-
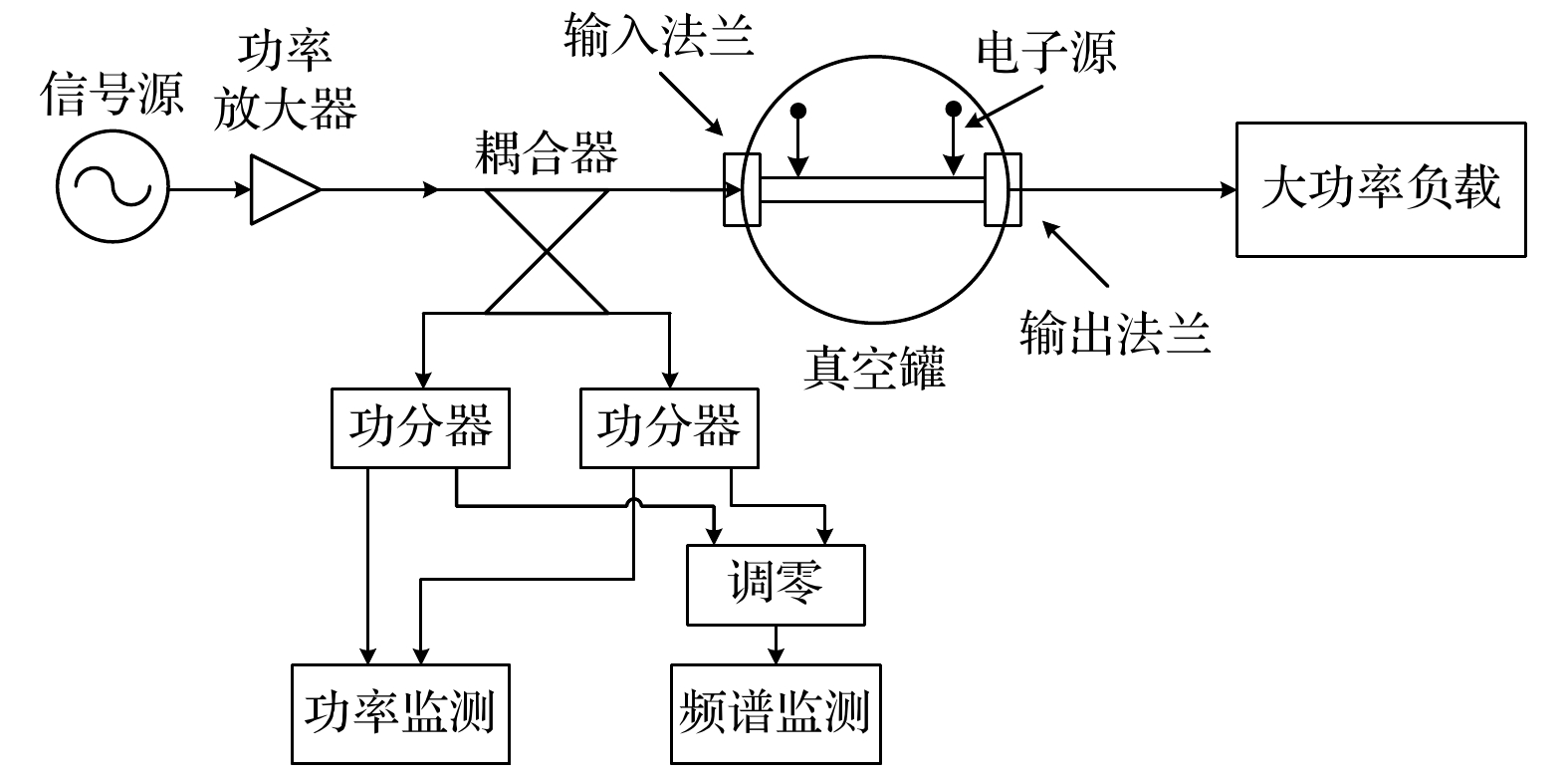
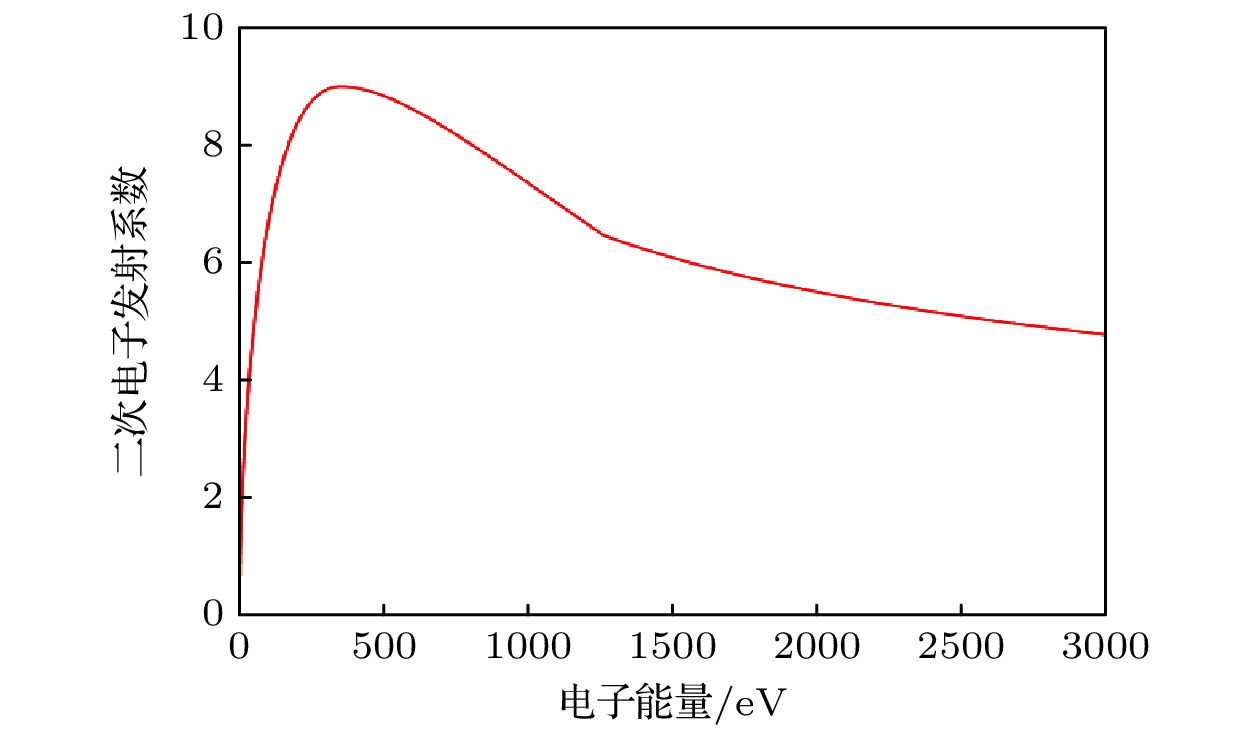
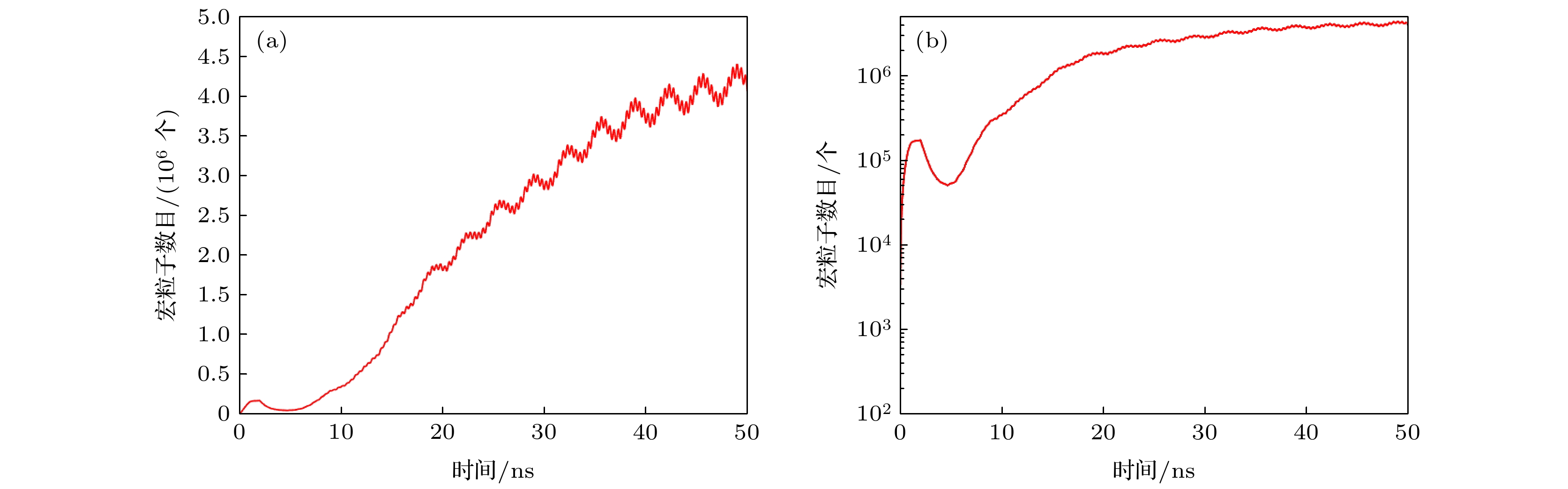
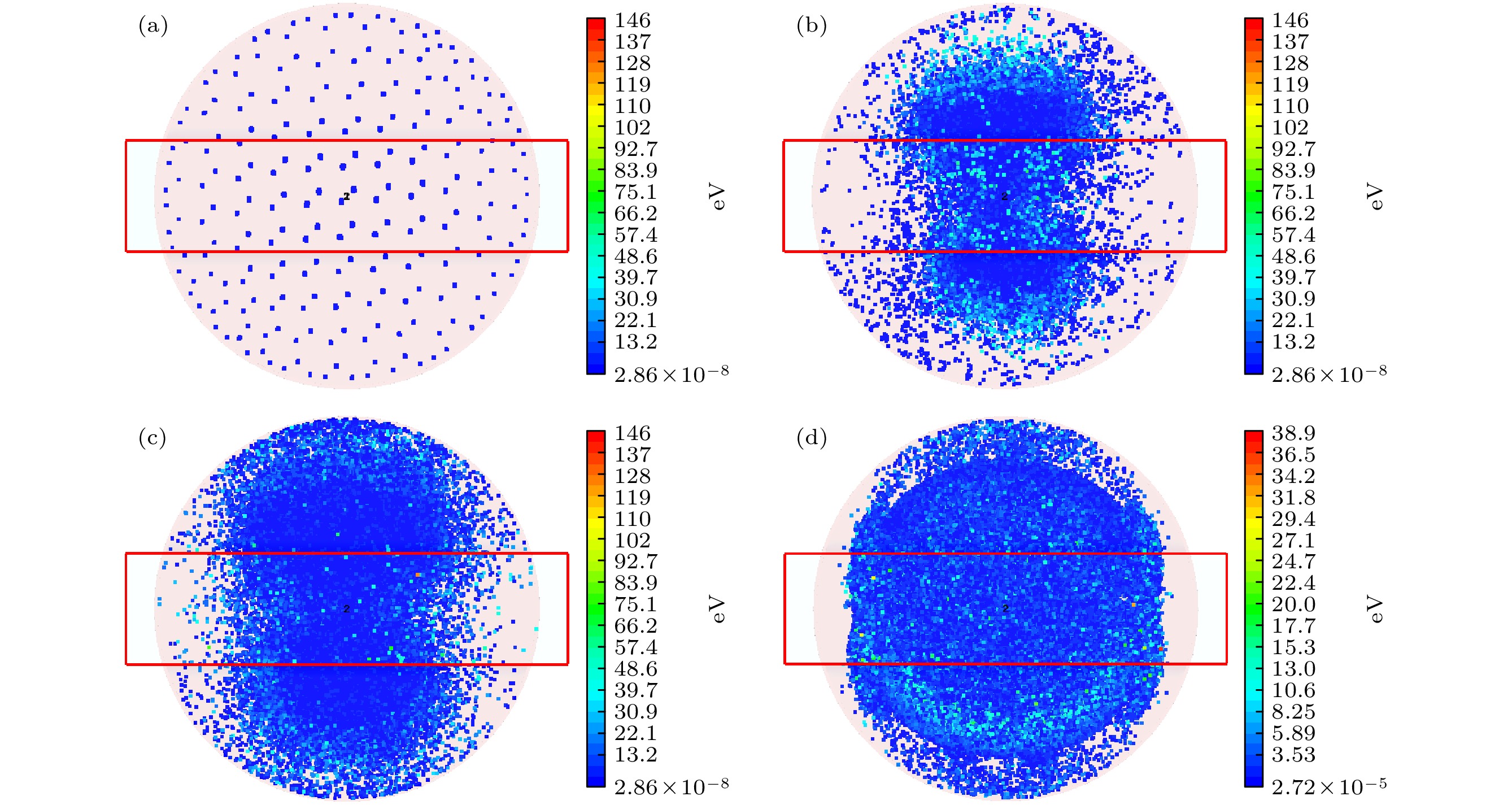
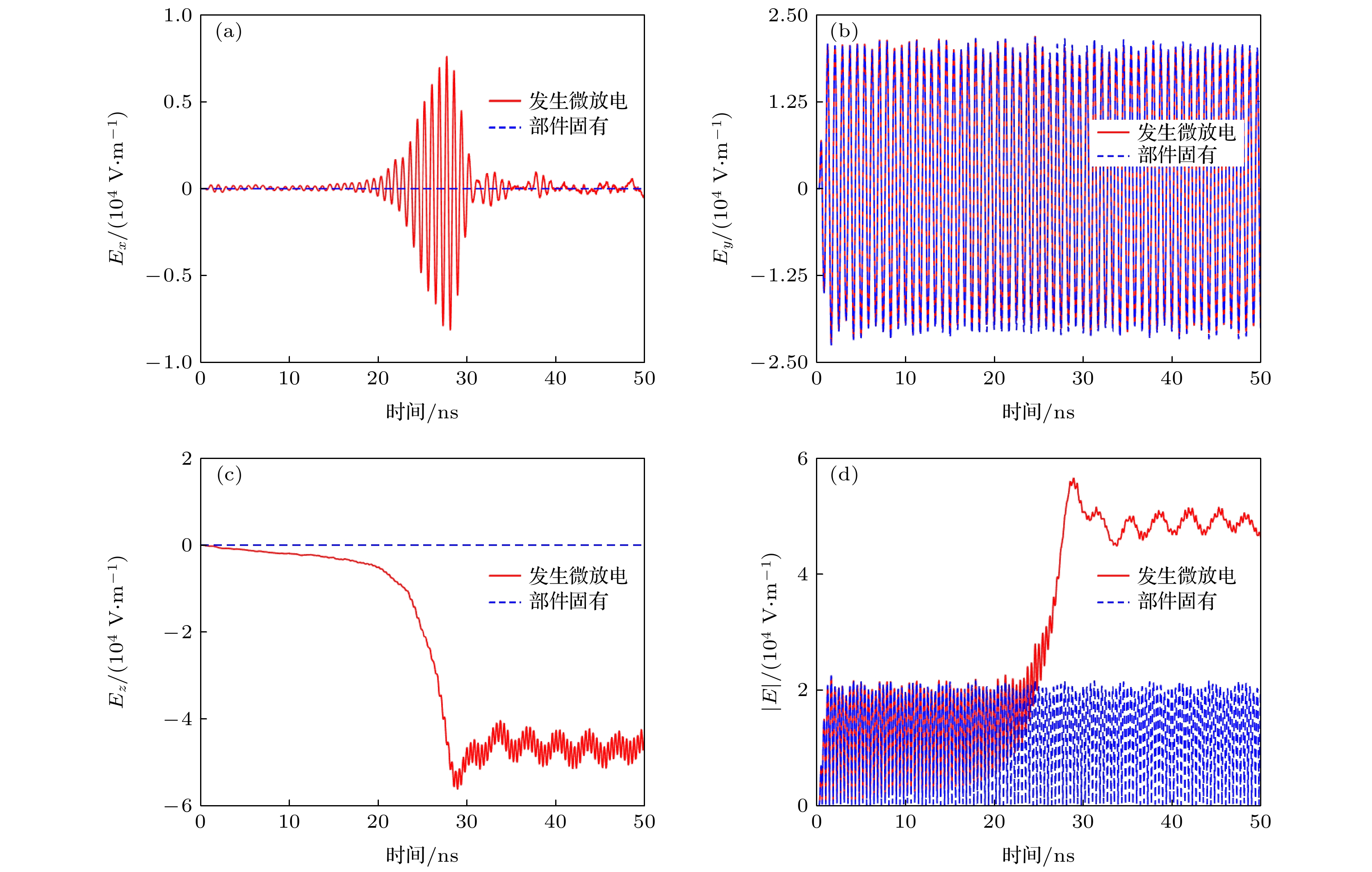
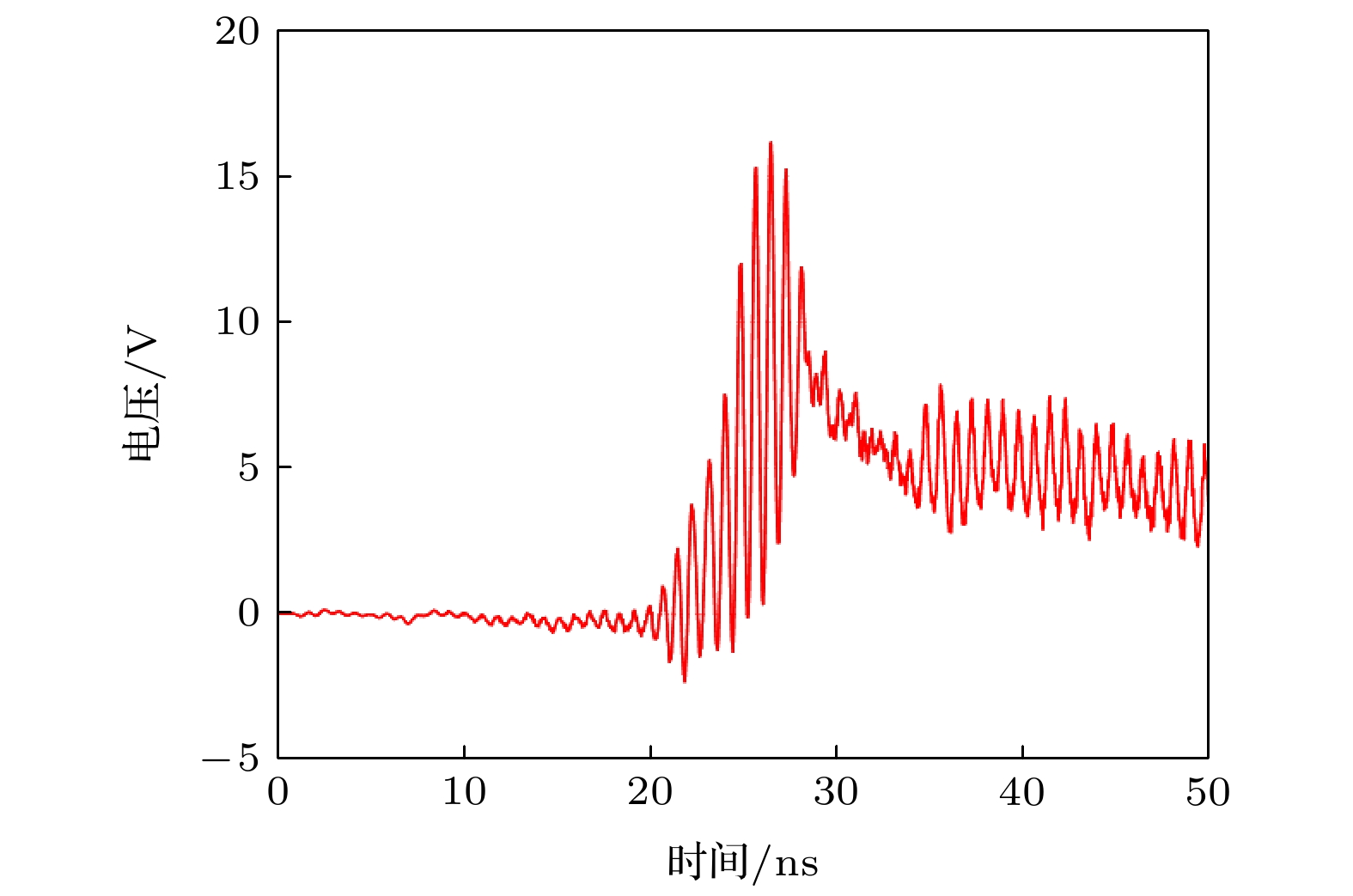
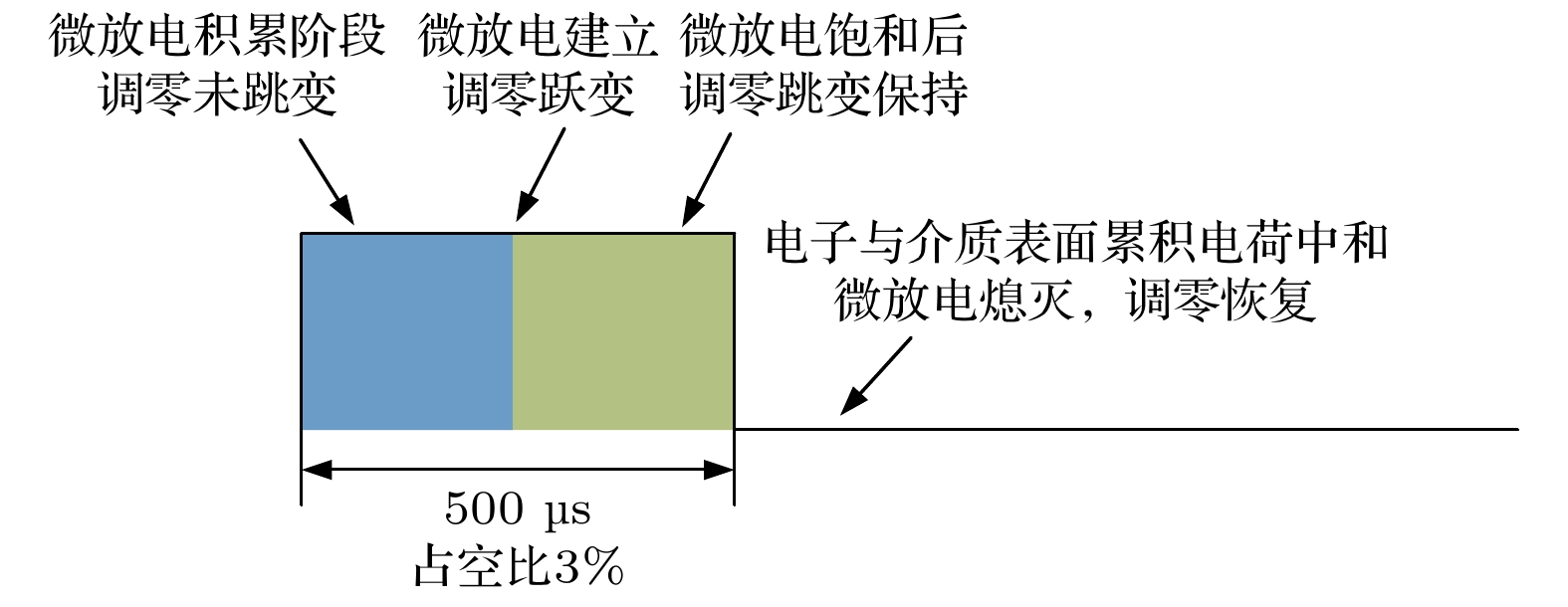
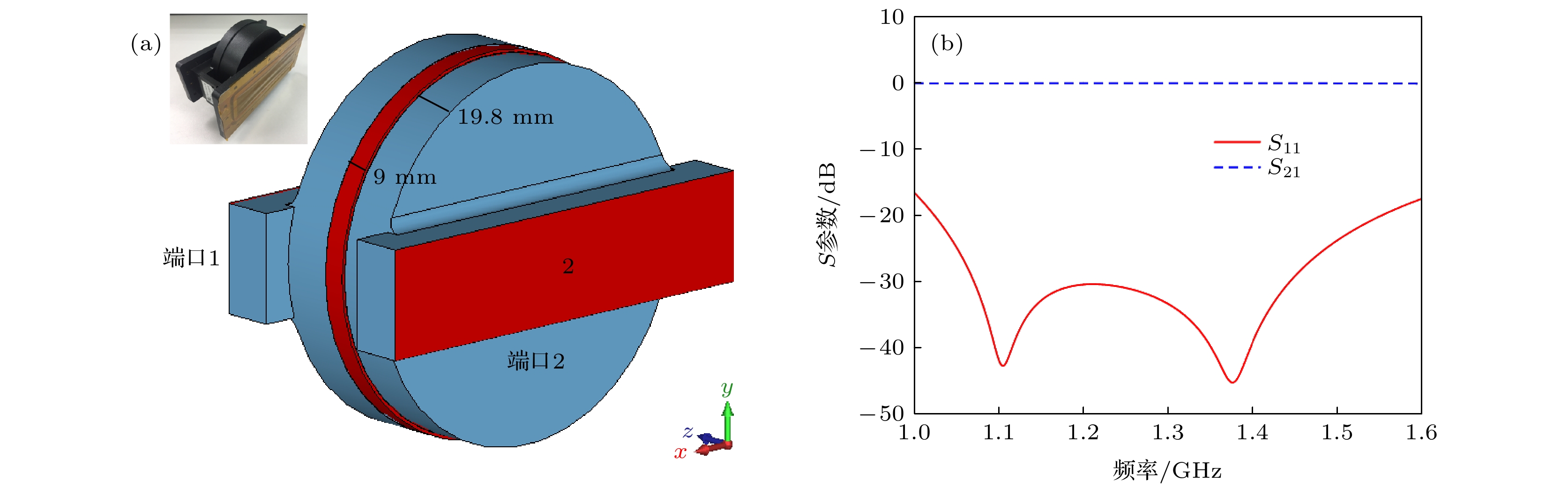
The potential, unexpected occurrence of dielectric multipactor on the dielectric surfaces in high-power radio frequency and microwave components has become a severe constraint in the research and development of space-borne payloads of space vehicles such as satellites and space stations on the ground and their long-term reliable operations in the orbit. In this experimental research, the single-surface multipactor occurring on the dielectric surface of a penetration flange originally designed for a vacuum chamber used in environmental simulation tests of spacecraft is experimentally investigated and compared with the corresponding full-wave simulated results. Under the excitation of periodic pulsed sinusoidal signals, the unusual experimental phenomena of intermittent local jumps of nulling signals in the process of multipactor are repeatedly observed based on an agile nulling experimental system. Taking advantage of the full-wave, three-dimensional (3D) particle-in-cell simulation tool, CST Particle Studio, the entire evolution process of the dielectric multipactor, from its onset to its saturation, is simulated and carefully examined. Combining the results obtained by full-wave 3D particle simulations, some physical explanations and discussion on such phenomena are presented. It is found that under the configuration parameters of pulse signals adopted in this multipactor experiment, the transition of a single-surface dielectric multipactor from its onset to the saturation state can be finished within a single pulse. However, its transition from the saturation state to turning off can last between consecutive pulses in the absence of any high-power radio frequency signals. The obtained result is important for both the theoretical study and the engineering development of high-power dielectric components, providing a new understanding of the dielectric multipactor occurring under the excitation of pulsed high-power electric fields.
-
Keywords:
- penetration flange /
- dielectric multipactor /
- experimental study /
- particle-in-cell
[1] Woode A, Petit J 1990 ESA J. 14 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rozario N, Lenzing H F, Reardon K F, Zarro M S, Baran C G 1994 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 42 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yu M 2007 IEEE Microwave Mag. 8 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kishek R A, Lau Y Y, Ang L K, Valfells A, Gilgenbach, R M 1998 Phys. Plasmas 5 2120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kishek R A, Lau Y Y 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chang C, Liu G, Tang C, Chen C, Fang J 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 055702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Hatch A J 1966 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 41 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Power J G, Gai W, Gold S H, et al. 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 164801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Neuber A, Hemmert D, Krompholz H, et al. 1999 J. Appl. Phys. 86 1724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chang C, Zhu M, Verboncoeur J, et al. 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 253504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Iqbal A, Wong P Y, Wen D Q, et al. 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 043201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Neuber A, Butch M, Krompholz H, et al. 2000 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 28 1593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Anderson R B, Getty W D, Brake M L, et al. 2001 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 72 3095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ang L K, Lau Y Y, Kishek R A, Gilgenbach R M 1998 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 26 290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kim H C, Verboncoeur J P 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 123504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sazontov A, Semenov V, Buyanova M, et al. 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 093501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Shen F Z, Wang X B, Cui W Z, Ran L X 2020 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 48 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang Z Y, Sun Y Z, Cui W Z, et al. 2019 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 66 4921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 董烨, 董志伟, 杨温渊, 周前红, 周海京 2013 62 197901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Dong Z W, Yang W Y, Zhou Q H, Zhou H J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 197901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张雪, 王勇, 范俊杰, 张瑞 2014 63 227901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Wang Y, Fan J J, Zhang R 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 227901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Langellotti S V, Jordan N M, Lau Y Y, et al. 2020 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 48 1942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hemmert D, Neuber A, Dickens J, et al. 2000 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 28 472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Vaughan J R M 1988 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 35 1172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang X B, Shen J H, Wang J Y, et al. 2017 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 65 2734
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Woode A, Petit J 1990 ESA J. 14 467
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rozario N, Lenzing H F, Reardon K F, Zarro M S, Baran C G 1994 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 42 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yu M 2007 IEEE Microwave Mag. 8 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Kishek R A, Lau Y Y, Ang L K, Valfells A, Gilgenbach, R M 1998 Phys. Plasmas 5 2120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Kishek R A, Lau Y Y 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chang C, Liu G, Tang C, Chen C, Fang J 2011 Phys. Plasmas 18 055702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Hatch A J 1966 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 41 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Power J G, Gai W, Gold S H, et al. 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 164801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Neuber A, Hemmert D, Krompholz H, et al. 1999 J. Appl. Phys. 86 1724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chang C, Zhu M, Verboncoeur J, et al. 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 253504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Iqbal A, Wong P Y, Wen D Q, et al. 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 043201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Neuber A, Butch M, Krompholz H, et al. 2000 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 28 1593
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Anderson R B, Getty W D, Brake M L, et al. 2001 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 72 3095
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ang L K, Lau Y Y, Kishek R A, Gilgenbach R M 1998 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 26 290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Kim H C, Verboncoeur J P 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 123504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sazontov A, Semenov V, Buyanova M, et al. 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 093501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Shen F Z, Wang X B, Cui W Z, Ran L X 2020 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 48 433
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhang Z Y, Sun Y Z, Cui W Z, et al. 2019 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 66 4921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 董烨, 董志伟, 杨温渊, 周前红, 周海京 2013 62 197901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Y, Dong Z W, Yang W Y, Zhou Q H, Zhou H J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 197901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张雪, 王勇, 范俊杰, 张瑞 2014 63 227901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Wang Y, Fan J J, Zhang R 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 227901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Langellotti S V, Jordan N M, Lau Y Y, et al. 2020 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 48 1942
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Hemmert D, Neuber A, Dickens J, et al. 2000 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 28 472
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Vaughan J R M 1988 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 35 1172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang X B, Shen J H, Wang J Y, et al. 2017 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 65 2734
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6570
- PDF Downloads: 63
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: