-
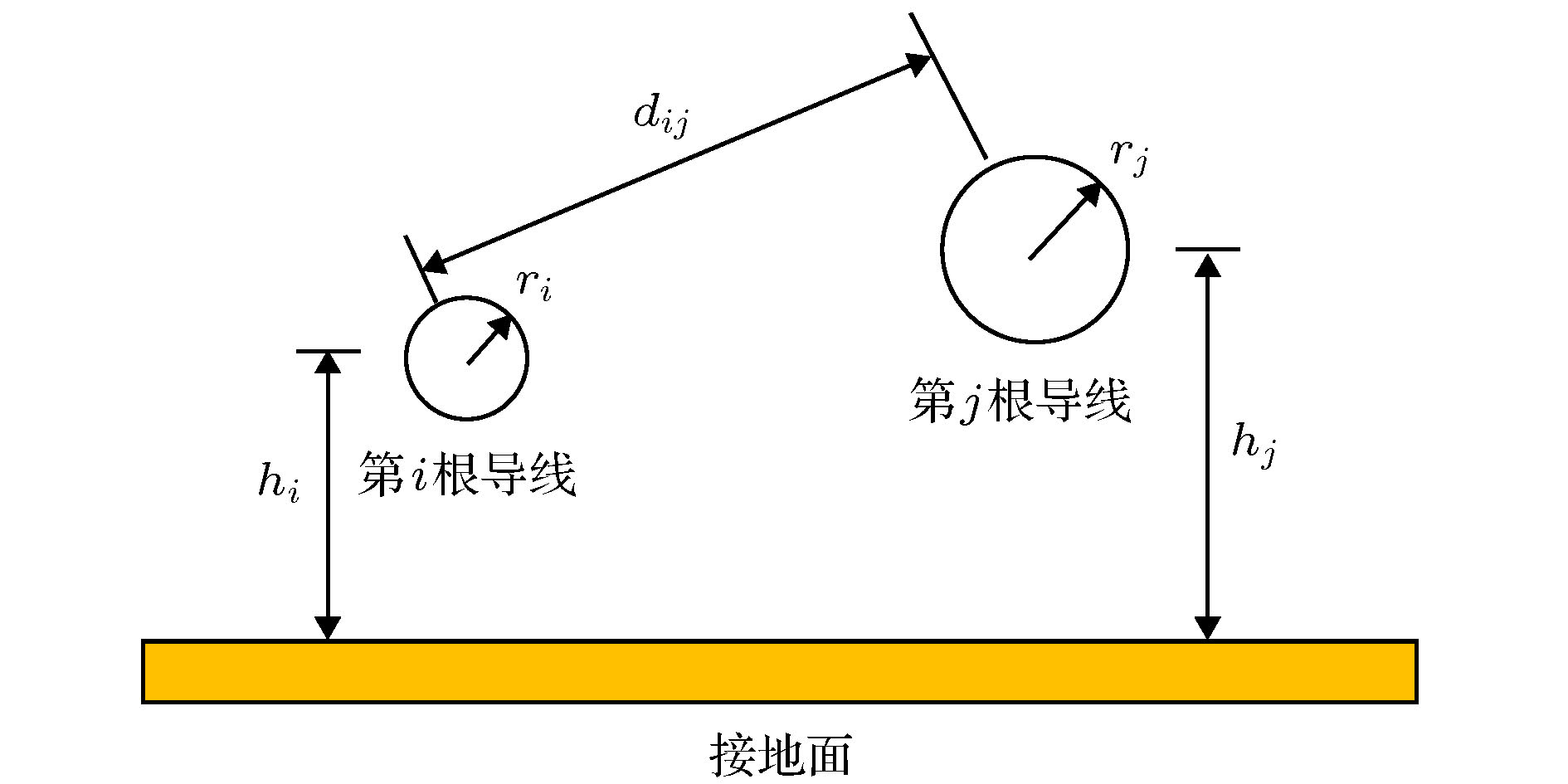
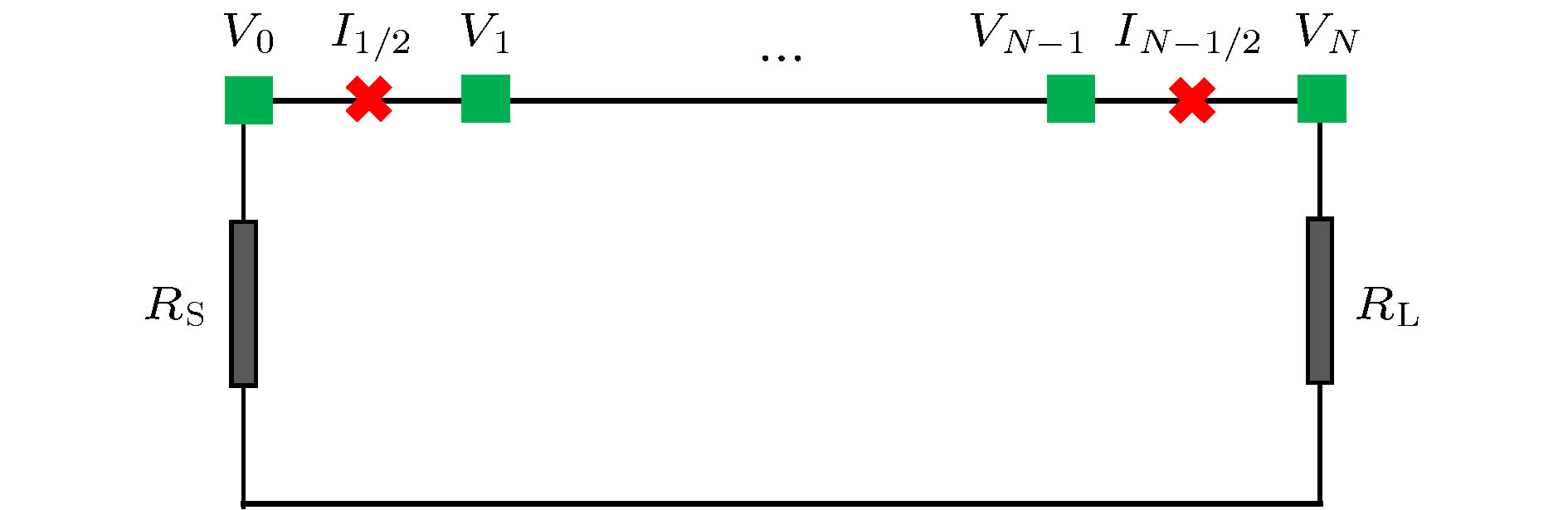
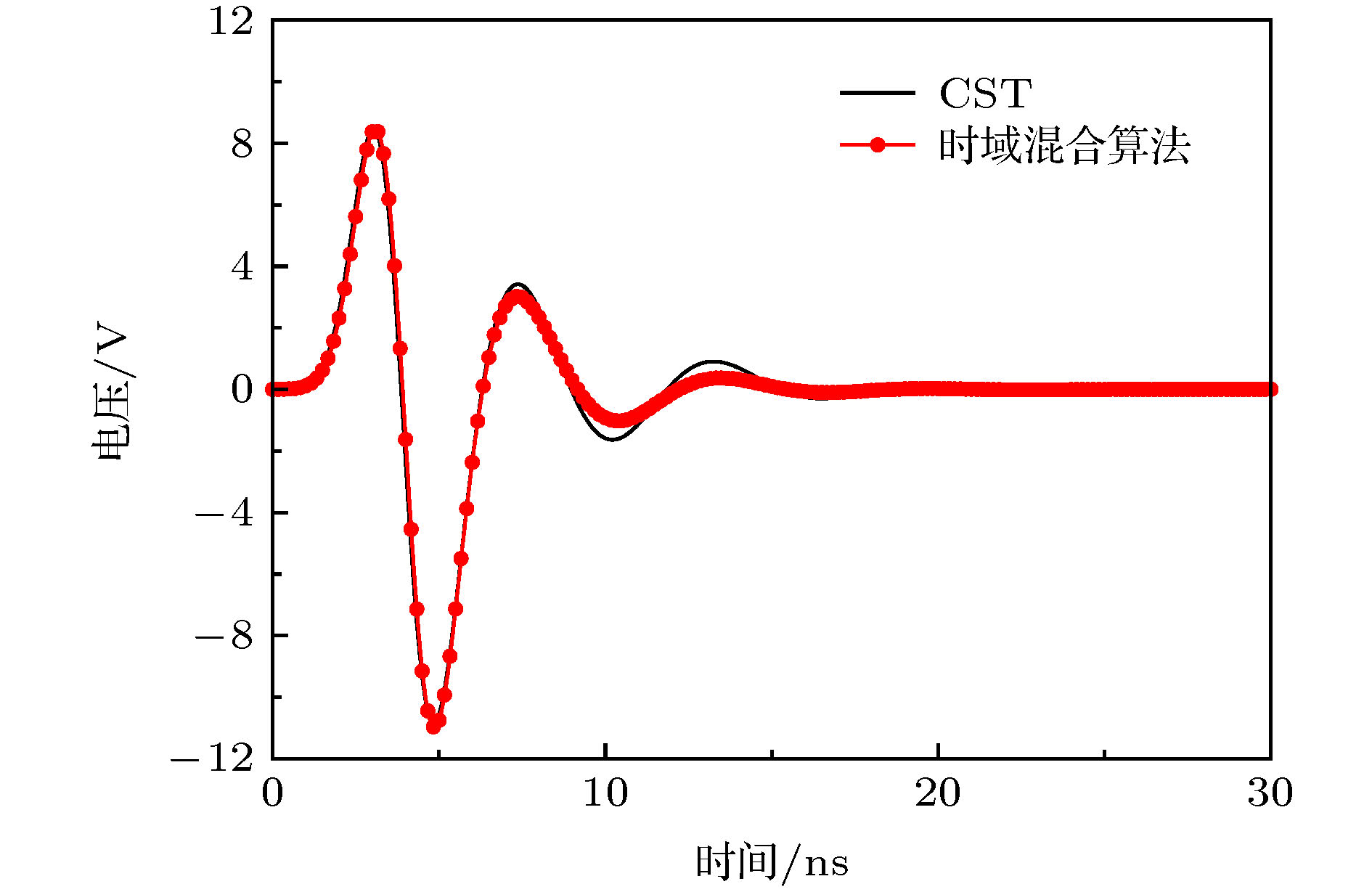
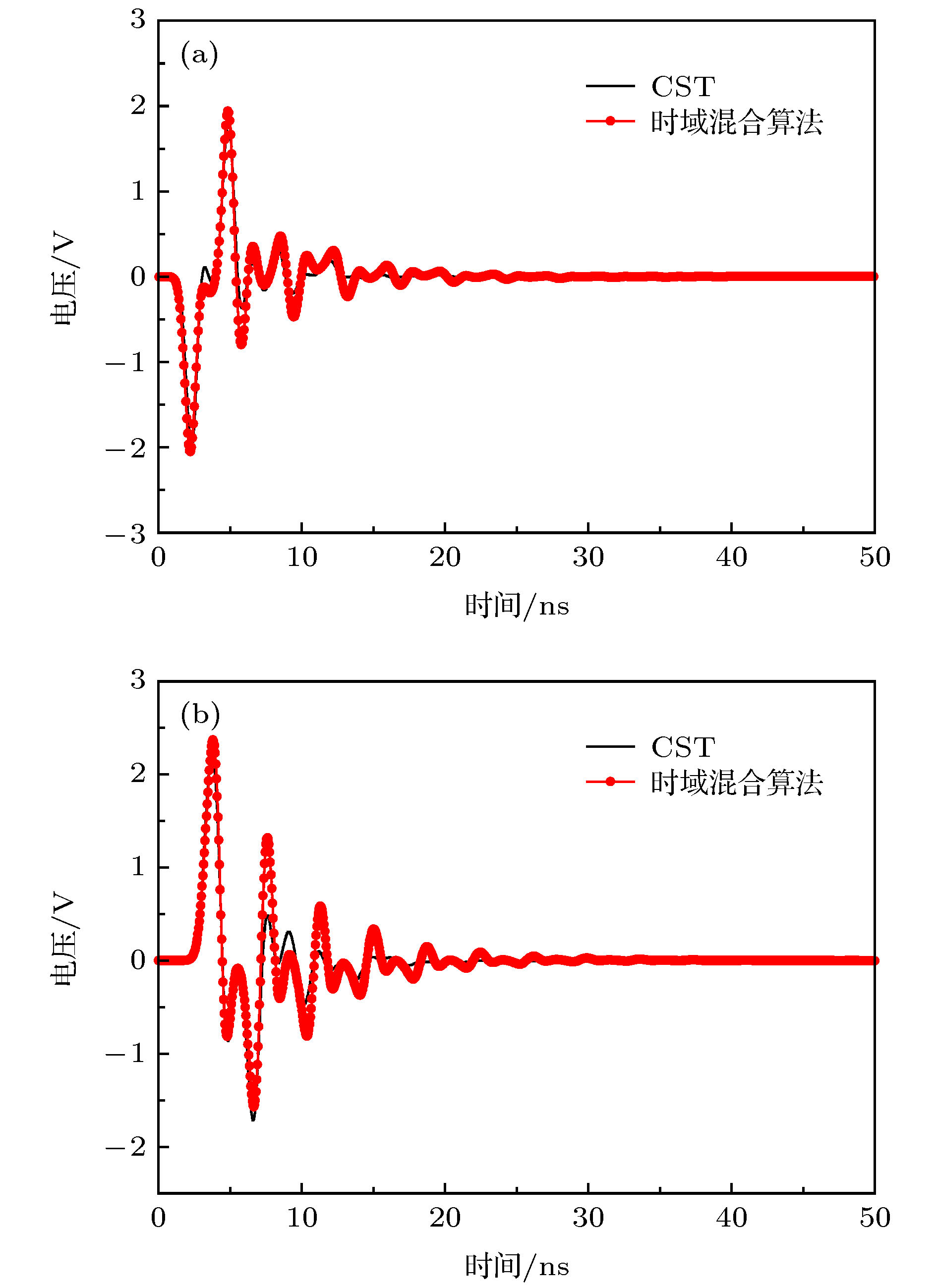
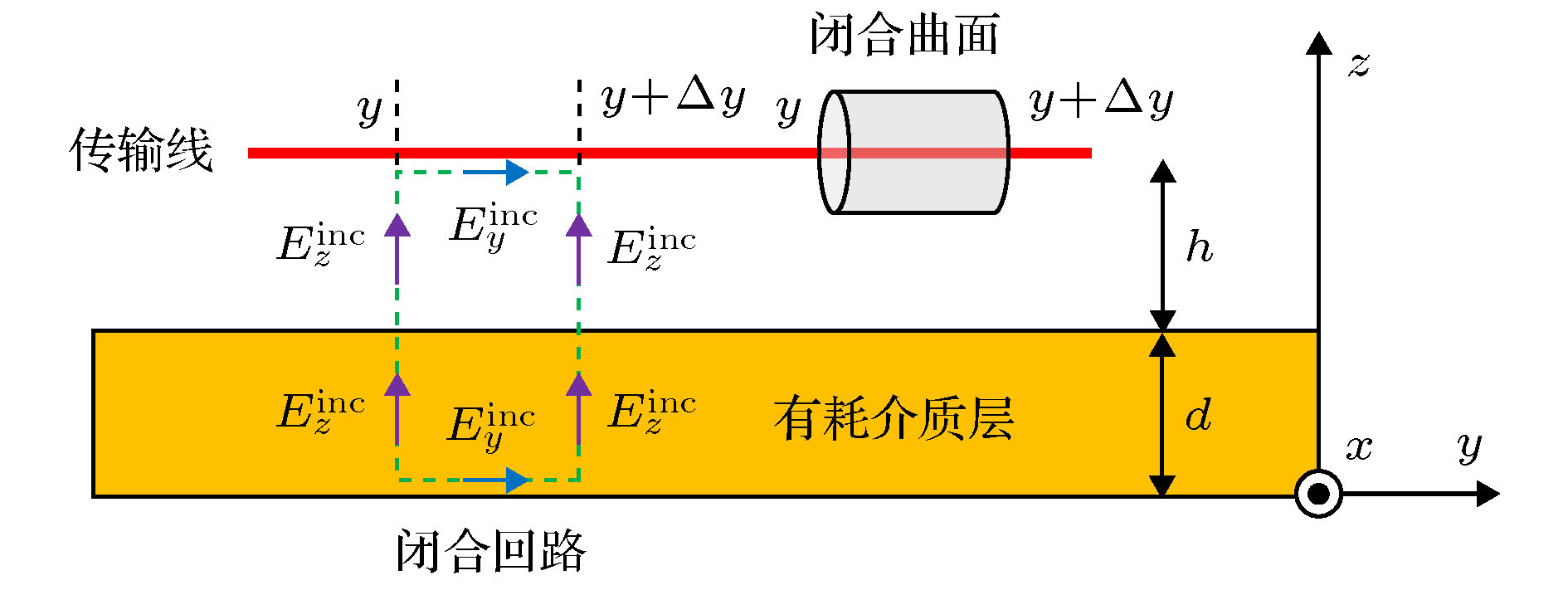
At present, numerical methods applied to the coupling analysis of transmission lines on the lossy dielectric layer excited by ambient wave are still rare in the literature. As a temptation to fill this gap, a novel time domain hybrid method is proposed, in which the modified transmission line (TL) equations, finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method, and some interpolation schemes are organically combined together. It can overcome the difficulty in building the coupling model of ambient wave to transmission lines on the lossy dielectric layer greatly. In this method, the modified transmission line (TL) equations suitable for the coupling analysis of multi-conductor transmission lines (MTLs) on the lossy dielectric layer are derived from the traditional TL equations firstly. Compared with the traditional TL equations, the electromagnetic fields in the lossy dielectric layer are introduced into the equivalent distribution sources of modified TL equations. Generally, the precision of TL equations is dependent on the accuracy of equivalent distribution sources, which are obtained from the incident electric fields parallel and perpendicular to the MTLs. Therefore, the FDTD method is utilized to model the structure of lossy dielectric layer to calculate the electromagnetic field distribution surrounding the MTLs and in the dielectric layer. Since the heights and distances of MTLs can be arbitrary values, the electric fields parallel and perpendicular to the MTLs cannot be obtained from the electric fields on the edges of FDTD grids directly, which should be computed via some interpolation schemes. Then the modified TL equations are established, which should be solved by the central difference scheme of FDTD method to obtain the voltages and currents on the MTLs and terminal loads. The significant feature of this proposed method is that it can realize the synchronous calculations of electromagnetic field radiation and transient responses on the MTLs. Finally, numerical simulations of single and multiconductor transmission lines on the lossy dielectric layer excited by ambient wave at different incident angles are employed to exhibit the accuracy and efficiency of the proposed method by comparing with the simulation software CST. Because the structures of MTLs do not need to be meshed, the proposed method outperforms the simulation software CST in both memory usage and computation time.
-
Keywords:
- transmission lines on the lossy dielectric layer /
- modified transmission line equations /
- interpolation schemes /
- finite-difference time-domain method
[1] Holland R, Simpson L 1981 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 23 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Berenger J P 2000 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 42 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 魏兵, 李小勇, 王飞 2009 58 6174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei B, Li X Y, Wang F 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 6174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] He X B, Wei B, Fan K H, Li Y W, Wei X L 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 074102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Agrawal A K, Harold J P, Shyam H G 1980 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 22 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王庆国, 周星, 李许东 2012 高电压技术 38 2205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q G, Zhou X, Li X 2012 High Voltage Eng. 38 2205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Xu Q X, Xie Y Z 2015 7th Asia-Pacific Conference on Environmental Electromagnetics, Hangzhou, China, November 4−7, 2015 p411
[8] Du J K, Hwang S M, Ahn J W, Yook J G 2013 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61 3514
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 罗静雯, 杜平安, 任丹, 聂宝林 2015 64 010701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo J W, Du P A, Ren D, Nie B L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 010701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 阚勇, 闫丽萍, 赵翔, 周海京, 刘强, 黄卡玛 2016 65 030702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kan Y, Yan L P, Zhao X, Zhou H J, Liu Q, Huang K M 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 030702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ni G Y, Yan L, Yuan N C 2008 Chin. Phys. B 17 3629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Paul C R 1994 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 36 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Erdin I, Dounavis A, Achar R 2001 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 43 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xie H Y, Wang J G, Fan R Y, Liu Y N 2009 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 51 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xie H Y, Wang J G, Fan R Y, Liu Y N 2010 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 52 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Xie H Y, Wang J G, Li Y, Xia H F 2014 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 56 1623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xie H Y, Li Y, Qiao H L, Wang J G 2016 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 58 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ye Z H, Xiong X Z, Liao C, Li Y 2015 Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 42 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ye Z H, Liao C, Xiong X Z, Zhang M 2016 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 58 964
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ye Z H, Liao C, Xiong X Z, Zhang M 2017 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 59 1211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 赵晓辉, 蔡理, 张鹏 2013 62 130506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao X H, Cai L, Zhang P 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 130506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 吴振军, 王丽芳, 廖承林 2009 58 6146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Z J, Wang L F, Liao C L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 6146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tesche F M, Ianoz M V, Karlsson T 1997 EMC Analysis Methods and Computational Models (New York: Wiley) p451
[24] Chen J, Wang J G 2007 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 49 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen J, Wang J G 2013 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 55 1239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 两种方法计算算例1时所需内存和时间对比
Table 1. Memories and computation time needed by the two methods for the first example.
方法 内存/MB 计算时间/min CST 63 19 时域混合算法 34 10 表 2 两种方法计算算例2时所需内存和时间对比
Table 2. Memories and computation time needed by the two methods for the second example.
方法 内存/MB 计算时间/min CST 217 64 时域混合算法 78 15 -
[1] Holland R, Simpson L 1981 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 23 88
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Berenger J P 2000 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 42 257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 魏兵, 李小勇, 王飞 2009 58 6174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei B, Li X Y, Wang F 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 6174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] He X B, Wei B, Fan K H, Li Y W, Wei X L 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 074102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Agrawal A K, Harold J P, Shyam H G 1980 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 22 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 王庆国, 周星, 李许东 2012 高电压技术 38 2205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q G, Zhou X, Li X 2012 High Voltage Eng. 38 2205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Xu Q X, Xie Y Z 2015 7th Asia-Pacific Conference on Environmental Electromagnetics, Hangzhou, China, November 4−7, 2015 p411
[8] Du J K, Hwang S M, Ahn J W, Yook J G 2013 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61 3514
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 罗静雯, 杜平安, 任丹, 聂宝林 2015 64 010701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo J W, Du P A, Ren D, Nie B L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 010701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 阚勇, 闫丽萍, 赵翔, 周海京, 刘强, 黄卡玛 2016 65 030702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Kan Y, Yan L P, Zhao X, Zhou H J, Liu Q, Huang K M 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 030702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ni G Y, Yan L, Yuan N C 2008 Chin. Phys. B 17 3629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Paul C R 1994 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 36 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Erdin I, Dounavis A, Achar R 2001 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 43 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Xie H Y, Wang J G, Fan R Y, Liu Y N 2009 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 51 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xie H Y, Wang J G, Fan R Y, Liu Y N 2010 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 52 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Xie H Y, Wang J G, Li Y, Xia H F 2014 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 56 1623
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Xie H Y, Li Y, Qiao H L, Wang J G 2016 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 58 581
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ye Z H, Xiong X Z, Liao C, Li Y 2015 Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 42 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ye Z H, Liao C, Xiong X Z, Zhang M 2016 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 58 964
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ye Z H, Liao C, Xiong X Z, Zhang M 2017 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 59 1211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 赵晓辉, 蔡理, 张鹏 2013 62 130506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao X H, Cai L, Zhang P 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 130506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 吴振军, 王丽芳, 廖承林 2009 58 6146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Z J, Wang L F, Liao C L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 6146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tesche F M, Ianoz M V, Karlsson T 1997 EMC Analysis Methods and Computational Models (New York: Wiley) p451
[24] Chen J, Wang J G 2007 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 49 354
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen J, Wang J G 2013 IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 55 1239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8522
- PDF Downloads: 114
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: