-
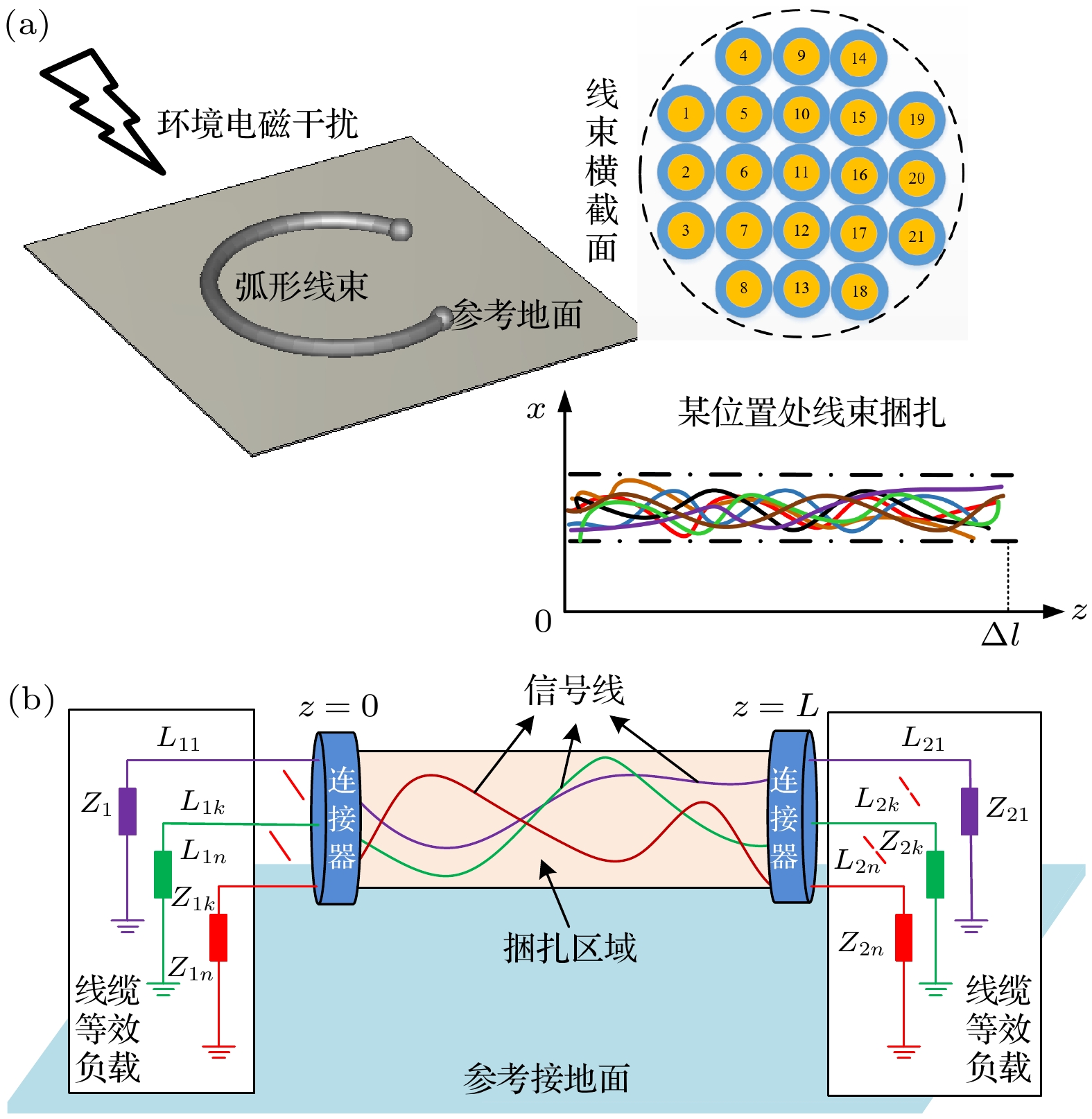
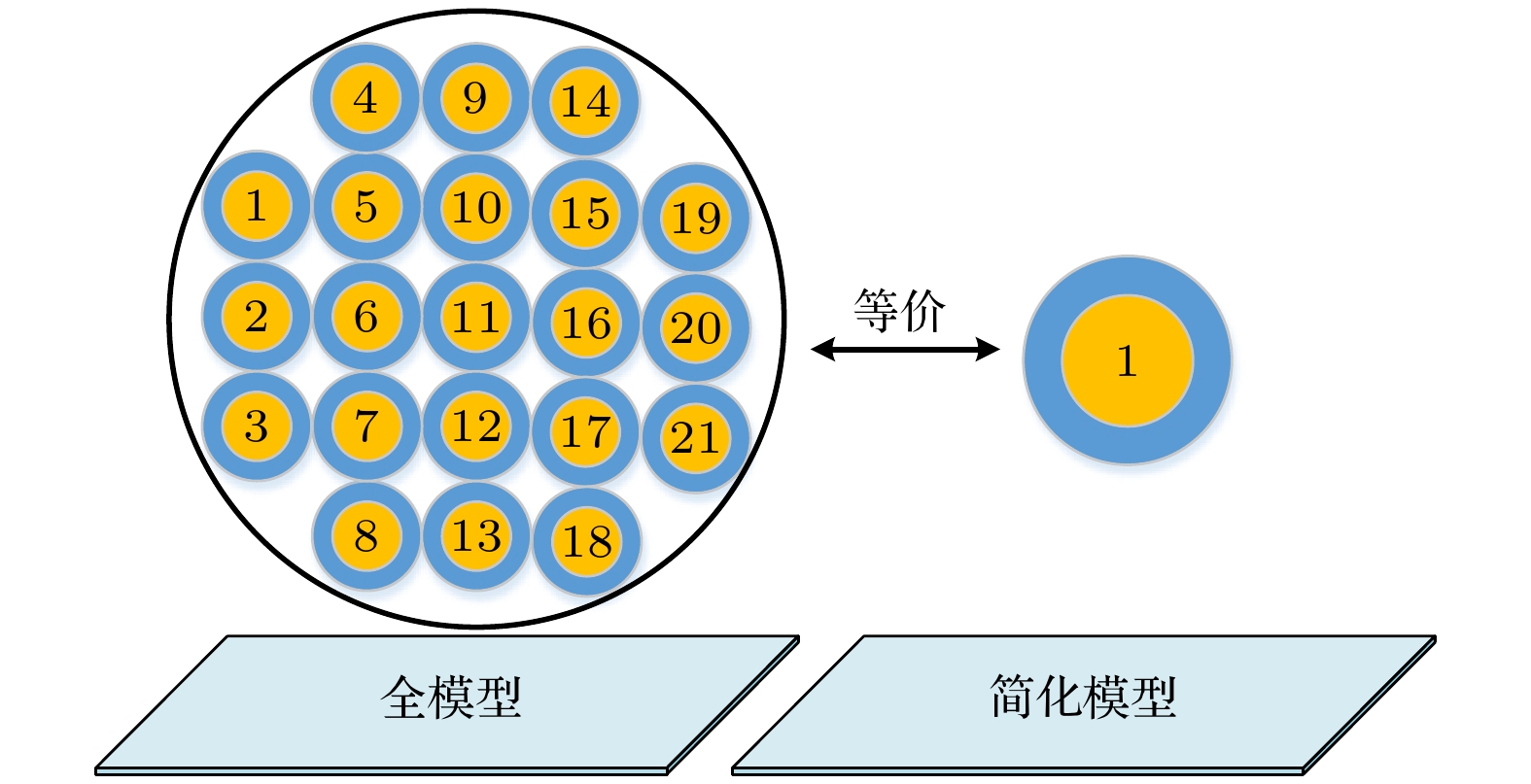
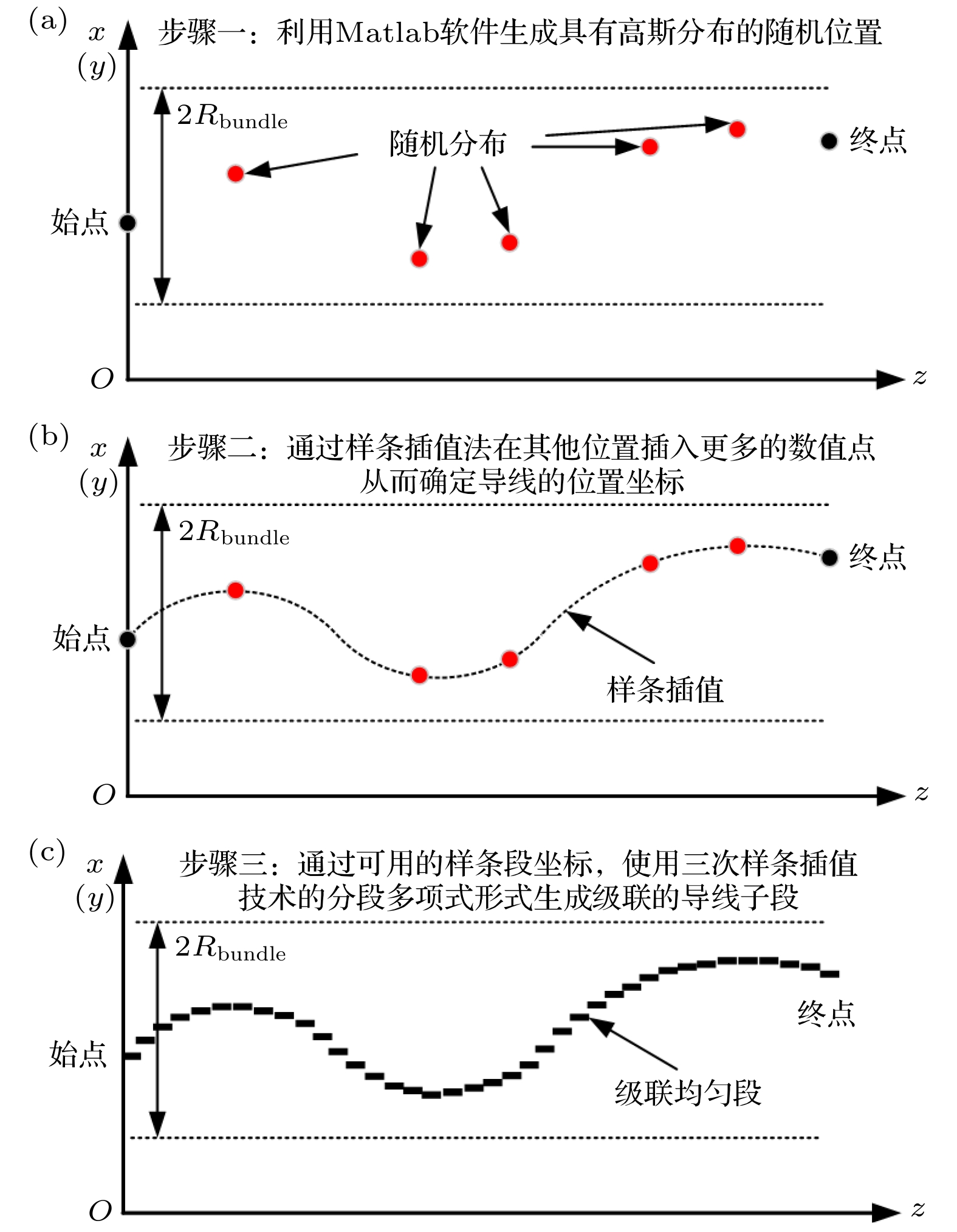
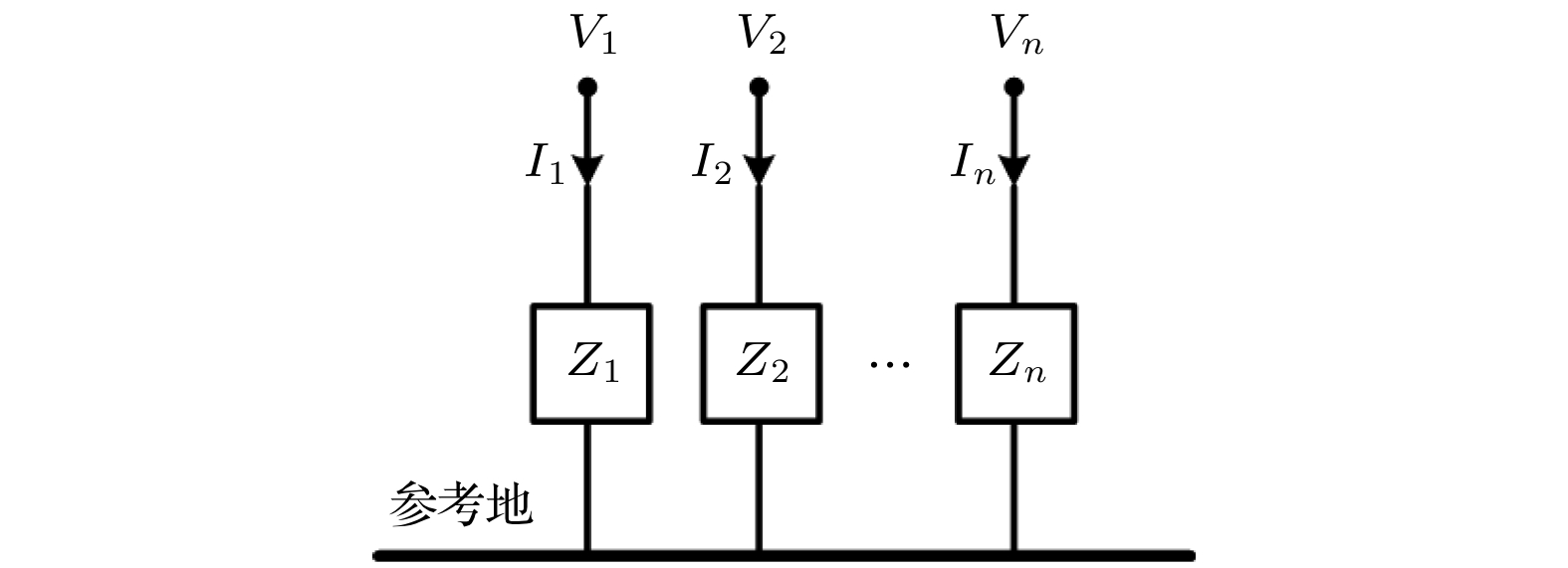
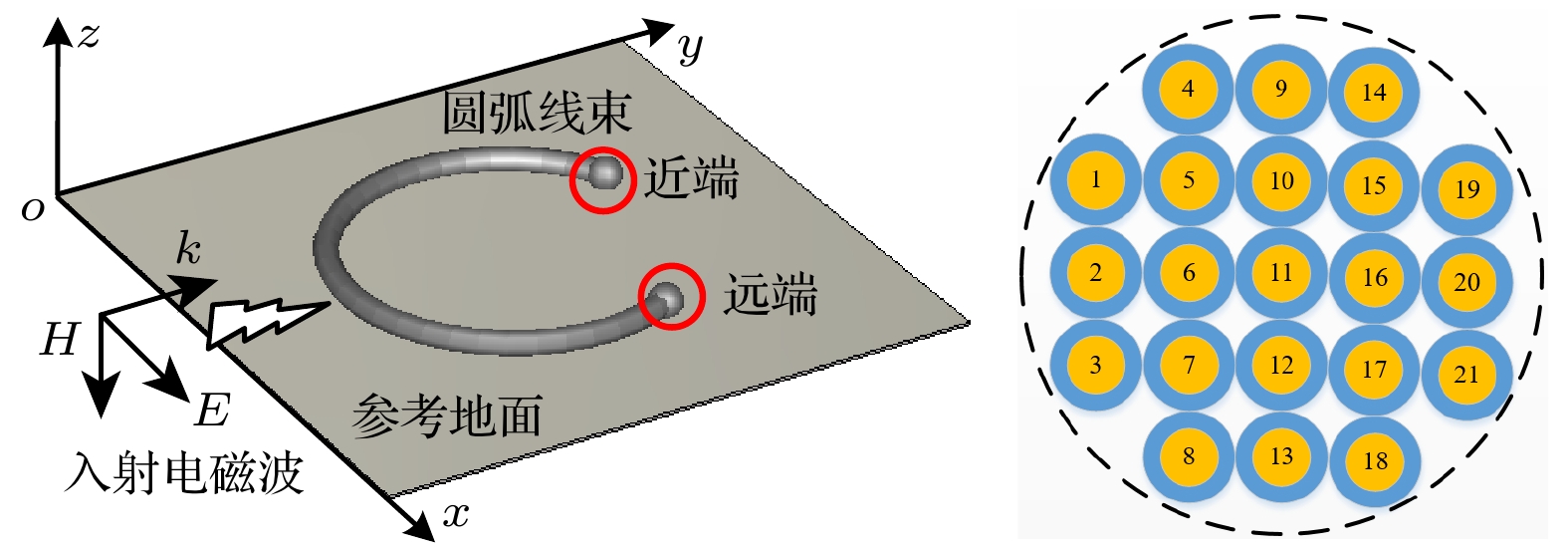
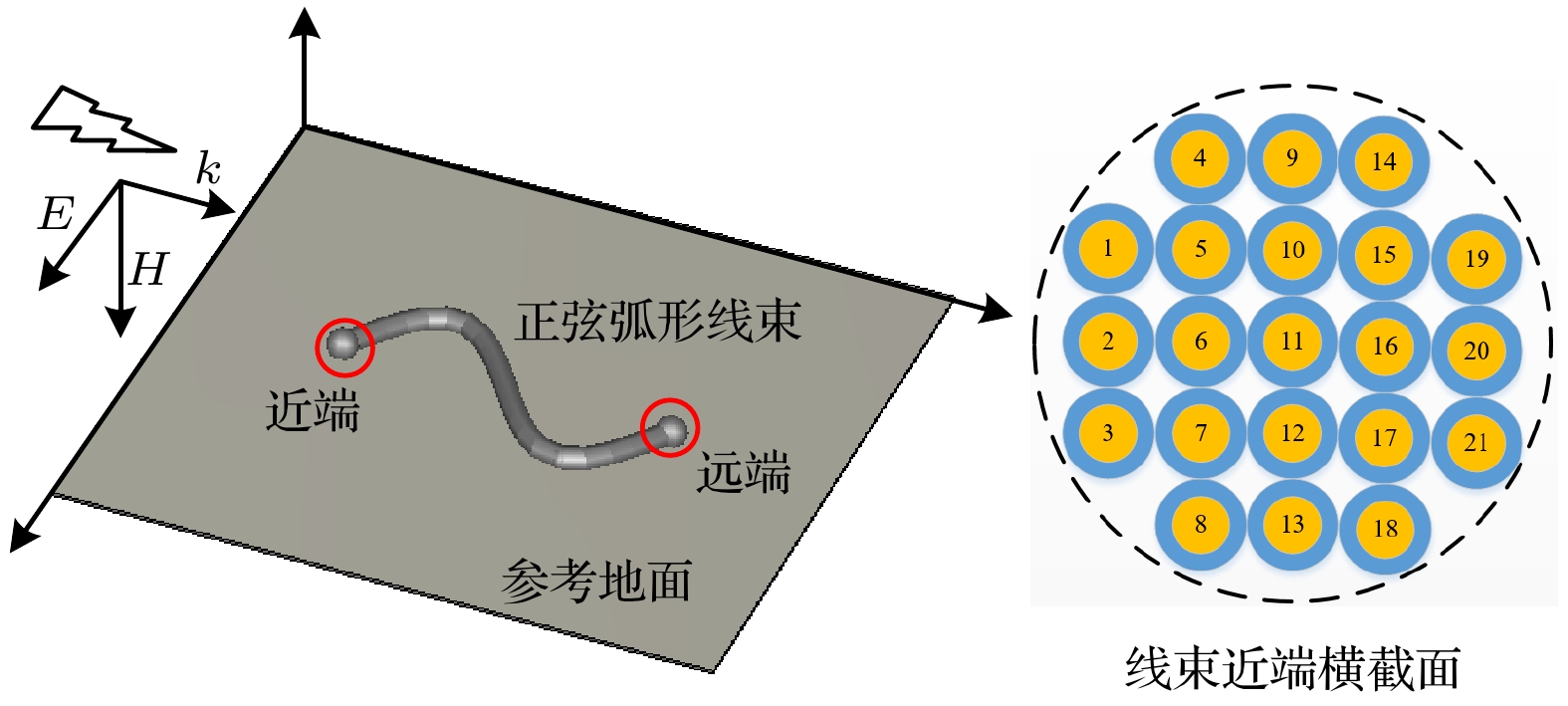
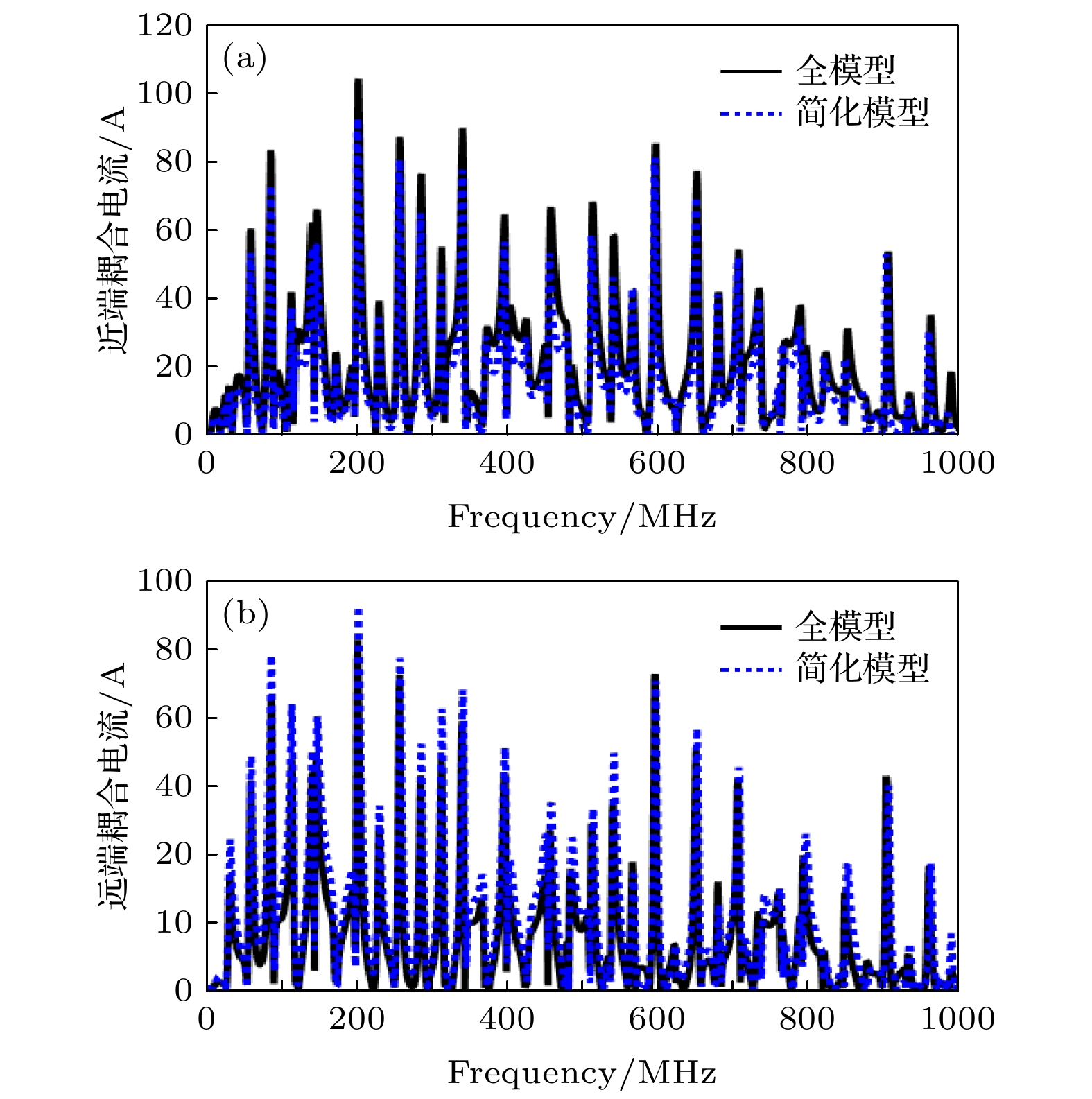
The cable harness provides a main gateway for electromagnetic interference(EMI) in electromechanical system. The unreasonable electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) design of cable harness will produce EMI to other on-board electronic equipment, bringing great safety risks to the system. Theoretical research and engineering practice indicate that most of the electromechanical systems cannot satisfy EMC standards, which can be attributed to the EMI generated by cables. As for the eletromagnetic(EM) illumination analysis, reliably and efficiently generating a full numerical model of cable harness is becoming more prominent for the EMC designers. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a more effective method to solve the modeling problem of cable harness. In the practical application, the cable harness has the characteristics of spatial layout, and its characteristics such as “large number of core wires”, “arbitrary curvature of space” and “randomness of wiring” bring challenges to the modeling of EM coupling to cable harness. The numerical simulation of the whole cable harness model requires severe conditions for computational resource and even makes the EM coupling analysis impossible. Thus, considering the uncertainty of wire position, this paper proposes a generalized simplified modeling method for the EM coupling effect of uncertainty strapping cable harness. Firstly, the Gaussian distribution and spline interpolation are used to determine the location of the core conductors in the random bundling. Then, the distribution parameters of the cable harness at different positions are established by using the transposition relationship between the subsegments of the wires. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by numerical examples of the arc-shaped and sine-shaped harness. In conclusion, this paper proposes a generalized simplification technique to model the EM illumination on cable harness with uncertainty wiring factors. By grouping the conductors together, the required computation time is markedly reduced and the complexity of modeling the completely cable harness is significantly simplified within a good accuracy. The proposed method provides a way of solving the modeling problem caused by “uncertainty strapping” of the complex wiring harnesses in electromechanical systems. -
Keywords:
- cable harness /
- electromagnetic coupling /
- uncertainty strapping /
- generalized simplified modeling method
[1] 任丹, 杜平安, 聂宝林, 曹钟, 刘文奎 2014 63 120701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren D, Du P A, Nie B L, Cao Z, Liu W Q 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 120701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 曹钟, 杜平安, 聂宝林, 任丹, 张其道 2014 63 124102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Z, Du P A, Nie B L, Ren D, Zhang Q D 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 124102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 叶志红, 张杰, 周健健, 苟丹 2020 69 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ye Z H, Zhang J, Zhou J J, Gou D 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 吴振军, 王丽芳, 廖承林 2009 59 6146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Z J, Wang L F, Liao C L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 6146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 孙亚秀, 卓庆坤, 姜庆辉, 李千 2015 64 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun Y X, Zhuo Q K, Jiang Q H, Li Q 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王海龙, 吴群, 孟繁义, 李乐伟 2007 56 2608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H L, Wu Q, Meng F Y, Li Y W 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 2608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Andrieu G, Kone L, Bocquet F 2008 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 50 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Andrieu G, Reineix A, Bunlon M 2009 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 51 108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Andrieu G, Reineix A 2013 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 55 798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Schetelig B, Keghie J, Kanyou R 2010 Adv. Radio Sci. 8 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li Z, Shao Z J, Ding J 2011 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 53 1040
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li Z, Liu L L, Ding J 2012 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 54 940
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Z, Liu L L, Yan J 2013 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 55 975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 汪泉弟, 郑亚利, 刘青松, 曾铉, 俞集辉 2012 电工技术学报 7 160
Wang Q D, Zheng Y L, Liu Q S, Zeng X, Yu J H 2012 Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society 7 160
[15] 高印寒, 安占扬, 王举贤 2015 吉林大学学报 45 946
Gao Y H, An Z Y, Wang J X 2015 J. Jilin Univ. 45 946
[16] 王天皓, 高印寒, 高乐 2017 吉林大学学报 47 392
Wang T H, Gao Y H, Gao L 2017 J. Jilin Univ. 47 392
[17] Paul C R 2008 Analysis of Multiconductor Transmission Lines (New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons)
[18] 高印寒, 王瑞宝, 马玉刚, 王莹莹, 杨开宇 2011 吉林大学学报 19 1088
Gao Y H, Wang R Z, Ma Y G, Wang Y Y, Yang K Y 2011 J. Jilin Univ. 19 1088
[19] Sun S, Liu G, Drewniak J L 2007 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 49 708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Duffy A P, Martin A J M, Orlandi A, Antonini G 2006 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 48 449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Orlandi A, Duffy A P, Archambeault B, Antonini G 2006 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 48 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 直角坐标系中21-线束模型近端位置(单位: mm)
Table 1. Coordinates of each conductor near end of the 21-conductor cable harness (unit: mm).
导线编号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 坐标x, y –8, 4 –8, 0 –8, –4 –4, 8 –4, 4 –4, 0 –4, 4 导线编号 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 坐标x, y –4, –8 0, 4 0, 4 0, 0 0, –4 0, –8 4, 8 导线编号 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 坐标x, y 4, 4 4, 0 4, –4 4, –8 8, 4 8, 0 8, –4 表 2 本文方法的FSV评价结果
Table 2. The FSV evaluation results of the proposed method.
线束终端 FSV ADMtot FDMtot GDMtot 圆弧线束 近端 0.265/good 0.181/very good 0.317/good 远端 0.289/good 0.200/very good 0.345/good 正弦线束 近端 0.313/good 0.172/very good 0.376/good 远端 0.290/good 0.157/very good 0.350/good 表 3 全模型和简化模型仿真时间分析
Table 3. Analysis time of the simplified and complete model.
模型 圆弧全
模型圆弧简化
模型正弦全
模型正弦简化
模型计算时间/s 3222 420 2919 336 -
[1] 任丹, 杜平安, 聂宝林, 曹钟, 刘文奎 2014 63 120701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren D, Du P A, Nie B L, Cao Z, Liu W Q 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 120701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 曹钟, 杜平安, 聂宝林, 任丹, 张其道 2014 63 124102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao Z, Du P A, Nie B L, Ren D, Zhang Q D 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 124102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 叶志红, 张杰, 周健健, 苟丹 2020 69 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ye Z H, Zhang J, Zhou J J, Gou D 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 060701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 吴振军, 王丽芳, 廖承林 2009 59 6146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Z J, Wang L F, Liao C L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 6146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 孙亚秀, 卓庆坤, 姜庆辉, 李千 2015 64 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun Y X, Zhuo Q K, Jiang Q H, Li Q 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王海龙, 吴群, 孟繁义, 李乐伟 2007 56 2608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H L, Wu Q, Meng F Y, Li Y W 2007 Acta Phys. Sin. 56 2608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Andrieu G, Kone L, Bocquet F 2008 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 50 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Andrieu G, Reineix A, Bunlon M 2009 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 51 108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Andrieu G, Reineix A 2013 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 55 798
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Schetelig B, Keghie J, Kanyou R 2010 Adv. Radio Sci. 8 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li Z, Shao Z J, Ding J 2011 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 53 1040
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li Z, Liu L L, Ding J 2012 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 54 940
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Z, Liu L L, Yan J 2013 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 55 975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 汪泉弟, 郑亚利, 刘青松, 曾铉, 俞集辉 2012 电工技术学报 7 160
Wang Q D, Zheng Y L, Liu Q S, Zeng X, Yu J H 2012 Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society 7 160
[15] 高印寒, 安占扬, 王举贤 2015 吉林大学学报 45 946
Gao Y H, An Z Y, Wang J X 2015 J. Jilin Univ. 45 946
[16] 王天皓, 高印寒, 高乐 2017 吉林大学学报 47 392
Wang T H, Gao Y H, Gao L 2017 J. Jilin Univ. 47 392
[17] Paul C R 2008 Analysis of Multiconductor Transmission Lines (New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons)
[18] 高印寒, 王瑞宝, 马玉刚, 王莹莹, 杨开宇 2011 吉林大学学报 19 1088
Gao Y H, Wang R Z, Ma Y G, Wang Y Y, Yang K Y 2011 J. Jilin Univ. 19 1088
[19] Sun S, Liu G, Drewniak J L 2007 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 49 708
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Duffy A P, Martin A J M, Orlandi A, Antonini G 2006 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 48 449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Orlandi A, Duffy A P, Archambeault B, Antonini G 2006 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 48 460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6094
- PDF Downloads: 69
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: