-
Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR)-entangled state light field at a telecommunication wavelength of 1.5 μm is an important quantum source for realizing the continuous variable quantum information processing and some quantum protocols over optical fiber channel. When the EPR-entangled state light field is distributed over the optical fiber channel, the disentanglement is always present because the the EPR entangled state interacts with the fiber channel. It affects the performance of quantum information processing. In this paper, we theoretically calculate the positive partial transposition (PPT) of the entangled state distributed over the optical fiber channel in the single-channel and dual-channel distribution scheme, respectively. Three types of initial entangled light field are considered and analyzed, they being an initial EPR entangled state, an EPR entangled state with asymmetric quadratures, and an EPR entangled state with asymmetric modes. Furthermore, the influence of the extra noise in the optical fiber on the transmission distance of EPR entangled state over the optical fiber channel is investigated. In the single-channel scheme or dual-channel scheme, the extra noise in the optical fiber channel leads the entangled state light field to be disentangled, and the transmission distance of EPR entangled state over the optical fiber channel to decrease rapidly with the increase of the extra noise. For maintaining the robustness of EPR entangled states in lossy optical fiber channels, the dual-channel scheme has more stringent requirements for the correlation quadrature symmetry and purity of the initial entangled state than the single-channel scheme. In the single fiber noise channel scheme, the maximum transmission distance and the robustness of the EPR entangled states with asymmetric modes are not sensitive to the asymmetry between modes. The change of asymmetry between modes does not lead to being disentangled. The maximum transmission distance does not change either. However, the decrease of asymmetry between modes results in the disentanglement in the double fiber noise channels’ scheme. The maximum transmission distance is reduced and the sudden death occurs to the entanglement. The present results will lay a foundation for continuous variables quantum information processing based on optical fiber, such as realizing continuous variables quantum communication over optical fiber and constructing metropolitan quantum network over optical fiber.
-
Keywords:
- continuous variable Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen entangled state /
- optical fiber channel /
- robustness /
- disentanglement
[1] Kimble H J 2008 Nature 453 1023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Weedbrook C, Pirandola S, García-Patrón R, Cerf N J, Ralph T C, Shapiro J H, Lloyd S 2012 Rev. Mod. Phys. 84 621
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ast M, Steinlechner S, Schnabel R 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 180801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Furusawa A, Sørensen J L, Braunstein S L, Fuchs C A, Kimble H J, Polzik E S 1998 Science 282 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li X Y, Pan Q, Jing J T, Zhang J, Xie C D, Peng K C 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 047904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jing J T, Zhang J, Yan Y, Zhao F G, Xie C D, Peng K C 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 167903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yu T, Eberly J H 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 140404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yu T, Eberly J H 2009 Science 323 598
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Almeida M P, Melo F D, Hor-Meyll M, Salles A, Walborn S P, Ribeiro P H S, Davidovich L 2007 Science 316 579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Vidal G, Tarrach R 1999 Phys. Rev. A 59 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Coelho A S, Barbosa F A S, Cassemiro K N, Villar A S, Martinelli M, Nussenzveig P 2009 Science 326 823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Barbosa F A S, Coelho A S, Faria A J, Cassemiro K N, Villar A S, Nussenzveig P, Martinelli M 2010 Nat. Photon. 4 858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Barbosa F A S, Faria A J, Coelho A S, Cassemiro K N, Villar A S, Nussenzveig P, Martinelli M 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 052330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Deng X W, Tian C X, Su X L, Xie C D 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 44475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Deng X W, Liu Y, Wang M H, Su X L, Peng K C 2021 npj Quantum Inf. 7 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 印娟, 雍海林, 吴裕平, 彭承志 2011 60 060307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin J, Yong H L, Wu Y P, Peng C Z 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 060307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Valivarthi R, Puigibert M G, Zhou Q, Aguilar G H, Verma V B, Marsili F, Shaw M D, Nam S W, Oblak D, Tittel W 2016 Nat. Photon. 10 676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wengerowsky S, Joshi S K, Steinlechner F, Zichi J R, Dobrovolskiy S M, Molen R V D, Losh J W N, Zwiller V, Versteeghg M A M, Mura A, Calonico D, Inguscio M, Hübel H, Liu B, Scheidl T, Zeilinger A, Xuereb A, Ursina R 2019 PNAS 116 66684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Feng J X, Wan Z J, Li Y J, Zhang K S 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 3399
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 万振菊, 冯晋霞, 成健, 张宽收 2018 67 024203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wan Z J, Feng J, Cheng J, Zhang K S 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 024203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Simon R 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 2726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jouguet P, Kunz-Jacques S, Leverrier A, Grangier P, Diamanti E 2013 Nat. Photon. 7 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang N, Du S N, Liu W Y, Wang X Y, Li Y M, Peng K C 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 064028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
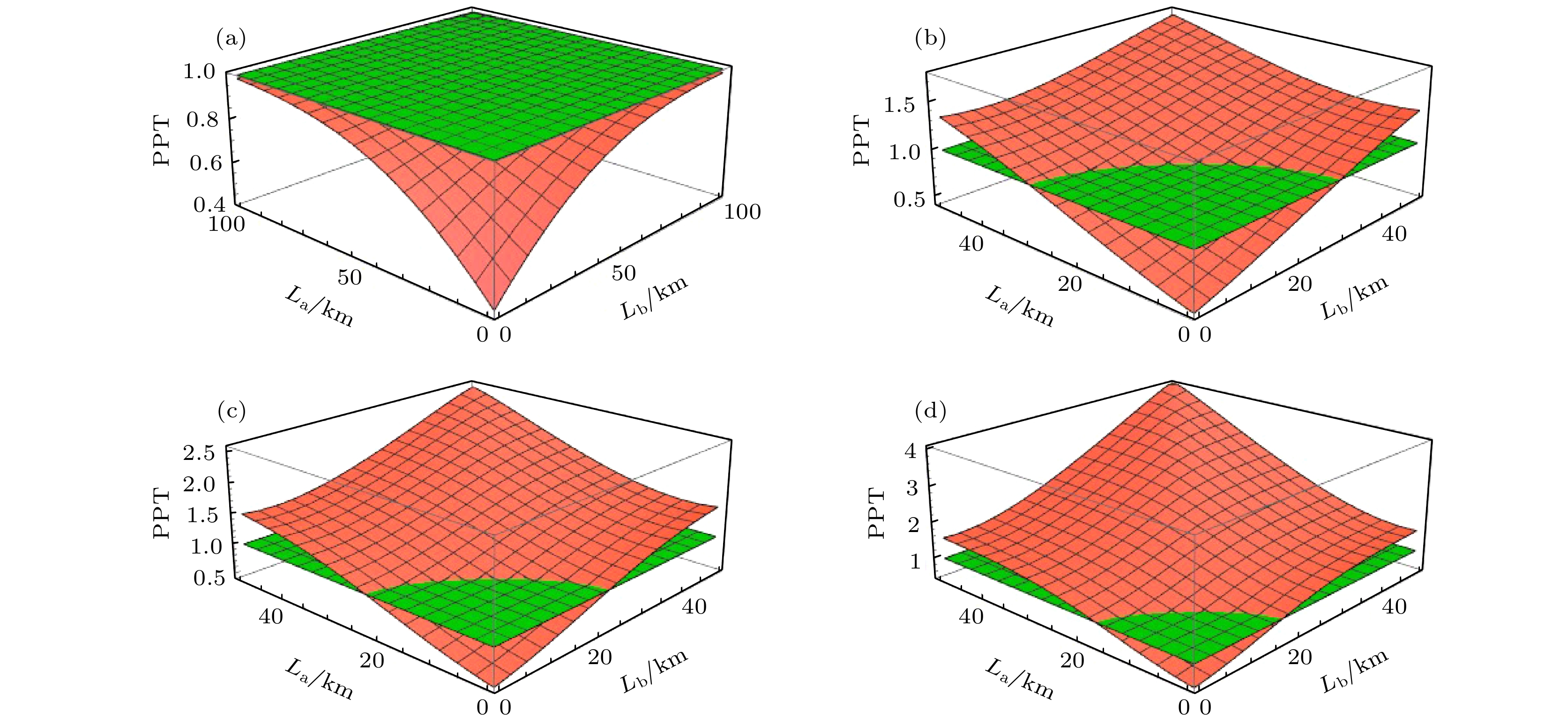
图 2 理想EPR纠缠态光场在光纤信道中的传输特性 (a) LO光功率为0 mW; (b) LO光功率为0.05 mW; (c) LO光功率为0.1 mW; (d) LO光功率为0.2 mW
Figure 2. Transmission characteristics of ideal EPR entangled state over optical fiber channel: (a) The power of the LO is 0 mW; (b) the power of the LO is 0.05 mW; (c) the power of the LO is 0.1 mW; (d) the power of the LO is 0.2 mW.
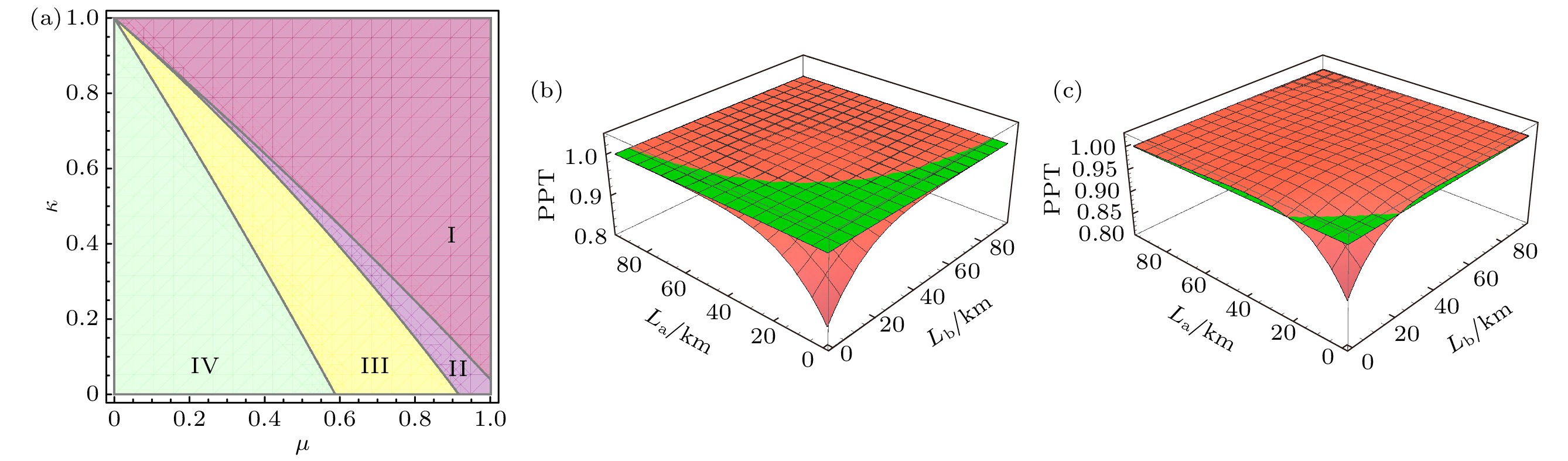
图 5 EPR纠缠态光场在光纤信道中的鲁棒性 (a)
$ 0 \leqslant \mu \leqslant 1 $ ,$ 0 \leqslant \kappa \leqslant 1 $ ; (b)$ \mu = 0.6 $ ,$ \kappa = 0.4 $ ; (c)$ \mu = 0.6 $ ,$ \kappa = 0.3 $ Figure 5. Robustness of EPR entangled state over optical fiber channel: (a)
$ 0 \leqslant \mu \leqslant 1 $ ,$ 0 \leqslant \kappa \leqslant 1 $ ; (b)$ \mu = 0.6 $ ,$ \kappa = 0.4 $ ; (c)$ \mu = 0.6 $ ,$ \kappa = 0.3 $ . -
[1] Kimble H J 2008 Nature 453 1023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Weedbrook C, Pirandola S, García-Patrón R, Cerf N J, Ralph T C, Shapiro J H, Lloyd S 2012 Rev. Mod. Phys. 84 621
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ast M, Steinlechner S, Schnabel R 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 180801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Furusawa A, Sørensen J L, Braunstein S L, Fuchs C A, Kimble H J, Polzik E S 1998 Science 282 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li X Y, Pan Q, Jing J T, Zhang J, Xie C D, Peng K C 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 047904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Jing J T, Zhang J, Yan Y, Zhao F G, Xie C D, Peng K C 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 167903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yu T, Eberly J H 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 140404
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yu T, Eberly J H 2009 Science 323 598
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Almeida M P, Melo F D, Hor-Meyll M, Salles A, Walborn S P, Ribeiro P H S, Davidovich L 2007 Science 316 579
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Vidal G, Tarrach R 1999 Phys. Rev. A 59 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Coelho A S, Barbosa F A S, Cassemiro K N, Villar A S, Martinelli M, Nussenzveig P 2009 Science 326 823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Barbosa F A S, Coelho A S, Faria A J, Cassemiro K N, Villar A S, Nussenzveig P, Martinelli M 2010 Nat. Photon. 4 858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Barbosa F A S, Faria A J, Coelho A S, Cassemiro K N, Villar A S, Nussenzveig P, Martinelli M 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 052330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Deng X W, Tian C X, Su X L, Xie C D 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 44475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Deng X W, Liu Y, Wang M H, Su X L, Peng K C 2021 npj Quantum Inf. 7 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 印娟, 雍海林, 吴裕平, 彭承志 2011 60 060307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin J, Yong H L, Wu Y P, Peng C Z 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 060307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Valivarthi R, Puigibert M G, Zhou Q, Aguilar G H, Verma V B, Marsili F, Shaw M D, Nam S W, Oblak D, Tittel W 2016 Nat. Photon. 10 676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wengerowsky S, Joshi S K, Steinlechner F, Zichi J R, Dobrovolskiy S M, Molen R V D, Losh J W N, Zwiller V, Versteeghg M A M, Mura A, Calonico D, Inguscio M, Hübel H, Liu B, Scheidl T, Zeilinger A, Xuereb A, Ursina R 2019 PNAS 116 66684
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Feng J X, Wan Z J, Li Y J, Zhang K S 2017 Opt. Lett. 42 3399
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 万振菊, 冯晋霞, 成健, 张宽收 2018 67 024203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wan Z J, Feng J, Cheng J, Zhang K S 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 024203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Simon R 2000 Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 2726
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jouguet P, Kunz-Jacques S, Leverrier A, Grangier P, Diamanti E 2013 Nat. Photon. 7 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Wang N, Du S N, Liu W Y, Wang X Y, Li Y M, Peng K C 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 064028
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5944
- PDF Downloads: 121
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: