-
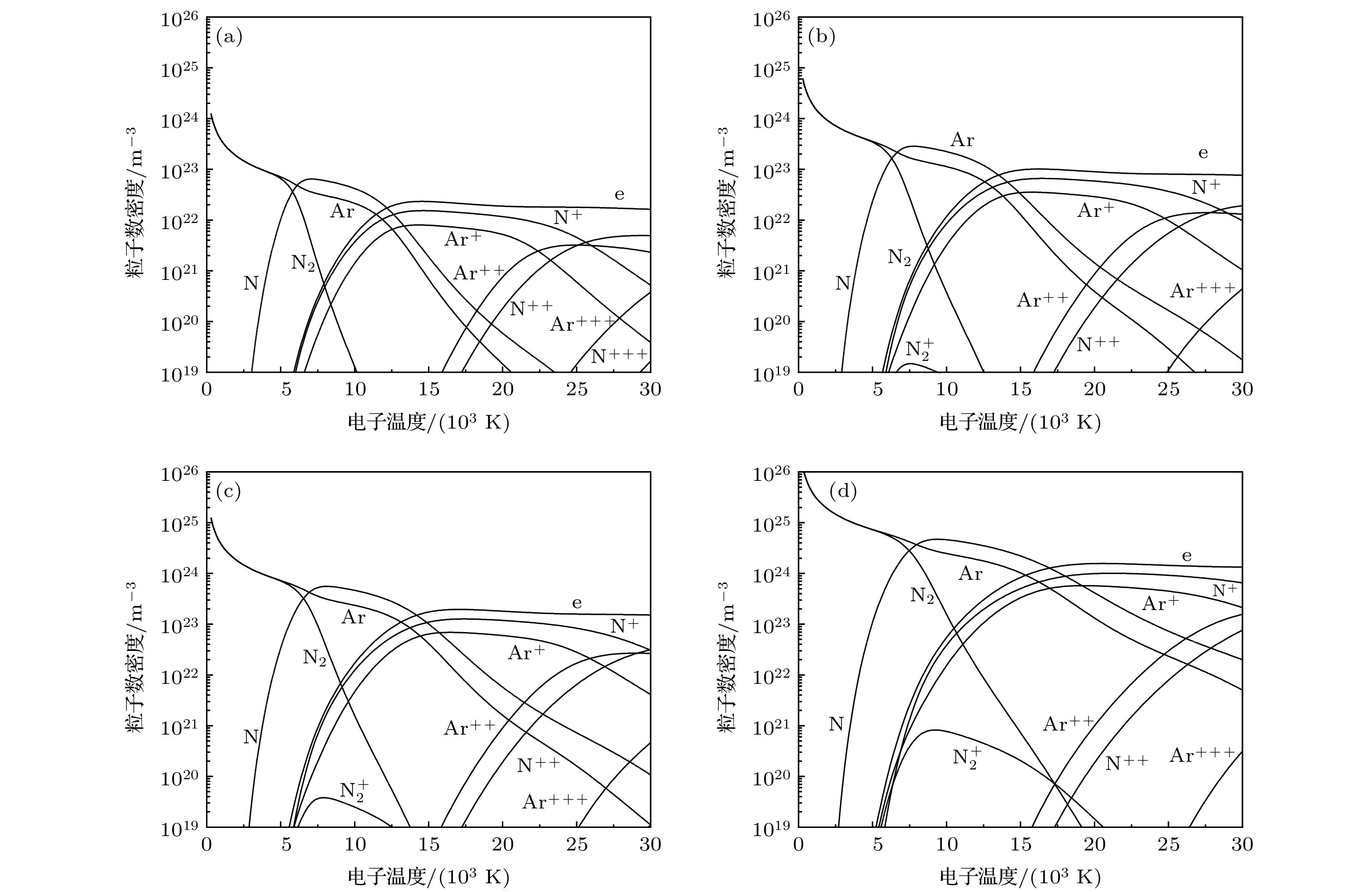
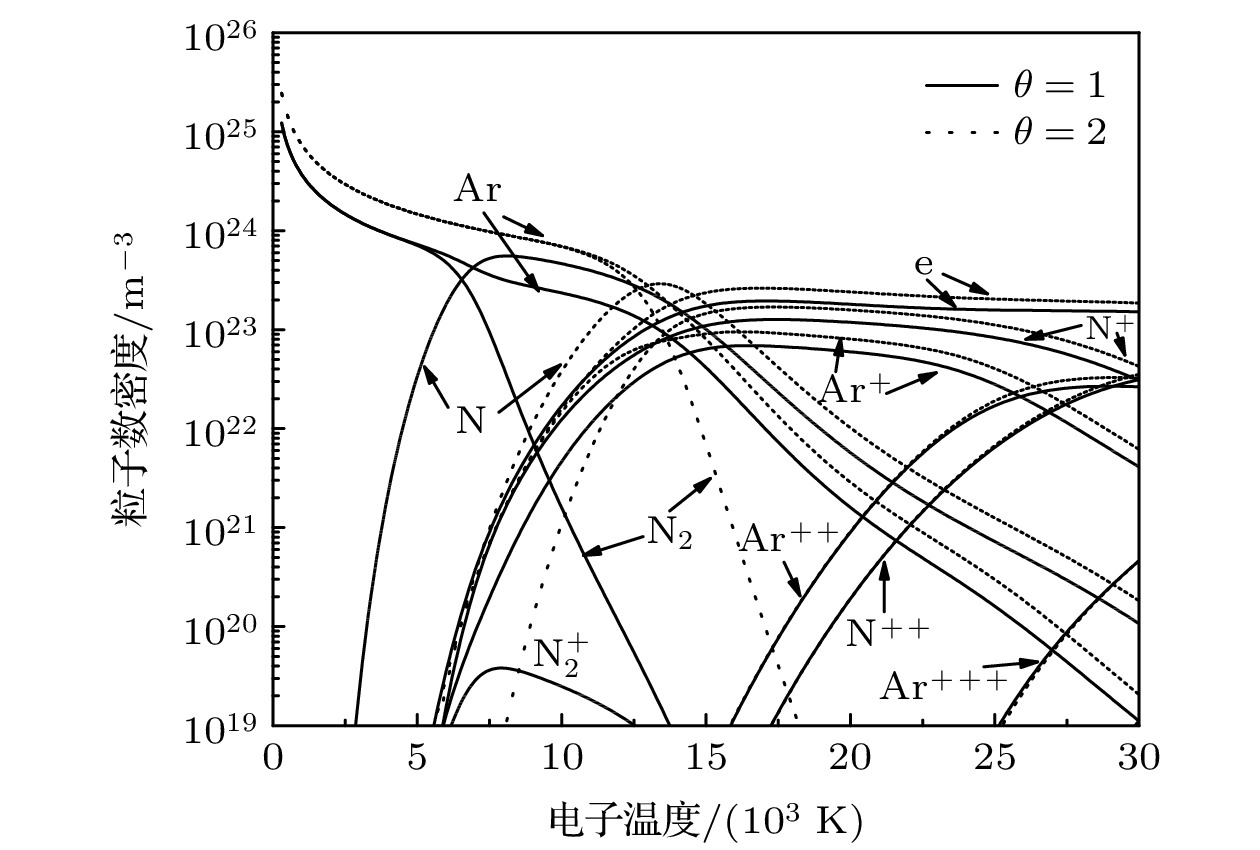
The thermodynamic and transport properties of plasmas over a wide range of temperature and pressure are necessary to model the heat transfer and flow processes in plasma. In this study, the plasma composition is solved by simultaneous Saha equation, Dalton's partial pressure law and charge quasi-neutral equation. The thermodynamic properties of plasma computation are based on the kinetic theory for ideal gas. While the calculation of transport properties is based on the solution of Boltzmann’s equation by the Chapman-Enskog method. The thermodynamic and transport properties of argon-nitrogen plasma at pressures of 0.1, 1.0 and 10.0 atm, electron temperatures ranging from 300 to 30000 K, and non-local thermodynamic equilibrium (NLTE), where the electron temperature is not equal to the temperature of heavy particles,, are investigated by using the above method. The results show that the value of non-equilibrium parameter has a great influence on the properties of the argon-nitrogen mixture. With the increase of non-equilibrium parameter, the dissociation reaction requires a higher electron temperature, which leads the dissociation peak to shift to a higher electron temperature. The ionization and dissociation reaction will enter into the high temperature region due to the increase in pressure. This change will affect the peak position and value of the specific heat, viscosity, thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity of plasma. In addition, since the electronic translational thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity mainly depend on the electron number density, when non-equilibrium parameter and pressure increase, the electron number density will increase at high electron temperature, thus improving the electronic translational thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. Under the condition of local thermodynamic equilibrium, the transport properties of argon-nitrogen plasma obtained by calculation are in good agreement with previously reported data.
-
Keywords:
- argon-nitrogen plasma /
- thermodynamic and transport property /
- non-local thermodynamic equilibrium plasma
[1] Fan X B, Ishigaki T 1998 Thin Solid Films. 316 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Abrar M, Farwa G U, Naseer S, Saeed A, Khan A W, Iqbal Z, Hussain S T, Zakaullah M 2013 Curr. Appl. Phys. 13 567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Selvan B, Ramachandran K, Pillai B C, Subhakar D 2011 J. Therm. Spray Technol. 20 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Dias A, Bundaleski N, Tatarova E, Dias F M, Abrashev M, Cvelbar U, Teodoro O M N D, Henriques J 2016 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49 055307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yamada M, Inamoto T, Fukumoto M, Yasui T 2004 Mater. Trans. 45 3304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hirschfelder J, Curtiss C F, Bird R 1954 Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids (New York: John Wiley and Sons) p464
[7] Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Hacala A, Michon U 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 095206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Murphy A B 2000 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 20 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Murphy A B, Arundelli C J 1994 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 14 451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Murphy A B, Tam E 2014 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 47 295202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sourd B, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Labrot M, Michon U 2006 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39 1105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Devoto R S 1967 Phys. Fluids. 10 2105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Lefort A 2001 Phys. Rev E. 64 026409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu Y, Chen Z X, Yang F, Cressault Y, Murphy A B, Guo A, Liu Z R, Rong M Z, Sun H 2015 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 48 415205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P 1998 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 18 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Colombo V, Ghedini E, Sanibondi P 2008 Prog. Nucl. Energy. 50 921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ghorui S, Heberlein J V R, Pfender E 2008 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 28 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ghorui S, Heberlein J V R, Pfender E 2007 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 27 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王海兴, 孙素蓉, 陈士强 2012 61 195203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H X, Sun S R, Chen S Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 195203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang H X, Chen S Q, Chen X 2012 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 45 165202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Aubreton A, Elchinger M F 2003 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36 1798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Rat V, Fauchais P 2003 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37 34
[23] Colombo V, Ghedini E, Sanibondi P 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 055213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Lefort A 2002 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 22 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Lefort A 2002 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 22 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Vacher D 2002 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 35 981
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Godin D, Trépanier J Y 2004 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 24 447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] van de Sanden M C M, Schram P P J M, Peeters A G, van der Mullen J A M, Kroesen G M W 1989 Phys. Rev. A 40 5273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kramida A, Ralchenko Y, Reader J, NIST ASD Team https://www.nist.gov/pml/atomic-spectra-database [2020-12-1]
[30] Chase M W, Davies C A, Downey J R, Frurip D J, McDonald R A, Syverud A N https://janaf.nist.gov/ [2020-12-1]
[31] Aziz R A, Slaman M J 1990 J. Chem. Phys. 92 1030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Capitelli M, Devoto R S 1973 Phys. Fluids. 16 1835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Levin E, Partridge H, Stallcop J R 1990 J. Thermophys Heat Transfer 4 469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Brunetti B, Liuti G, Luzzatti E, Pirani F, Volpi G G 1983 J. Chem. Phys. 79 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Murphy A B 1995 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process 15 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Phelps A V 1991 J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data. 20 557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Stallcop J R, Partridge H, Levin E 1991 J. Chem. Phys. 95 6429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Murphy A B 1993 Phys. Rev. E 48 3594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Engelhardt A G, Phelps A V, Risk C G 1964 Phys. Rev. 135 1566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Neynaber R H, Marino L L, Rothe E W, Trujillo S M 1963 Phys. Rev. 129 2069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Mason E A, Munn R J, Smith F J 1967 Phys. Fluids. 10 1827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Devoto R S 1966 Phys. Fluids. 9 1230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Chen X, Li H P 2003 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 46 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Wang W Z, Rong M Z, Yan J D, Murphy A B, Spencer J W 2011 Phys. Plasmas. 18 113502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 4 不同非平衡参数下50%
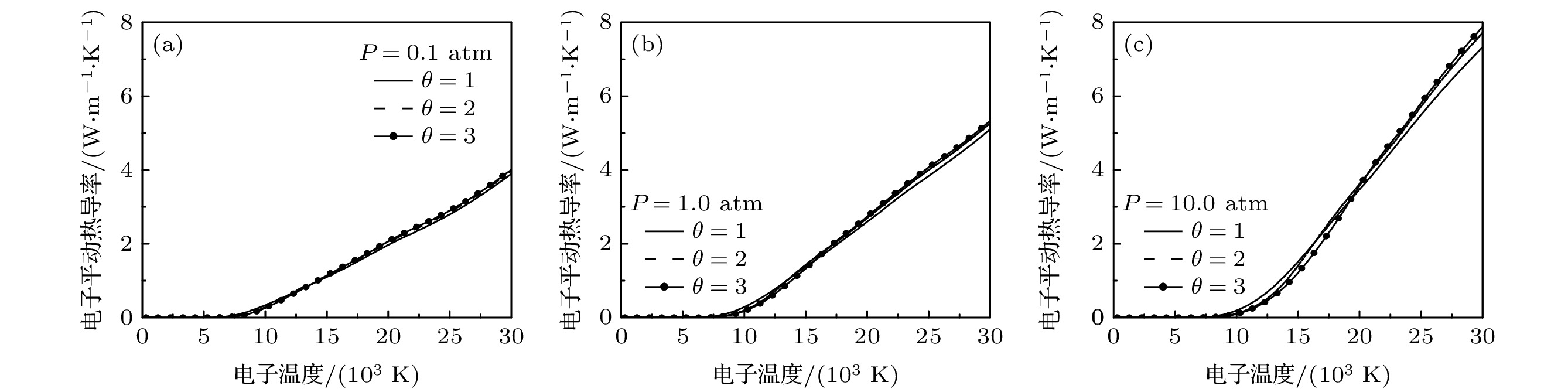
$ {\rm{Ar}} $ 和50%$ {\rm{N}}_{2} $ 混合物反应热导率随电子温度的变化 (a)电子反应热导率; (b) 重粒子反应热导率; (c) 总反应热导率(1 atm)Figure 4. Electron temperature dependence of reactive thermal conductivity of 50% argon-50% nitrogen mixtures for different values of non-equilibrium parameter: (a) Reactive thermal conductivity of electrons; (b) reactive thermal conductivity of heavy particles; (c) total reactive thermal conductivity(1 atm).
图 5 不同压力和非平衡度下50%
$ {\rm{Ar}} $ 和50%$ {\rm{N}}_{2} $ 混合物热导率随电子温度的变化, 符号$ \times $ 代表Murphy和Arundelli[9]计算结果Figure 5. Electron temperature dependence of total thermal conductivity of 50% argon-50% nitrogen mixtures for different values of non-equilibrium parameter and pressure, the symbol
$ \times $ shows results of Murphy and Arundelli[9].图 7 不同压力和非平衡度下50%
$ {\rm{Ar}} $ 和50%$ {\rm{N}}_{2} $ 混合物热导率随电子温度的变化, 符号$ \times $ 代表Murphy和Arundelli[9]计算结果Figure 7. Electron temperature dependence of viscosity of 50% argon-50% nitrogen mixtures for different values of non-equilibrium parameter and pressure, the symbol
$ \times $ shows results of Murphy and Arundelli[9].图 8 不同压力和非平衡度下50%
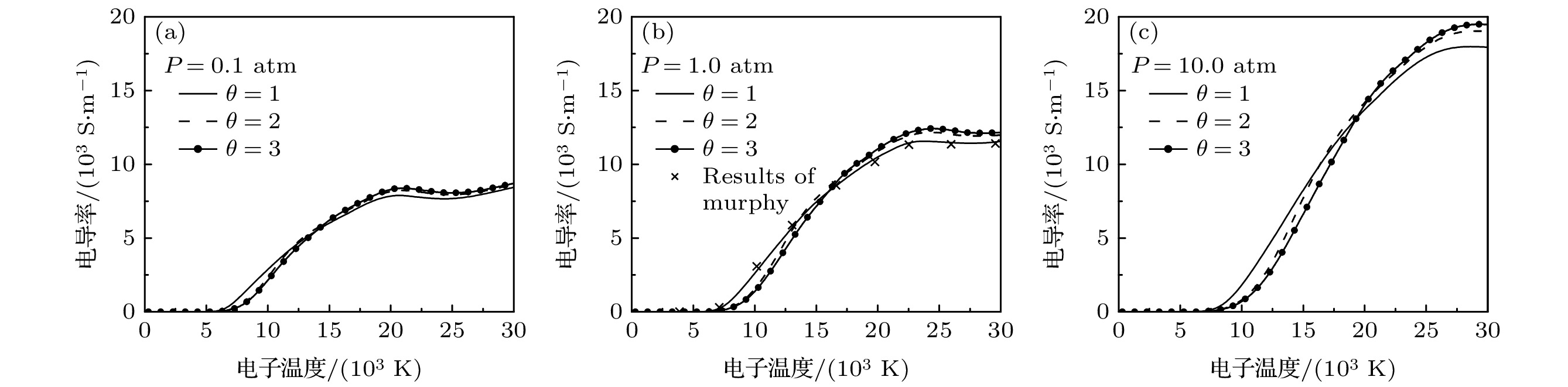
$ {\rm{Ar}} $ 和50%$ {\rm{N}}_{2} $ 混合物电导率随电子温度的变化, 符号$ \times $ 代表Murphy和Arundelli[9]计算结果Figure 8. Electron temperature dependence of electrical conductivity of 50% argon-50% nitrogen mixtures for different values of non-equilibrium parameter and pressure, the symbol
$ \times $ shows results of Murphy and Arundelli[9].表 1 中性粒子之间相互作用
Table 1. Data source of neutral-neutral interaction
表 2 中性粒子与离子相互作用
Table 2. Data source of neutral-ion interaction.
相互作用 弹性碰撞 文献 非弹性碰撞 文献 Ar+-Ar 2∑1/2u Morse势 [35] ∑ 电荷转移 [35] 2∑1/2g Exponential势 [35] Π 电荷转移 [35] 2Π3/2g Morse势 [35] 2Π3/2u Exponential势 [35] 2Π1/2g Morse势 [35] 2Π1/2u Exponential势 [35] ${\rm{N}}_2^+ $-N2 极化势 积分输运截面 [36] ${\rm{N}}_2^+ $-N 极化势 N+-N2 极化势 积分输运截面 [36] N+-N2 碰撞积分表 [37] 碰撞积分表 [37] Ar+-N2 极化势 Ar+-N 极化势 ${\rm{N}}_2^+ $-Ar 极化势 N+-Ar 3∑– Morse势 [38] 3Π Morse势 [38] Xn+-X, Y
(n ≥ 2)极化势 表 3 电子与中性粒子相互作用
Table 3. Data source of electron-neutral interaction
-
[1] Fan X B, Ishigaki T 1998 Thin Solid Films. 316 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Abrar M, Farwa G U, Naseer S, Saeed A, Khan A W, Iqbal Z, Hussain S T, Zakaullah M 2013 Curr. Appl. Phys. 13 567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Selvan B, Ramachandran K, Pillai B C, Subhakar D 2011 J. Therm. Spray Technol. 20 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Dias A, Bundaleski N, Tatarova E, Dias F M, Abrashev M, Cvelbar U, Teodoro O M N D, Henriques J 2016 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 49 055307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yamada M, Inamoto T, Fukumoto M, Yasui T 2004 Mater. Trans. 45 3304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Hirschfelder J, Curtiss C F, Bird R 1954 Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids (New York: John Wiley and Sons) p464
[7] Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Hacala A, Michon U 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 095206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Murphy A B 2000 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 20 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Murphy A B, Arundelli C J 1994 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 14 451
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Murphy A B, Tam E 2014 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 47 295202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Sourd B, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Labrot M, Michon U 2006 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39 1105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Devoto R S 1967 Phys. Fluids. 10 2105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Lefort A 2001 Phys. Rev E. 64 026409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wu Y, Chen Z X, Yang F, Cressault Y, Murphy A B, Guo A, Liu Z R, Rong M Z, Sun H 2015 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 48 415205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P 1998 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 18 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Colombo V, Ghedini E, Sanibondi P 2008 Prog. Nucl. Energy. 50 921
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ghorui S, Heberlein J V R, Pfender E 2008 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 28 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ghorui S, Heberlein J V R, Pfender E 2007 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 27 267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 王海兴, 孙素蓉, 陈士强 2012 61 195203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H X, Sun S R, Chen S Q 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 195203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang H X, Chen S Q, Chen X 2012 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 45 165202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Aubreton A, Elchinger M F 2003 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36 1798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Rat V, Fauchais P 2003 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37 34
[23] Colombo V, Ghedini E, Sanibondi P 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 055213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Lefort A 2002 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 22 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Lefort A 2002 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 22 475
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rat V, André P, Aubreton J, Elchinger M F, Fauchais P, Vacher D 2002 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 35 981
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Godin D, Trépanier J Y 2004 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 24 447
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] van de Sanden M C M, Schram P P J M, Peeters A G, van der Mullen J A M, Kroesen G M W 1989 Phys. Rev. A 40 5273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Kramida A, Ralchenko Y, Reader J, NIST ASD Team https://www.nist.gov/pml/atomic-spectra-database [2020-12-1]
[30] Chase M W, Davies C A, Downey J R, Frurip D J, McDonald R A, Syverud A N https://janaf.nist.gov/ [2020-12-1]
[31] Aziz R A, Slaman M J 1990 J. Chem. Phys. 92 1030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Capitelli M, Devoto R S 1973 Phys. Fluids. 16 1835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Levin E, Partridge H, Stallcop J R 1990 J. Thermophys Heat Transfer 4 469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Brunetti B, Liuti G, Luzzatti E, Pirani F, Volpi G G 1983 J. Chem. Phys. 79 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Murphy A B 1995 Plasma Chem. Plasma Process 15 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Phelps A V 1991 J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data. 20 557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Stallcop J R, Partridge H, Levin E 1991 J. Chem. Phys. 95 6429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Murphy A B 1993 Phys. Rev. E 48 3594
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Engelhardt A G, Phelps A V, Risk C G 1964 Phys. Rev. 135 1566
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Neynaber R H, Marino L L, Rothe E W, Trujillo S M 1963 Phys. Rev. 129 2069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Mason E A, Munn R J, Smith F J 1967 Phys. Fluids. 10 1827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Devoto R S 1966 Phys. Fluids. 9 1230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Chen X, Li H P 2003 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 46 1443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Wang W Z, Rong M Z, Yan J D, Murphy A B, Spencer J W 2011 Phys. Plasmas. 18 113502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9917
- PDF Downloads: 209
- Cited By: 0
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: