-
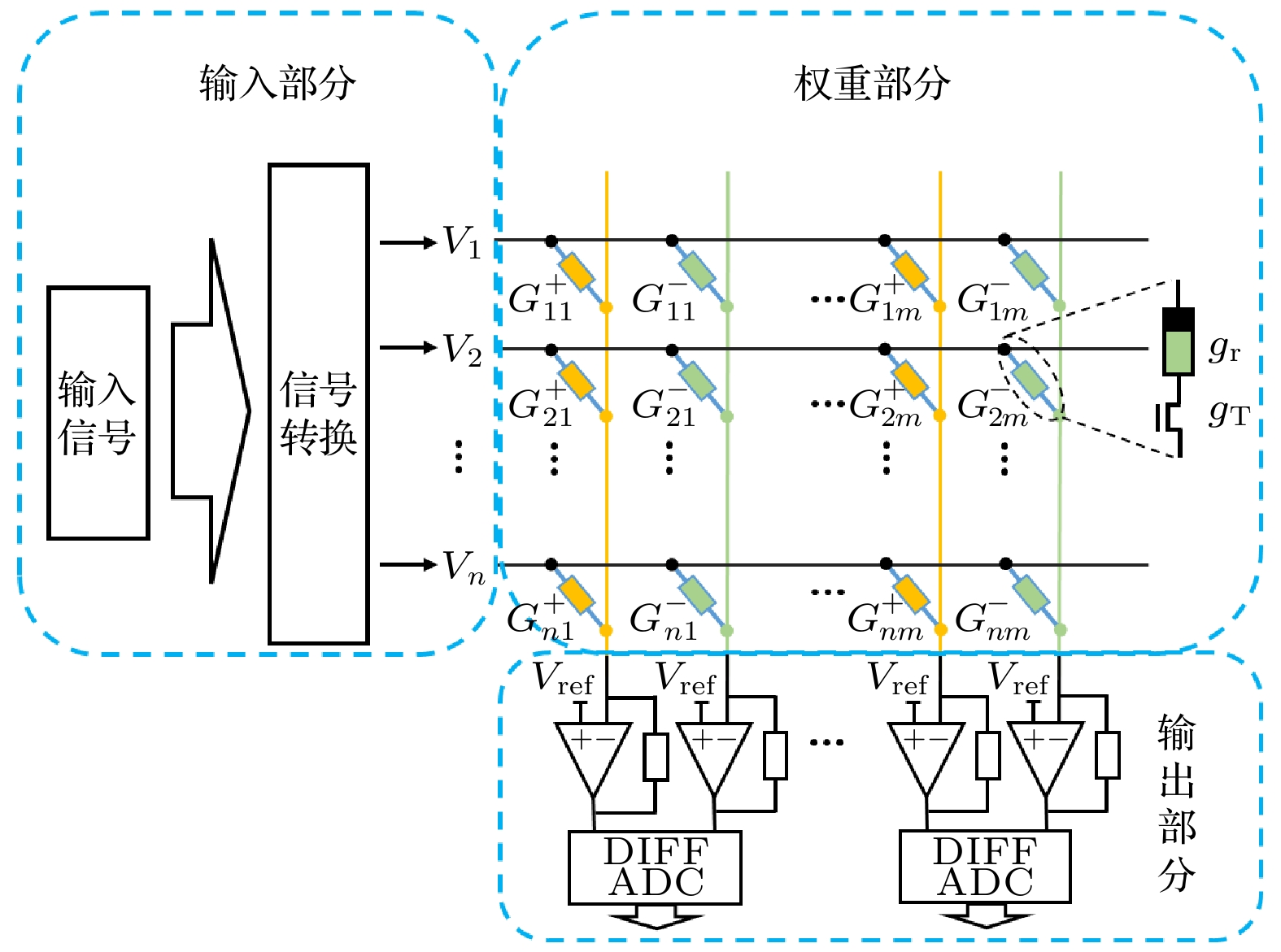
As a kind of brain-inspired computing, reservoir computing (RC) has great potential applications in time sequence signal processing and chaotic dynamics system prediction due to its simple structure and few training parameters. Since in the RC randomly initialized network weights are used, it requires abundant data and calculation time for warm-up and parameter optimization. Recent research results show that an RC with linear activation nodes, combined with a feature vector, is mathematically equivalent to a nonlinear vector autoregression (NVAR) machine, which is named next-generation reservoir computing (NGRC). Although the NGRC can effectively alleviate the problems which traditional RC has, it still needs vast computing resources for multiplication operations. In the present work, a hardware implementation method of using computing-in memory paradigm for NGRC is proposed for the first time. We use memristor array to perform the matrix vector multiplication involved in the nonlinear vector autoregressive process for the improvement of the energy efficiency. The Lorenz63 time series prediction task is performed by simulation experiments with the memristor array, demonstrating the feasibility and robustness of this method, and the influence of the weight precision of the memristor devices on the prediction results is discussed. These results provide a promising way of implementing the hardware NGRC.
[1] Guillem C, Jordi F 2015 Front. Psychol. 6 818
[2] Dayan P, Abbott L F 2001 J. Cogn. Neurosci. 15 154
[3] Vogels T P, Rajan K, Abbott L F 2005 Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 28 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tian Y, Li G, Sun P 2021 Phys. Rev. Res. 3 043085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Borst A, Theunissen F E 1999 Nat. Neurosci. 2 947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Amit D J, Gutfreund H, Sompolinsky H 1987 Phys. Rev. A 35 2293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Danilo P, Mandic J A C 2001 Recurrent Neural Networks Architecture (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Ltd) pp69–89
[8] Choi E, Schuetz A, Stewart W F, Sun J 2016 J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 24 361
[9] Pascanu R, Mikolov T, Bengio Y 2013 Proceedings of the 30 th International Conference on Machine Learning Atlanta, Georgia, USA, June 16–21, 2013 p1310
[10] Dominey P, Arbib M, Joseph J P 1995 J. Cogn. Neurosci. 7 311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jaeger H 2001 German National Research Institute for Computer ScienceGerman National Research Centre for Information Technology, GMD Technical Reports Bonn, Germany, January 01, 2001 p13
[12] Jaeger H, Haas H 2004 Science 304 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Maass W, Natschlager T, Markram H 2002 Neural Comput. 14 2531
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kan S, Nakajima K, Takeshima Y, Asai T, Kuwahara Y, Akai-Kasaya M 2021 Phys. Rev. Appl. 15 024030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pathak J, Hunt B, Girvan M, Lu Z, Ott E 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 024102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chattopadhyay A, Hassanzadeh P, Subramanian D 2020 Nonlinear Processes Geophys. 27 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lukoševičius M, Jaeger H, Schrauwen B 2012 KI - Künstliche Intelligenz 26 365
[18] Boyd S, Chua L 1985 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 32 1150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Grigoryeva L, Ortega J P 2018 Neural Networks 108 495
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao C, Li J, Liu L, Koutha L S, Liu J, Yi Y 2016 Proceedings of the 3 rd ACM International Conference on Nanoscale Computing and Communication New York, New York, USA, September 28–30, 2016 p1
[21] Canaday D, Griffith A, Gauthier D 2018 Chaos:An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science 28 123119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yi Y, Liao Y, Fu X 2016 Microprocess. Microsyst. 46 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bertschinger N, Natschlager T 2004 Neural Comput. 16 1413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yang X, Chen W, Wang F 2016 Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 87 263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Merkel C, Saleh Q, Donahue C, Kudithipudi D 2014 5 th Annual International Conference on Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures (BICA) MIT Campus, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, November 7–9, 2014 p249
[26] Donahue C, Merkel C, Saleh Q, Dolgovs L, Ooi Y, Kudithipudi D, Wysocki B 2015 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications (CISDA) Verona, New York, May 26–28, 2015 p24
[27] Demis E, Aguilera R, Scharnhorst K, Aono M, Stieg A, Gimzewski J 2016 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55 1102B2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lilak S, Woods W, Scharnhorst K, Dunham C, Teuscher C, Stieg A, Gimzewski J 2021 Front. in Nanotechnol. 3 1
[29] Vandoorne K, Mechet P, van Vaerenbergh T, et al. 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 3541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Milano G, Pedretti G, Montano K, Ricci S, Hashemkhani S, Boarino L, Ielmini D, Ricciardi C 2021 Nat. Mater. doi: 10.1038/s41563-021-01099-9
[31] Gallicchio C, Micheli A, Pedrelli L 2017 Neurocomputing 268 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Qiao J, Li F, Han H G, Li W 2016 IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 28 391
[33] Tong Z Q, Tanaka G 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR) Beijing, China, August 20–24, 2018 p1289
[34] Murakamli M, Kroger B, Birkholz P, Triesch J 2015 5th IEEE Joint International Conference on Development and Learning and on Epigenetic Robotics (IEEE ICDL-EpiRob) Providence, Rhode Island, August 13–16, 2015 p208
[35] Sussillo D, Abbott L F 2009 Neuron 63 544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Tanaka G, Yamane T, Heroux J B, et al. 2019 Neural Networks 115 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Lepri S, Giacomelli G, Politi A, Arecchi F T 1994 Physica D 70 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Appeltant L, Soriano M C, van der Sande G, et al. 2011 Nat. Commun. 2 468 468
[39] Brunner D, Penkovsky B, Marquez B A, Jacquot M, Fischer I, Larger L 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 152004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Penkovsky B, Larger L, Brunner D 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 162101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Yu J, Li Y, Sun W, et al. 2021 Symposium on VLSI Technology Kyoto, Japan, June 13–19, 2021 p1
[42] Gauthier D J, Bollt E, Griffith A, Barbosa W A S 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 5564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Strukov D B, Snider G S, Stewart D R, Williams R S 2008 Nature 453 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Li H, Wang S, Zhang X, Wang W, Yang R, Sun Z, Feng W, Lin P, Wang Z, Sun L, Yao Y 2021 Adv. Intell. Syst. 3 2100017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Li Y, Loh L, Li S, Chen L, Li B, Bosman M, Ang K W 2021 Nat. Electron. 4 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Kim H, Mahmoodi M R, Nili H, Strukov D B 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 5198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Xiao T P, Bennett C H, Feinberg B, Agarwal S, Marinella M J 2020 Appl. Phys. Rev. 7 031301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Lorenz E N 2004 The Theory of Chaotic Attractors (New York: Springer New York) pp25–36
[49] Zhang W, Gao B, Tang J, Yao P, Yu S, Chang M F, Yoo H J, Qian H, Wu H 2020 Nat. Electron. 3 371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
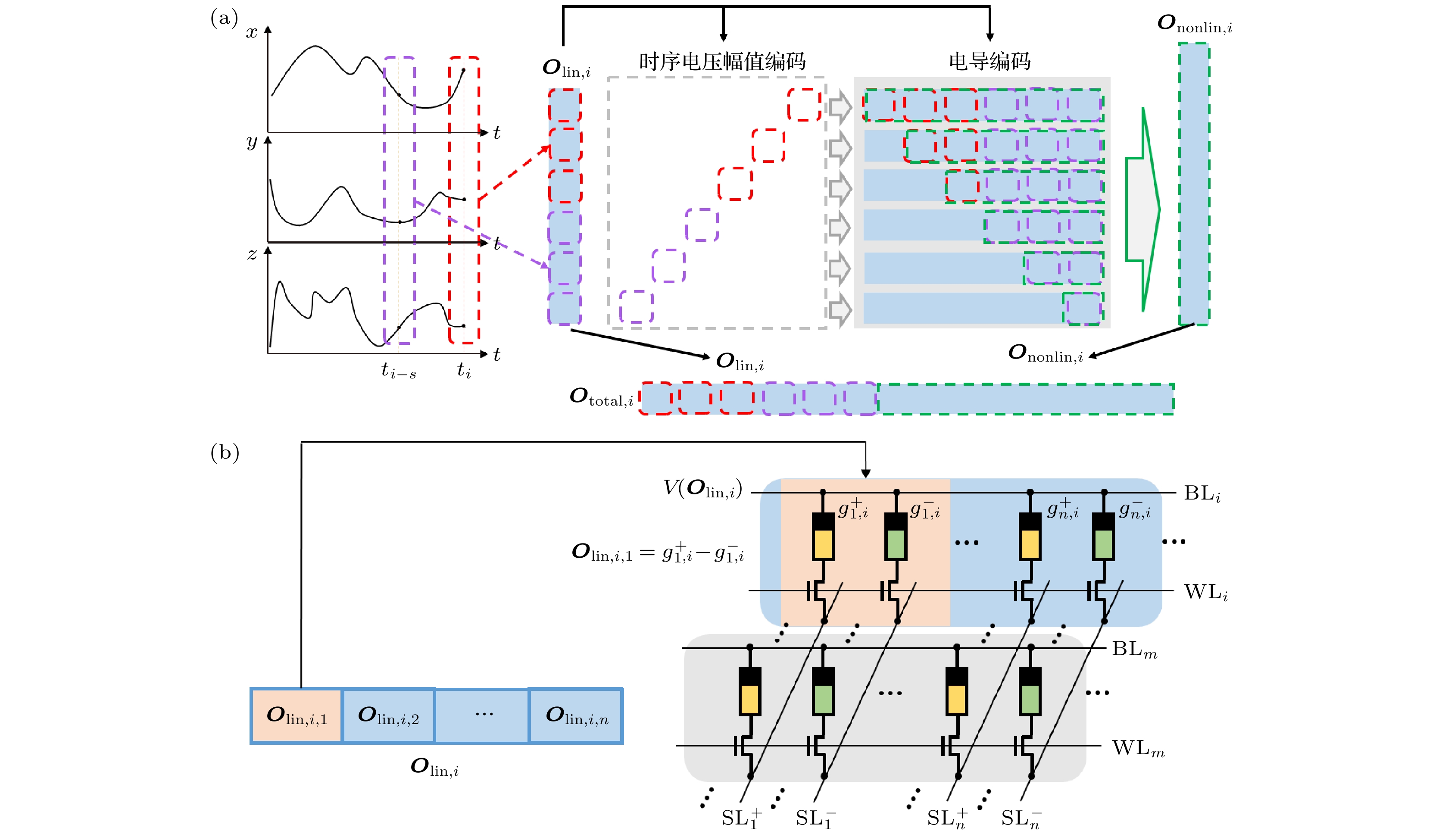
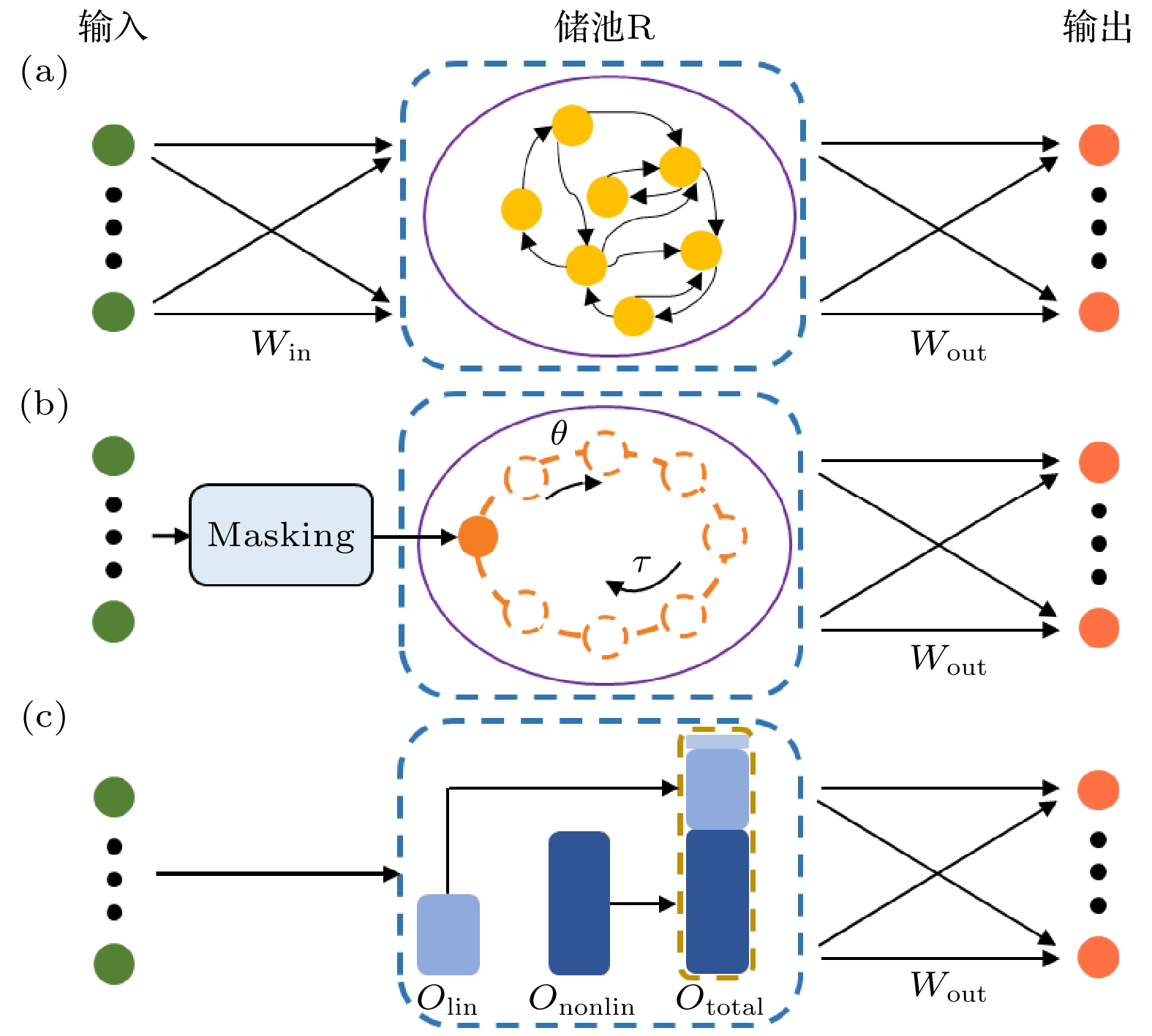
图 2 基于忆阻阵列的NGRC储池结构 (a)用于预测三维时序信号的NGRC储池结构. 输入为三维时序信号; 提取ti时刻(红色框)和ti-s(紫色框)时刻信号的值组成线性特征向量Olin, 将第i个线性特征向量编码为时序电压和电导, 时序电压作为忆阻器阵列的输入, 电导映射到忆阻器阵列上作为权重; 非线性特征向量
${\boldsymbol{O}}_{{\rm{nonlin}}}$ 由忆阻器阵列特定单元(绿色方框)的输出构成; 总特征向量由$ {\boldsymbol{O}}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $ 与$ {\boldsymbol{O}}_{\mathrm{n}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $ 直接拼接而成. (b) 图(a)中的线性特征向量$ {\boldsymbol{O}}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}, i} $ 映射到忆阻器阵列的方式.$ {\boldsymbol{O}}_{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}, i} $ 中的每一个值都由两个忆阻器电导的差分g+, g–表示Figure 2. Structure of the NGRC based on memristor-based crossbar. (a) Structure of the NGRC reservoir for three dimensional (3D) timing signals predicting. The input is a 3D timing signal. The linear feature vector Olin is formed by extracting the signal values of ti time (red box) and ti-s time (purple box). The ith linear feature vector is encoded as timing voltage and conductance, and the timing voltage is the input of the memristor array, and the conductance is mapped to the memristor array as weight. The nonlinear feature vector Ononlin consists of the outputs of specific elements of the memristor array (green boxes). The total feature vector is directly spliced by Olin and Ononlin. (b) The way the linear feature vector Olin, i in panel (a) mapping to the memristor array. The g+ and g– represent the device conductance values for the positive and negative weights in the differential pair, respectively.
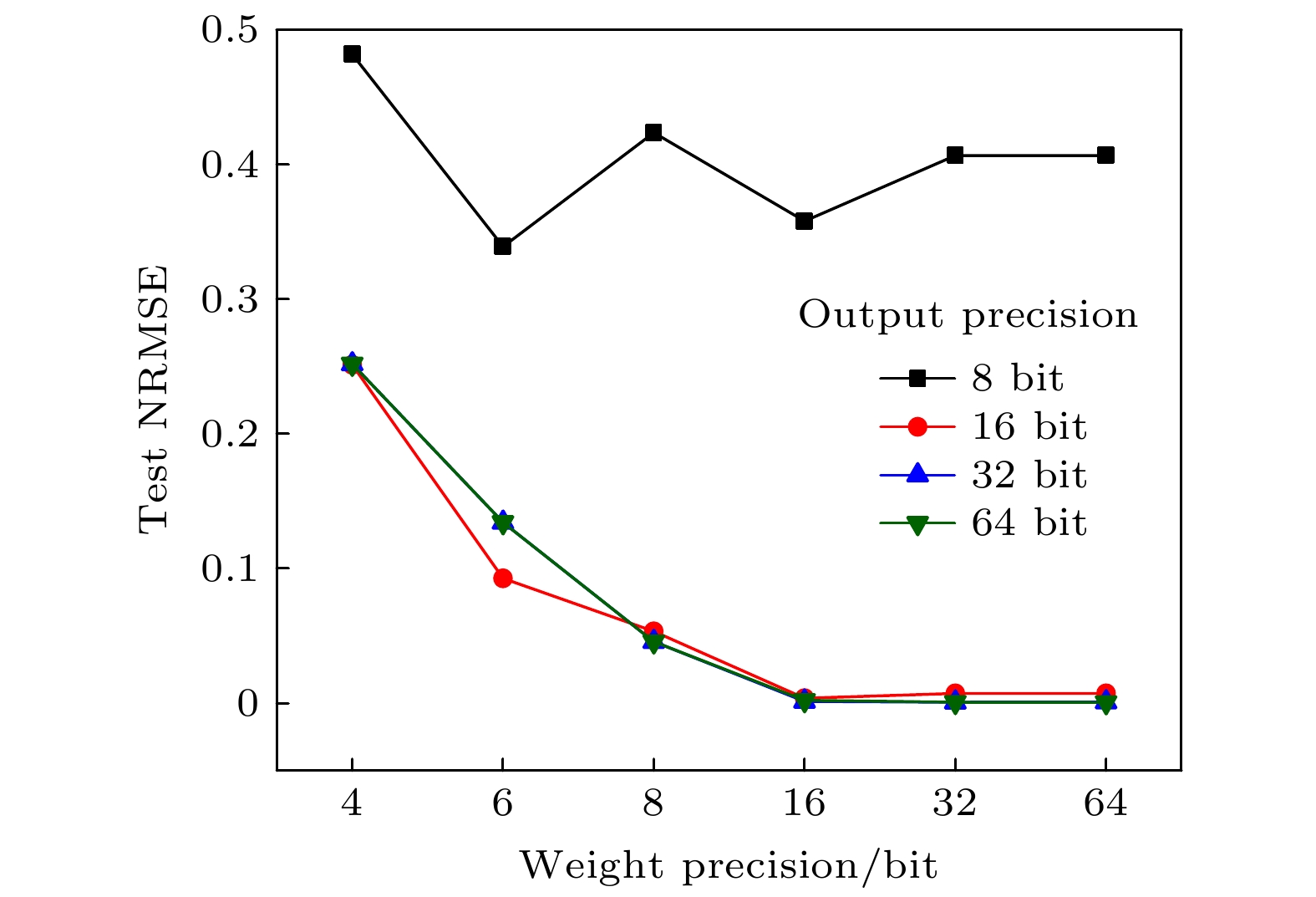
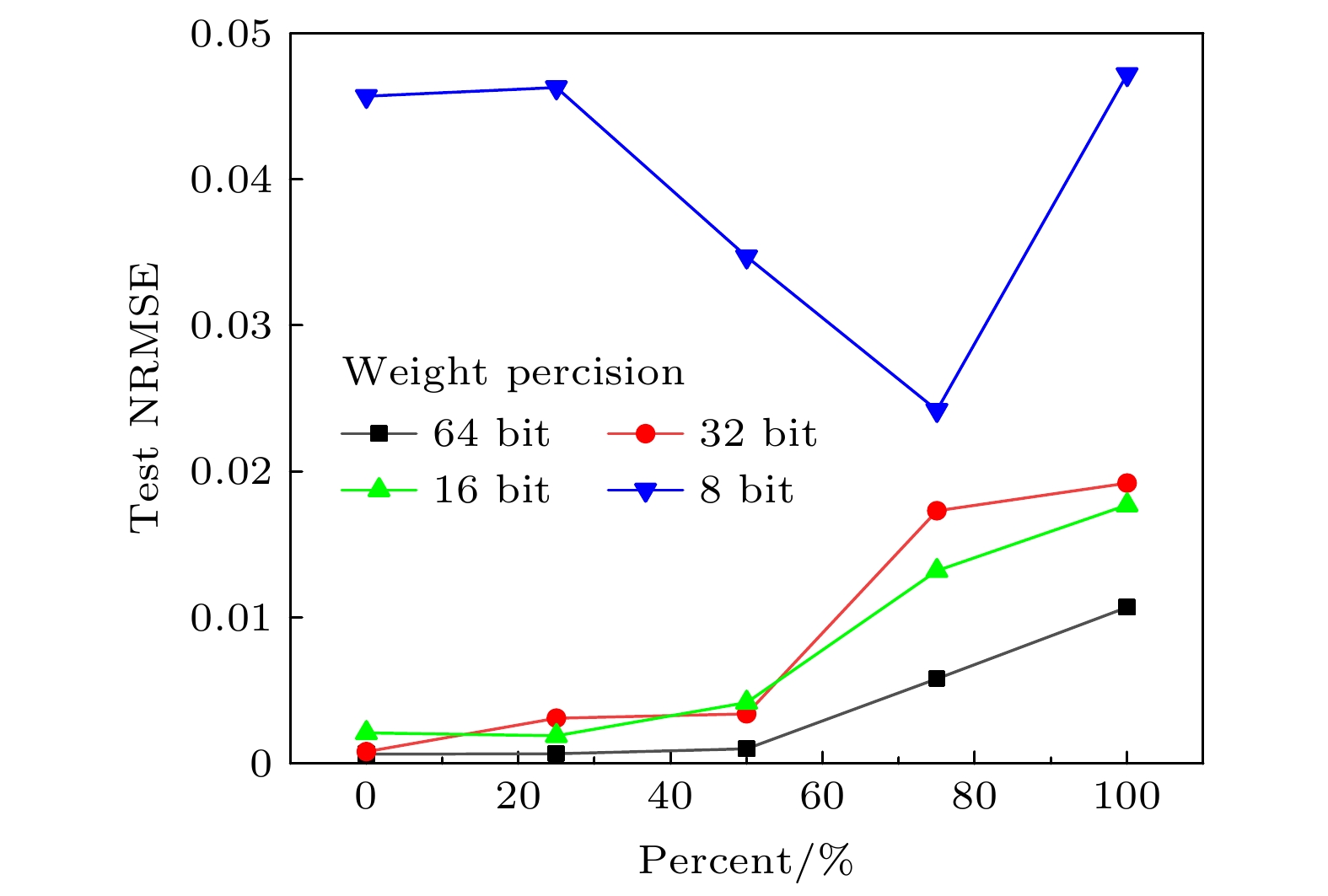
图 4 输入精度为定点32 bit, 输出精度为定点64 bit, 不同权重精度下800个时间步的预测XZ截面图 (a) 64 bit; (b) 32 bit; (c) 16 bit; (d) 8 bit; (e) 6 bit; (f) 4 bit
Figure 4. The XZ cross sections of 800 time steps with different weight precision, when input precision of integer is 32 bit and output precision of integer is 64 bit: (a) 64 bit; (b) 32 bit; (c) 16 bit; (d) 8 bit; (e) 6 bit; (f) 4 bit.
-
[1] Guillem C, Jordi F 2015 Front. Psychol. 6 818
[2] Dayan P, Abbott L F 2001 J. Cogn. Neurosci. 15 154
[3] Vogels T P, Rajan K, Abbott L F 2005 Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 28 357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Tian Y, Li G, Sun P 2021 Phys. Rev. Res. 3 043085
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Borst A, Theunissen F E 1999 Nat. Neurosci. 2 947
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Amit D J, Gutfreund H, Sompolinsky H 1987 Phys. Rev. A 35 2293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Danilo P, Mandic J A C 2001 Recurrent Neural Networks Architecture (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Ltd) pp69–89
[8] Choi E, Schuetz A, Stewart W F, Sun J 2016 J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 24 361
[9] Pascanu R, Mikolov T, Bengio Y 2013 Proceedings of the 30 th International Conference on Machine Learning Atlanta, Georgia, USA, June 16–21, 2013 p1310
[10] Dominey P, Arbib M, Joseph J P 1995 J. Cogn. Neurosci. 7 311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jaeger H 2001 German National Research Institute for Computer ScienceGerman National Research Centre for Information Technology, GMD Technical Reports Bonn, Germany, January 01, 2001 p13
[12] Jaeger H, Haas H 2004 Science 304 78
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Maass W, Natschlager T, Markram H 2002 Neural Comput. 14 2531
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kan S, Nakajima K, Takeshima Y, Asai T, Kuwahara Y, Akai-Kasaya M 2021 Phys. Rev. Appl. 15 024030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pathak J, Hunt B, Girvan M, Lu Z, Ott E 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 024102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Chattopadhyay A, Hassanzadeh P, Subramanian D 2020 Nonlinear Processes Geophys. 27 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lukoševičius M, Jaeger H, Schrauwen B 2012 KI - Künstliche Intelligenz 26 365
[18] Boyd S, Chua L 1985 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 32 1150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Grigoryeva L, Ortega J P 2018 Neural Networks 108 495
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhao C, Li J, Liu L, Koutha L S, Liu J, Yi Y 2016 Proceedings of the 3 rd ACM International Conference on Nanoscale Computing and Communication New York, New York, USA, September 28–30, 2016 p1
[21] Canaday D, Griffith A, Gauthier D 2018 Chaos:An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science 28 123119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Yi Y, Liao Y, Fu X 2016 Microprocess. Microsyst. 46 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bertschinger N, Natschlager T 2004 Neural Comput. 16 1413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yang X, Chen W, Wang F 2016 Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 87 263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Merkel C, Saleh Q, Donahue C, Kudithipudi D 2014 5 th Annual International Conference on Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures (BICA) MIT Campus, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, November 7–9, 2014 p249
[26] Donahue C, Merkel C, Saleh Q, Dolgovs L, Ooi Y, Kudithipudi D, Wysocki B 2015 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications (CISDA) Verona, New York, May 26–28, 2015 p24
[27] Demis E, Aguilera R, Scharnhorst K, Aono M, Stieg A, Gimzewski J 2016 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55 1102B2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lilak S, Woods W, Scharnhorst K, Dunham C, Teuscher C, Stieg A, Gimzewski J 2021 Front. in Nanotechnol. 3 1
[29] Vandoorne K, Mechet P, van Vaerenbergh T, et al. 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 3541
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Milano G, Pedretti G, Montano K, Ricci S, Hashemkhani S, Boarino L, Ielmini D, Ricciardi C 2021 Nat. Mater. doi: 10.1038/s41563-021-01099-9
[31] Gallicchio C, Micheli A, Pedrelli L 2017 Neurocomputing 268 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Qiao J, Li F, Han H G, Li W 2016 IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 28 391
[33] Tong Z Q, Tanaka G 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR) Beijing, China, August 20–24, 2018 p1289
[34] Murakamli M, Kroger B, Birkholz P, Triesch J 2015 5th IEEE Joint International Conference on Development and Learning and on Epigenetic Robotics (IEEE ICDL-EpiRob) Providence, Rhode Island, August 13–16, 2015 p208
[35] Sussillo D, Abbott L F 2009 Neuron 63 544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Tanaka G, Yamane T, Heroux J B, et al. 2019 Neural Networks 115 100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Lepri S, Giacomelli G, Politi A, Arecchi F T 1994 Physica D 70 235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Appeltant L, Soriano M C, van der Sande G, et al. 2011 Nat. Commun. 2 468 468
[39] Brunner D, Penkovsky B, Marquez B A, Jacquot M, Fischer I, Larger L 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 152004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Penkovsky B, Larger L, Brunner D 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 124 162101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Yu J, Li Y, Sun W, et al. 2021 Symposium on VLSI Technology Kyoto, Japan, June 13–19, 2021 p1
[42] Gauthier D J, Bollt E, Griffith A, Barbosa W A S 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 5564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Strukov D B, Snider G S, Stewart D R, Williams R S 2008 Nature 453 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Li H, Wang S, Zhang X, Wang W, Yang R, Sun Z, Feng W, Lin P, Wang Z, Sun L, Yao Y 2021 Adv. Intell. Syst. 3 2100017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Li Y, Loh L, Li S, Chen L, Li B, Bosman M, Ang K W 2021 Nat. Electron. 4 348
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Kim H, Mahmoodi M R, Nili H, Strukov D B 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 5198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Xiao T P, Bennett C H, Feinberg B, Agarwal S, Marinella M J 2020 Appl. Phys. Rev. 7 031301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Lorenz E N 2004 The Theory of Chaotic Attractors (New York: Springer New York) pp25–36
[49] Zhang W, Gao B, Tang J, Yao P, Yu S, Chang M F, Yoo H J, Qian H, Wu H 2020 Nat. Electron. 3 371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 11380
- PDF Downloads: 528
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: