 0.67 $ {f}_{{\mathrm{s}}{\mathrm{t}}} $<140 MHz 279 99 118 55 7 0.54 0.93 2.05 0.68 0.25 0.55 $ {f}_{{\mathrm{s}}{\mathrm{t}}} $≥140 MHz 38 13 15 8 2 0.54 0.87 1.87 0.65 0.21 0.55 $ {f}_{{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{d}}} $ < 0.1 MHz 45 22 17 4 2 0.44 0.92 1.63 0.81 0.11 0.58 $ {f}_{{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{d}}} $ ≥ 0.1 MHz 272 90 116 59 7 0.56 0.93 2.08 0.66 0.27 0.55 m-DH-km II型射电暴 127 61 45 18 3 0.42 0.95 1.66 0.71 0.24 0.62 DH-km II型射电暴 107 36 44 22 5 0.55 0.88 1.95 0.66 0.22 0.54 m-DH-km + DH-km (行星际II型射电暴) 234 97 89 40 8 0.48 0.92 1.77 0.69 0.23 0.59 -
[1] 王劲松, 吕建永 2010 空间天气学 第1版 (北京: 气象出版社) 第16—31页
Wang J S, Lü J Y 2010 Space Weather Science (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Meteorological Press) pp16–31
[2] Kahler S W 2001 J. Geophys. Res. 106 20947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Reams D V 1999 Space. Sci. Rev. 90 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cliver E W, Kahler S W 2004 Astrophys. J. 605 902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kahler S W 1992 Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 30 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Gopalswamy N, Yashiro S, Krucker S, Stenborg G, Howard R A 2004 J. Geophys. Res. 109 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ding L G, Jiang Y, Zhao L, Li G 2013 Astrophys. J. 763 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cane H V, Von Rosenvinge T T, Cohen C M S, Mewaldt R A 2003 Geophys. Res. Lett. 30 12
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Cane H V, Mewaldt R A, Cohen C M S, Von Rosenvinge T T 2006 J. Geophys. Res. 111 90
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Le G M, Zhang X F 2017 Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 17 123
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Le G M, Li C, Zhang X F 2017 Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 17 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y, Lyu D, Wu X H, Qin G 2022 Astrophys. J. 940 67
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Stewart R T, McCabe M K, Koomen M J, Hansen R T, Dulk G A 1974 Sol. Phys. 36 203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hundhausen A J, Holzer T E, Low B C 1987 J. Geophys. Res. 92 0148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Vršnak B, Lulić S 2000 Sol. Phys. 196 181
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Vršnak B, Cliver E 2008 Sol. Phys. 253 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kahler S W 1982 J. Geophys. Res. 87 2439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cane H V, Erickson W C, Prestage N P 2002 J. Geophys. Res. 107 1315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wild J, McCready L 1950 Aust. J. Sci. Res. Ser. A: Phys. Sci. 3 387
[20] Cane H V, Stone R G, Fainberg J, Stewart R T, Steinberg J L, Hoang S 1981 Geophys. Res. Lett. 8 1285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Prakash O, Umapathy S, Shanmugaraju A, Vršnak B 2009 Sol. Phys. 258 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kahler S W 1996 Amer. Inst. Phys. 374 61
[23] Gopalswamy N, Aguilar-Rodriguez E, Yashiro S, Nunes S, Kaiser M L, Howard R A 2005 J. Geophys. Res. 110 07
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Winter L M, Ledbetter K 2015 Astrophys. J. 809 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Kahler S W, Ling A G, Gopalswamy N 2019 Sol. Phys. 294 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 朱聪, 丁留贯, 周坤论, 钱天麒 2021 70 099601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu C, Ding L G, Zhou K L, Qian T Q 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 099601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Marqué C, Posner A, Klein K L 2006 Astrophys. J. 642 1222
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gopalswamy N, Yashiro S, Akiyama S, Mäkelä P, Xie H, Kaiser M, Howard R, Bougeret J 2008 Ann. Geophys. 26 3033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kahler S W, Reames D V, Burkepile J T 2000 High Energy Solar Physics- Anticipating Hessi 206 468
[30] Shen C, Li G, Kong X, Hu J, Sun X D, Ding L, Chen Y, Wang Y M, Xia L 2013 Astrophys. J. 763 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Ding L G, Li G, Dong L H, Jiang Y, Jian Y, Gu B 2014 J. Geophys. Res. 119 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Gopalswamy N, Yashiro S, Kaiser M L, Howard R A, Bougeret J L 2001 Astrophys. J. 548 L91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Ding L G, Wang Z W, Feng L, Li G, Jiang Y 2019 Res. Astron. Astrophys. 19 001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] 周坤论, 丁留贯, 钱天麒, 朱聪, 王智伟, 封莉 2020 69 169601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou K L, Ding L G, Qian T Q, Zhu C, Wang Z W, Feng L 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 169601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Posner A 2007 Space Weather 5 05001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Richardson I G, Mays M L, Thompson B J 2018 Space Weather 16 1862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Falconer D, Barghouty A F, Khazanov I, Moore R 2011 Space Weather 9 04003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Papaioannou A, Anastasiadis A, Kouloumvakos A, Paassilta M, Vainio R, Valtonen E, Belov A V, Eroshenko E, Abunina M, Abunin A 2018 Sol. Phys. 293 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Laurenza M, Cliver E W, Hewitt J, Storini M, Ling A G, Balch C C, Kaiser M L 2009 Space Weather 7 4
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Balch C C 1999 Radiat. Meas. 30 231
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Bruno A, Richardson I G 2021 Sol. Phys. 296 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Garcia H A 2004 Space Weather 2 02002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Huang X, Wang H N, Li L P 2012 Res. Astron. Astrophys. 12 313
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Núñez M 2011 Space Weather 9 07003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Núñez M 2015 Space Weather 13 727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Núñez M, Santiago P, Malandraki O 2017 Space Weather 15 861
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Núñez M 2018 J. Space Weather Space Clim. 8 A36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Richardson L G, von Rosenvinge T T, Cane H V, Christian E R, Cohen C M S, Labrador A W, Leske R A, Mewaldt R A, Wiedenbeck M E, Stone E C 2014 Sol. Phys. 289 3059
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Torres J, Zhao L, Chan P K, Zhang M 2022 Space Weather 20 002797
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] 王智伟, 丁留贯, 周坤论, 乐贵明 2018 地球 61 3515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z W, Ding L G, Zhou K L, Le G M 2018 Chin. J. Geophys. 61 3515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Hanssen A W, Kuipers W J A 1965 Koninklijk Ned. Meteor. Instit. 81 2
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4017
- PDF Downloads: 148
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: