-
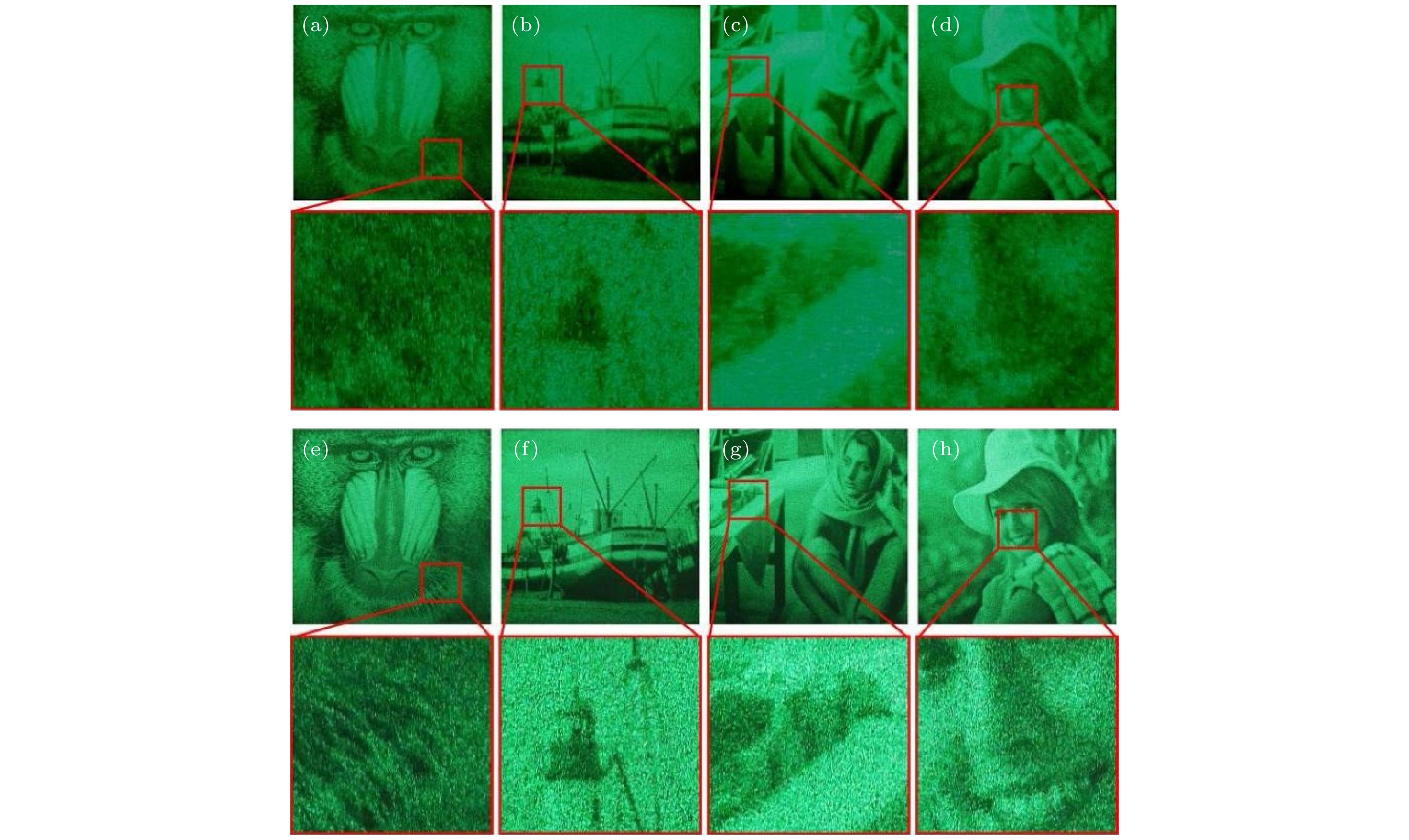
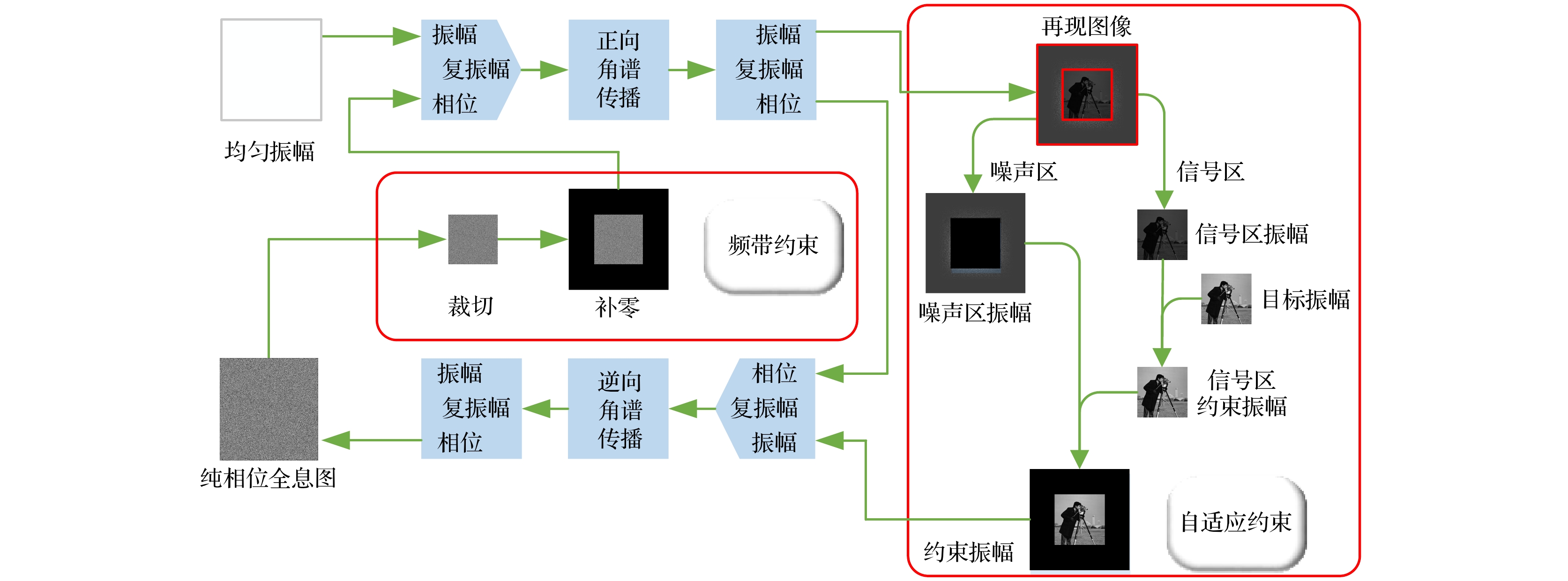
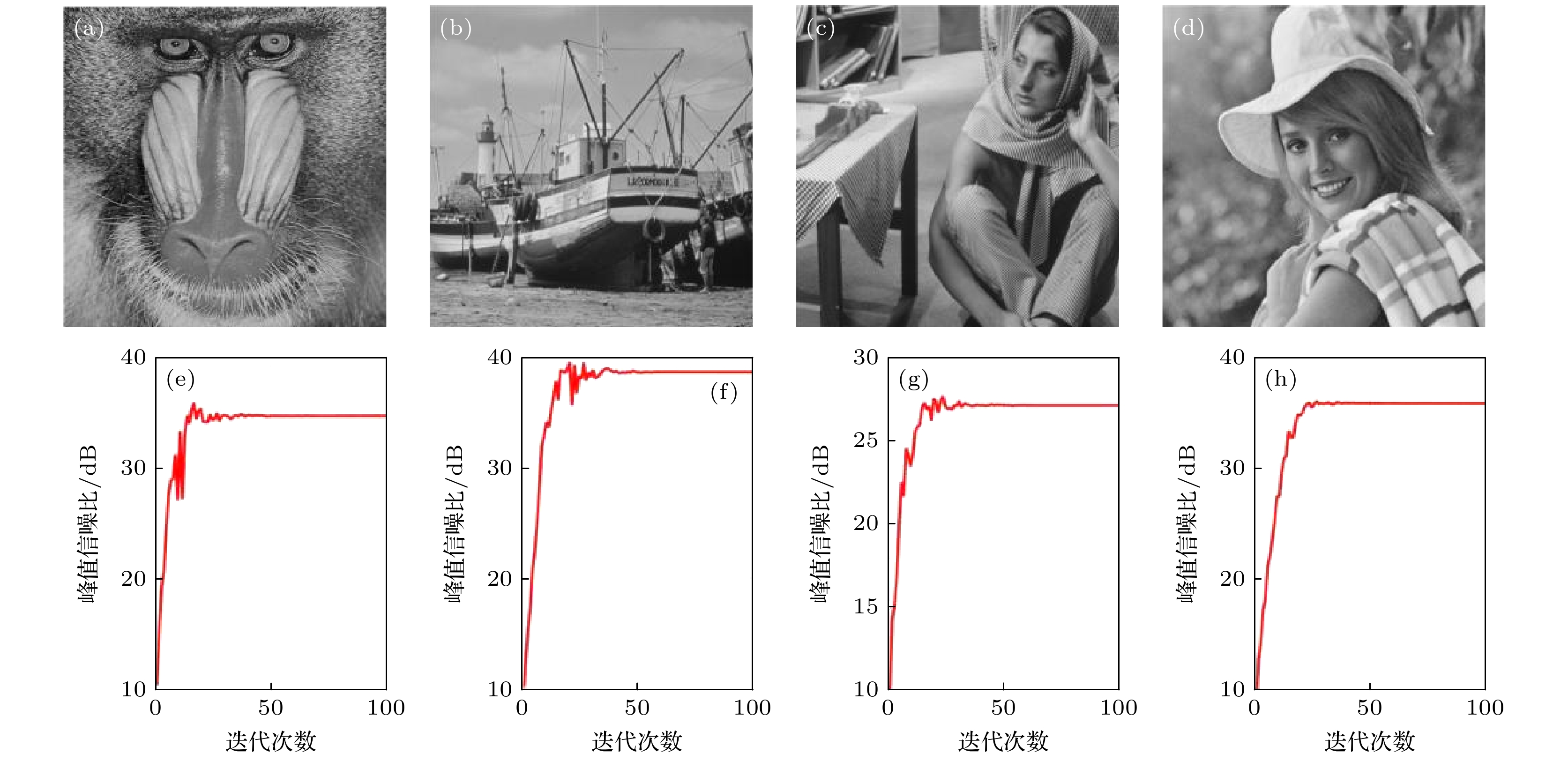
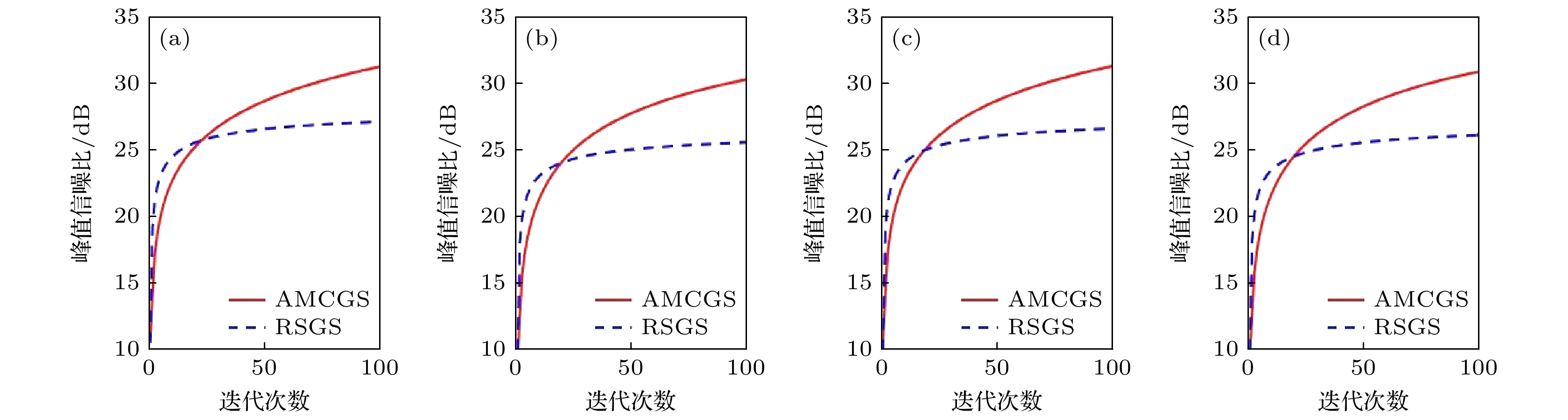
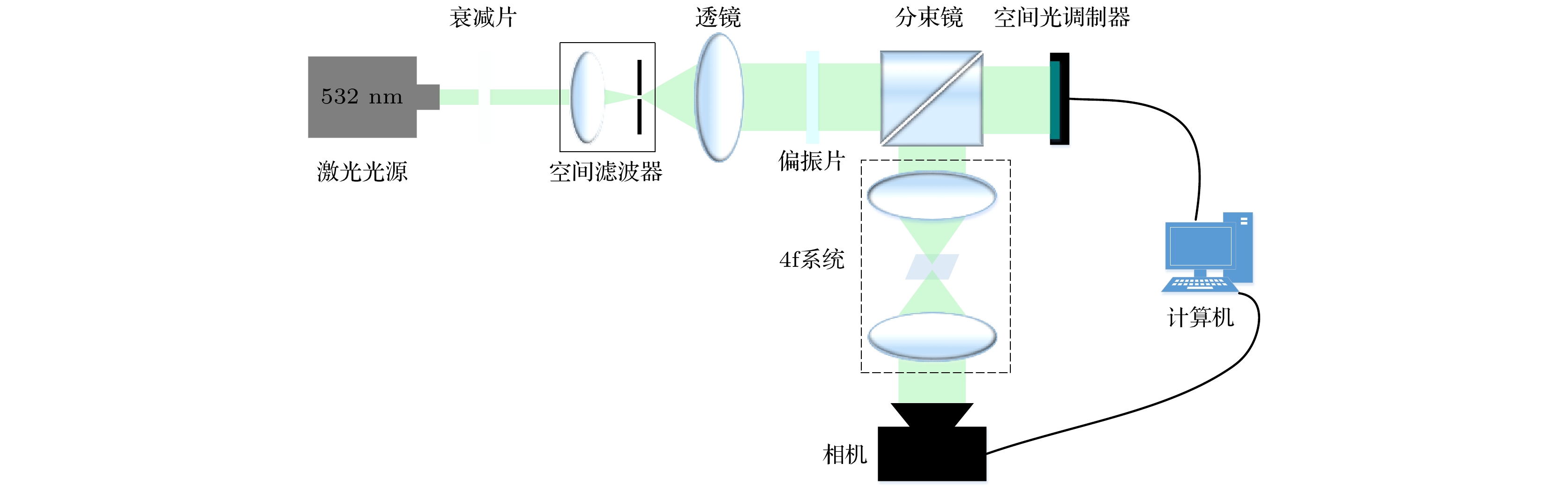
At present, spatial light modulators are incapable of modulating both the amplitude and phase of the wavefront simultaneously. Therefore, when a spatial light modulator is used for holographic display, it is necessary to encode the complex amplitude of the object wave into amplitude-only or phase-only computer-generated-hologram. The phase-only holographic display has attracted much attention of researchers due to its characteristics of high diffraction efficiency and no conjugate image. However, current optimization algorithms for generating phase-only hologram have the problems of iterative divergence, slow convergence speed, and poor reconstruction quality, which is difficult to satisfy the requirements for high-quality holographic display. In this work, we propose an accurate adaptive mixed constraint Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm by constraining the frequency bandwidth in the hologram plane and adaptively constraining the amplitude of the reconstructed image in the image plane based on the angular spectrum propagation theory. Firstly, we use the angular spectrum propagation model without paraxial approximation to simulate the forward and backward propagation of the light wave for ensuring the accuracy of the wavefront propagation. Secondly, dividing the image plane into signal area and noise area according to the spatial distribution of target image, and different adaptive feedback strategies are set up for the two regions based on the optimized effect of the phase-only hologram. The adaptive feedback strategy is established, which can accelerate the convergence speed of the proposed algorithm and enhance the hologram of freedom of the optimization. Finally, the frequency bandwidth constraint strategy is introduced in the hologram plane to optimize the edge pixels and compensate for the frequency information loss of the phase-only computer-generated hologram, which improves the reconstruction quality of the hologram. After 100 iterations, the average correlation coefficient of the holographic reconstructed image of the proposed algorithm is about 0.9857, and the average peak signal-to-noise ratio is about 31.02 dB. The correlation coefficient and the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the reconstructed images of the proposed algorithm are better than those of the Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm with only frequency bandwidth constraint strategy, and the proposed algorithm has clearer texture and better display effect. The results of numerical simulations and optical experiments show the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method. The proposed adaptive mixed constraint Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm is a promising technology for high-quality holographic display.
-
Keywords:
- computer-generated holograms /
- holographic display /
- phase-only hologram /
- phase optimization
[1] Goodman J W, Lawrence R W 1967 Appl. Phys. Lett. 11 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gabor D 1948 Nature 161 777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang H, Zhao Y, Cao L C, Jin G F 2014 Chin. Opt. Lett. 12 060002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] He Z H, Sui X M, Jin G F, Cao L C 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 A74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ma Q G, Cao L C, He Z H, Zhang S D 2019 Chin. Opt. Lett. 17 111001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 贾甲, 王涌天, 刘娟, 李昕, 谢敬辉 2012 激光与光电子学进展 49 050002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia J, Wang Y T, Liu J, Li X, Xie J H 2012 Lasers Optoelectron. Prog. 49 050002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chang C L, Bang Kiseung, Wetzstein Gordon, Lee Byoungho, Gao L 2020 Optica 7 1563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang H, Xie J H, Liu J, Wang Y T 2009 Appl. Opt. 48 5834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王迪, 侯页好, 黄倩, 郑义微, 王琼华 2022 中国激光 49 1909001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D, Hou Y H, Huang Q, Zheng Y W, Wang Q H 2022 Chin. J. Lasers 49 1909001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王一同, 周宏强, 闫景逍, 合聪, 黄玲玲 2021 中国激光 48 1918004
Wang Y T, Zhou H Q, Yan J X, He C, Huang L L 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 1918004
[11] 范爽, 张亚萍, 王帆, 高云龙, 钱晓凡, 张永安, 许蔚, 曹良才 2018 67 094203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan S, Zhang Y P, Wang F, Gao Y L, Qian X F, Zhang Y A, Xu W, Cao L C 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 094203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 席思星, 于娜娜, 王晓雷, 朱巧芬, 董昭, 王微, 刘秀红, 王华英 2019 68 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xi S X, Yu N N, Wang X L, Zhu Q F, Dong Z, Wang W, Liu X H, Wang H Y 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 曹良才, 何泽浩, 刘珂瑄, 隋晓萌 2022 红外与激光工程 51 20210935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao L C, He Z H, Liu K X, Sui X M 2022 Inf. Laser. Eng. 51 20210935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 何泽浩, 隋晓萌, 曹良才, 金国藩 2021 中国激光 48 1209002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He Z H, Sui X M, Cao L C, Jin G F 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 1209002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] He Z H, Sui X M, Jin G F, Chu D P, Cao L C 2021 Opt. Express 29 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu K X, He Z H, Cao L C 2021 Chin. Opt. Lett. 19 50501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sui X M, He Z H, Jin G F, Chu D P, Cao L C 2021 Opt. Express 29 2597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu K, He Z H, Cao L C 2022 Appl. Phys. Lett. 120 061103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wu J C, Liu K X, Sui X M, Cao L C 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 2908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gerchberg R W, Saxton W O 1972 Optik 35 237
[21] Zhou P C, Bi Y, Sun M Y, Wang H, Li F, Qi Y 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 G209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chang C L, Xia J, Yang L, Lei W, Yang Z M, Chen J H 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 6994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen L Z, Zhang H, He Z H, Wang X Y, Cao L C, Jin G F 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 3652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu Y, Wang J, Chen C, Liu C J, Jin F M, Chen N 2021 Opt. Express 29 1412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 传统GS算法, RSGS算法以及AMCGS算法迭代100次所需时间
Table 1. Time required for 100 iterations of GS algorithm, RSGS algorithm and AMCGS algorithm.
算法类型 时间/s Baboon Barbara Ship Women 传统GS算法 3.02 2.98 2.96 3.12 RSGS算法 10.05 10.03 10.06 10.10 AMCGS算法 10.47 10.11 10.08 10.26 -
[1] Goodman J W, Lawrence R W 1967 Appl. Phys. Lett. 11 77
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gabor D 1948 Nature 161 777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhang H, Zhao Y, Cao L C, Jin G F 2014 Chin. Opt. Lett. 12 060002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] He Z H, Sui X M, Jin G F, Cao L C 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 A74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Ma Q G, Cao L C, He Z H, Zhang S D 2019 Chin. Opt. Lett. 17 111001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 贾甲, 王涌天, 刘娟, 李昕, 谢敬辉 2012 激光与光电子学进展 49 050002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jia J, Wang Y T, Liu J, Li X, Xie J H 2012 Lasers Optoelectron. Prog. 49 050002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Chang C L, Bang Kiseung, Wetzstein Gordon, Lee Byoungho, Gao L 2020 Optica 7 1563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang H, Xie J H, Liu J, Wang Y T 2009 Appl. Opt. 48 5834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王迪, 侯页好, 黄倩, 郑义微, 王琼华 2022 中国激光 49 1909001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang D, Hou Y H, Huang Q, Zheng Y W, Wang Q H 2022 Chin. J. Lasers 49 1909001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 王一同, 周宏强, 闫景逍, 合聪, 黄玲玲 2021 中国激光 48 1918004
Wang Y T, Zhou H Q, Yan J X, He C, Huang L L 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 1918004
[11] 范爽, 张亚萍, 王帆, 高云龙, 钱晓凡, 张永安, 许蔚, 曹良才 2018 67 094203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan S, Zhang Y P, Wang F, Gao Y L, Qian X F, Zhang Y A, Xu W, Cao L C 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 094203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 席思星, 于娜娜, 王晓雷, 朱巧芬, 董昭, 王微, 刘秀红, 王华英 2019 68 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xi S X, Yu N N, Wang X L, Zhu Q F, Dong Z, Wang W, Liu X H, Wang H Y 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 110502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 曹良才, 何泽浩, 刘珂瑄, 隋晓萌 2022 红外与激光工程 51 20210935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao L C, He Z H, Liu K X, Sui X M 2022 Inf. Laser. Eng. 51 20210935
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 何泽浩, 隋晓萌, 曹良才, 金国藩 2021 中国激光 48 1209002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He Z H, Sui X M, Cao L C, Jin G F 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 1209002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] He Z H, Sui X M, Jin G F, Chu D P, Cao L C 2021 Opt. Express 29 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Liu K X, He Z H, Cao L C 2021 Chin. Opt. Lett. 19 50501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Sui X M, He Z H, Jin G F, Chu D P, Cao L C 2021 Opt. Express 29 2597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu K, He Z H, Cao L C 2022 Appl. Phys. Lett. 120 061103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wu J C, Liu K X, Sui X M, Cao L C 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 2908
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Gerchberg R W, Saxton W O 1972 Optik 35 237
[21] Zhou P C, Bi Y, Sun M Y, Wang H, Li F, Qi Y 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 G209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chang C L, Xia J, Yang L, Lei W, Yang Z M, Chen J H 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 6994
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chen L Z, Zhang H, He Z H, Wang X Y, Cao L C, Jin G F 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 3652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu Y, Wang J, Chen C, Liu C J, Jin F M, Chen N 2021 Opt. Express 29 1412
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7248
- PDF Downloads: 141
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: