-
In this paper we predict and evaluate the value of the nuclear charge radius by analyzing the relationship between nuclear mass and nuclear charge radius.We obtain 884 nuclei (Z, N ≥ 8) with known mass and known charge radii by combining AME2020 database with CR2013 database, and calculate the mass densities
$ \rho_\text{m} $ of the 884 nuclei. We aim to obtain an empirical formula of one constant which is useful in describing and predicting nuclear charge radius. With the empirical formula and the AME2020 database, the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) of the nuclear charge radius of$ \sigma = 0.093 $ fm is successfully obtained.Considering the influence of neutron numbers on$\rho_{\rm{m}}$ , we use the neutron factor${1}/{N} $ to correct the empirical formula, and the RMSD is reduced to σ = 0.047 fm (the accuracy is increased by about 50%). The second correction is shell effect of neutrons. The results show that the RMSD of nuclear charge radius is reduced to 0.034 fm based on shell effect of neutrons. We use the empirical formula with corrections to predict the nuclear charge radius (1573 nuclear charge radius with Z, N ≥ 8) which is difficult to measure experimentally. The difference between our predicted values based on AME2020 database and the experimental values measured in recent years is in the allowable range of deviation. The result shows that the new relation for nuclear charge radius is simple and reliable. In addition, the RMSD of the calculation value for 791 nuclei is reduced to σ = 0.032 fm after we have removed some nuclei with special shell effect and isotope chains. These results show that the new relation proposed in this paper can be comparable to$ A^{1/3} $ and$ Z^{1/3} $ formulas with corrections.Moreover, we study the 884 and 791 nuclear mass densities by using L-M neural network method to build description and prediction models. Comparing with CR2013, the RMSDs of nuclear charge radius are σ = 0.018 fm and σ = 0.014 fm, respectively. The RMSDs are reduced by about 50% compared with that from the empirical formula with corrections, and the predicted values are closer to the experimental values measured in recent years.-
Keywords:
- nuclear charge radius /
- shell effect of neutrons /
- neural network
[1] Campbell P, Moore I D, Pearson M R 2016 Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 86 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cheal B, Flanagan K T 2010 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Par. 37 113101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Blaum K, Dilling J, Nötershäser M 2013 Phys. Scr. T152 014017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Angeli I, Marinova K P 2013 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 99 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Marinova K P, Angeli I https://www-nds.iaea.org/radii/.
[6] Angeli I 2004 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 87 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Angeli I 1999 International Nuclear Data Commitee online: http://iaeand.iaea.or.at/indcsel.html.
[8] De Groote R P, Billowes J, Binnersley C L, et al. 2020 Nat. Phys. 16 620
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Koszorús Á, Yang X F, Jiang W G, et al. 2021 Nat. Phys. 17 439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bissell M L, Carette T, Flanagan K T, et al. 2016 Phys. Rev. C 93 064318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Xie L, Yang X F, Wraith C, et al. 2019 Phys. Lett. B 797 134805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Nerlo-Pomorska B, Pomorski K 1993 Z. Phys. A 344 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Nerlo-Pomorska B, Pomorski K 1994 Z. Phys. A 348 169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 圣宗强, 樊广伟, 钱建发 2015 64 112101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sheng Z Q, Fan G W, Qian J F 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 112101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 曹颖逾, 郭建友 2020 69 162101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Y Y, Guo J Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 162101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Goriely S, Chamel N, Pearson J M 2016 Phys. Rev. C 93 034337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhao P W, Li Z P, Yao J M, Meng J 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 054319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xia X W, Lim Y, Zhao P W, Liang H Z, Qu X Y, Chen Y, Liu H, Zhang L F, Zhang S Q, Kim Y, Meng J 2018 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 121-122 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Iimura H, Buchinger F 2008 Phys. Rev. C 78 067301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Buchinger F, Pearson J M 2005 Phys. Rev. C 72 057305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dieperink A E L, Van Isacker P 2009 Eur. Phys. J. A 42 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang N, Li T 2013 Phys. Rev. C 88 011301R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Stoitsov M V, Dobaczewski J, Nazarewicz W, et al. 2003 Phys. Rev. C 68 054312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Goriely S, Chamel N, Pearson J M 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 035804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Bao M, Zong Y Y, Zhao Y M, Arima A 2020 Phys. Rev. C 102 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Garvey G T, Gerace W J, Jaffe R L, Talmi I, Kelson I 1969 Rev. Mod. Phys. 41 S1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sun B H, Lu Y, Peng J P, Liu C Y, Zhao Y M 2014 Phys. Rev. C 90 054318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Bao M, Lu Y, Zhao Y M, Arima A 2016 Phys. Rev. C 94 064315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 焦宝宝 2022 71 152101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiao B B 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 152101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ma C, Zong Y Y, Zhao Y M, Arima A 2021 Phys. Rev. C 104 014303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Von Weizsäcker C F 1935 Z. Phys 96 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Möller P, Myers W D, Sagawa H, Yoshida S 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 052501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Geng L, Toki H, Meng J 2005 Prog. Theor. Phys. 113 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Goriely S, Chamel N, Pearson J M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 152503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Duflo J, Zuker A P 1995 Phys. Rev. C 52 R23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Qi C 2015 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Par. 42 045104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wang N, Liang Z, Liu M, et al. 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 044304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Garvey G T, Kelson I 1966 Phys. Rev. Lett. 16 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Fu G J, Lei Y, Jiang H, Zhao Y M, et al. 2011 Phys. Rev. C 84 034311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Jiang H, Fu G J, Zhao Y M, et al. 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 054317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Jiao B B 2018 Mod. Phys. Lett. A 33 1850156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Jiao B B 2020 Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 29 2050024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Yang G L, Qi B, Wang X D, Qi C 2022 Phys. Rev. C 106 024325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Utama R, Piekarewicz J 2017 Phys. Rev. C 96 044308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Utama R, Piekarewicz J 2018 Phys. Rev. C 97 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Zhang H F, Wang L H, Yin J P, Chen P H, Zhang H F 2017 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Par. 44 045110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Niu Z M, Liang H Z 2022 Phys. Rev. C 106 L021303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Shang T S, Li J, Niu Z M 2022 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 33 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Z M Niu and H Z Liang 2018 Phys. Lett. B 778 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Ma Y F, Su C, Liu J, Ren Z Z, Xu C, Gao Y H 2020 Phys. Rev. C 101 014304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Audi G, Kondev F G, Wang M, Huang W J, Naimi S 2017 Chin. Phys. C 41 030001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Wang M, Huang W J, Kondev F G, Audi G, Naimi S 2021 Chin. Phys. C 45 030003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] 卢希庭, 江栋兴, 叶沿林 2000 原子核物理 (北京: 原子能出版社) 第7—9 页
Lu X T, Jiang D X, Ye Y L 2000 Nuclear Physics (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp7–9 (in Chinese)
[54] Fu G J, Bao M, He Z, Jiang H, Zhao Y M, Arima A 2012 Phys. Rev. C 86 054303
-
图 2 884个原子核密度 (绿色折线表示的是原子核密度平均值线, 黑色光滑曲线是基于(6)式得到的拟合线, 粉色竖线分别表示中子数 N = 20, 28, 50, 82 和126的位置)
Figure 2. The green zigzag line is plotted by using the average values of
$ \rho_\text{m} $ for nuclei with the same mass number N. The black curve is plotted in terms of empirical formula Eq. (6). The vertical lines are plotted at the major neutron closure N = 20, 28, 50, 82 126.图 3 从上到下依次为884个核电荷半径的实验值与(2)式、(6)式、(7)式理论计算值的差值. 粉色竖直虚线分别表示中子数 N = 20, 28, 50, 82 和126的位置
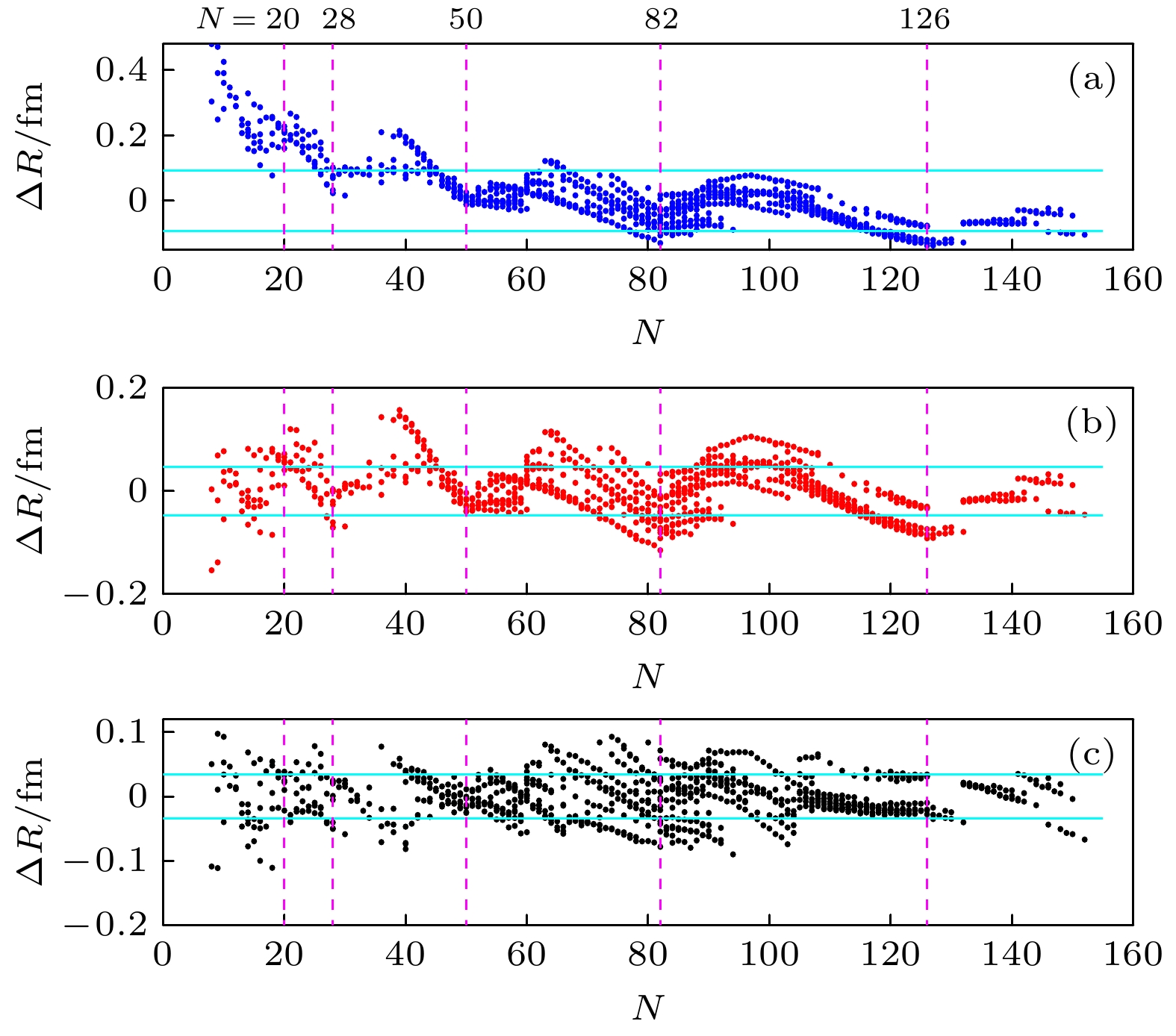
Figure 3. The difference between the experimental value of 884 nuclear charge radii and the theoretical value calculated by Eq.(2),Eq.(6) and Eq.(7), respectively. A dash vertical line is plotted at the major neutron closure N = 20, 28, 50, 82 and 126.
图 4 核电荷半径的计算值与CR2013数据库中实验值之间的误差. 粉色竖直虚线分别表示中子数 N = 20, 28, 50, 82 和126的位置, 黑色横虚线分别表示质子数 Z = 20, 28, 50 和 82 的位置 (单位: fm)
Figure 4. The difference between the calculated values of nuclear charge radius and experimental values in the CR2013 database. A dash vertical line is plotted at the major neutron closure N = 20, 28, 50, 82 and 126. The dash horizontal line is plotted at the major proton closure Z = 20, 28, 50 and 82 (in units of fm).
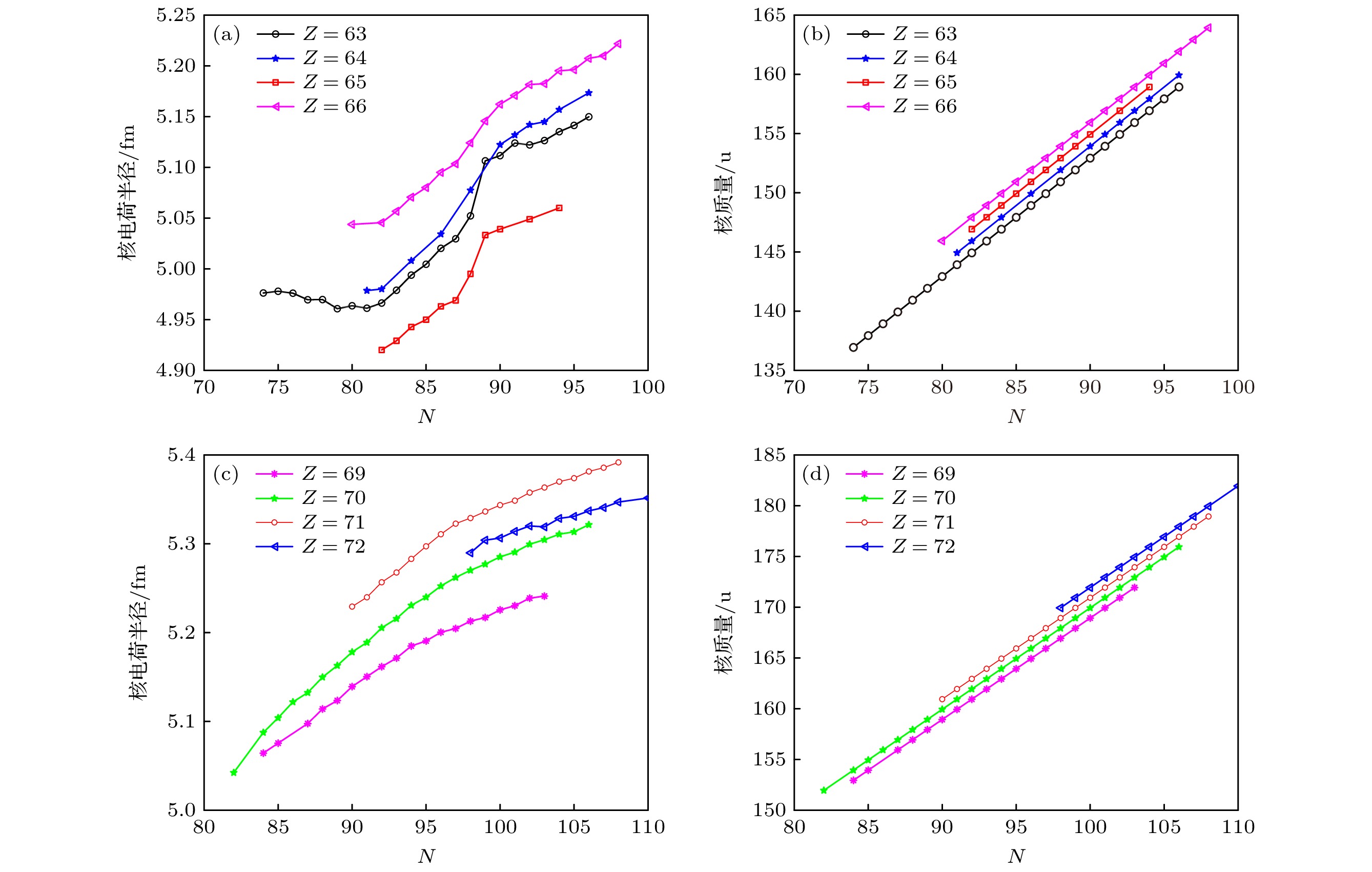
图 5 (a) 和 (b)分别表示 Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy 同位素链核电荷半径与核质量的实验值; (c) 和 (d)分别表示Tm, Yb, Lu, Hf同位素链核电荷半径与核质量的实验值
Figure 5. (a) and (b) represent the nuclear charge radii and nuclear mass of Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy elements, respectively; (c) and (d) represent the nuclear charge radii and nuclear mass of Tm, Yb, Lu, Hf elements, respectively.
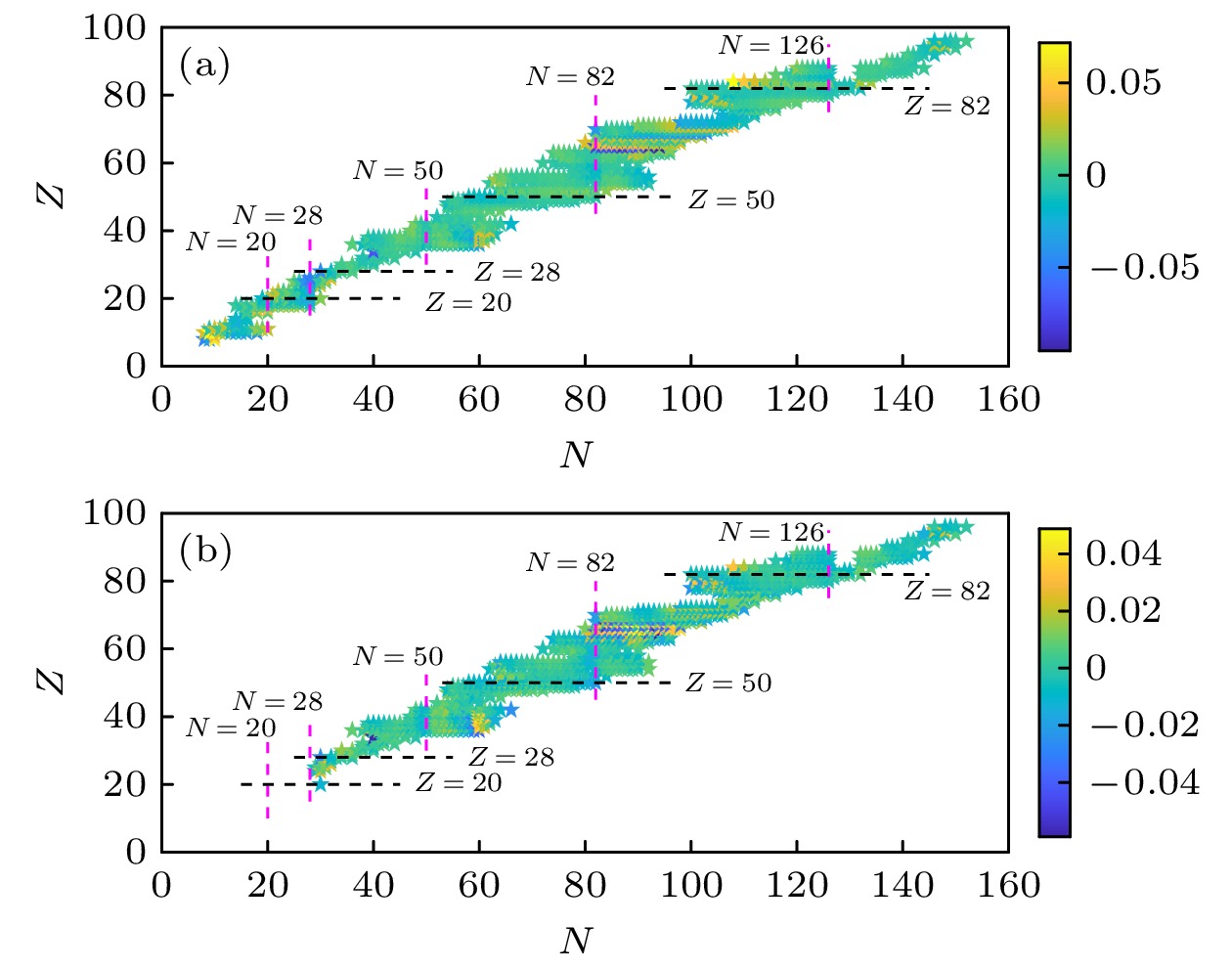
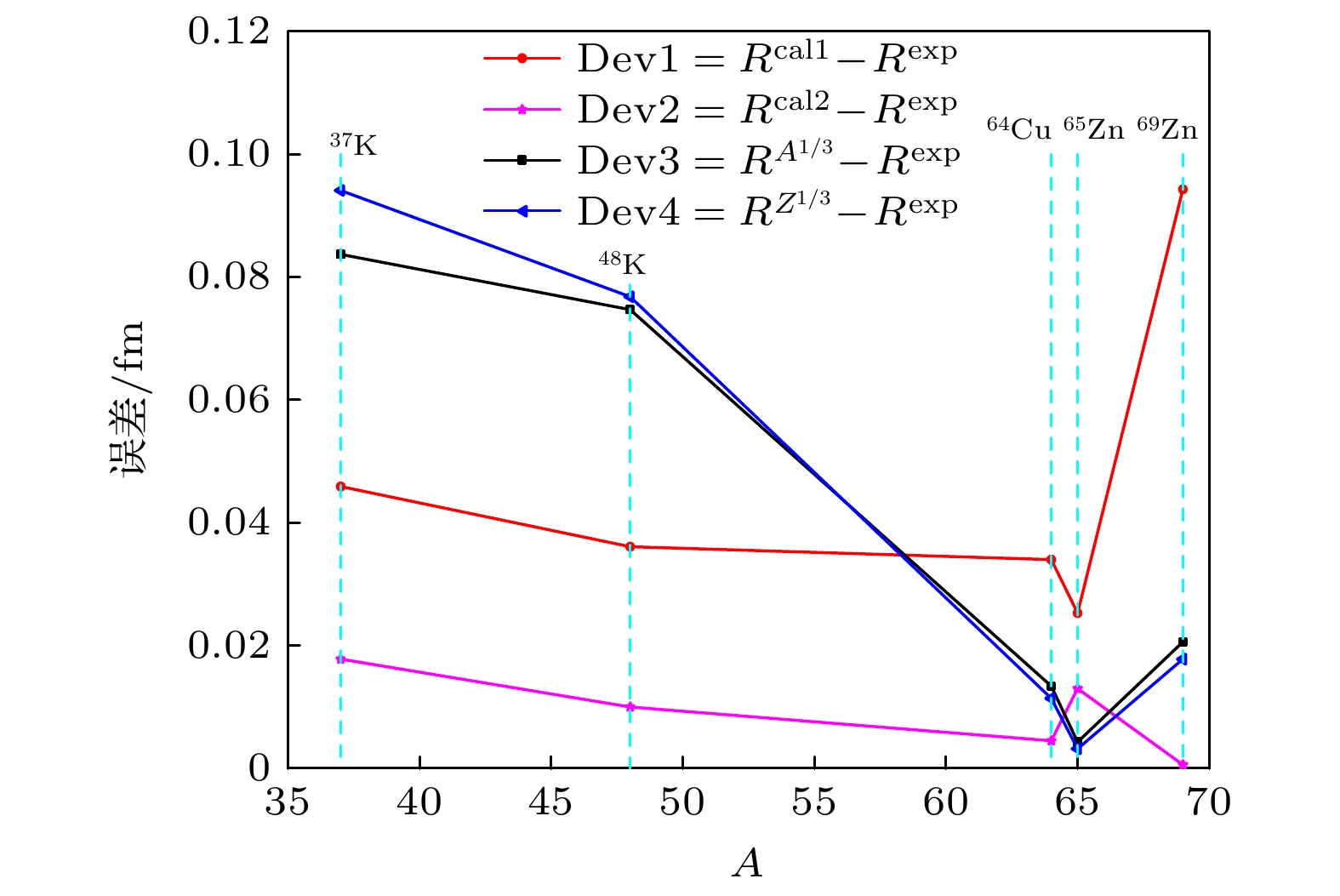
图 7 利用不同模型结合CR2013数据库预得到的预言值与近几年测得的实验值
$ ^{37}\text{K} $ [9],$ ^{48}\text{K} $ [9],$ ^{64}\text{Cu} $ [8,10],$ ^{65}\text{Zn} $ [11],$ ^{69}\text{Zn} $ [11]之间的差值Figure 7. The difference between the predicted values of nuclear charge radius (obtained by the CR2013 database) and experimental values
$ ^{37}\text{K} $ [9],$ ^{48}\text{K} $ [9],$ ^{64}\text{Cu} $ [8,10],$ ^{65}\text{Zn} $ [11],$ ^{69}\text{Zn} $ [11] in recent years.表 1 不同壳层范围的拟合参数 (单位: u/fm3)
Table 1. The parameter of different shell regions (in units of u/fm3).
Region $C_n$ $\delta1$ $a_n$ $\delta2$ 8 ≤ N ≤ 20 0.276 0.010 –0.828 0.153 21 ≤ N ≤ 28 0.363 0.007 –2.86 0.171 29 ≤ N ≤ 39 0.206 0.007 1.649 0.256 40 ≤ N ≤ 50 0.383 0.005 –5.387 0.217 51 ≤ N ≤ 66 0.242 0.005 1.812 0.316 67 ≤ N ≤ 82 0.345 0.007 –4.754 0.557 83 ≤ N ≤ 104 0.227 0.006 4.774 0.573 105 ≤ N ≤ 126 0.371 0.003 –9.614 0.433 127 ≤ N 0.230 0.003 8.088 0.516 -
[1] Campbell P, Moore I D, Pearson M R 2016 Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 86 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Cheal B, Flanagan K T 2010 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Par. 37 113101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Blaum K, Dilling J, Nötershäser M 2013 Phys. Scr. T152 014017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Angeli I, Marinova K P 2013 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 99 69
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Marinova K P, Angeli I https://www-nds.iaea.org/radii/.
[6] Angeli I 2004 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 87 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Angeli I 1999 International Nuclear Data Commitee online: http://iaeand.iaea.or.at/indcsel.html.
[8] De Groote R P, Billowes J, Binnersley C L, et al. 2020 Nat. Phys. 16 620
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Koszorús Á, Yang X F, Jiang W G, et al. 2021 Nat. Phys. 17 439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bissell M L, Carette T, Flanagan K T, et al. 2016 Phys. Rev. C 93 064318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Xie L, Yang X F, Wraith C, et al. 2019 Phys. Lett. B 797 134805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Nerlo-Pomorska B, Pomorski K 1993 Z. Phys. A 344 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Nerlo-Pomorska B, Pomorski K 1994 Z. Phys. A 348 169
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 圣宗强, 樊广伟, 钱建发 2015 64 112101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sheng Z Q, Fan G W, Qian J F 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 112101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 曹颖逾, 郭建友 2020 69 162101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Y Y, Guo J Y 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 162101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Goriely S, Chamel N, Pearson J M 2016 Phys. Rev. C 93 034337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Zhao P W, Li Z P, Yao J M, Meng J 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 054319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Xia X W, Lim Y, Zhao P W, Liang H Z, Qu X Y, Chen Y, Liu H, Zhang L F, Zhang S Q, Kim Y, Meng J 2018 At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 121-122 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Iimura H, Buchinger F 2008 Phys. Rev. C 78 067301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Buchinger F, Pearson J M 2005 Phys. Rev. C 72 057305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dieperink A E L, Van Isacker P 2009 Eur. Phys. J. A 42 269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang N, Li T 2013 Phys. Rev. C 88 011301R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Stoitsov M V, Dobaczewski J, Nazarewicz W, et al. 2003 Phys. Rev. C 68 054312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Goriely S, Chamel N, Pearson J M 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 035804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Bao M, Zong Y Y, Zhao Y M, Arima A 2020 Phys. Rev. C 102 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Garvey G T, Gerace W J, Jaffe R L, Talmi I, Kelson I 1969 Rev. Mod. Phys. 41 S1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sun B H, Lu Y, Peng J P, Liu C Y, Zhao Y M 2014 Phys. Rev. C 90 054318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Bao M, Lu Y, Zhao Y M, Arima A 2016 Phys. Rev. C 94 064315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 焦宝宝 2022 71 152101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiao B B 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 152101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ma C, Zong Y Y, Zhao Y M, Arima A 2021 Phys. Rev. C 104 014303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Von Weizsäcker C F 1935 Z. Phys 96 431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Möller P, Myers W D, Sagawa H, Yoshida S 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 052501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Geng L, Toki H, Meng J 2005 Prog. Theor. Phys. 113 785
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Goriely S, Chamel N, Pearson J M 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 152503
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Duflo J, Zuker A P 1995 Phys. Rev. C 52 R23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Qi C 2015 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Par. 42 045104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Wang N, Liang Z, Liu M, et al. 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 044304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Garvey G T, Kelson I 1966 Phys. Rev. Lett. 16 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Fu G J, Lei Y, Jiang H, Zhao Y M, et al. 2011 Phys. Rev. C 84 034311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Jiang H, Fu G J, Zhao Y M, et al. 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 054317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Jiao B B 2018 Mod. Phys. Lett. A 33 1850156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Jiao B B 2020 Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 29 2050024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Yang G L, Qi B, Wang X D, Qi C 2022 Phys. Rev. C 106 024325
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Utama R, Piekarewicz J 2017 Phys. Rev. C 96 044308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Utama R, Piekarewicz J 2018 Phys. Rev. C 97 014306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Zhang H F, Wang L H, Yin J P, Chen P H, Zhang H F 2017 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Par. 44 045110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Niu Z M, Liang H Z 2022 Phys. Rev. C 106 L021303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Shang T S, Li J, Niu Z M 2022 Nucl. Sci. Tech. 33 153
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Z M Niu and H Z Liang 2018 Phys. Lett. B 778 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Ma Y F, Su C, Liu J, Ren Z Z, Xu C, Gao Y H 2020 Phys. Rev. C 101 014304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Audi G, Kondev F G, Wang M, Huang W J, Naimi S 2017 Chin. Phys. C 41 030001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Wang M, Huang W J, Kondev F G, Audi G, Naimi S 2021 Chin. Phys. C 45 030003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] 卢希庭, 江栋兴, 叶沿林 2000 原子核物理 (北京: 原子能出版社) 第7—9 页
Lu X T, Jiang D X, Ye Y L 2000 Nuclear Physics (Beijing: Atomic Energy Press) pp7–9 (in Chinese)
[54] Fu G J, Bao M, He Z, Jiang H, Zhao Y M, Arima A 2012 Phys. Rev. C 86 054303
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8075
- PDF Downloads: 113
- Cited By: 0























 DownLoad:
DownLoad: