-
The experiment on collision between 50-keV/u Ne8+ ion and C3H4 molecule is carried out by reaction microscopic imaging spectrometer. The process of forming the
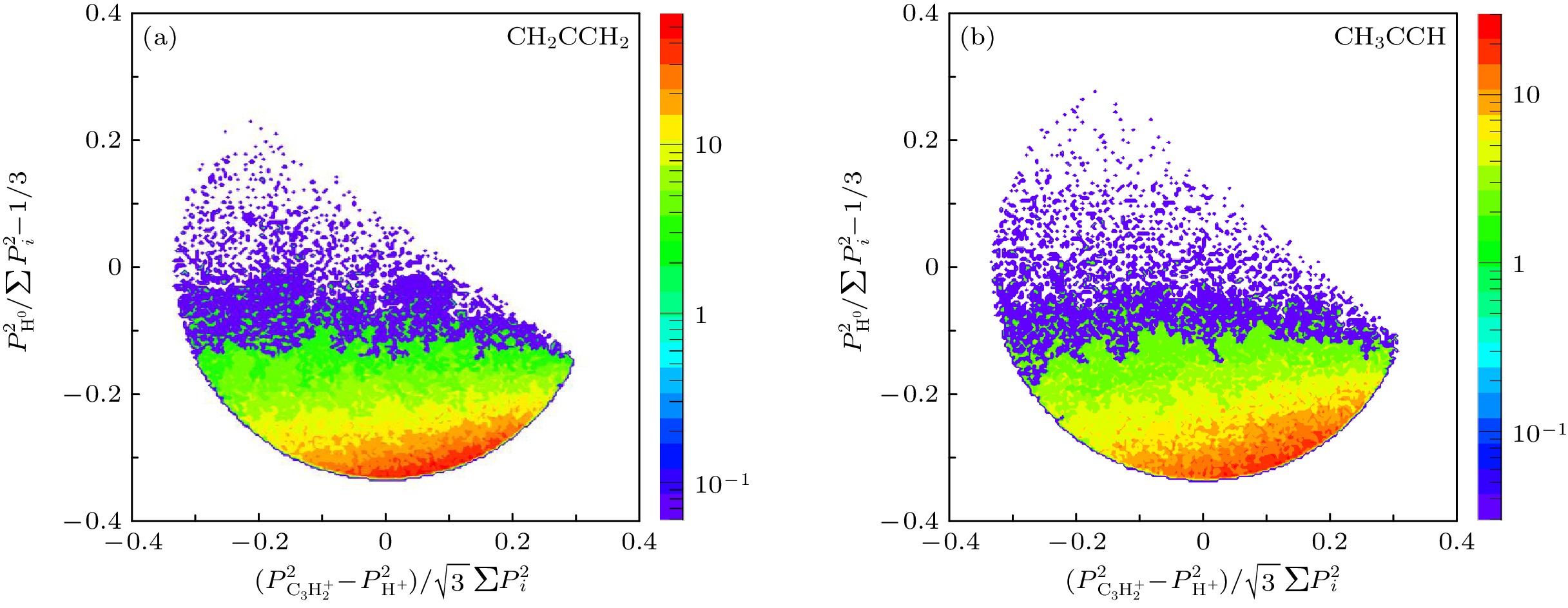
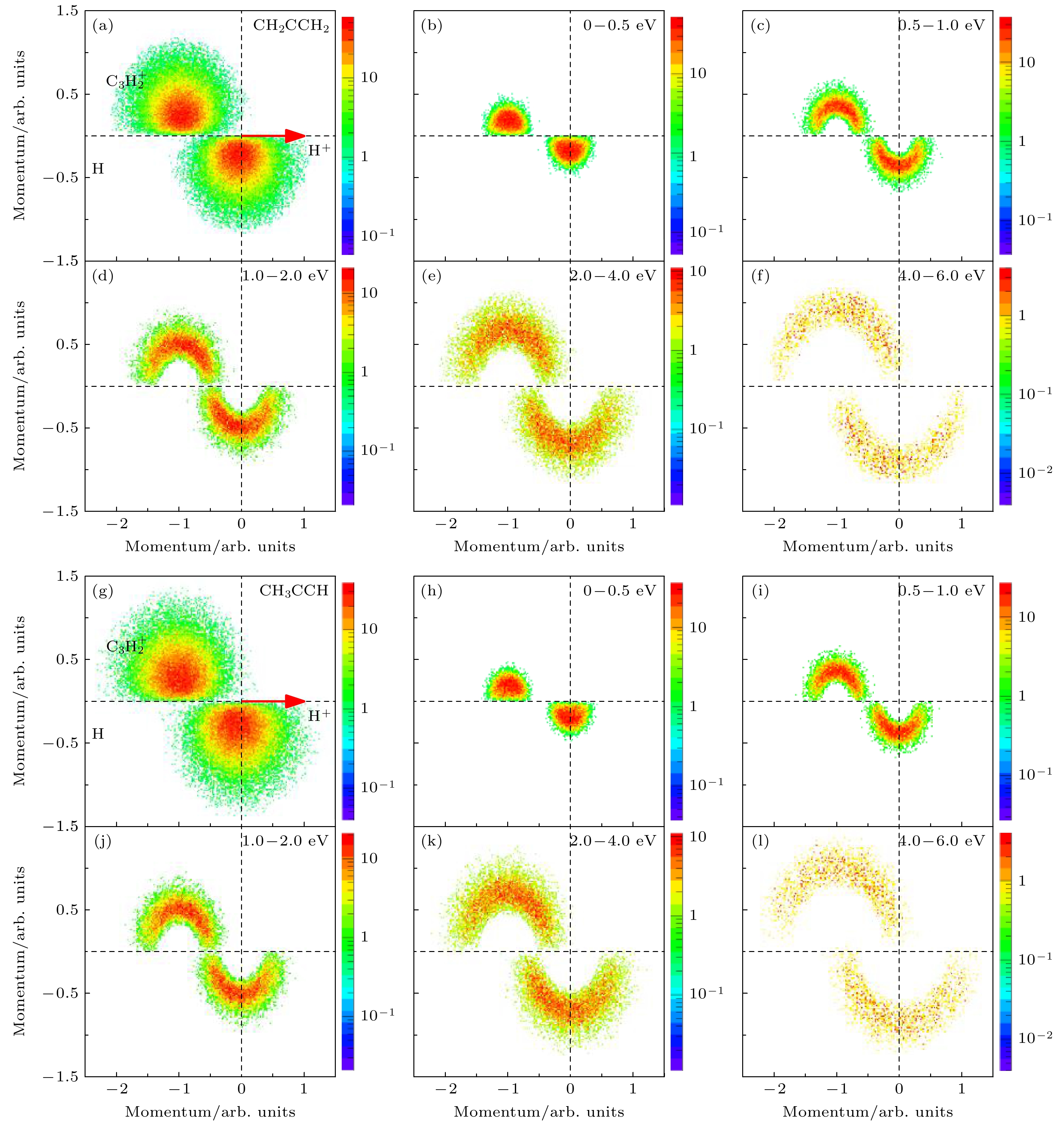
$\rm C_3H_4^{2+}$ divalent ion from propylene (CH2CCH2) and proacetylene (CH3CCH) and then dissociating to produce H+ and C3H2+$\rm C_3H_2^+$ ions and H atom is studied. Using the reaction microscope, the momentum vector of H+ ion and the momentum vector of$\rm C_3H_2^+$ ion are directly obtained, and then the momentum of the undetected fragment is reconstructed according to momentum conservation. By analyzing the kinetic energy of the three fragments and the total kinetic energy released from the dissociation process, the events with H atom as the third fragment are discriminated from H+, and thus the H+ ion,$ \rm C_3H_2^+ $ ion, and H atom are identified. In addition, it is found that the sequential fragmentation pathway in which H+ ion and$\rm C_3H_3^+$ ion are produced in the first step followed by dissociation of$ \rm C_3H_3^+ $ into$ \rm C_3H_2^+ $ ion and H atom in the second step is the dominant dissociation mechanism according to the detailed analyses of the Dalitz plot, Newton diagram and α distribution.-
Keywords:
- highly charged ions /
- isomers /
- fragmentation mechanism /
- sequential dissociation
[1] Janev R K 1995 Atomic and Molecular Processes in Fusion Edge Plasmas (Boston: Springer) p3
[2] Sada P V, Bjoraker G L, Jennings D E, McCabe G H, Romani P N 1998 Icarus 136 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xu S Y, Zhu X L, Feng W T, Guo D L, Zhao Q S, Yan S C, Zhang P J, Zhao D M, Gao Y, Zhang S F, Yang J, Ma X 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 062701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Neumann N, Hant D, Schmidt L Ph H, Titze J, Jahnke T, Czasch A, Schöffler M S, Kreidi K, Jagutzki O, Schmidt-Böcking H, Döner R 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 103201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hsieh S, Eland J H D 1997 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 30 4515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wu C, Wu C Y, Song D, Su H M, Yang Y D, Wu Z F, Liu X R, Liu H, Li M, Deng Y K, Liu Y Q, Peng L Y, Jiang H B, Gong Q H 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 103601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yan S C, Zhu X L, Zhang P J, Ma X, Feng W T, Gao Y, Xu S Y, Zhao Q S, Zhang S F, Guo D L, Zhao D M, Zhang R T, Huang Z K, Wang H B, Zhang X J 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 032708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang H, Wang E L, Dong W X, Gong M M, Shen Z J, Tang Y G, Shan X, Chen X J 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 052703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu J, Kunitski M, Schmidt L Ph H, Jahnke T, Dörner R 2012 J. Chem. Phys. 137 104308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gong X C, Kunitski M, Ph H Schmidt L, Jahnke T, Czasch A, Dörner R, Wu J 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 013422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ding X Y, Haertelt M, Schlauderer S, Schuurman M, Naumov A, Villeneuve D, McKellar A, Corkum P, Staudte A 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 153001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tielens A 2013 Rev. Mod. Phys. 85 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang Y, Jiang T, Wei L, Luo D, Wang X, Yu W, Hutton R, Zou Y, Wei B 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 022703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang E L, Shan X, Shen Z J, Gong M M, Tang Y G, Pan Y, Lau K C, Chen X J 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 052711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X C, Zhang Y, Lu D, Lu G C, Wei B R, Zhang B H, Tang Y J, Hutton R, Zou Y M 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 062705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kusakabe T, Satoh S, Tawara H, Kimura M 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Scully S, Senthil V, Wyer J, Shah M, Montenegro E, Kimura M, Tawara H 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Mebel A M, Bandrauk A D 2008 J. Chem. Phys. 129 224311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Psciuk B T, Tao P, Schlegel H B 2010 J. Phys. Chem. A 114 7653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xu H L, Okino T, Yamanouchi K 2009 J. Chem. Phys. Chem. Phys. Lett. 469 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xu H L, Okino T, Yamanouchi K 2009 J. Chem. Phys. 131 1659 151102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xu H L, Okino T, Yamanouchi K 2011 Appl. Phys. A 104 941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Okino T, Watanabe A, Xu H L, Yamanouchi K 2012 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14 4230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Okino T, Watanabe A, Xu H L, Yamanouchi K 2012 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14 10640
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ma C, Xu S Y, Zhao D M, Guo D L, Yan S C, Feng W T, Zhu X L, Ma X W 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 052701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ma X W, Zhang R T, Zhang S F, Zhu X L, Feng W T, Guo D L, Li B, Liu H P, Li C Y, Wang J G, Yan S C, Zhang P J, Wang Q 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 052707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yuan H, Xu S Y, Li T T, Liu Y, Qian D B, Guo D L, Zhu X L, Ma X W 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 062808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y T, Xu S Y, Guo D L, Jia S K, Jiang X J, Zhu X L, Ma X W 2019 J. Chem. Phys. 150 144311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a) CH2CCH2和(b) CH3CCH 二维飞行时间谱[8], 其中红色椭圆对应H+ +
${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_2^ + $ 的事件; (c) CH2CCH2和 (d) CH3CCH分子的KER-H+能量的二维符合谱; (e) CH2CCH2和 (f) CH3CCH三体碎裂${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_4^{2 + }$ → H+ +${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_2^ + $ + H通道的KER分布; (g) CH2CCH2和(h) CH3CCH对应的H+和未探测粒子动能(H+/H0)的二维符合谱Figure 1. Two-dimensional time-of-flight (TOF) spectra, in which the events of red oval corresponds to the H+ +
${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_2^ + $ for (a) CH2CCH2 and (b) CH3CCH; two-dimensional coincidence correlation spectra of KER-H+ energy of (c) CH2CCH2 and (d) CH3CCH; the KER distribution of (e) CH2CCH2 and (f) CH3CCH for three-body fragmentation of${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_4^{2 + }$ → H+ +${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_2^ + $ + H channel; two-dimensional coincidence spectra of kinetic energies between H+ and undetected particle (H+/H0) of (g) CH2CCH2 and (h) CH3CCH.图 3 CH2CCH2 (a)—(f) 和 CH3CCH (g)—(l)三体解离
${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_4^{2 + }$ → H+ +${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_2^ + $ + H过程的Newton图 (a)和(g) 包含所有事件, 其他为以第3个粒子H的能量为选择条件的Newton图, 相应能量分别为0—0.5 eV (b), (h); 0.5—1.0 eV (c), (i); 1.0—2.0 eV (d), (j); 2.0—4.0 eV (e), (k); 4.0—6.0 eV (f), (l)Figure 3. Newton diagrams of CH2CCH2 (a)−(f) and CH3CCH (g)−(l) for three-body fragmentation channel
${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_4^{2 + }$ →H+ +${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_2^ + $ + H. (a) and (g) are Newton diagrams for all the events. The others are for different energy ranges of the neutral H: 0−0.5 eV for (b), (h), 0.5−1.0 eV for (c), (i); 1.0−2.0 eV for (d), (j); 2.0−4.0 eV for (e), (k); 4.0−6.0 eV for (f), (l).图 4 (a) CH2CCH2 和 (b) CH3CCH 分子次序解离路径
${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_4^{2 + }$ →H++${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_3^ + $ →H++${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_2^ + $ +H中两步解离过程之间夹角α分布; (c), (d) 不同H 碎片能量条件(0—0.5 eV, 0.5—1.0 eV, 1.0—2.0 eV, 2.0—4.0 eV, 4.0—6.0 eV) 下α分布. 图中蓝色曲线为标准的正弦分布曲线, 所有曲线都在最大值处作归一化处理Figure 4. Intensity distribution of the angle α between the first dissociation and second step for sequential dissociation
${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_4^{2 + }$ →H++${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_3^ + $ →H++${{\text{C}}_3}{\text{H}}_2^ + $ +H of (a) CH2CCH2 and (b) CH3CCH; (c), (d) the intensity distributions of the angle α for different energy region of H (0−0.5 eV, 0.5−1.0 eV, 1.0−2.0 eV, 2.0−4.0 eV, 4.0−6.0 eV). The blue lines are the standard sinusoidal distribution curves. All curves are normalized at the maximum value. -
[1] Janev R K 1995 Atomic and Molecular Processes in Fusion Edge Plasmas (Boston: Springer) p3
[2] Sada P V, Bjoraker G L, Jennings D E, McCabe G H, Romani P N 1998 Icarus 136 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Xu S Y, Zhu X L, Feng W T, Guo D L, Zhao Q S, Yan S C, Zhang P J, Zhao D M, Gao Y, Zhang S F, Yang J, Ma X 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 062701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Neumann N, Hant D, Schmidt L Ph H, Titze J, Jahnke T, Czasch A, Schöffler M S, Kreidi K, Jagutzki O, Schmidt-Böcking H, Döner R 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 103201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hsieh S, Eland J H D 1997 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 30 4515
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wu C, Wu C Y, Song D, Su H M, Yang Y D, Wu Z F, Liu X R, Liu H, Li M, Deng Y K, Liu Y Q, Peng L Y, Jiang H B, Gong Q H 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 103601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yan S C, Zhu X L, Zhang P J, Ma X, Feng W T, Gao Y, Xu S Y, Zhao Q S, Zhang S F, Guo D L, Zhao D M, Zhang R T, Huang Z K, Wang H B, Zhang X J 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 032708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yang H, Wang E L, Dong W X, Gong M M, Shen Z J, Tang Y G, Shan X, Chen X J 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 052703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Wu J, Kunitski M, Schmidt L Ph H, Jahnke T, Dörner R 2012 J. Chem. Phys. 137 104308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gong X C, Kunitski M, Ph H Schmidt L, Jahnke T, Czasch A, Dörner R, Wu J 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 013422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ding X Y, Haertelt M, Schlauderer S, Schuurman M, Naumov A, Villeneuve D, McKellar A, Corkum P, Staudte A 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 153001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tielens A 2013 Rev. Mod. Phys. 85 1021
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang Y, Jiang T, Wei L, Luo D, Wang X, Yu W, Hutton R, Zou Y, Wei B 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 022703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang E L, Shan X, Shen Z J, Gong M M, Tang Y G, Pan Y, Lau K C, Chen X J 2015 Phys. Rev. A 91 052711
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X C, Zhang Y, Lu D, Lu G C, Wei B R, Zhang B H, Tang Y J, Hutton R, Zou Y M 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 062705
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kusakabe T, Satoh S, Tawara H, Kimura M 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 328
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Scully S, Senthil V, Wyer J, Shah M, Montenegro E, Kimura M, Tawara H 2005 Phys. Rev. A 72 030701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Mebel A M, Bandrauk A D 2008 J. Chem. Phys. 129 224311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Psciuk B T, Tao P, Schlegel H B 2010 J. Phys. Chem. A 114 7653
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xu H L, Okino T, Yamanouchi K 2009 J. Chem. Phys. Chem. Phys. Lett. 469 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xu H L, Okino T, Yamanouchi K 2009 J. Chem. Phys. 131 1659 151102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xu H L, Okino T, Yamanouchi K 2011 Appl. Phys. A 104 941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Okino T, Watanabe A, Xu H L, Yamanouchi K 2012 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14 4230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Okino T, Watanabe A, Xu H L, Yamanouchi K 2012 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14 10640
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Ma C, Xu S Y, Zhao D M, Guo D L, Yan S C, Feng W T, Zhu X L, Ma X W 2020 Phys. Rev. A 101 052701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Ma X W, Zhang R T, Zhang S F, Zhu X L, Feng W T, Guo D L, Li B, Liu H P, Li C Y, Wang J G, Yan S C, Zhang P J, Wang Q 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 052707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Yuan H, Xu S Y, Li T T, Liu Y, Qian D B, Guo D L, Zhu X L, Ma X W 2020 Phys. Rev. A 102 062808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y T, Xu S Y, Guo D L, Jia S K, Jiang X J, Zhu X L, Ma X W 2019 J. Chem. Phys. 150 144311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4693
- PDF Downloads: 129
- Cited By: 0


























 DownLoad:
DownLoad: