-
The secondary electron multipactor on the inner surface of the output window is one of the main factors limiting the power capacity of high power microwave. Therefore, it is of great significance to carry out relevant research. In this work, the process of secondary electron multipactor and the resulting loss of power are numerically simulated by using the electromagnetic particle model with one-dimensional spatial distribution and three-dimensional velocity distribution at the microwave frequency of 110 GHz. The influences of microwave electric field at the surface and dielectric material type on the power loss are studied. The simulation results show that the electron number density is higher than the critical cut-off number density after the secondary electron multipactor has reached the steady state, but the microwave electric field does not show obvious change. This is because the electrons in a very high electrostatic field are mainly concentrated in the domain of several micrometers near the dielectric surface, which is far less than the corresponding skin depth. The electron number density in the multipactor steady state increases with the microwave electric field increasing, but the ratio of the power loss to the microwave power at the surface increases slowly. After the multipactor reaches the steady state, the number density of electrons near the sapphire surface is the highest, followed by the number density near the crystal quartz surface, and the number density near the fused quartz surface is the lowest, so the corresponding power loss decreases successively. In order to verify the accuracy of the model, the simulated value of the multipactor threshold is compared with the experimental data, and the difference between them is discussed.
[1] 常超 2018 科学通报 63 1391
Chang C 2018 Chin Sci. Bull. 63 1391
[2] 杨德文, 陈昌华, 史彦超, 肖仁珍, 滕雁, 范志强, 刘文元, 宋志敏, 孙钧 2020 69 164102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang D W, Chen C H, Shi Y C, Xiao R Z, Teng Y, Fan Z Q, Liu W Y, Song Z M, Sun J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 164102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 刘振帮, 黄华, 金晓, 王腾钫, 李士锋 2020 69 218401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Wang T F, Li S F 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 218401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chang C, Liu G, Tang C, Chen C, Fang J 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 055702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 蔡利兵, 王建国 2011 18 025217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai L B, Wang J G 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 18 025217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhao P, Wang R, Guo L 2022 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 31 095005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kishek R A, Lau Y Y 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kim H C, Verboncoeur J P 2006 Phys. Plasmas 13 123506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 蔡利兵, 王建国 2010 59 1143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai L B, Wang J G 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 李爽, 常超, 王建国, 刘彦升, 朱梦, 郭乐田, 谢佳玲 2015 64 137701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S, Chang C, Wang J G, Liu Y S, Zhu M, Guo L T, Xie J L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 137701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 左春彦, 高飞, 戴忠玲, 王友年 2018 67 225201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zuo C Y, Gao F, Dai Z L, Wang Y N 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 225201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Iqbal A, Wong P Y, Wen D Q, Lin S, Verboncoeur J, Zhang P 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 043201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 董烨, 周前红, 董志伟, 杨温渊, 周海京, 孙会芳 2013 强激光与粒子束 25 950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Zhou Q H, Dong Z W, Yang W Y, Zhou H J, Sun H F 2013 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 25 950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 董烨, 董志伟, 周前红, 杨温渊, 周海京 2014 63 067901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Dong Z W, Zhou Q H, Yang W Y, Zhou H J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 067901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 董烨, 周前红, 杨温渊, 董志伟, 周海京 2014 63 185206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Zhou Q H, Yang W Y, Dong Z W, Zhou H J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 185206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chang C, Liu G Z, Huang H J, Chen C, Fang J 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 083501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chang C, Huang H J, Liu G Z, Chen C H, Hou Q, Fang J Y 2009 J. Appl. Phys. 105 123305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chang C, Fang J Y, Zhang Z Q, Chen C, Tang C, Jin Q 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 141501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chang C, Liu Y S, Verboncoeur J, Chen C H, Guo L T, Li S, Wu X L 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 014102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 翁明, 谢少毅, 殷明, 曹猛 2020 69 087901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Weng M, Xie S Y, Yin M, Cao M 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 087901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Schaub S C, Shapiro M A, Temkin R J 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 175001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Birdsall C K 1991 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 19 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Taflove A, Hagness S C 2000 Computational Electrodynamics: The Finite-Difference Time Domain Method (Boston, MA: Artech House Publishers) pp10−150
[24] Vaughan J R M 1989 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 36 1963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Cheng G, Liu L 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 3109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
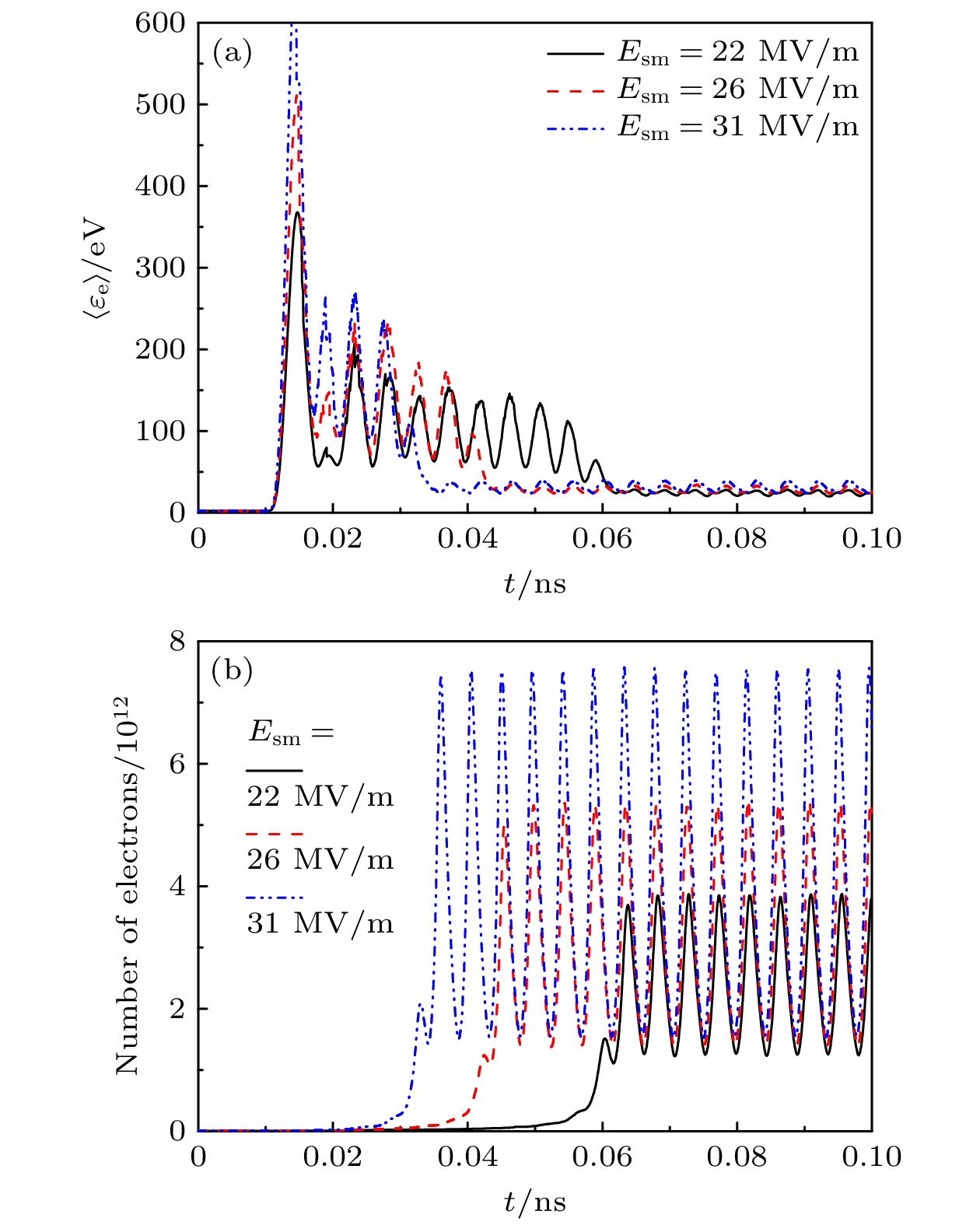
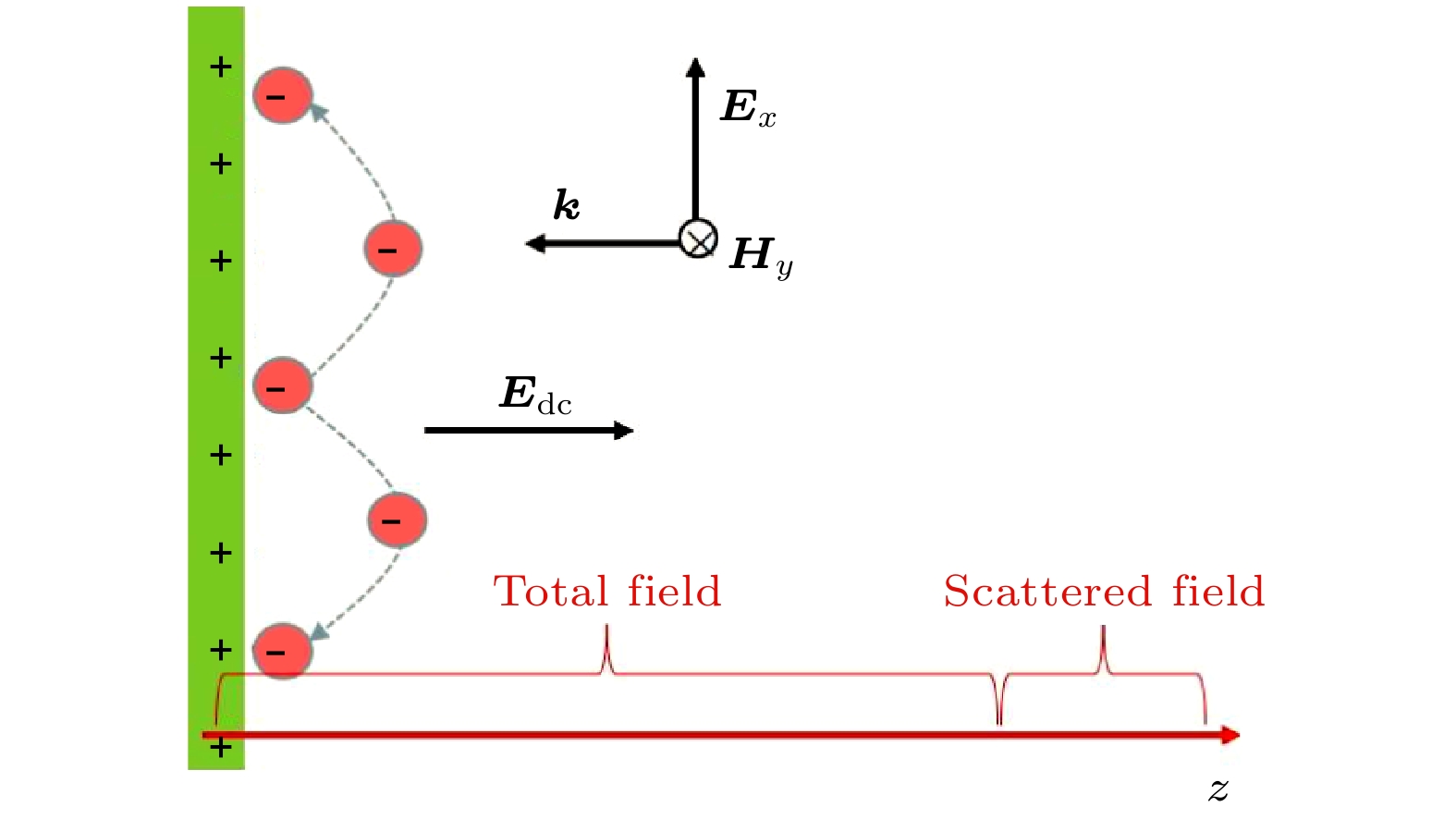
图 3 在介质材料为蓝宝石, 介质表面附近的微波电场振幅
$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ 取为不同值下, (a)平均电子能量$\langle\varepsilon_\mathrm{e}\rangle$ 和(b)电子数量随时间的变化Figure 3. Variation of (a) mean electron energy
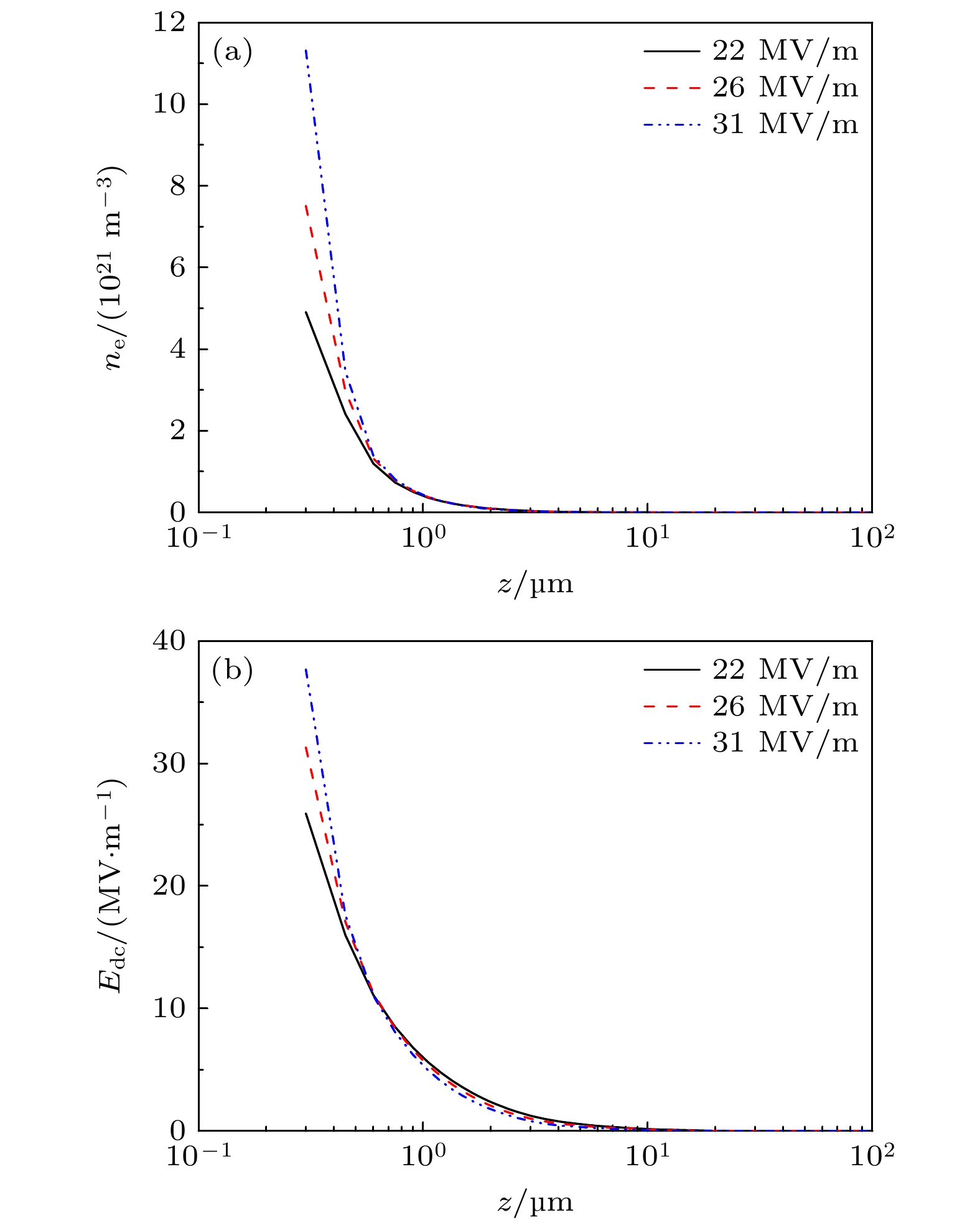
$\langle\varepsilon_\mathrm{e}\rangle$ and (b) number of electrons over time when the dielectric material is sapphire and the amplitude$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ of microwave electric field near the dielectric surface takes different values图 4 在次级电子倍增达到稳态之后, (a)电子数密度
$n_\mathrm{e}$ 和(b)法向静电场$E_{\mathrm{dc}}$ 随z的变化, 其中模拟条件与图3相同Figure 4. Spatial distributions of (a) electron number density
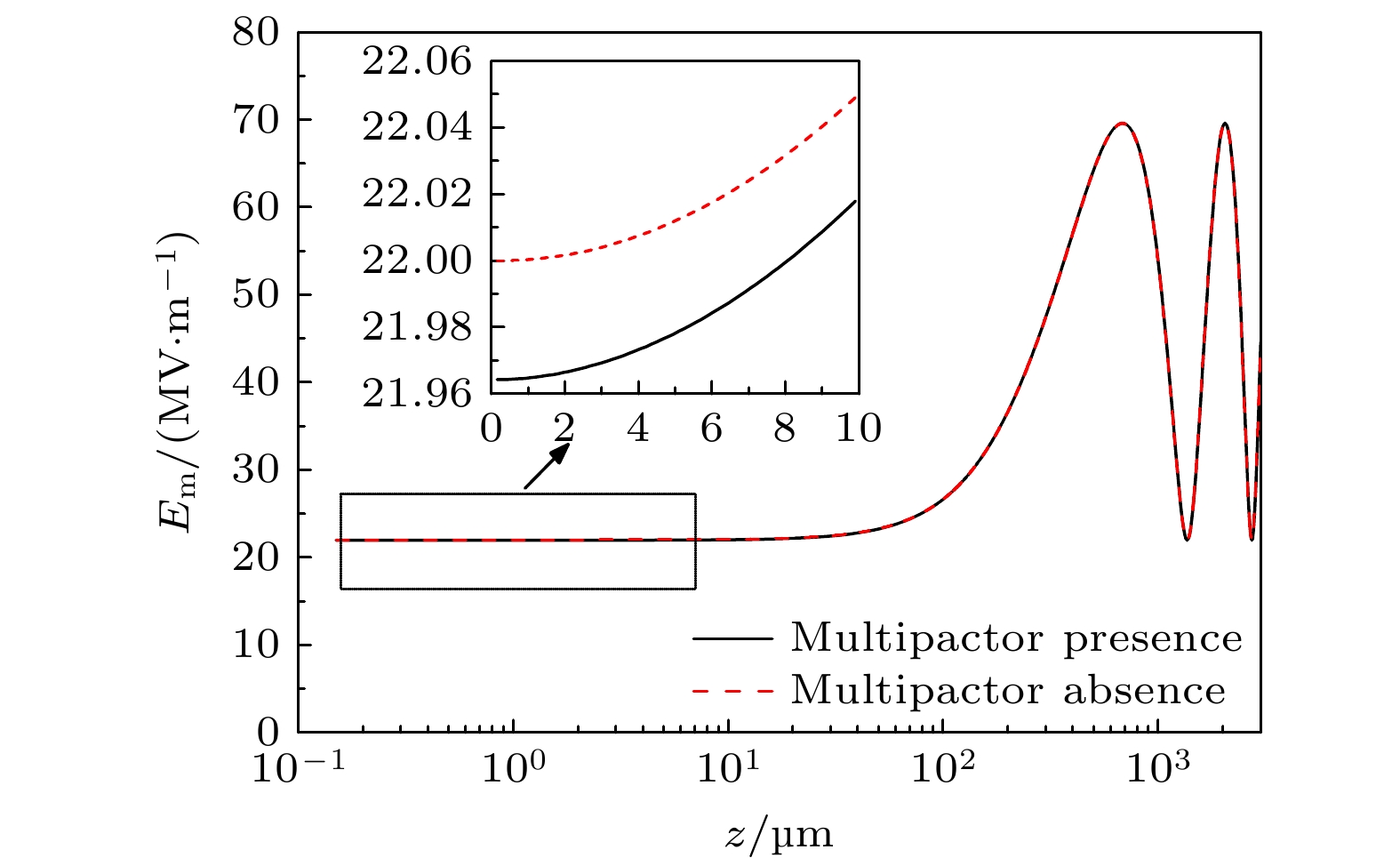
$n_\mathrm{e}$ and (b) the normal electrostatic field$E_{\mathrm{dc}}$ after the secondary electron multipactor reaches the steady state, where the simulation conditions are the same as Fig. 3图 5 电子倍增发生之前的微波电场振幅与电子倍增稳态之后的电场振幅之间的比较, 其中介质材料为蓝宝石, 表面处的电场振幅为22 MV/m
Figure 5. Comparison of microwave electric field amplitude without electron multipactor with that after the secondary electron multipactor reaches the steady state. The dielectric material is sapphire, and the electric field amplitude at the surface is 22 MV/m
图 6 在介质材料为蓝宝石, 介质表面附近的微波电场振幅
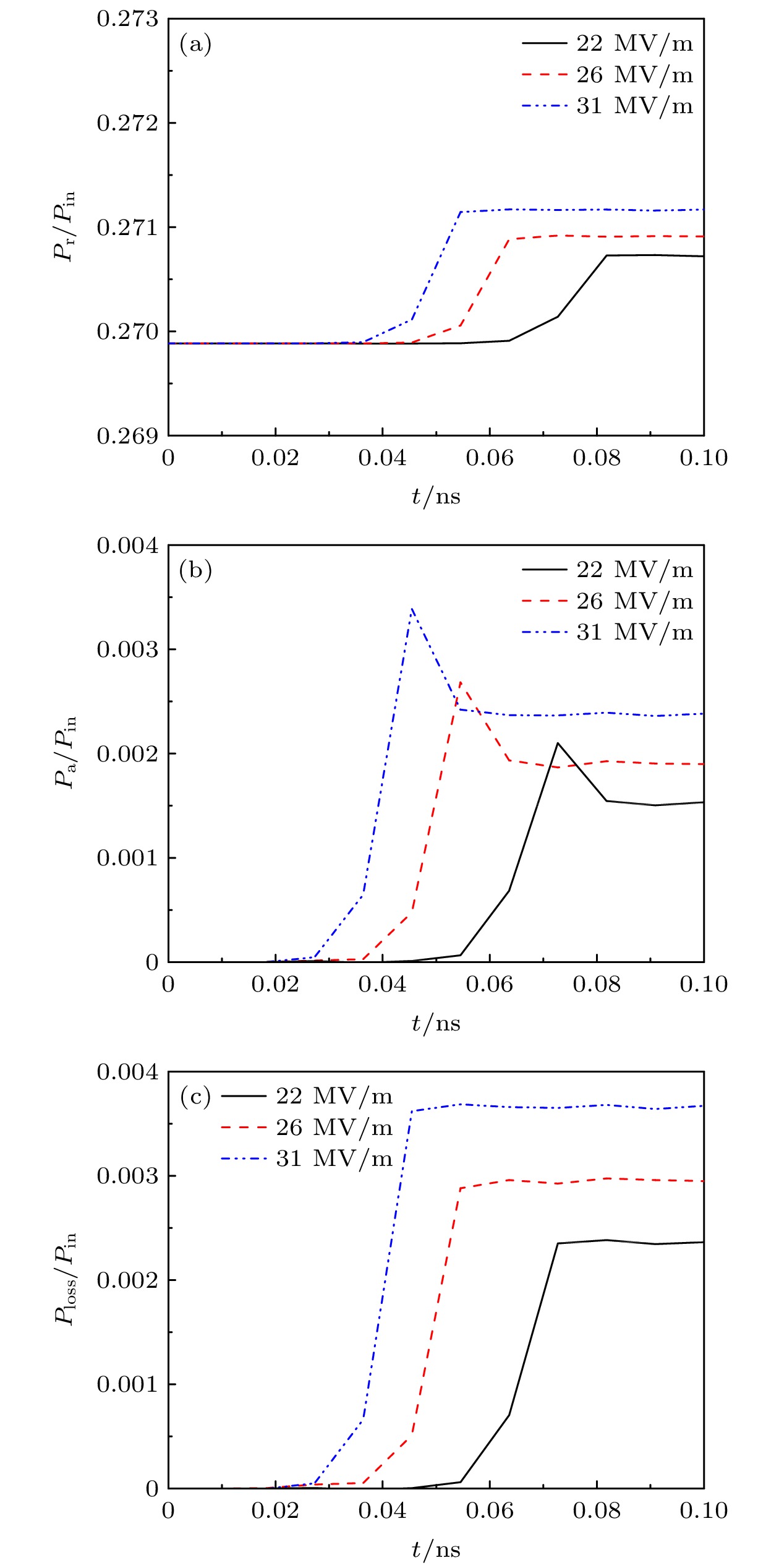
$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ 取为不同值下, (a)反射功率与入射功率之比$P_{\mathrm{r}}/P_{\mathrm{in}}$ , (b)吸收功率与入射功率之比$P_{\mathrm{a}}/P_{\mathrm{in}}$ 和(c)损失功率与入射功率之比$P_{\mathrm{loss}}/P_{\mathrm{in}}$ 随时间的变化Figure 6. (a) The ratio
$P_{\mathrm{r}}/P_{\mathrm{in}}$ of reflected power to incident power, (b) the ratio$P_{\mathrm{a}}/P_{\mathrm{in}}$ of absorbed power to incident power, and (c) the ratio$P_{\mathrm{loss}}/P_{\mathrm{in}}$ of loss power to incident power as a function of time when the dielectric material is sapphire and the amplitude$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ of microwave electric field near the dielectric surface takes different values图 7 在介质材料为蓝宝石, 介质表面附近的微波电场振幅
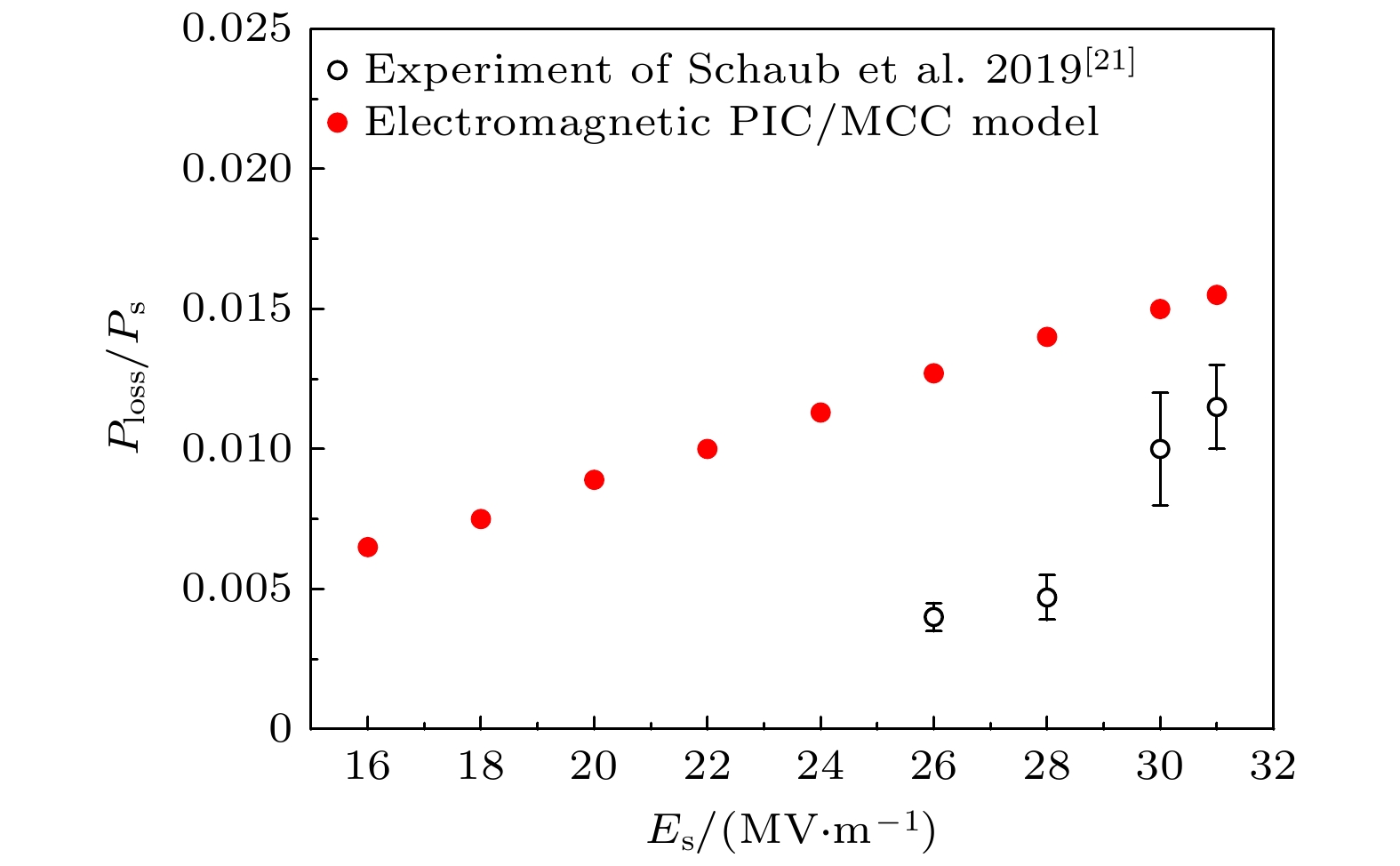
$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ 取为不同值下, 损失功率与介质表面处功率之比的模拟值与实验数据的比较Figure 7. Comparison between simulated value and experimental data of the ratio of loss power to power near dielectric surface when the dielectric material is sapphire and the amplitude
$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ of microwave electric field near the dielectric surface takes different values图 8 在介质材料分别为蓝宝石、熔融石英、石英晶体且介质表面附近的微波电场振幅
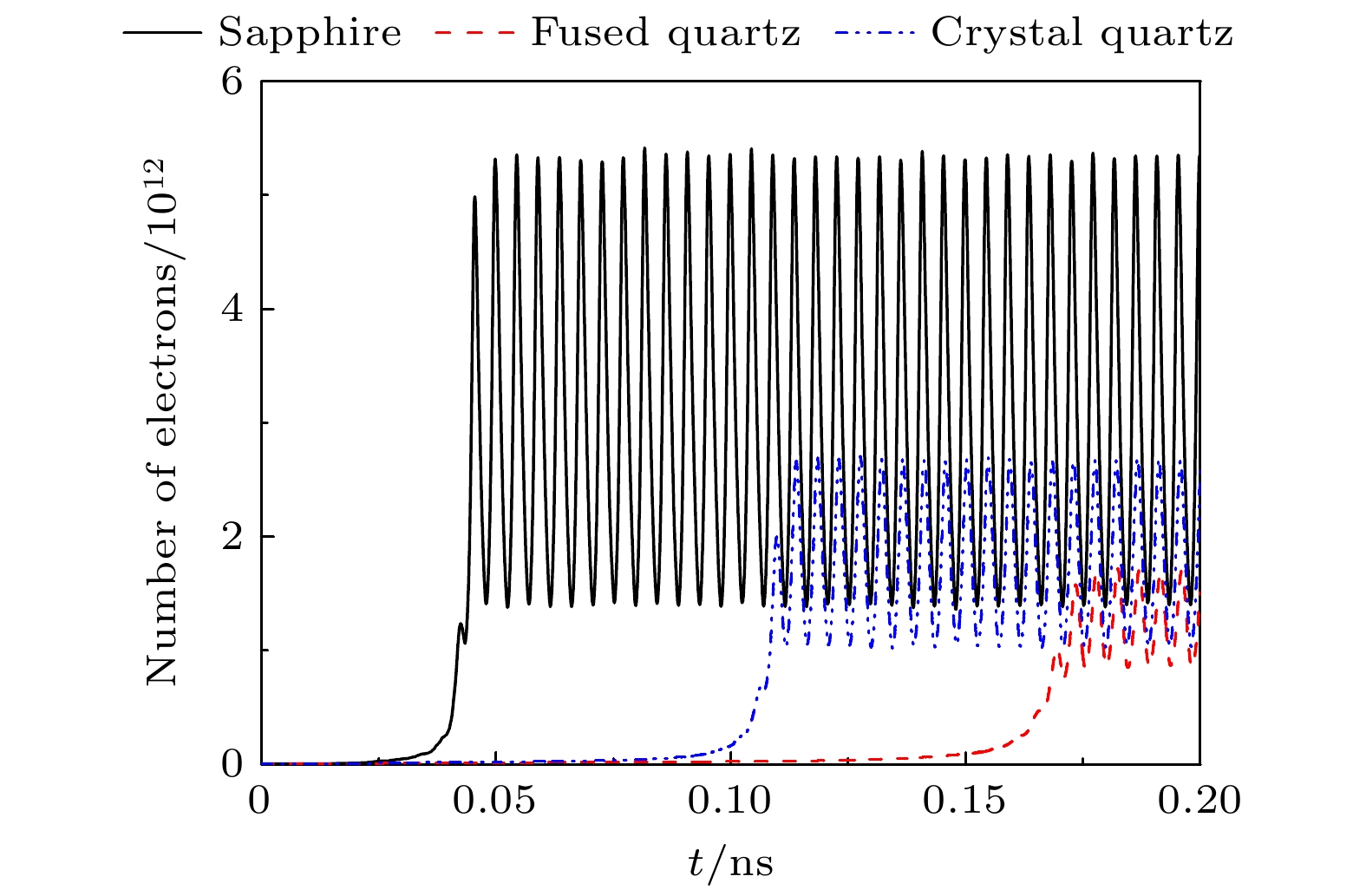
$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ 均取为$26\;{\rm{MV}}\cdot \rm{m}^{-1}$ 下, 电子数量随时间的变化Figure 8. Number of electrons as a function of time when the dielectric materials are sapphire, fused quartz, and crystal quartz and the amplitude
$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ of the microwave electric field near the dielectric surface is$26\;{\rm{MV}}\cdot \mathrm{m}^{-1}$ 图 9 在介质材料分别为蓝宝石、熔融石英、石英晶体且介质表面附近的微波电场振幅
$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ 均取为$26\;{\rm{MV}}\cdot \mathrm{m}^{-1}$ 下, 电子倍增达到稳态之后的电子数密度随z的变化Figure 9. Number density of electrons as a function of z after the secondary electron multipactor reaches steady state. The dielectric materials are sapphire, fused quartz, and crystal quartz and the amplitude
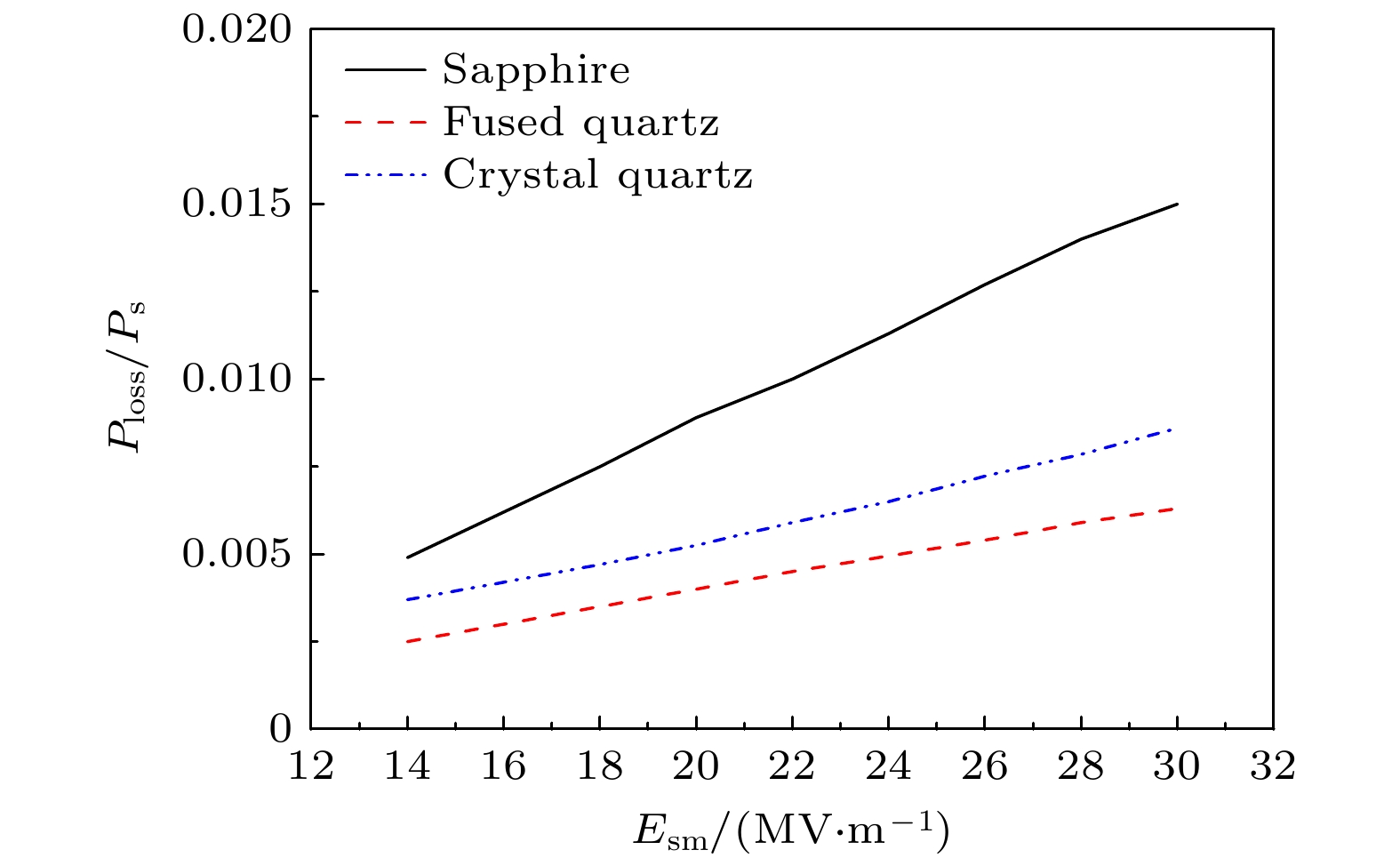
$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ of the microwave electric field near the dielectric surface is$26\;{\rm{MV}}\cdot \mathrm{m}^{-1}$ 图 10 在电子倍增达到稳态之后, 损失功率与介质表面处的功率之比
$P_{\mathrm{loss}}/P_{\mathrm{s}}$ 随微波电场振幅$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ 的变化, 其中介质材料分别为蓝宝石、熔融石英、石英晶体Figure 10. Ratio of the loss power to the power at the surface
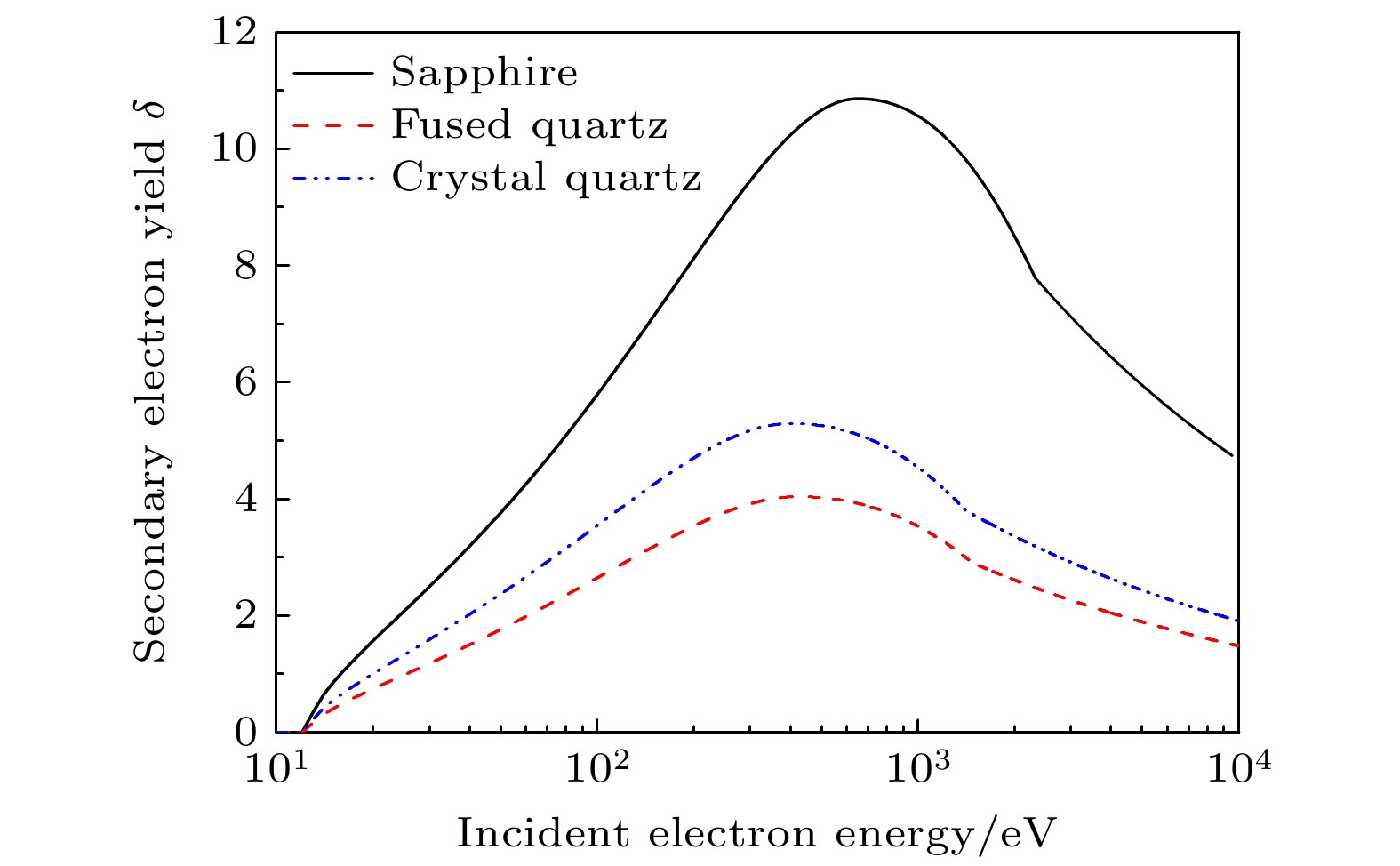
$P_{\mathrm{loss}}/P_{\mathrm{s}}$ as a function of the amplitude of the microwave electric field$E_\mathrm{{sm}}$ after the electron multipactor reaches the steady state. The dielectric materials are sapphire, fused quartz and quartz crystal, respectively表 1 介质材料的次级电子发射参数[21]和电磁参数
Table 1. Secondary electron emission parameters[21] and electromagnetic parameters of dielectric materials
材料类型 次级电子发射参数 电磁参数 $\delta_{\mathrm{max0}}$ $\varepsilon_{\mathrm{max0}}$/eV $\epsilon_{\mathrm{r}}$ $\mu_\mathrm{r}$ 蓝宝石 7.8 650 10 1.0 熔融石英 2.9 420 3.6 1.0 石英晶体 3.8 400 4.6 1.0 -
[1] 常超 2018 科学通报 63 1391
Chang C 2018 Chin Sci. Bull. 63 1391
[2] 杨德文, 陈昌华, 史彦超, 肖仁珍, 滕雁, 范志强, 刘文元, 宋志敏, 孙钧 2020 69 164102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang D W, Chen C H, Shi Y C, Xiao R Z, Teng Y, Fan Z Q, Liu W Y, Song Z M, Sun J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 164102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 刘振帮, 黄华, 金晓, 王腾钫, 李士锋 2020 69 218401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Wang T F, Li S F 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 218401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Chang C, Liu G, Tang C, Chen C, Fang J 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 055702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 蔡利兵, 王建国 2011 18 025217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai L B, Wang J G 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 18 025217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhao P, Wang R, Guo L 2022 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 31 095005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Kishek R A, Lau Y Y 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Kim H C, Verboncoeur J P 2006 Phys. Plasmas 13 123506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 蔡利兵, 王建国 2010 59 1143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cai L B, Wang J G 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 1143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 李爽, 常超, 王建国, 刘彦升, 朱梦, 郭乐田, 谢佳玲 2015 64 137701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S, Chang C, Wang J G, Liu Y S, Zhu M, Guo L T, Xie J L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 137701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 左春彦, 高飞, 戴忠玲, 王友年 2018 67 225201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zuo C Y, Gao F, Dai Z L, Wang Y N 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 225201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Iqbal A, Wong P Y, Wen D Q, Lin S, Verboncoeur J, Zhang P 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 043201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 董烨, 周前红, 董志伟, 杨温渊, 周海京, 孙会芳 2013 强激光与粒子束 25 950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Zhou Q H, Dong Z W, Yang W Y, Zhou H J, Sun H F 2013 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 25 950
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 董烨, 董志伟, 周前红, 杨温渊, 周海京 2014 63 067901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Dong Z W, Zhou Q H, Yang W Y, Zhou H J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 067901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 董烨, 周前红, 杨温渊, 董志伟, 周海京 2014 63 185206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Zhou Q H, Yang W Y, Dong Z W, Zhou H J 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 185206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chang C, Liu G Z, Huang H J, Chen C, Fang J 2009 Phys. Plasmas 16 083501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chang C, Huang H J, Liu G Z, Chen C H, Hou Q, Fang J Y 2009 J. Appl. Phys. 105 123305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chang C, Fang J Y, Zhang Z Q, Chen C, Tang C, Jin Q 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 141501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chang C, Liu Y S, Verboncoeur J, Chen C H, Guo L T, Li S, Wu X L 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 014102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 翁明, 谢少毅, 殷明, 曹猛 2020 69 087901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Weng M, Xie S Y, Yin M, Cao M 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 087901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Schaub S C, Shapiro M A, Temkin R J 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 175001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Birdsall C K 1991 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 19 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Taflove A, Hagness S C 2000 Computational Electrodynamics: The Finite-Difference Time Domain Method (Boston, MA: Artech House Publishers) pp10−150
[24] Vaughan J R M 1989 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 36 1963
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Cheng G, Liu L 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 3109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5915
- PDF Downloads: 94
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: