-
In this paper, we demonstrate a new imaging architecture called time-space united coding spread spectrum single photon counting imaging technique by combining the space coding based single-pixel imaging technology and spread spectrum time coding based scanning imaging technology. This method has the advantages of range ambiguity-free and large time-bandwidth product. Under the interference of noise, this method can accurately restore depth images. In this work, the time-space united correlation nonlinear detection model based on single photon detection, forward imaging model and signal-to-noise ratio model is derived, and the depth image is restored by convex optimization inversion algorithm. The theoretical model and simulation experiments show that compared with the traditional single pixel imaging method based on spatial coding, this method improves the quality of scene reconstruction. Using m-sequence as time coding, imaging has higher noise robustness. In addition, compared with the traditional space coding single pixel imaging technology, the imaging mean square error of the proposed method is reduced by 4/5 and the imaging mean squared error is reduced by 9/10 after introducing the second correlated method. The proposed imaging architecture in this paper may provide a new path for non-scanning lidar imaging methods.
-
Keywords:
- time-space united coding /
- single photon detection /
- m-sequence /
- second correlated method
[1] Rehain P, Sua Y M, Zhu S Y, Dickson I, Muthuswamy B, Ramanathan J, Shahverdi A, Huang Y P 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tachella J, Altmann Y, Mellado N, McCarthy A, Tobin R, Buller G S, Tourneret J Y, McLaughlin S 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 4984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Brock J C, Purkis S J 2009 J. Coastal Res. 25 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Howland G A, Lum D J, Ware M R, Howell J C 2013 Opt. Express 21 23822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao Y N, Hou H Y, Han J C, Liu H C, Zhang S H, Cao D Z, Liang B L 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 4900
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Radwell N, Johnson S D, Edgar M P, Higham C F, Murray-Smith R, Padget M J 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 115 231101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li F Q, Chen H J, Pediredla A, Yeh C, He K, Veeraraghavan A, Cossairt O 2017 Opt. Express 11 31096
[8] Liu X L, Shi J H, Sun L, Li Y H, Fan J P, Zeng G H 2020 Opt. Express 28 8132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Asmann A, Mota J F C, Stewart B D, Wallace A M 2019 IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 8 385
[10] Misra P, Hu W, Yang M R, Duarte M, Jha S 2017 IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 16 2037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Krichel N J, McCarthy A, Buller G S 2010 Opt. Express 18 9192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Y F, He Y, Yang F, Luo Y, Chen W B 2016 Chin. Opt. Lett. 14 111101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu Y, Liu B, Chen Z 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 7733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Norman D M, Gardner C S 1988 Appl. Opt. 27 3650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ding Y C, Wu H X, Gao X L, Wu B, Shen Y H 2022 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 39 206
[16] Hiskett P A, Parry C S, McCarthy A, Buller G S 2008 Opt. Express 16 13685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yu Y, Liu B, Chen Z, Kang Li Z K 2020 Sensors 20 2204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu F, Yang L, Chen X L, Li Z H, Wu G 2022 Chin. Opt. Lett. 20 021202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bioucas-Dias J M, Figueiredo M A T 2007 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16 2992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Mandel L, Wolf E 1995 Optical Coherence and Quantum Optics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p123
[21] 冒添逸, 陈钱, 何伟基, 庄佳衍, 邹云浩, 戴慧东, 顾国华 2016 65 08427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mao T Y, Chen Q, He W J, Zhuang J Y, Zou Y H, Dai H D, Gu G H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 08427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gatt P, Johnson S, Nichols T 2009 Appl. Opt. 48 3261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 沈姗姗, 陈钱, 何伟基, 陈云飞, 尹文也, 戴慧东 2014 光学学报 34 1012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen S S, Chen Q, He W J, Chen Y F, Yin W Y, Dai H D 2014 Acta Opt. Sin. 34 1012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dai H D, Gu G H, He W J, Liao F J, Zhuang J Y, Liu Xiao J, Chen Q 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 6619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zierler N, Siam J 1996 Electron. Commun. Eng. J. 1996 79
[26] Molisch A F 2011 Wireless Communications (2nd Ed.) (New York: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.) p334
[27] Shen S S, Chen Q, He W J, Gu G H 2020 Opt. Quantum Electron. 52 2020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Shen S S, Chen Q, He W J, Wang Y Q 2017 Chin. Opt. Lett. 15 090101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
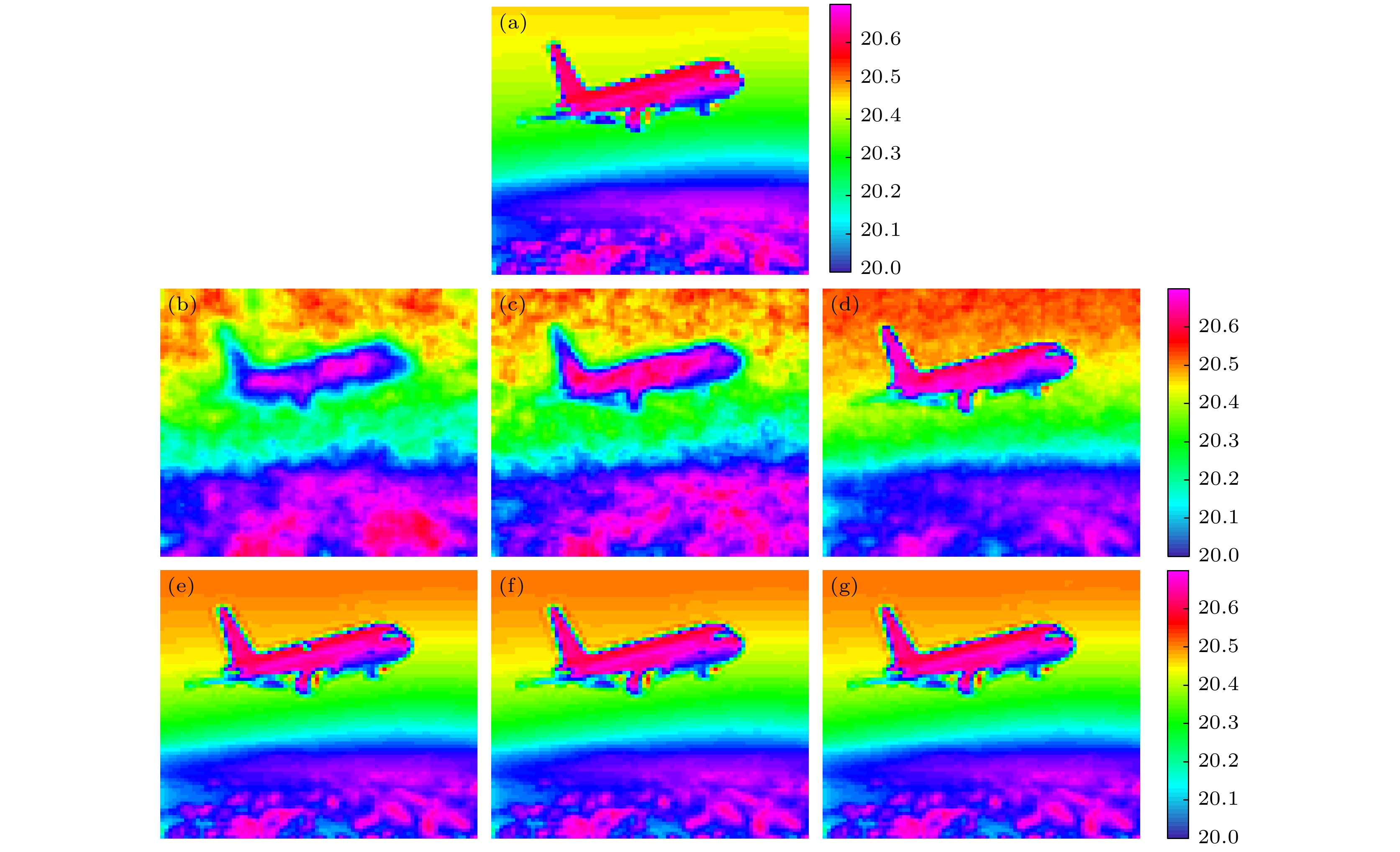
图 2 不同压缩比的时空域联合编码扩频单光子计数成像 (a) “飞机”深度真值; (b)−(g)不同压缩比的深度成像 (b) 5%, (c)15%, (d) 25%, (e) 45%, (f) 65%, (g) 85%. 颜色条表示深度数值, 单位为m
Figure 2. Time-space united coding spread spectrum single photon counting image with different compression proportions: (a) Depth ground truth of ‘airplane’; (b)−(g) depth maps with different compression proportions of (b) 5%, (c)15%, (d) 25%, (e) 45%, (f) 65% and (g) 85%. Colorbars show the depth with unit of meter.
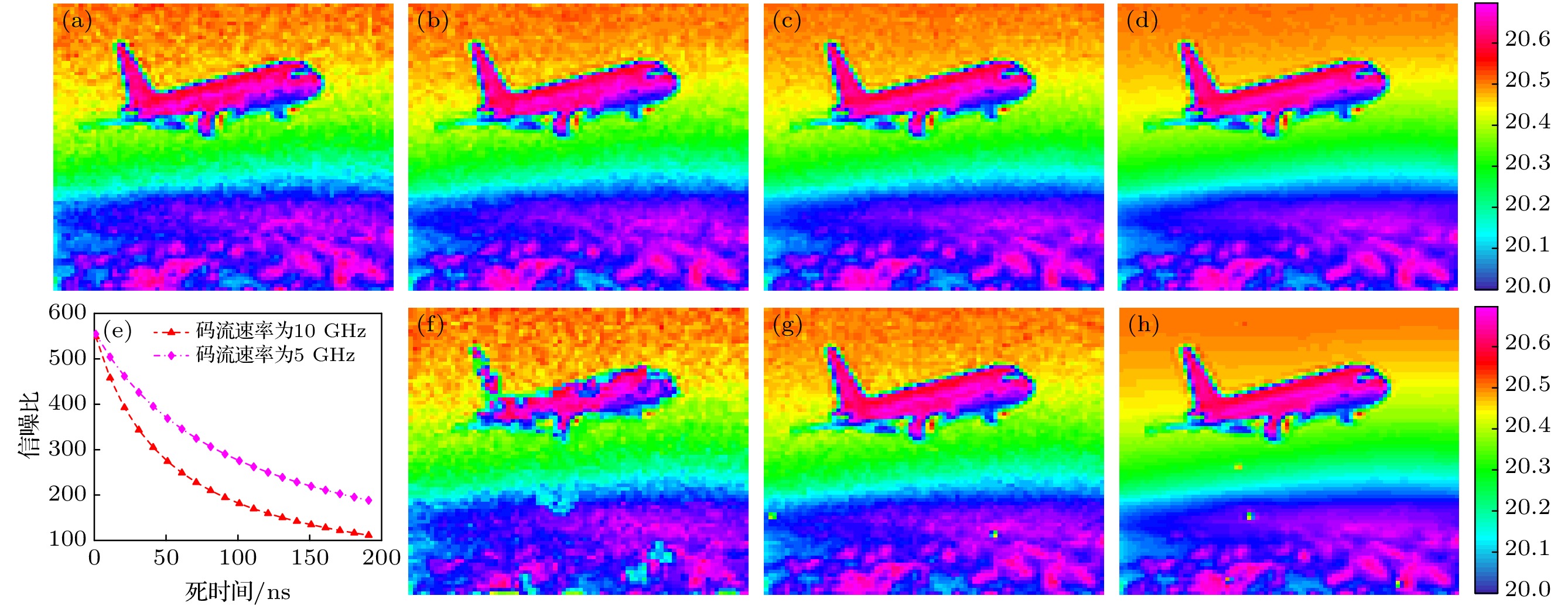
图 3 时空域联合编码扩频单光子计数成像性能模拟 (a) 1码概率为0.1的伪随机序列深度图像; (b) 1码概率为0.3的伪随机序列深度图像; (c) Gold序列的深度图像; (d) m序列的深度图像; (e) 死时间对成像性能的影响理论模拟; (f) 死时间为200 ns; (g) 死时间为20 ns; (h) 死时间为1ns. 颜色条表示深度数值, 单位为m
Figure 3. Time-space united coding image spread spectrum single photon counting imaging performance simulation: (a) Depth maps by pseudo-random sequences with ‘1’ bit of 0.1; (b) depth maps by pseudo-random sequences with ‘1’ bit of 0.3; (c) depth maps by Gold sequences; (d) depth maps by m-sequences; (e) theoretical simulation of dead time influence on imaging performance; (f) dead time is 200 ns; (g) dead time is 20 ns; (d) dead time is 1 ns. Colorbars show the depth information with unit of meter.
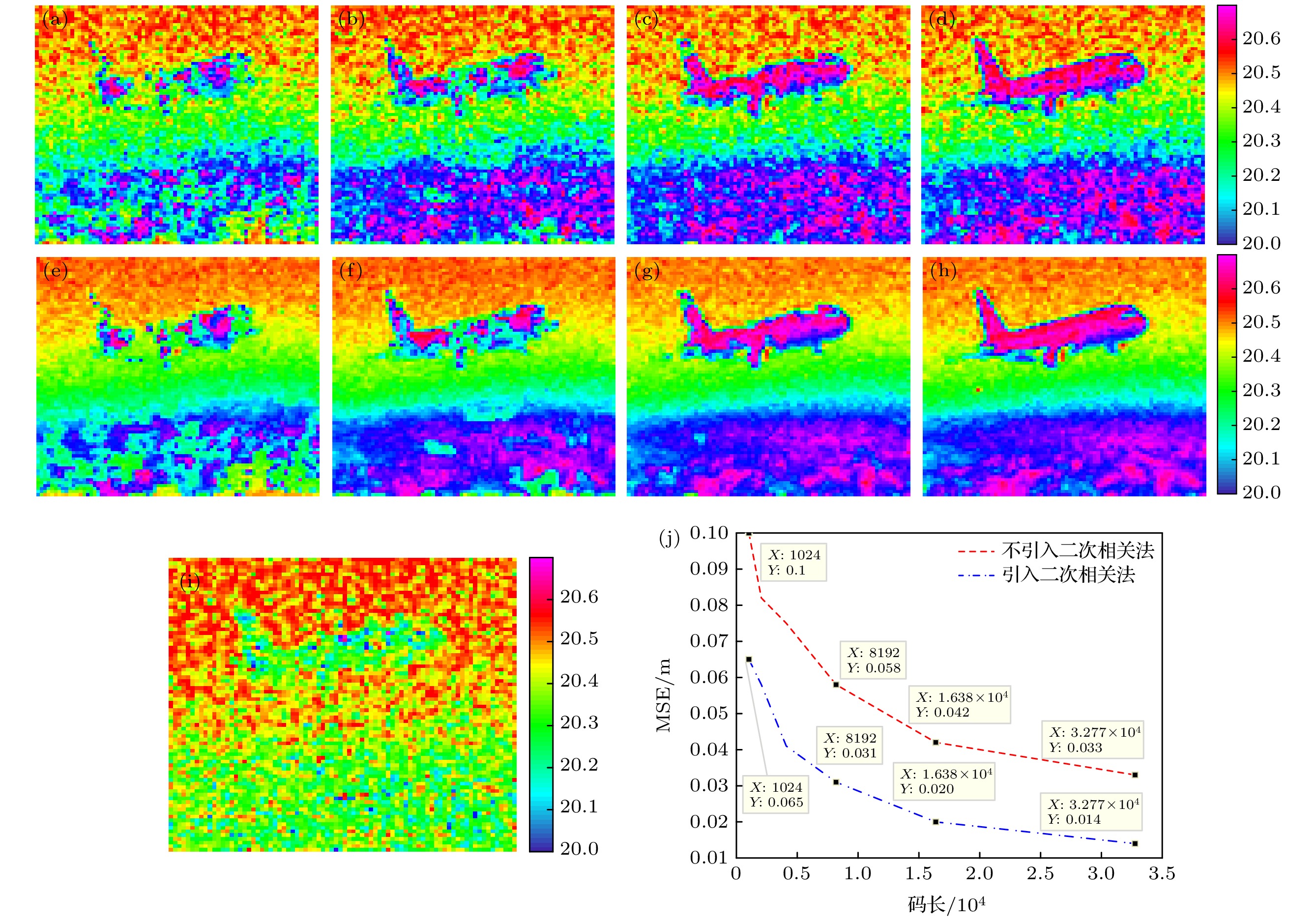
图 4 不引入二次相关法的时空域联合编码扩频单光子计数深度成像, 码长为 (a) 2048, (b) 4096, (c) 8192, (d) 16384. 引入二次相关法的时空域联合编码扩频单光子计数深度图像, 码长为(e) 2048, (f) 4096, (g) 8192, (h)16384; (i) 传统的基于空间编码的单像素深度图像; (j) 引入二次相关法(点虚线)和不引入二次相关法(虚线)的深度MSE
Figure 4. Time-space united coding image spread spectrum single photon counting imaging without second correlated method by code length of (a) 2048, (b) 4096, (c) 8192, (d)16384. Depth maps simulations with second correlated method by code length of (e) 2048, (f) 4096, (g) 8192 and (h) 16384. (i) Traditional single pixel imaging method based on space coding. (j) The depth MSE with second correlated method (dot dashed line) and without second correlated method (dashed line).
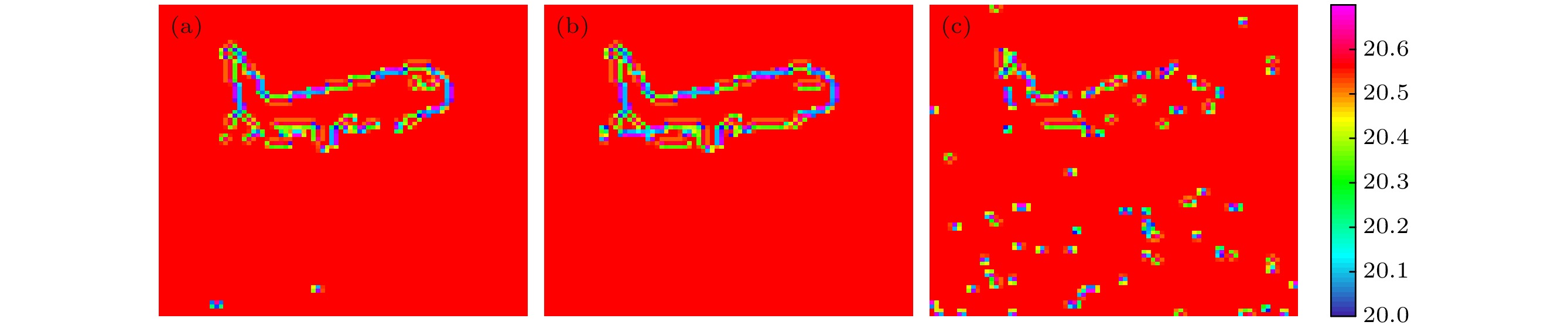
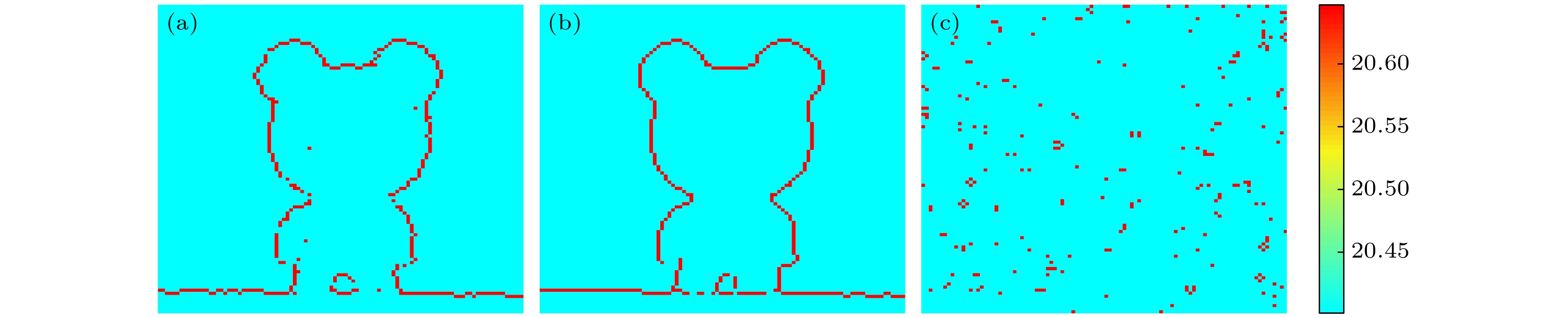
图 5 成像边缘检测 (a) 不引入二次相关法的时空域联合编码扩频单光子成像边缘检测; (b) 引入二次相关法的时空域联合编码扩频单光子计数成像边缘检测; (c) 传统的基于空间编码的单像素成像边缘检测
Figure 5. Image edge detection: (a) Time-space united coding spread spectrum single photon counting imaging without second correlated method image edge detection; (b) time-space united coding spread spectrum single photon counting imaging with second correlated method image edge detection; (c) traditional single pixel imaging method based on space coding image edge detection.
图 6 单光子计数扫描成像测试图像深度重建仿真 (a) 玩偶深度真值; (b)
$ {m_n} = 10 $ ,$ {\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.176 m}} $ , 传统的基于空间编码的单像素成像深度图; 在(c)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 5$ ,$ {\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.019 m}} $ , (d)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 8$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.03\; m}}$ , (e)$ {m_n} = 10 $ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.035 \;m}}$ 条件下, 不引入二次相关法的时空域联合编码扩频单光子计数深度图; 在(f)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 5$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.005\; m}}$ , (g)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 8$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.011\; m}}$ , (h)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 10$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.017 \;m}}$ 条件下, 引入二次相关法的时空域编码扩频单光子计数深度图, 深度单位为mFigure 6. Depth reconstruction simulation by using single photon counting scanning imaging test image: (a) Ground truth of ‘doll’; (b) the depth map by traditional single pixel imaging method based on space coding image when
${m_{\rm{n}}} = 10$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.176\; m}}$ . Depth maps by time-space united coding spread spectrum single photon counting imaging without second correlated method when (c)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 5$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.019\; m}}$ , (d)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 8$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.03\; m}}$ and (e)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 10$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.035\; m}}$ . Depth maps by time-space united coding spread spectrum single photon counting imaging with second correlated method when (f)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 5$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.005\; m}}$ , (g)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 8$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.011\; m}}$ , and (h)${m_{\rm{n}}} = 10$ ,${\text{MSE = 0}}{\text{.017\; m}}$ . The depth unit is m.图 7 成像边缘检测 (a) 不引入二次相关法的时空域联合编码扩频单光子成像边缘检测; (b) 引入二次相关法的时空域联合编码扩频单光子成像边缘检测; (c) 传统的基于空间编码的单像素成像边缘检测
Figure 7. Image edge detection: (a) Time-space united coding spread spectrum single photon counting imaging without second correlated method image edge detection; (b) time-space united coding spread spectrum single photon counting imaging with second correlated method image edge detection; (c) traditional single pixel imaging method based on space coding image edge detection.
表 1 不同重建方法的性能统计
Table 1. Performance statistical record of different reconstruction methods.
MSE/m Time/s Method ${m_{\rm{n} } } = 5$ ${m_{\rm{n}}} = 10$ ${m_{\rm{n}}} = 5$ ${m_{\rm{n}}} = 10$ TVAL3 0.033 0.011 35 57 GPSR 0.060 0.018 13 24 FISTA 0.042 0.019 16 24 -
[1] Rehain P, Sua Y M, Zhu S Y, Dickson I, Muthuswamy B, Ramanathan J, Shahverdi A, Huang Y P 2020 Nat. Commun. 11 921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Tachella J, Altmann Y, Mellado N, McCarthy A, Tobin R, Buller G S, Tourneret J Y, McLaughlin S 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 4984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Brock J C, Purkis S J 2009 J. Coastal Res. 25 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Howland G A, Lum D J, Ware M R, Howell J C 2013 Opt. Express 21 23822
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Zhao Y N, Hou H Y, Han J C, Liu H C, Zhang S H, Cao D Z, Liang B L 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 4900
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Radwell N, Johnson S D, Edgar M P, Higham C F, Murray-Smith R, Padget M J 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 115 231101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Li F Q, Chen H J, Pediredla A, Yeh C, He K, Veeraraghavan A, Cossairt O 2017 Opt. Express 11 31096
[8] Liu X L, Shi J H, Sun L, Li Y H, Fan J P, Zeng G H 2020 Opt. Express 28 8132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Asmann A, Mota J F C, Stewart B D, Wallace A M 2019 IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 8 385
[10] Misra P, Hu W, Yang M R, Duarte M, Jha S 2017 IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 16 2037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Krichel N J, McCarthy A, Buller G S 2010 Opt. Express 18 9192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang Y F, He Y, Yang F, Luo Y, Chen W B 2016 Chin. Opt. Lett. 14 111101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yu Y, Liu B, Chen Z 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 7733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Norman D M, Gardner C S 1988 Appl. Opt. 27 3650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ding Y C, Wu H X, Gao X L, Wu B, Shen Y H 2022 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 39 206
[16] Hiskett P A, Parry C S, McCarthy A, Buller G S 2008 Opt. Express 16 13685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yu Y, Liu B, Chen Z, Kang Li Z K 2020 Sensors 20 2204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wu F, Yang L, Chen X L, Li Z H, Wu G 2022 Chin. Opt. Lett. 20 021202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bioucas-Dias J M, Figueiredo M A T 2007 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16 2992
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Mandel L, Wolf E 1995 Optical Coherence and Quantum Optics (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p123
[21] 冒添逸, 陈钱, 何伟基, 庄佳衍, 邹云浩, 戴慧东, 顾国华 2016 65 08427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Mao T Y, Chen Q, He W J, Zhuang J Y, Zou Y H, Dai H D, Gu G H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 08427
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gatt P, Johnson S, Nichols T 2009 Appl. Opt. 48 3261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 沈姗姗, 陈钱, 何伟基, 陈云飞, 尹文也, 戴慧东 2014 光学学报 34 1012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shen S S, Chen Q, He W J, Chen Y F, Yin W Y, Dai H D 2014 Acta Opt. Sin. 34 1012001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dai H D, Gu G H, He W J, Liao F J, Zhuang J Y, Liu Xiao J, Chen Q 2014 Appl. Opt. 53 6619
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zierler N, Siam J 1996 Electron. Commun. Eng. J. 1996 79
[26] Molisch A F 2011 Wireless Communications (2nd Ed.) (New York: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.) p334
[27] Shen S S, Chen Q, He W J, Gu G H 2020 Opt. Quantum Electron. 52 2020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Shen S S, Chen Q, He W J, Wang Y Q 2017 Chin. Opt. Lett. 15 090101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5965
- PDF Downloads: 91
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: