-
经过几十年的发展, 全息成像已成为展示信息的成熟光学技术. 然而, 仅通过光的波长和偏振作为信息传递的载体的传统全息技术, 在信息传播的安全性和容量方面存在一定的不足. 将一种新的光学维度, 轨道角动量(orbital angular momentum, OAM), 引入全息成像为这些问题提供了一个有效的解决方案. 通过使用OAM复用的全息技术进行理论分析和仿真计算, 二维图像被加密和存储. 然后三维物体被切片为多幅二维图像, 通过OAM复用的全息技术被存储于一个相位阵列中, 实现了信息存储维度的有效降低, 并且经过OAM复用的全息技术被成功复现, 因而三维全息被实现. 此外, 每幅图按照相应拓扑荷进行加密, 信息传递的安全性被显著提升. 这种具有OAM选择性的全息技术更为安全, 信息通量更大, 具有广泛的应用潜力.
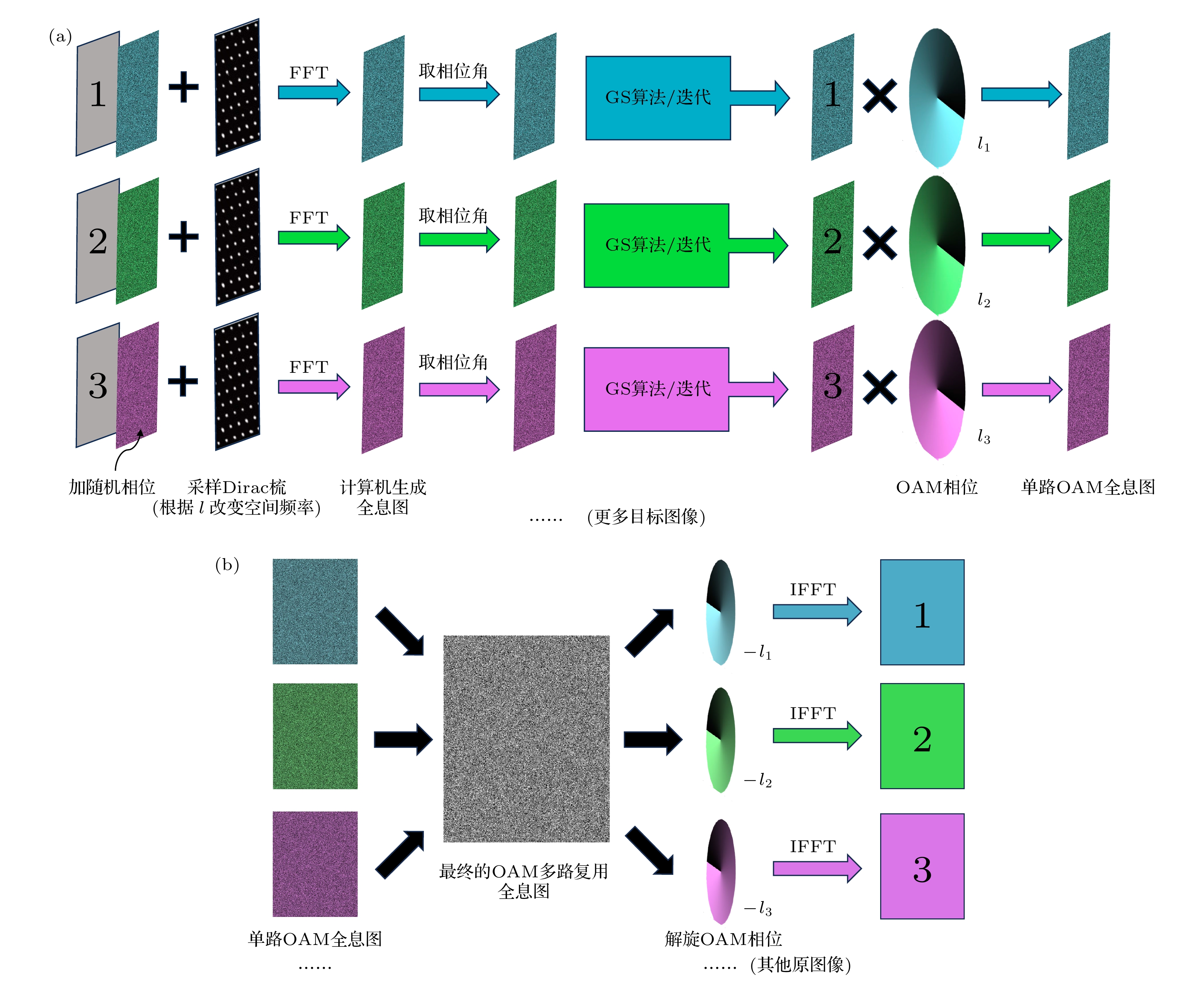
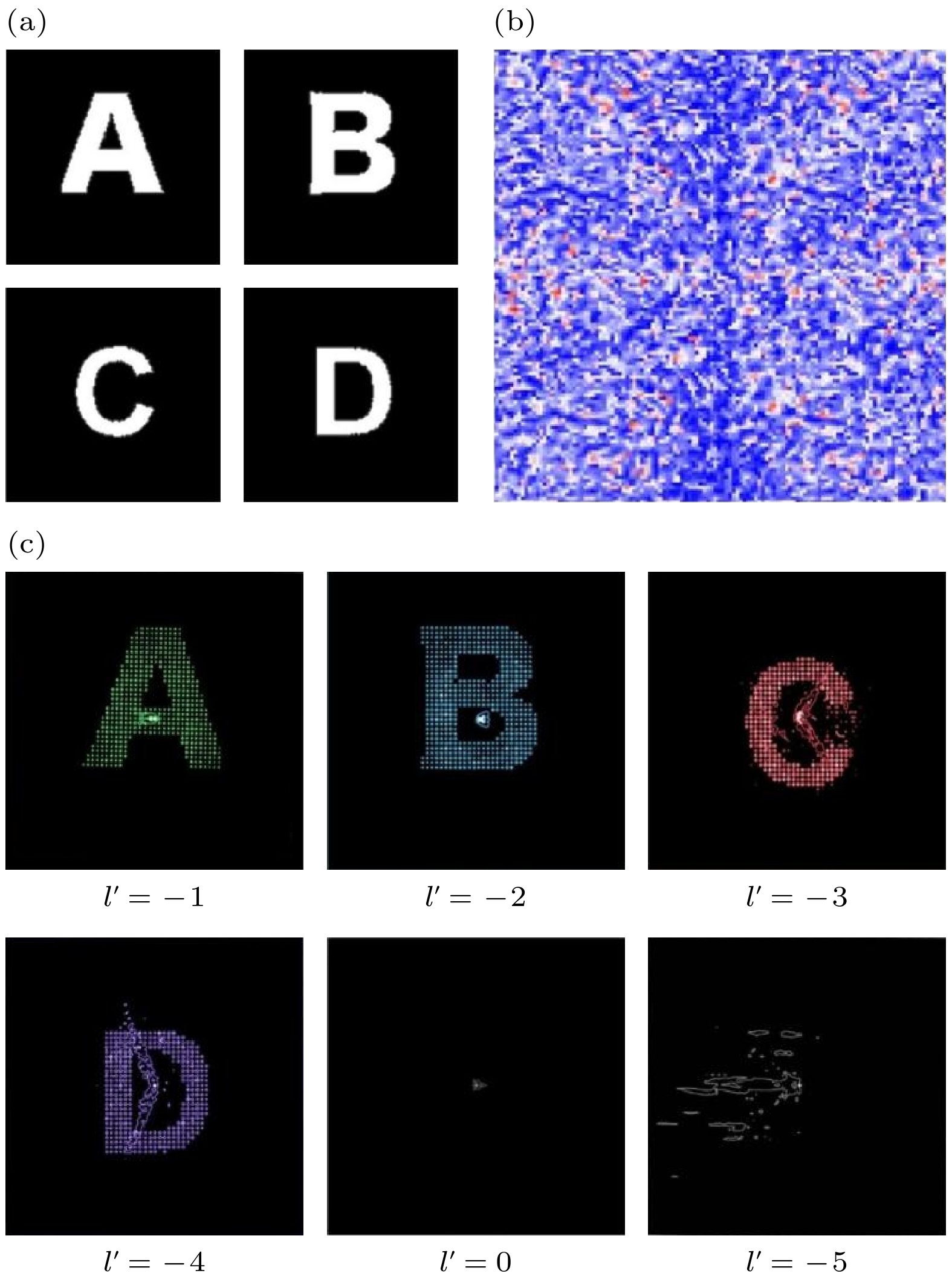
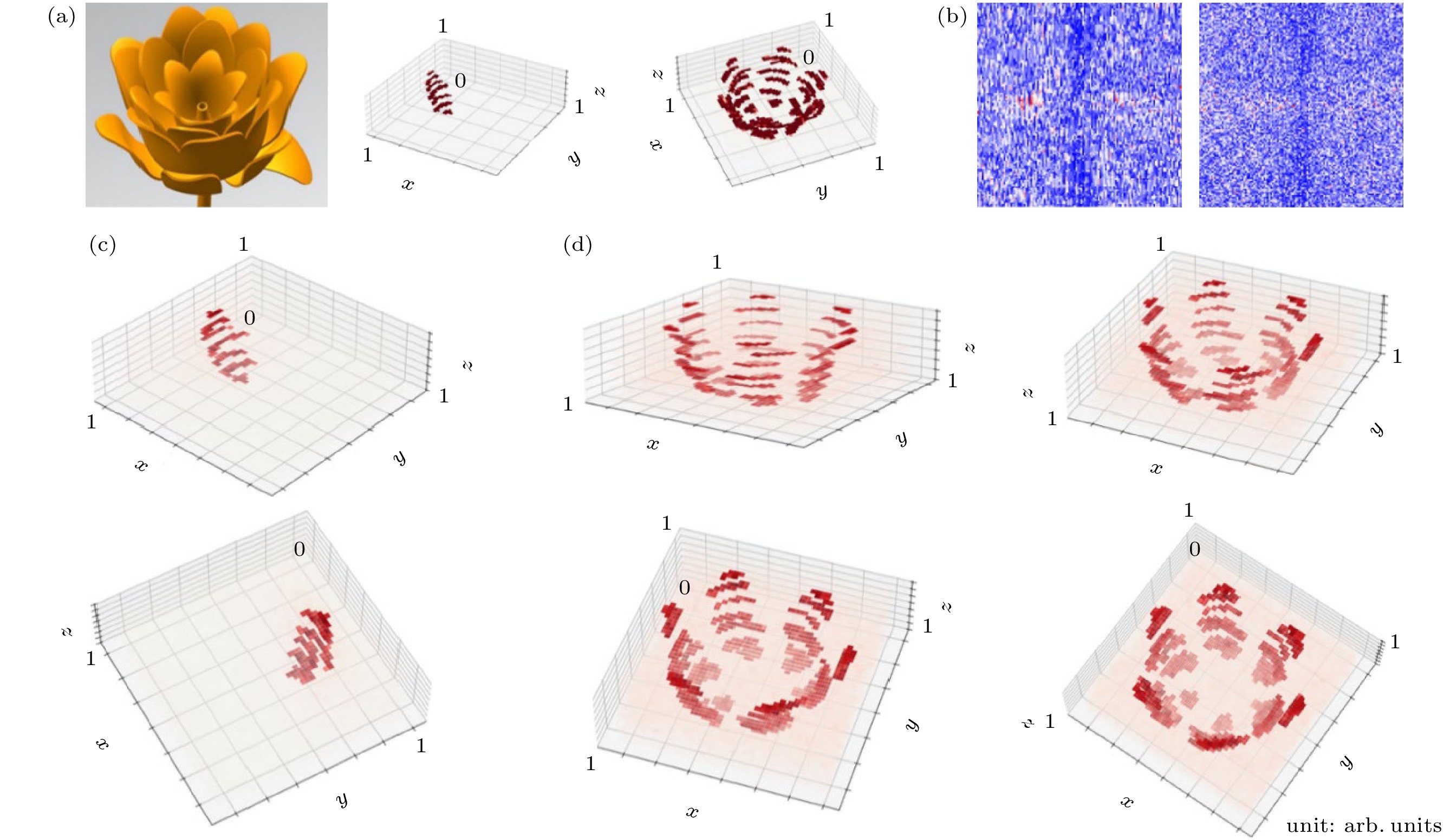
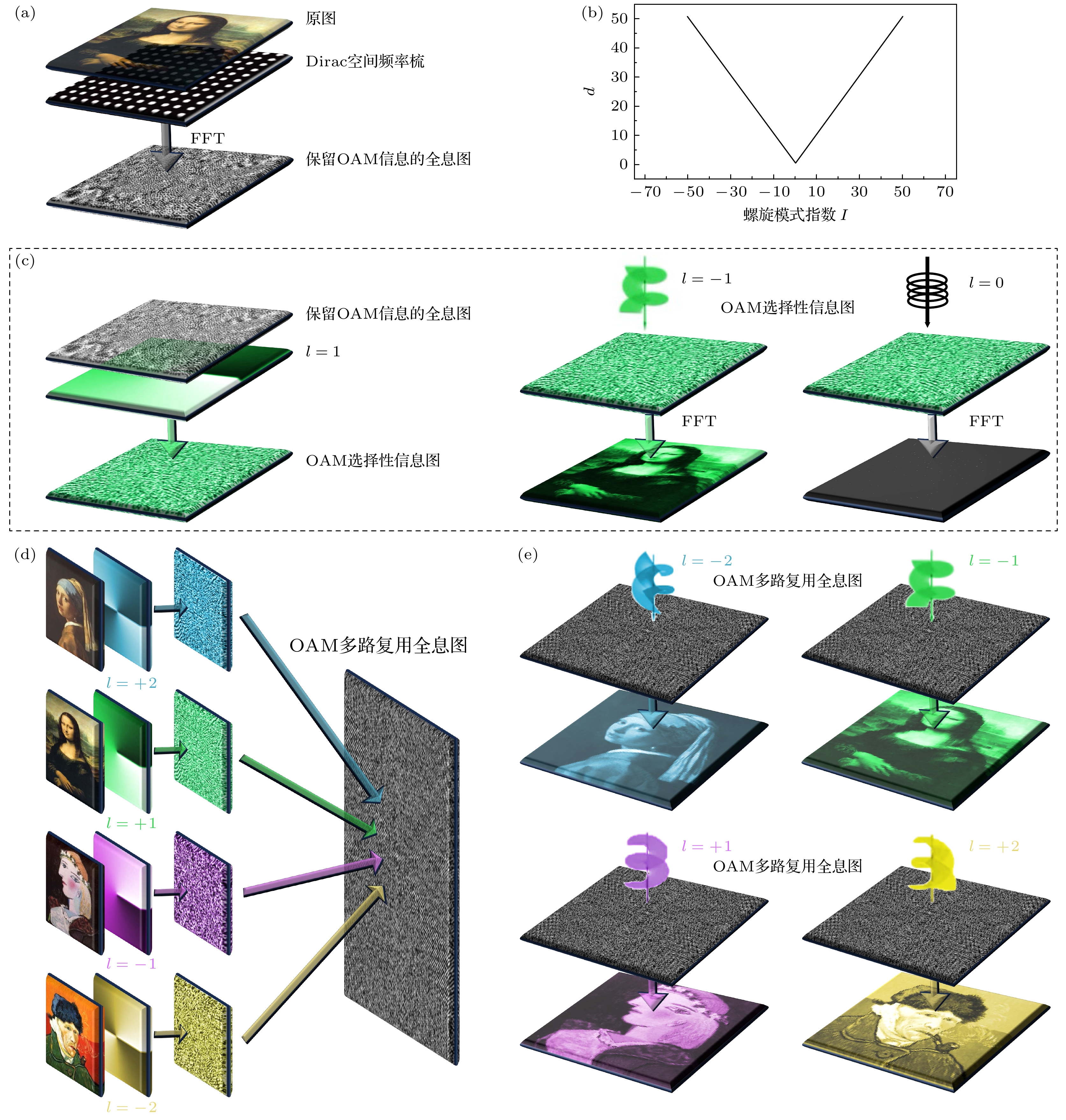
After decades of development, holography has evolved into a sophisticated optical technology for information display. Traditional holographic techniques, which rely solely on the wavelength and polarization of light as information carriers, are limited in both security and capacity of information. The introduction of orbital angular momentum (OAM) as an additional optical dimension into holography effectively addresses these challenges. In order to maintain the OAM mode characteristics of the original image, spatial discrete sampling must be performed first. The sampled image undergoes Fourier transform to generate a discrete hologram. An OAM-selective hologram is then constructed by multiplying the discrete hologram with a spiral phase factor. By superimposing multiple selective holograms with varying topological charges, an OAM-multiplexing hologram is generated. Using this approach, computer simulations of OAM-based holography demonstrate the encryption of multiple two-dimensional images with different topological charges ($ {l}_{i} $) into an OAM-multiplexing hologram for storage. Decryption is achieved by illuminating the multiplexing hologram with a reproduction beam of a specific topological charge. When the condition ($ l'_{i}+{l}_{i}= 0 $) is satisfied, the original image associated with the corresponding topological charge is successfully reproduced. Furthermore, a three-dimensional object, such as a rose in the article, can be decomposed into multiple two-dimensional planes by using a layering method. Holograms for each layer are generated based on their spatial positions and a custom function f that assigns topological charges ($ {l}_{j} $). These holograms are stored in a phase array through OAM-multiplexing holography, effectively reducing the dimensionality of information storage. By setting different reproduction charges ($ l'_{j} $), the holograms are successfully reconstructed. The spatial position of each layer is determined by the function f, enabling the replicating and stacking of layers to achieve a three-dimensional reconstruction of the rose, including its petals, from different perspectives. This process realizes three-dimensional holography. Notably, the combination of topological charge and the function f servesacts as a cryptographic key, significantly enhancing the security of information transmission. This OAM-selective holography technology not only improves security, but also achieves higher information throughput, indicating its enormous potential in various applications. -
Keywords:
- orbital angular momentum /
- hologram /
- 3D imaging
[1] Lin S F, Wang D, Wang Q H, Kim E S 2020 Opt. Laser Eng. 126 105895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lin X, Liu J, Jia J, Pan Y J, Wang Y T 2013 Opt. Express 21 20577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shi L, Li B, Kim C, Kellnhofer P, Matusik W 2021 Nature 591 234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Choi S, Gopakumar M, Peng Y, Kim J, Wetzstein G 2021 ACM Trans. 40 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li X P, Ren H R, Chen X, Liu J, Li Q, Li C M Y, Xue G L, Jia J, Cao L C, Sahu A, Hu B, Wang Y T, Jin G F, Gu M 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 6984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Blanche P A 2021 Light Adv. Manuf. 2 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Blinder D, Birnbaum T, Ito T, Shimobaba T 2022 Light Adv. Manuf. 3 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Vyas S, Chia Y, Luo Y 2018 Opt. Express 26 21979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] He Z H, Sui X M, Jin G F, Cao L C 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 A74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bruckheimer E, Rotschild C, Dagan T, Amir G, Kaufman A, Gelman S, Birk E 2016 Eur. Heart J. Card. Img. 17 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gibby W, Cvetko S, Gibby A, Gibby C, Sorensen K, Andrews E G, Maroon J, Parr R 2021 J. Neurosurg. 137 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wan Z S, Wang Z Y, Yang X L, Shen Y J, Fu X 2020 Opt. Express 28 31043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ngcobo S, Litvin I, Burger L, Forbes A 2013 Nat. Commun. 4 2289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ahmed N H, Ahmed M S 2021 Int. Design J. 11 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kong D Z, Cao L C, Jin G F, Javidi B 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 8296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 赫明钊, 曹良才, 谭峭峰, 何庆声, 金国藩 2009 光学学报 29 2709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He M Z, Cao L C, Tan Q F, He Q S, Jin G F 2009 Acta Opt. Sin. 29 2709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yan L, Xiao J, Plaskocinski T, Biabanifard M, Persheyev S, Askari M, Di Falco A 2022 Opt. Express 30 19145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhao R Z, Sain B, Wei Q S, Tang C C, Li X W, Weiss T, Huang LL, Wang Y T, Zentgraf T 2018 Light Sci. Appl. 7 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chen W, Chen X D 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 6740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kim J, Choi J, An J, Kim N, Lee K 2005 Opt. Commun. 247 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhou H, Sain B, Wang Y 2020 ACS Nano 14 5553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Fang X Y, Ren H R, Gu M 2020 Nat. Photonics 14 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 程鹏雨 2023博士学位论文 (上海: 上海大学)
Cheng P Y 2023 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai University
[24] Wen DD, Yue F Y, Li G X, Zheng G X, Chan K L, Chen S M, Chen M, Li K F, Wong P W H, Cheah K W, Pun E Y B, Zhang S, Chen X Z 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 8241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Willner A E, Huang H, Yan Y 2015 Adv. Opt. Photon. 7 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 柯熙政, 谢炎辰, 张颖 2019 光学学报 39 0126017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ke X Z, Xie Y C, Zhang Y 2019 Acta Opt. Sin. 39 0126017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lei T, Zhang M, Li Y, Jia P, Liu G N, Xu X, Li Z, Min C, Lin J, Yu C, Niu H, Yuan X 2015 Light Sci. Appl. 4 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lim K T, Liu H, Liu Y, Yang J K 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gibson G, Courtial J, Padgett M, Vasnetsov M , Pas’ko V 2004 Opt. Express 12 5448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Gong L, Zhao Q, Zhang H, Hu XY, Huang K, Yang JM, Li Y M 2019 Light Sci. Appl. 8 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Paturzo M, Memmolo P, Finizio A, Näsänen R, Naughton T J, Ferraro P 2010 Opt. Express 18 8806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang J, Liu J, Li S H, Zhao Y F, Du J, Zhu L 2022 Nanophotonics 11 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhong Z Q, Tang WH, Yuan H, Zhang B 2023 Opt. Laser Technol. 169 110081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Raveh D, Pokharel S, Korotkova O 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 2405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Willner A E, Pang K, Song H, Zou K, Zhou H 2021 Appl. Phys. Rev. 8 041312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Pizzo A, Sanguinetti L, Marzetta T L 2022 IEEE Trans. Wire. Commun. 21 6890
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Salgado-Remacha F J 2016 Opt. Laser Technol. 85 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a)得到离散全息图的示意图, 其能保留OAM模式特征; (b)最小采样间距-拓扑荷关系示意图; (c) OAM选择性全息图的示意图和使用不同拓扑荷进行解旋的效果示意图; (d)多路复用全息图制作示意图; (e)使用携带不同拓扑荷的光对多路复用全息图进行解旋的过程示意图
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic of obtaining a discrete hologram, which preserves the OAM mode characteristics; (b) schematic of the relationship between the minimum sampling interval and topological charge; (c) schematic of an OAM-selective hologram and the effect of demodulating with different topological charges; (d) schematic of the process of creating a OAM-multiplexing hologram; (e) schematic of the process of demodulating the OAM-multiplexing hologram using light with different topological charges.
图 4 (a)左图为三维玫瑰建模图, 中间图为3D单瓣玫瑰原图, 右图为简化的3D玫瑰原图; (b)左图为单瓣玫瑰的OAM多通道复用相位全息图, 右图为简化玫瑰的OAM多通道复用相位全息图; (c)多视角下的单瓣花瓣的三维全息复现还原图; (d)多视角下的玫瑰的三维全息复现还原图, 每个坐标图的x, y, z坐标轴的单位是任意单位
Fig. 4. (a) Left image shows a 3D rose model, the middle image is the original 3D single-petal rose, and the right image is a simplified version of the original 3D rose; (b) the left image is the OAM-multiplexing phase hologram of the single-petal rose, and the right image is the OAM-multiplexing phase hologram of the simplified rose; (c) 3D holographic reconstruction of the single-petal rose from multiple perspectives; (d) 3D holographic reconstruction of the rose from multiple perspectives, with the units of the x, y, z axes in each coordinate plot being arbitrary units.
-
[1] Lin S F, Wang D, Wang Q H, Kim E S 2020 Opt. Laser Eng. 126 105895
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Lin X, Liu J, Jia J, Pan Y J, Wang Y T 2013 Opt. Express 21 20577
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shi L, Li B, Kim C, Kellnhofer P, Matusik W 2021 Nature 591 234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Choi S, Gopakumar M, Peng Y, Kim J, Wetzstein G 2021 ACM Trans. 40 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li X P, Ren H R, Chen X, Liu J, Li Q, Li C M Y, Xue G L, Jia J, Cao L C, Sahu A, Hu B, Wang Y T, Jin G F, Gu M 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 6984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Blanche P A 2021 Light Adv. Manuf. 2 28
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Blinder D, Birnbaum T, Ito T, Shimobaba T 2022 Light Adv. Manuf. 3 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Vyas S, Chia Y, Luo Y 2018 Opt. Express 26 21979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] He Z H, Sui X M, Jin G F, Cao L C 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 A74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Bruckheimer E, Rotschild C, Dagan T, Amir G, Kaufman A, Gelman S, Birk E 2016 Eur. Heart J. Card. Img. 17 845
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gibby W, Cvetko S, Gibby A, Gibby C, Sorensen K, Andrews E G, Maroon J, Parr R 2021 J. Neurosurg. 137 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wan Z S, Wang Z Y, Yang X L, Shen Y J, Fu X 2020 Opt. Express 28 31043
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ngcobo S, Litvin I, Burger L, Forbes A 2013 Nat. Commun. 4 2289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ahmed N H, Ahmed M S 2021 Int. Design J. 11 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kong D Z, Cao L C, Jin G F, Javidi B 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 8296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 赫明钊, 曹良才, 谭峭峰, 何庆声, 金国藩 2009 光学学报 29 2709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
He M Z, Cao L C, Tan Q F, He Q S, Jin G F 2009 Acta Opt. Sin. 29 2709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Yan L, Xiao J, Plaskocinski T, Biabanifard M, Persheyev S, Askari M, Di Falco A 2022 Opt. Express 30 19145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhao R Z, Sain B, Wei Q S, Tang C C, Li X W, Weiss T, Huang LL, Wang Y T, Zentgraf T 2018 Light Sci. Appl. 7 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Chen W, Chen X D 2016 Appl. Opt. 55 6740
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Kim J, Choi J, An J, Kim N, Lee K 2005 Opt. Commun. 247 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhou H, Sain B, Wang Y 2020 ACS Nano 14 5553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Fang X Y, Ren H R, Gu M 2020 Nat. Photonics 14 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 程鹏雨 2023博士学位论文 (上海: 上海大学)
Cheng P Y 2023 Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai: Shanghai University
[24] Wen DD, Yue F Y, Li G X, Zheng G X, Chan K L, Chen S M, Chen M, Li K F, Wong P W H, Cheah K W, Pun E Y B, Zhang S, Chen X Z 2015 Nat. Commun. 6 8241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Willner A E, Huang H, Yan Y 2015 Adv. Opt. Photon. 7 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 柯熙政, 谢炎辰, 张颖 2019 光学学报 39 0126017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ke X Z, Xie Y C, Zhang Y 2019 Acta Opt. Sin. 39 0126017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Lei T, Zhang M, Li Y, Jia P, Liu G N, Xu X, Li Z, Min C, Lin J, Yu C, Niu H, Yuan X 2015 Light Sci. Appl. 4 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lim K T, Liu H, Liu Y, Yang J K 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gibson G, Courtial J, Padgett M, Vasnetsov M , Pas’ko V 2004 Opt. Express 12 5448
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Gong L, Zhao Q, Zhang H, Hu XY, Huang K, Yang JM, Li Y M 2019 Light Sci. Appl. 8 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Paturzo M, Memmolo P, Finizio A, Näsänen R, Naughton T J, Ferraro P 2010 Opt. Express 18 8806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Wang J, Liu J, Li S H, Zhao Y F, Du J, Zhu L 2022 Nanophotonics 11 645
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Zhong Z Q, Tang WH, Yuan H, Zhang B 2023 Opt. Laser Technol. 169 110081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Raveh D, Pokharel S, Korotkova O 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 2405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Willner A E, Pang K, Song H, Zou K, Zhou H 2021 Appl. Phys. Rev. 8 041312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Pizzo A, Sanguinetti L, Marzetta T L 2022 IEEE Trans. Wire. Commun. 21 6890
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Salgado-Remacha F J 2016 Opt. Laser Technol. 85 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1517
- PDF下载量: 89
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: