-
We investigate the stability and nonlinear dynamics of the Kerr optical frequency comb inside a dual coupled microcavity with high-order dispersion effect based on the theoretical model of coupled nonlinear Schrödinger equation. The effects of different high-order dispersion parameters on the evolution and spectral characteristics of the optical field in the cavity are also explored. Theoretical results indicate that the addition of the third-order dispersion enlarges the stability domain of the parametric space and transforms the periodically varying soliton breathers and chaos into stable bright soliton. In order to obtain an accurate Kerr optical frequency comb spectral envelope, higher-order dispersion should be considered. Moreover, high-order dispersion terms have a significant effect on the spectral characteristics of the optical frequency comb, such as the spectral envelope frequency shift and the dispersive wave spectral position. Specifically, the third-order dispersion and positive fourth-order dispersion can broaden the spectrum and enhance the dispersive waves; while the negative fourth-order dispersion can suppress the dispersive wave generation and obtain a symmetric soliton frequency comb; the fifth-order dispersion can regulate the drift direction and speed of the optical solitons. The theoretical results are of great value for dispersion regulation and design and also for stability studies in double-coupled microcavity experiments.
-
Keywords:
- lasers /
- nonlinear optics /
- optical microcavities
[1] Newman Z L, Maurice V, Drake T, Stone J R, Briles T C, Spencer D T, Fredrick C, Li Q, Westly D, Ilic B R, Shen B, Suh M G, Yang K Y, Johnson C, Johnson D M S, Hollberg L, Vahala K J, Srinivasan K, Diddams S A, Kitching J, Papp S B, Hummon M T 2019 Optica 6 680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Torres-Company V, Weiner A M 2014 Laser & Photonics Rev. 8 368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Trocha P, Karpov M, Ganin D, Pfeiffer M H P, Kordts A, Wolf S, Krockenberger J, Marin-Palomo P, Weimann C, Randel S, Freude W, Kippenberg T J, Koos C 2018 Science 359 887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cruz F C, Maser D L, Johnson T, Ycas G, Klose A, Giorgetta F R, Coddington I, Diddams S A 2015 Opt. Express 23 26814
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kippenberg T J, Holzwarth R, Diddams S A 2011 Science 332 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Coillet A, Balakireva I, Henriet R, Saleh K, Larger L, Dudley J M, Menyuk C R, Chembo Y K 2013 IEEE Photonics J. 5 6100409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Matsko A B, Liang W, Savchenkov A A, Maleki L 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xue X, Xuan Y, Liu Y, Wang P H, Chen S, Wang J, Leaird D E, Qi M, Weiner A M 2015 Nat. Photon. 9 594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kippenberg T J, Gaeta A L, Lipson M, Gorodetsky M L 2018 Science 361 567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Tikan A, Wang R N, Riemensberger J, Liu J, Seidler P, Komagata K, Kippenberg T J, Hönl S, Churaev M, Skehan C, Guo H 2021 Nat. Phys. 17 604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tikan A, Tusnin A, Riemensberger J, Churaev M, Ji X, Komagata K N, Wang R N, Liu J, Kippenberg T J 2022 Science Advan. 8 6982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Brasch V, Herr T, Geiselmann M, Lihachev G, Pfeiffer M H P, Gorodetsky M L, Kippenberg T J 2015 Science 351 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Parra-Rivas P, Gomila D, Leo F, Coen S, Gelens L 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 2971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Okawachi Y, Lamont M R, Luke K, Carvalho D O, Yu M, Lipson M, Gaeta A L 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 3535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cherenkov A V, Lobanov V E, Gorodetsky M L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 033810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Xue X, Zheng X, Zhou B 2019 Nat. Photon. 13 616
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 徐昕, 金雪莹, 高浩然, 陈杰, 陆洋, 陈东, 于连栋 2020 69 184207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X, Jin X Y, Gao H R, Chen J, Lu Y, Chen D, Yu L D 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 184207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Maes B, Fiers M, Bienstman P 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 033805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xu X, Jin X, Lu Y, Gao H, Cheng J, Yu L 2020 J. Optics 22 115501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xu Y, Coen S 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 3492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王景灏 2018 博士学位论文 (武汉: 华中科技大学)
Wang J H 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[22] Wang J, Zhou R, Lai D, Che K, Chen L, Jiang S, Xu H, Cai Z 2019 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 31 1175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Dinyari K N, Barbour R J, Golter D A, Wang H 2011 Opt. Express 19 17966
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Milian C, Skryabin D V 2014 Opt. Express 22 3732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Leo F, Mussot A, Kockaert P, Emplit P, Haelterman M, Taki M 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 104103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Mussot A, Louvergneaux E, Akhmediev N, Reynaud F, Delage L, Taki M 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 113904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Gomila D, Scroggie A J, Firth W J 2007 Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenomena 227 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] He Y, Wang S, Zeng X 2016 IEEE Photonics J. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bao C, Taheri H, Zhang L, Matsko A, Yan Y, Liao P, Maleki L, Willner A E 2017 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 34 715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Roy S, Bhadra S K, Agrawal G P 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 2072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Skryabin D V, Luan F, Knight J C, Russell P S J 2003 Science 301 1705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Taheri H, Eftekhar A A, Wiesenfeld K, Adibi A 2015 IEEE Photon. J. 7 2200309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Milián C, Gorbach A V, Taki M, Yulin A V, Skryabin D V 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 033851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 三阶色散对孤子腔内周期振荡的呼吸孤子态的影响 (a), (c) 仅包含二阶色散时呼吸孤子态的(a)时域演化图和(c)光谱演化图; (b), (d) 当加入三阶色散后, 腔内呈现的稳定单孤子态的(b)时域演化图和(d)光谱演化图. 子图顶部为t = 3000 ns时对应的时域光场/光谱分布
Figure 2. Effect of third-order dispersion on periodically oscillating breathing soliton states in a soliton cavity: (a), (c) Without third-order dispersion, the evolution of the temporal intensity profile (a) of breathers states and the corresponding comb spectrum (c); (b), (d) with third-order dispersion, the evolution of the temporal intensity profile (b) of soliton state and the corresponding comb spectrum (d). Temporal profile/comb spectrum at t = 3000 ns are shown on the top of each panel.
图 3 三阶色散对混沌态的影响 (a), (c) 仅包含二阶色散时, 腔内呈现振荡的呼吸孤子态(a)的时域演化和(c)光谱演化图; (b), (d) 当加入三阶色散后, 腔内呈现的稳定单孤子态的(b)时域演化图和(d)光谱演化图. 子图顶部为t = 3000 ns时对应的时域光场/光谱分布
Figure 3. Effect of third-order dispersion on chaos: (a), (c) Without third-order dispersion, the evolution of the temporal intensity profile (a) of chaos states and the corresponding comb spectrum (c); (b), (d) with third-order dispersion, the evolution of the temporal intensity profile (b) of soliton state and the corresponding comb spectrum (d). Temporal profile/comb spectrum at t = 3000 ns are shown on the top of each panel.
图 4 三阶色散系数对光场稳定性和孤子存在状态的影响 (a) d13 = 0; (b) d13 = –0.0563; (c) d13 = –0.0938. I, 稳定孤子域(包含单孤子态和双孤子态); II, 时域振荡域(呼吸孤子态); III, 混沌域; Ⅳ, 连续波域
Figure 4. Influence of different third-order dispersion coefficients on the stability region and soliton state: (a) d13 = 0; (b) d13 = –0.0563; (c) d13 = –0.0938. I, stable soliton region (including single soliton and multi soliton); II, time domain oscillation domain (breathers soliton); III, chaotic domain; Ⅳ, continuous wave domain.
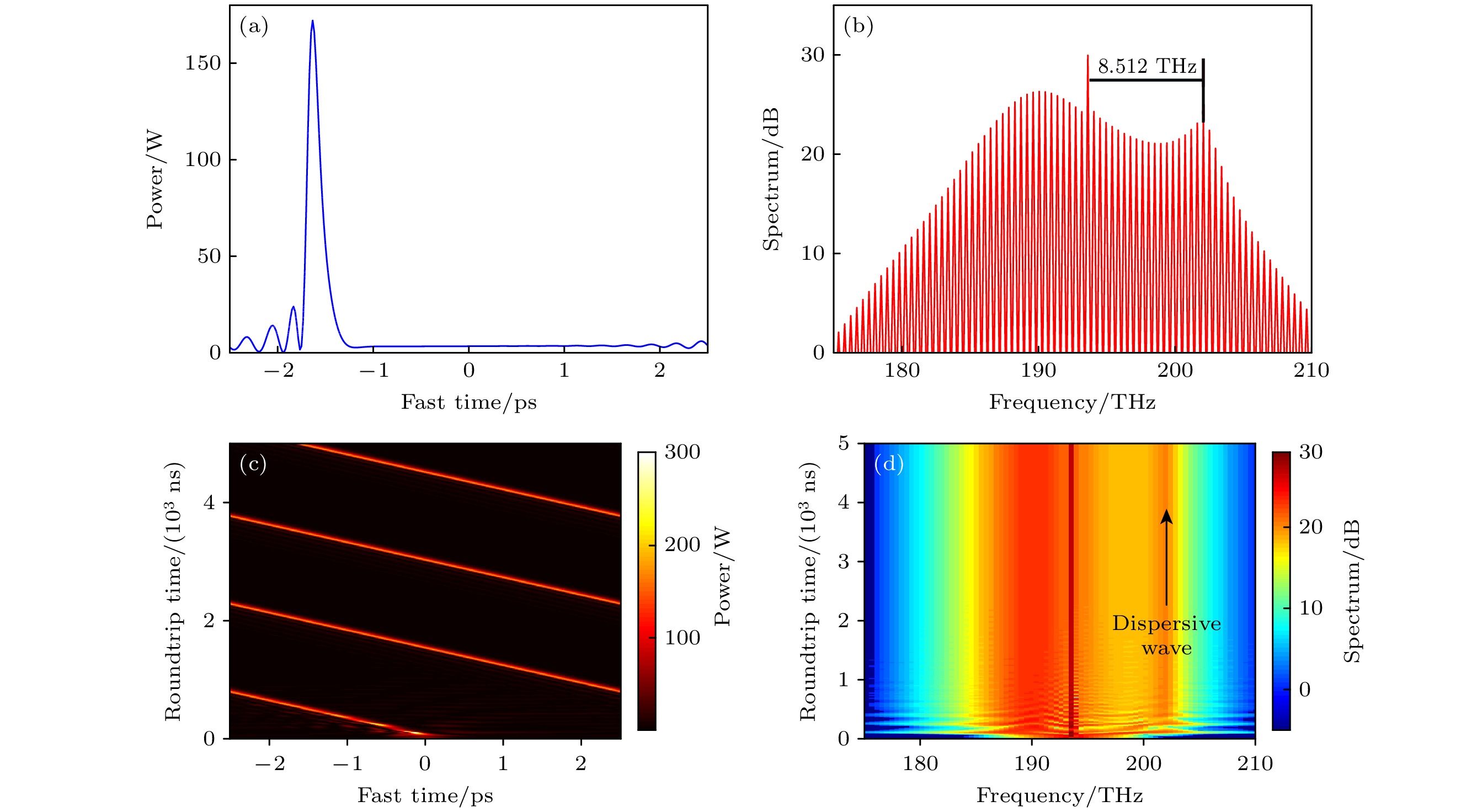
图 5 三阶色散对耦合微环腔内光场分布和光谱演化的影响 (a) t = 5000 ns时腔内的光场分布; (b) t = 5000 ns时腔内光谱图; (c) 孤子的时域演化图; (d) 孤子的光谱演化图
Figure 5. Influence of third-order dispersion on the optical field and spectrum of coupled micro-ring resonators: (a) Optical field distribution in the cavity at t = 5000 ns; (b) intracavity optical spectrum at t = 5000 ns; (c) temporal evolution of solitons; (d) optical spectrum evolution of solitons.
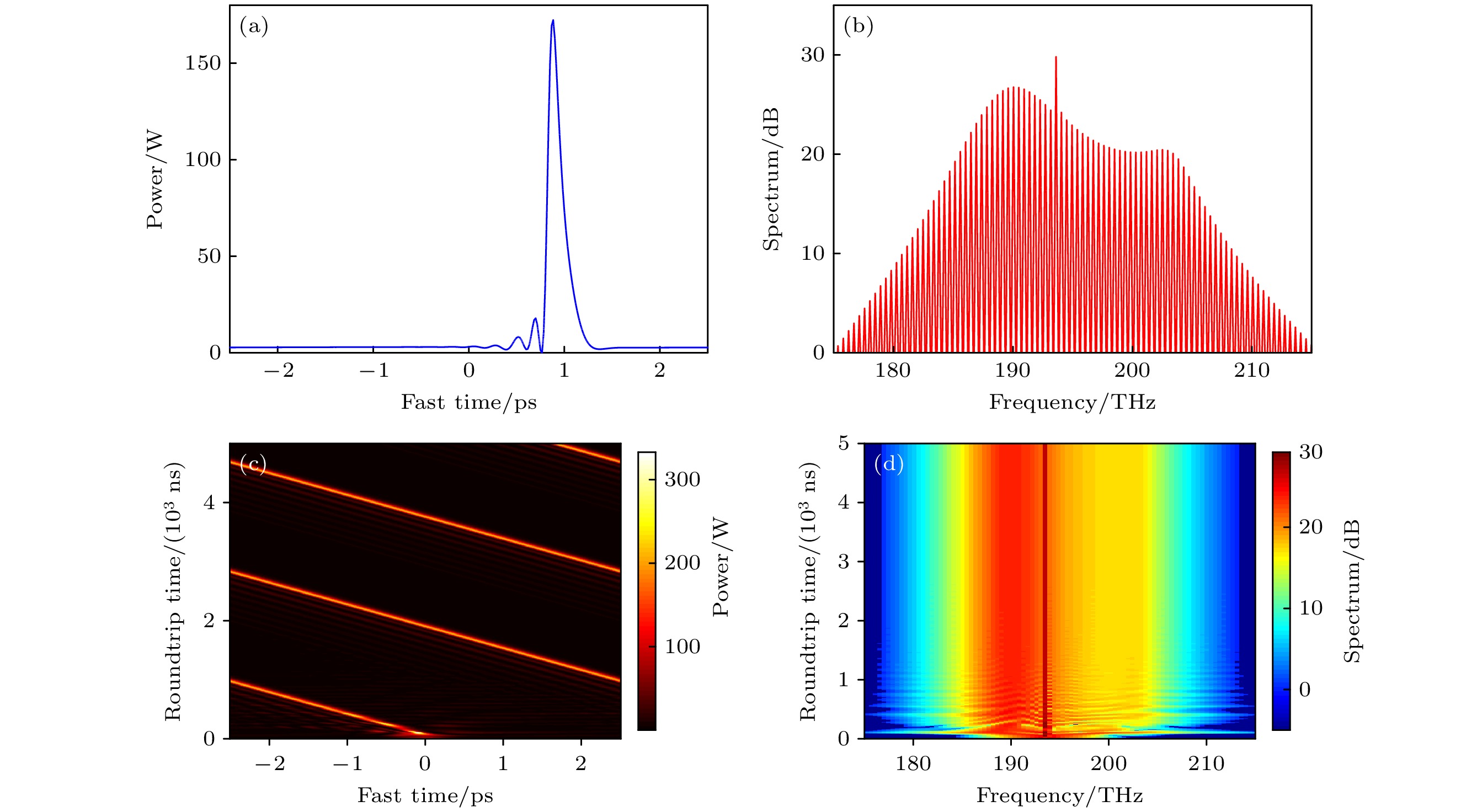
图 6 正四阶色散对耦合微腔光频梳的色散波增强作用 (a) t = 5000 ns, 腔内的光场分布; (b) t = 5000 ns, 腔内光谱图; (c) 孤子的时域演化图; (d) 孤子的光谱演化图
Figure 6. Impact of positive fourth-order dispersion on comb in coupled microcavities: (a) Optical field distribution in the cavity at t = 5000 ns; (b) intracavity optical spectrum at t = 5000 ns; (c) temporal evolution of solitons; (d) optical spectrum evolution of solitons.
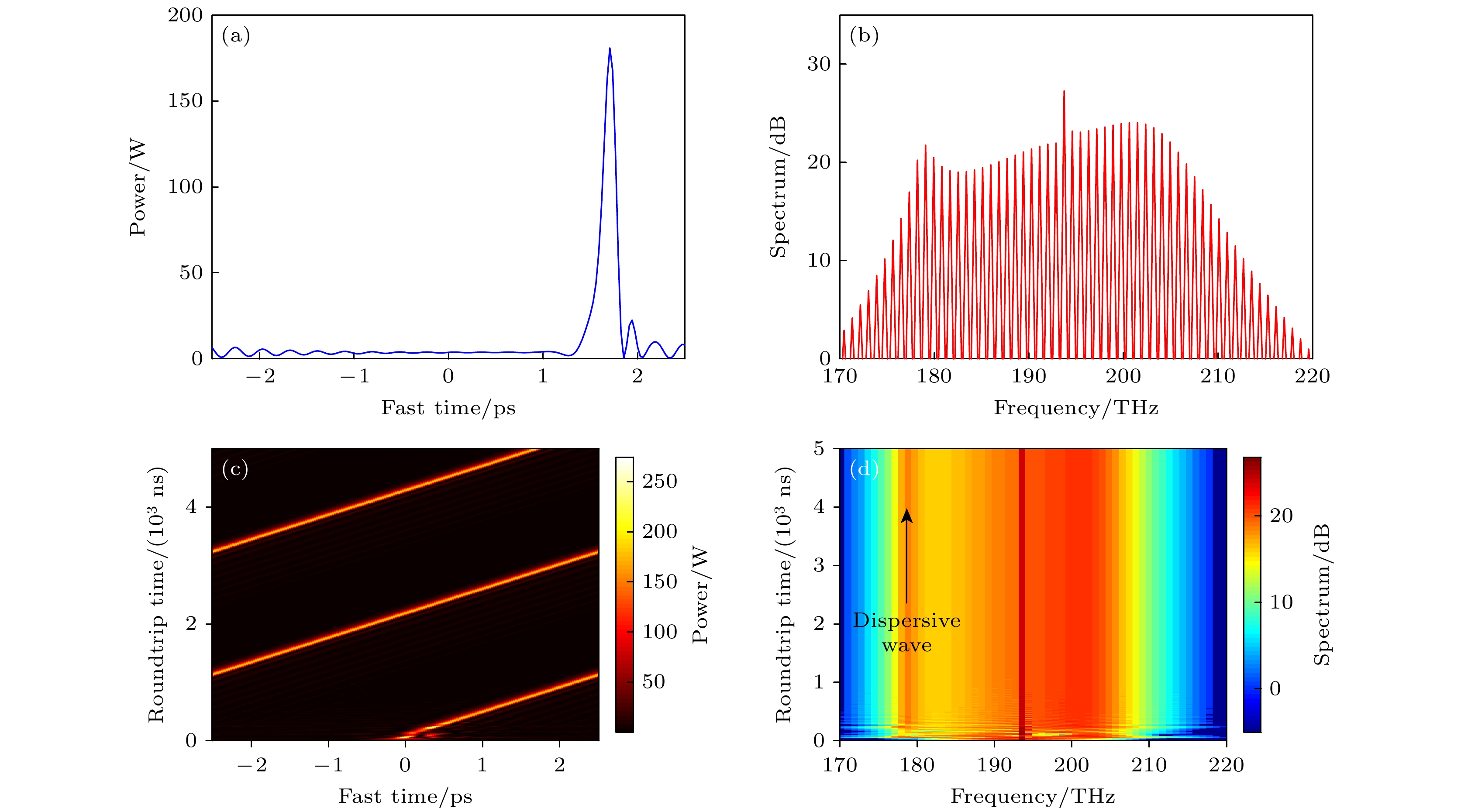
图 7 负四阶色散对梳状光谱色散波的抑制作用 (a) t = 5000 ns, 腔内的光场分布; (b) t = 5000 ns, 腔内光谱图; (c) 孤子的时域演化图; (d) 孤子的光谱演化图
Figure 7. Suppression of dispersion waves of comb spectrum by negative fourth-order dispersion: (a) Optical field distribution in the cavity at t = 5000 ns; (b) intracavity optical spectrum at t = 5000 ns; (c) temporal evolution of solitons; (d) optical spectrum evolution of solitons.
图 8 五阶色散对耦合微腔光频梳的影响 (a) t = 5000 ns时腔内的光场分布; (b) t = 5000 ns时腔内光谱图; (c) 孤子的时域演化图; (d) 孤子的光谱演化图
Figure 8. Impact of positive fifth-order dispersion on comb in coupled microcavities: (a) Intracavity field distribution in the cavity at t = 5000 ns; (b) intracavity optical spectrum at t = 5000 ns; (c) temporal evolution of solitons; (d) optical spectrum evolution of solitons.
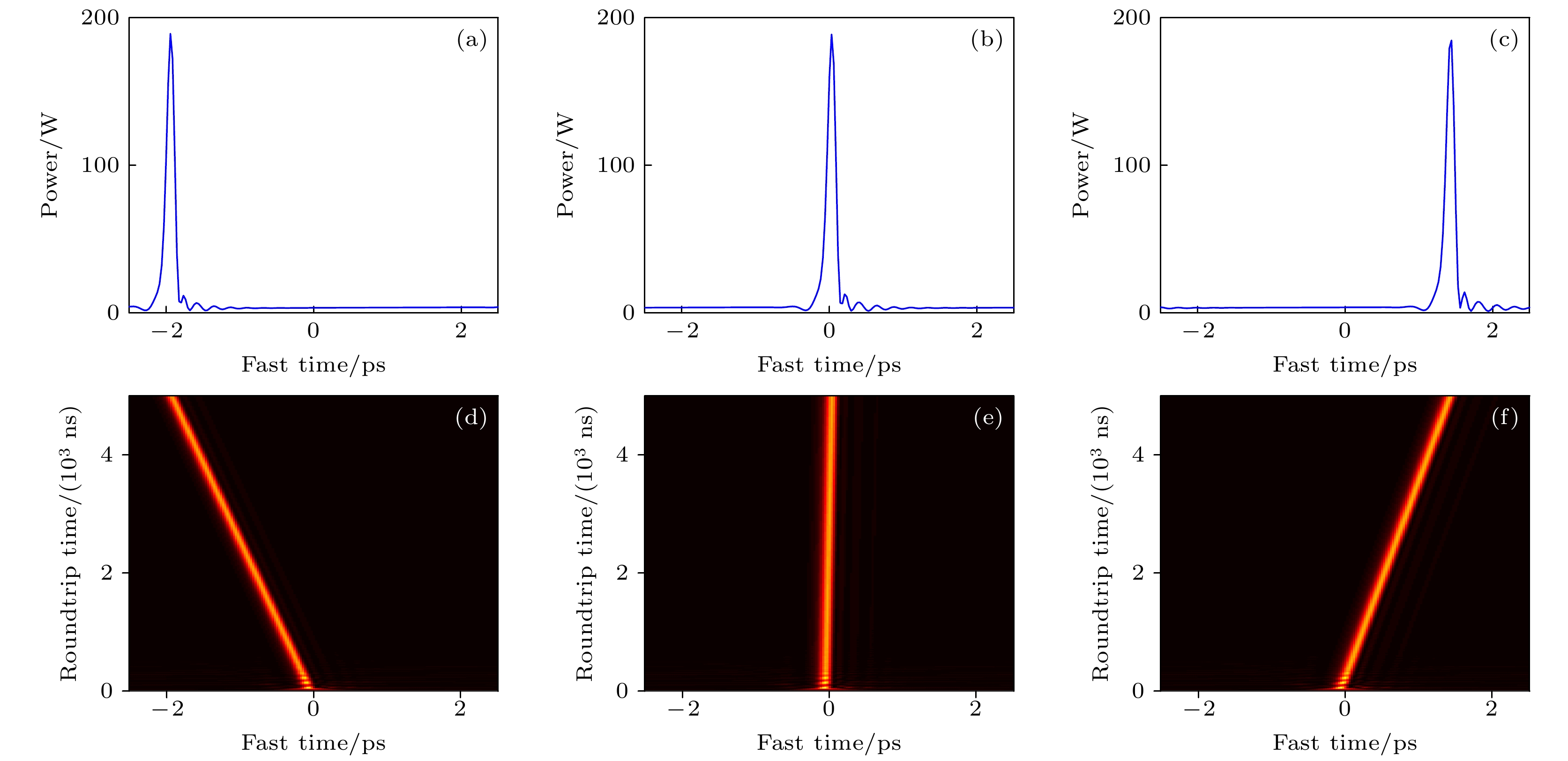
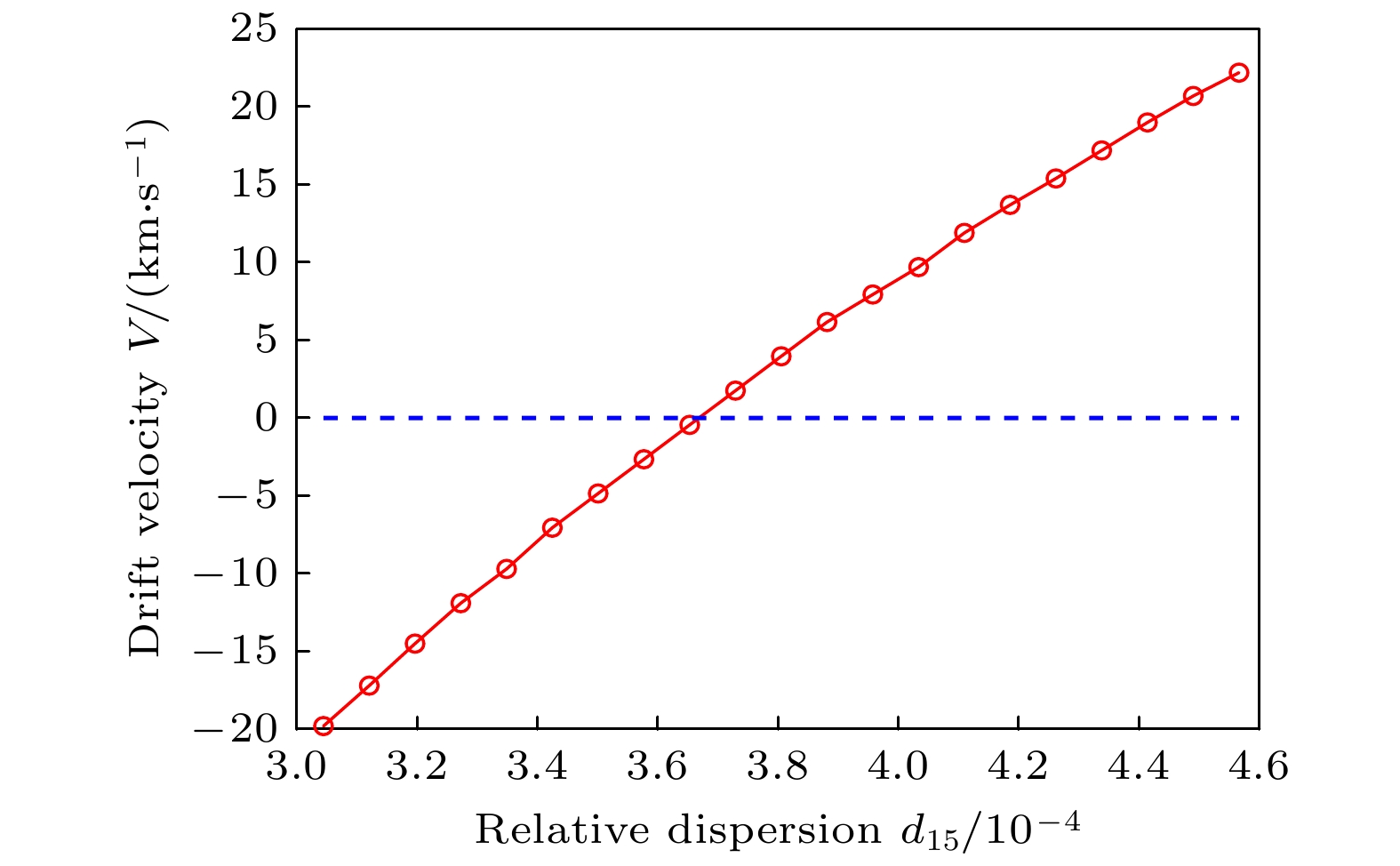
图 9 五阶色散对孤子漂移方向的控制作用 (a)—(c) t = 5000 ns时, d15 = 3.0443×10–4 (a), 3.6532 × 10–4 (b), 4.5665 × 10–4 (c)条件下腔内光场分布; (d)—(f) 与图(a)—(c)对应的时域演化图和孤子漂移
Figure 9. Control of soliton drift direction by fifth-order dispersion: (a)–(c) Intracavity field distribution of soliton at t = 5000 ns and d15 = (a) 3.0443 × 10–4, (b) 3.6532 × 10–4, (c) 4.5665 × 10–4; (d)–(f) corresponding temporal evolution and soliton drift of panel (a)–(c).
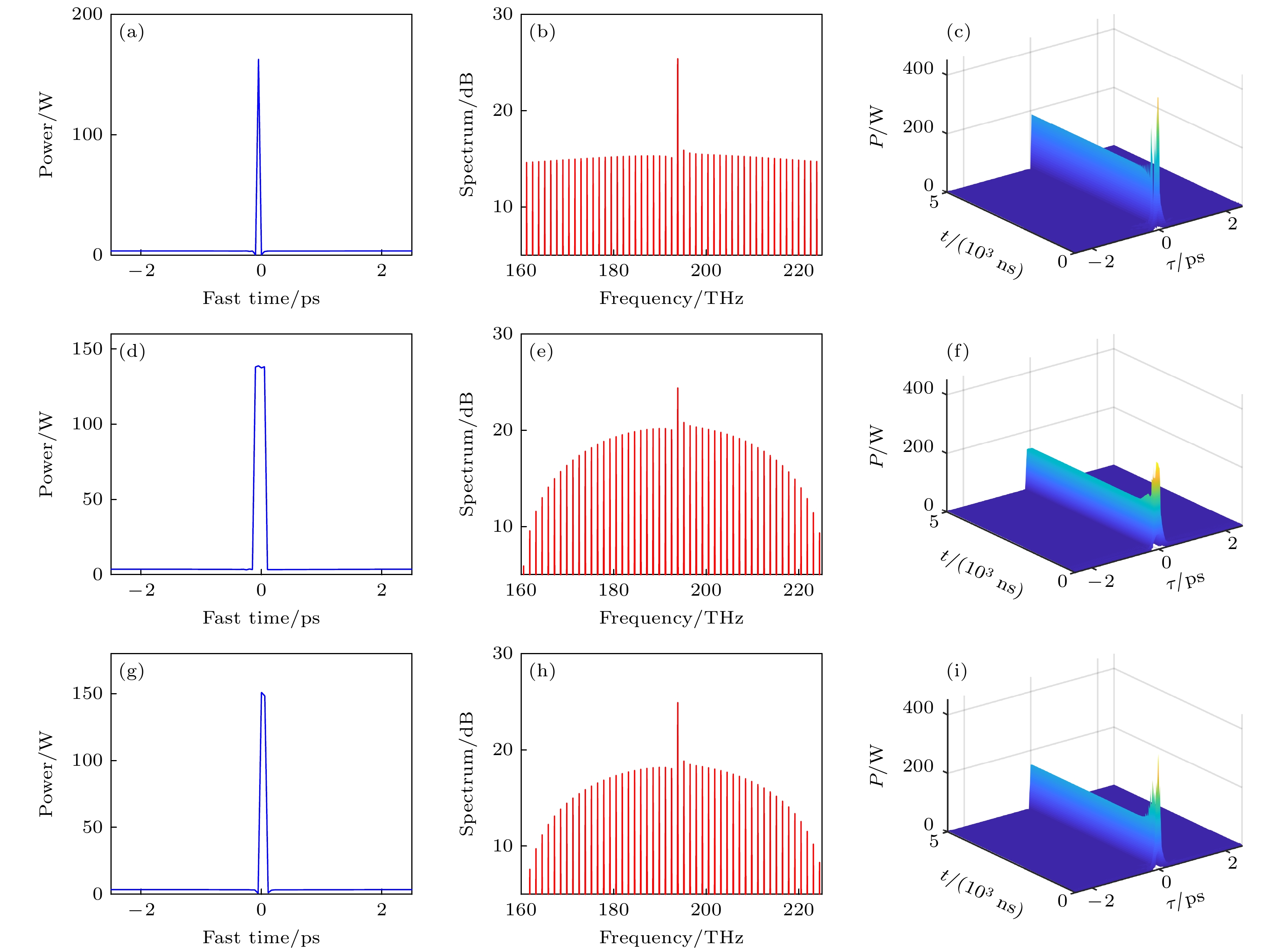
图 11 二阶色散与四阶色散的竞争作用对光梳光谱的影响 (a)—(c) 仅含有二阶色散时腔内光场(a)、光谱(b)和时域(c)演化图; (d)—(f) 仅含有四阶色散时腔内光场(d)、光谱(e)和时域(f)演化图; (g)—(i) 二阶和四阶共同作用下腔内光场(g)、光谱(h)和时域(i)演化图
Figure 11. Influence of the competition between second-order and fourth-order dispersion on comb spectra: (a)–(c) Intracavity optical field (a), spectrum (b) and time domain (c) with second-order dispersion; (d)–(f) intracavity optical field (d), spectrum (e) and time domain (f) with fourth-order dispersion; (g)–(i) intracavity optical field (g), spectrum (h) and time domain (i) with second-order and fourth-order dispersion.
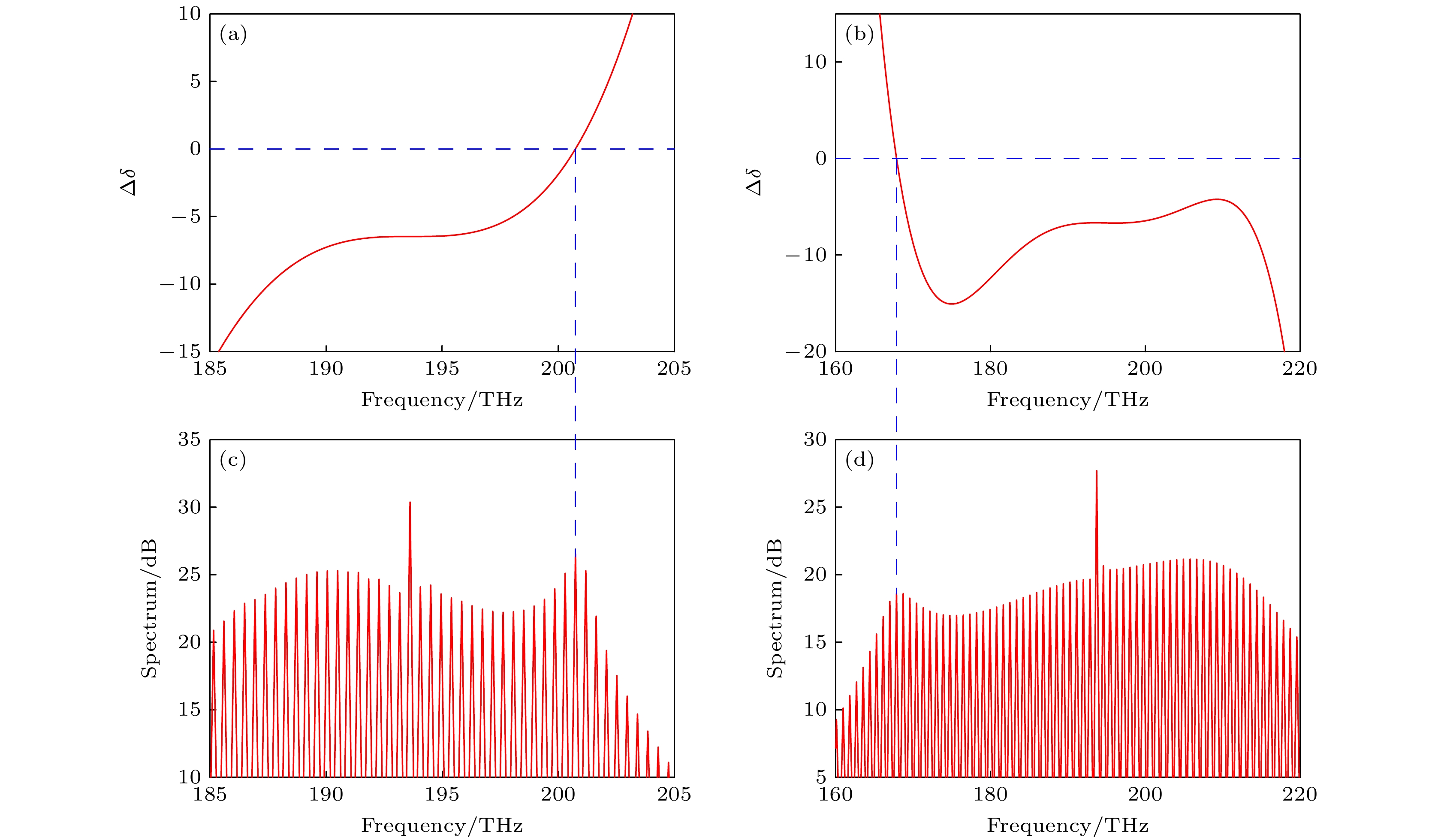
图 12 各高阶色散组合对光频梳光谱的影响 (a) 包含二阶、三阶和四阶色散的相位匹配曲线; (b) 包含二阶到五阶色散的相位匹配曲线; (c), (d)与(a), (b)色散波位置对应的光谱图
Figure 12. Influence of combined high-order dispersion on spectral characteristics: (a) Phase matching curve of second, third and fourth order dispersion; (b) phase matching curve of 2nd–5th order dispersion; (c), (d) spectrogram corresponding to dispersion wave position in (a), (b).
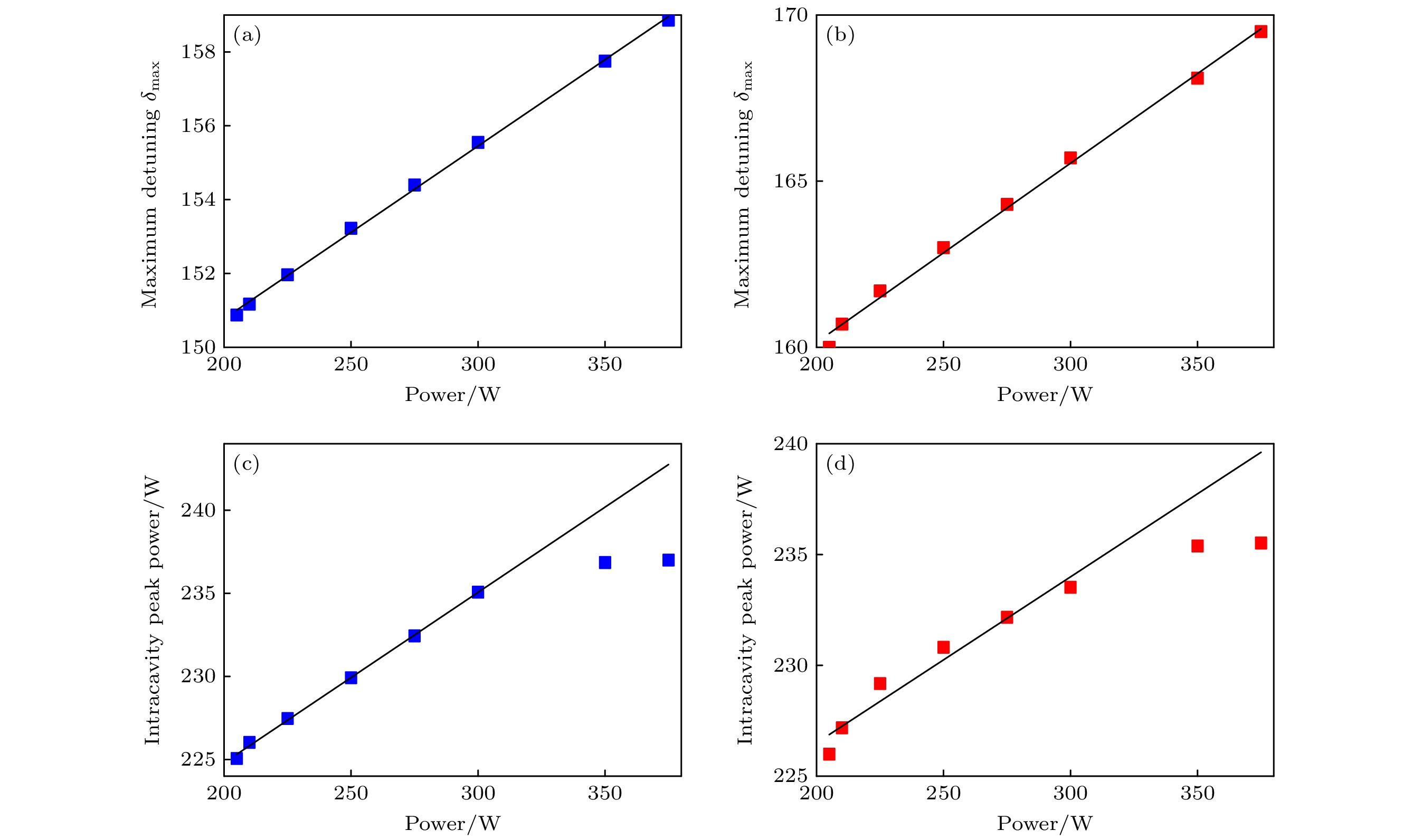
图 13 各阶色散组合对光谱特性的影响 (a) 包含二阶和三阶色散时δmax与Pin的关系; (b) 包含二阶、三阶和四阶色散时δmax与Pin的关系; (c) 包含二阶和三阶色散时腔内峰值功率与Pin的关系; (d) 包含二阶、三阶和四阶色散时腔内峰值功率与Pin的关系
Figure 13. Effect of various dispersion combinations on spectral characteristics: (a) Relationship between δmax and Pin with second and third order dispersion; (b) relationship between δmax and Pin with second, third and fourth order dispersion; (c) relationship between peak power in cavity and with second and third order dispersion; (d) relationship between peak power in cavity and Pin with second, third and fourth order dispersion.
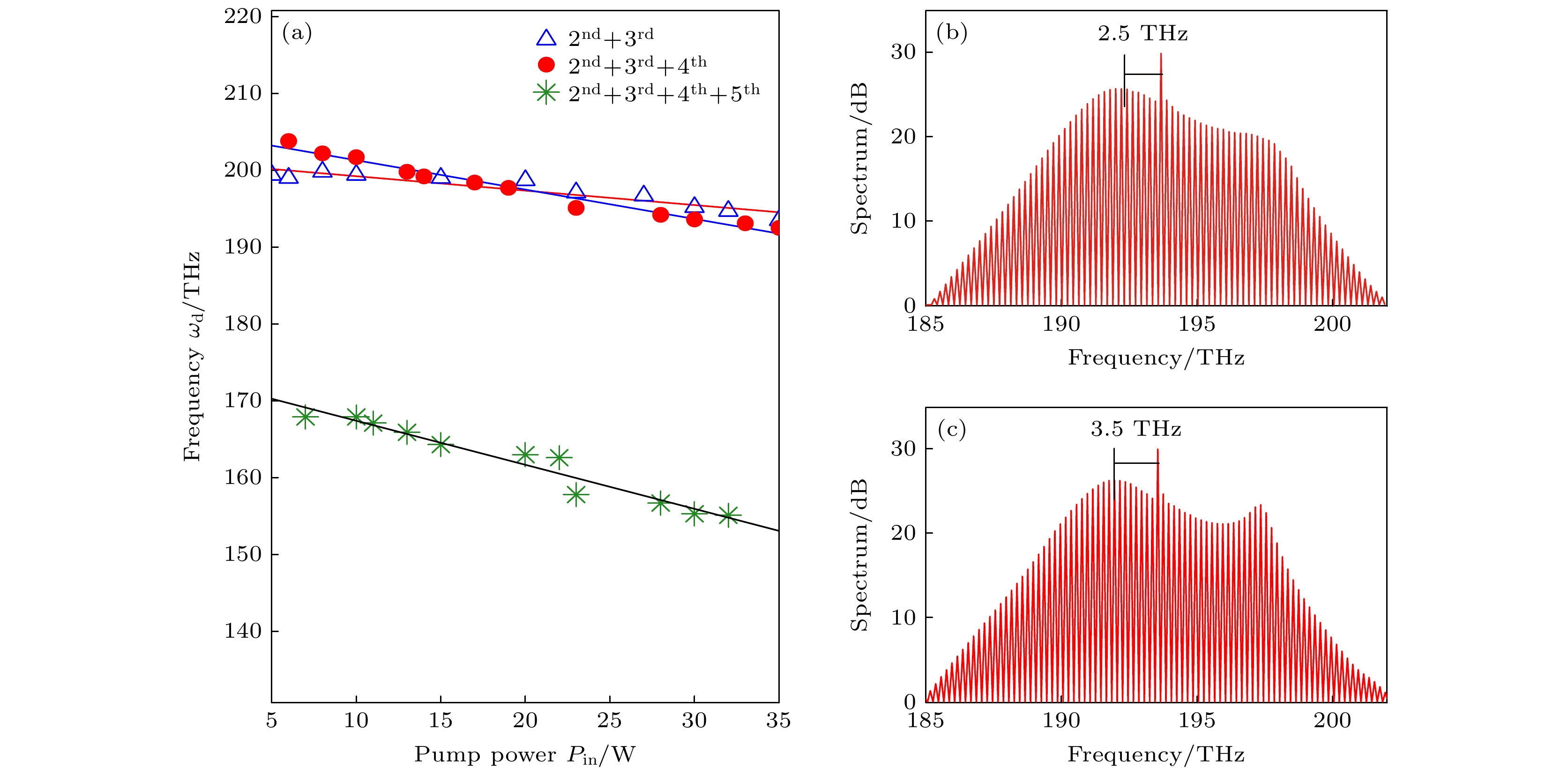
图 14 (a) 随Pin的增加, 不同高阶色散组合情况下ωd的变化; (b) Pin = 5 W和(c) 15 W 时, 包含二阶到四阶色散情况下的腔内梳状谱
Figure 14. (a) Under the condition of different orders of high-order dispersion, the variation of ωd with the increase of Pin; (b), (c) the intracavity comb spectrum with 2nd–4th order dispersion at (b) Pin = 5 W and (c) 15 W.
-
[1] Newman Z L, Maurice V, Drake T, Stone J R, Briles T C, Spencer D T, Fredrick C, Li Q, Westly D, Ilic B R, Shen B, Suh M G, Yang K Y, Johnson C, Johnson D M S, Hollberg L, Vahala K J, Srinivasan K, Diddams S A, Kitching J, Papp S B, Hummon M T 2019 Optica 6 680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Torres-Company V, Weiner A M 2014 Laser & Photonics Rev. 8 368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Trocha P, Karpov M, Ganin D, Pfeiffer M H P, Kordts A, Wolf S, Krockenberger J, Marin-Palomo P, Weimann C, Randel S, Freude W, Kippenberg T J, Koos C 2018 Science 359 887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cruz F C, Maser D L, Johnson T, Ycas G, Klose A, Giorgetta F R, Coddington I, Diddams S A 2015 Opt. Express 23 26814
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kippenberg T J, Holzwarth R, Diddams S A 2011 Science 332 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Coillet A, Balakireva I, Henriet R, Saleh K, Larger L, Dudley J M, Menyuk C R, Chembo Y K 2013 IEEE Photonics J. 5 6100409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Matsko A B, Liang W, Savchenkov A A, Maleki L 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 525
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xue X, Xuan Y, Liu Y, Wang P H, Chen S, Wang J, Leaird D E, Qi M, Weiner A M 2015 Nat. Photon. 9 594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kippenberg T J, Gaeta A L, Lipson M, Gorodetsky M L 2018 Science 361 567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Tikan A, Wang R N, Riemensberger J, Liu J, Seidler P, Komagata K, Kippenberg T J, Hönl S, Churaev M, Skehan C, Guo H 2021 Nat. Phys. 17 604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Tikan A, Tusnin A, Riemensberger J, Churaev M, Ji X, Komagata K N, Wang R N, Liu J, Kippenberg T J 2022 Science Advan. 8 6982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Brasch V, Herr T, Geiselmann M, Lihachev G, Pfeiffer M H P, Gorodetsky M L, Kippenberg T J 2015 Science 351 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Parra-Rivas P, Gomila D, Leo F, Coen S, Gelens L 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 2971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Okawachi Y, Lamont M R, Luke K, Carvalho D O, Yu M, Lipson M, Gaeta A L 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 3535
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cherenkov A V, Lobanov V E, Gorodetsky M L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 95 033810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Xue X, Zheng X, Zhou B 2019 Nat. Photon. 13 616
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 徐昕, 金雪莹, 高浩然, 陈杰, 陆洋, 陈东, 于连栋 2020 69 184207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X, Jin X Y, Gao H R, Chen J, Lu Y, Chen D, Yu L D 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 184207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Maes B, Fiers M, Bienstman P 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 033805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Xu X, Jin X, Lu Y, Gao H, Cheng J, Yu L 2020 J. Optics 22 115501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xu Y, Coen S 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 3492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 王景灏 2018 博士学位论文 (武汉: 华中科技大学)
Wang J H 2018 Ph. D. Dissertation (Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
[22] Wang J, Zhou R, Lai D, Che K, Chen L, Jiang S, Xu H, Cai Z 2019 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 31 1175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Dinyari K N, Barbour R J, Golter D A, Wang H 2011 Opt. Express 19 17966
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Milian C, Skryabin D V 2014 Opt. Express 22 3732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Leo F, Mussot A, Kockaert P, Emplit P, Haelterman M, Taki M 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 104103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Mussot A, Louvergneaux E, Akhmediev N, Reynaud F, Delage L, Taki M 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 113904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Gomila D, Scroggie A J, Firth W J 2007 Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenomena 227 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] He Y, Wang S, Zeng X 2016 IEEE Photonics J. 8 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Bao C, Taheri H, Zhang L, Matsko A, Yan Y, Liao P, Maleki L, Willner A E 2017 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 34 715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Roy S, Bhadra S K, Agrawal G P 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 2072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Skryabin D V, Luan F, Knight J C, Russell P S J 2003 Science 301 1705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Taheri H, Eftekhar A A, Wiesenfeld K, Adibi A 2015 IEEE Photon. J. 7 2200309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Milián C, Gorbach A V, Taki M, Yulin A V, Skryabin D V 2015 Phys. Rev. A 92 033851
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9866
- PDF Downloads: 229
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: