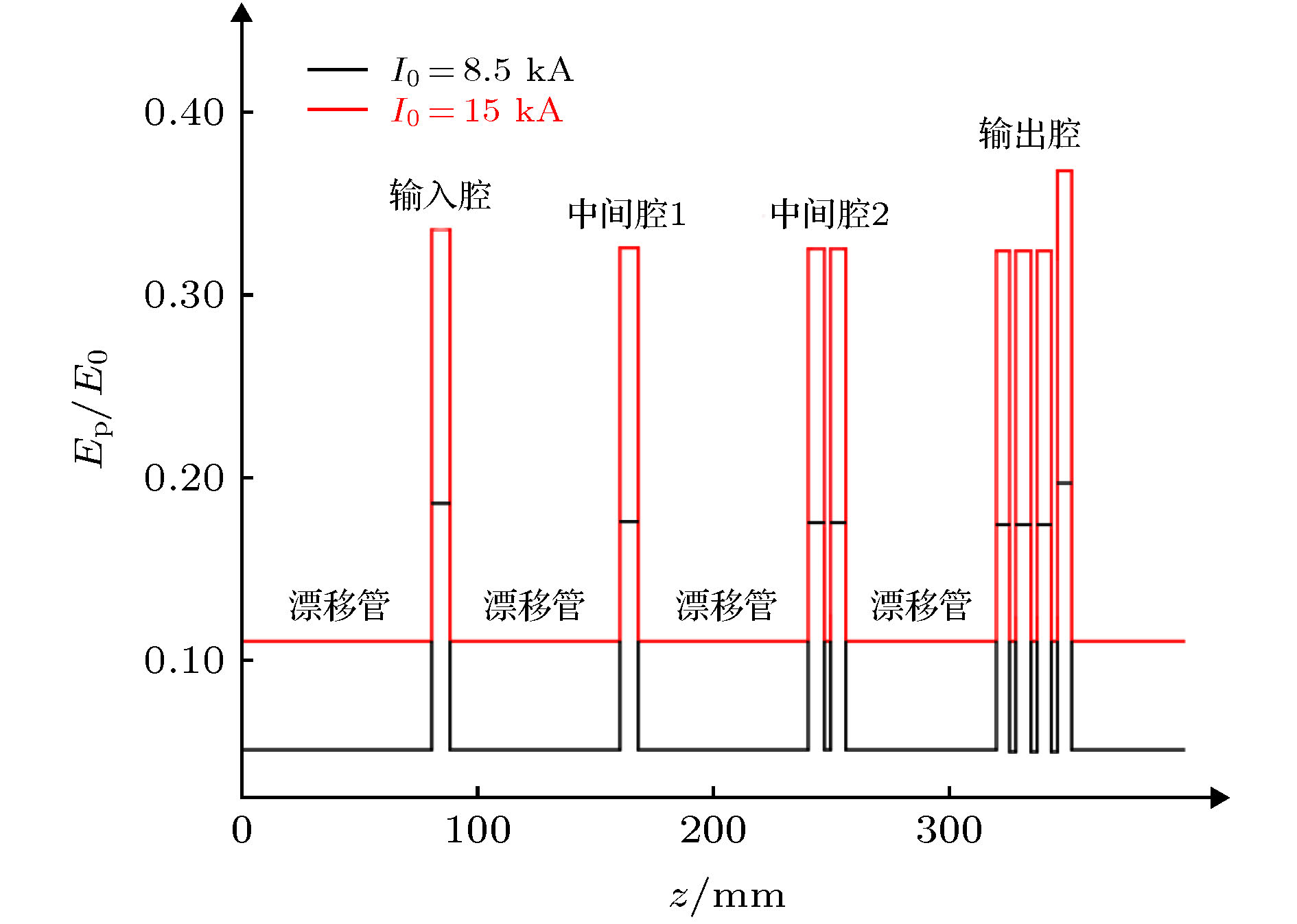
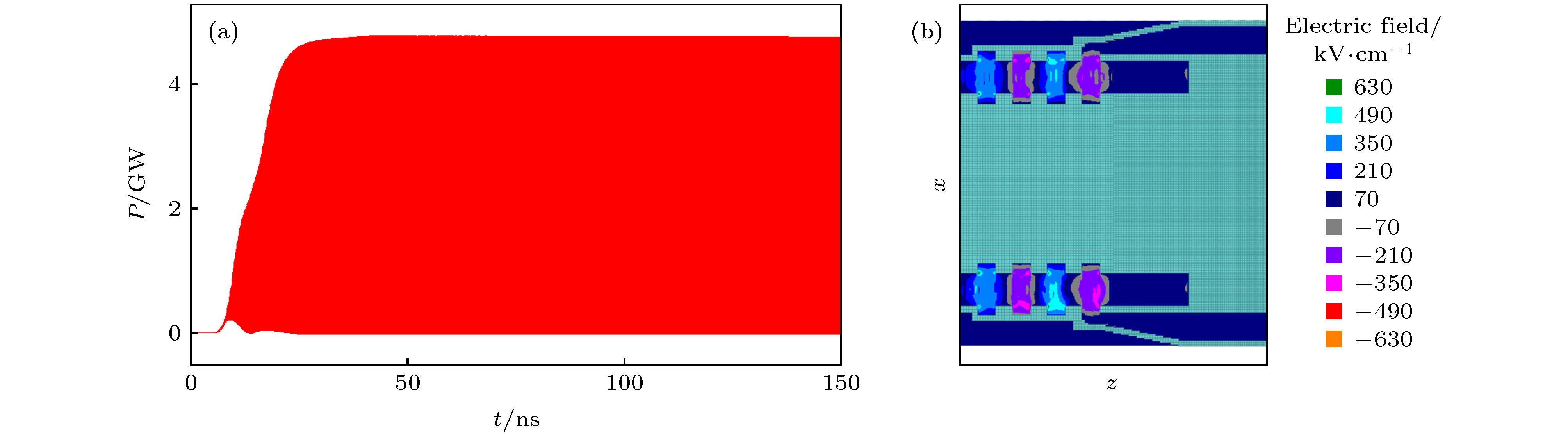
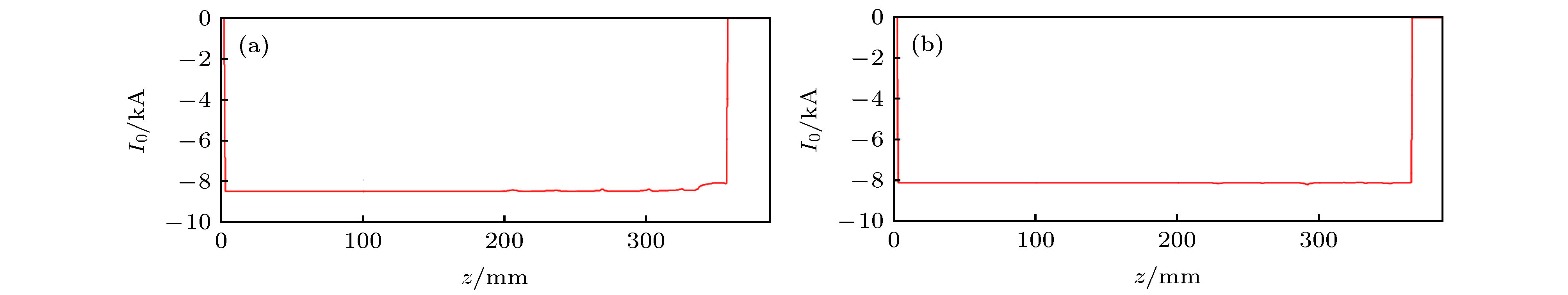
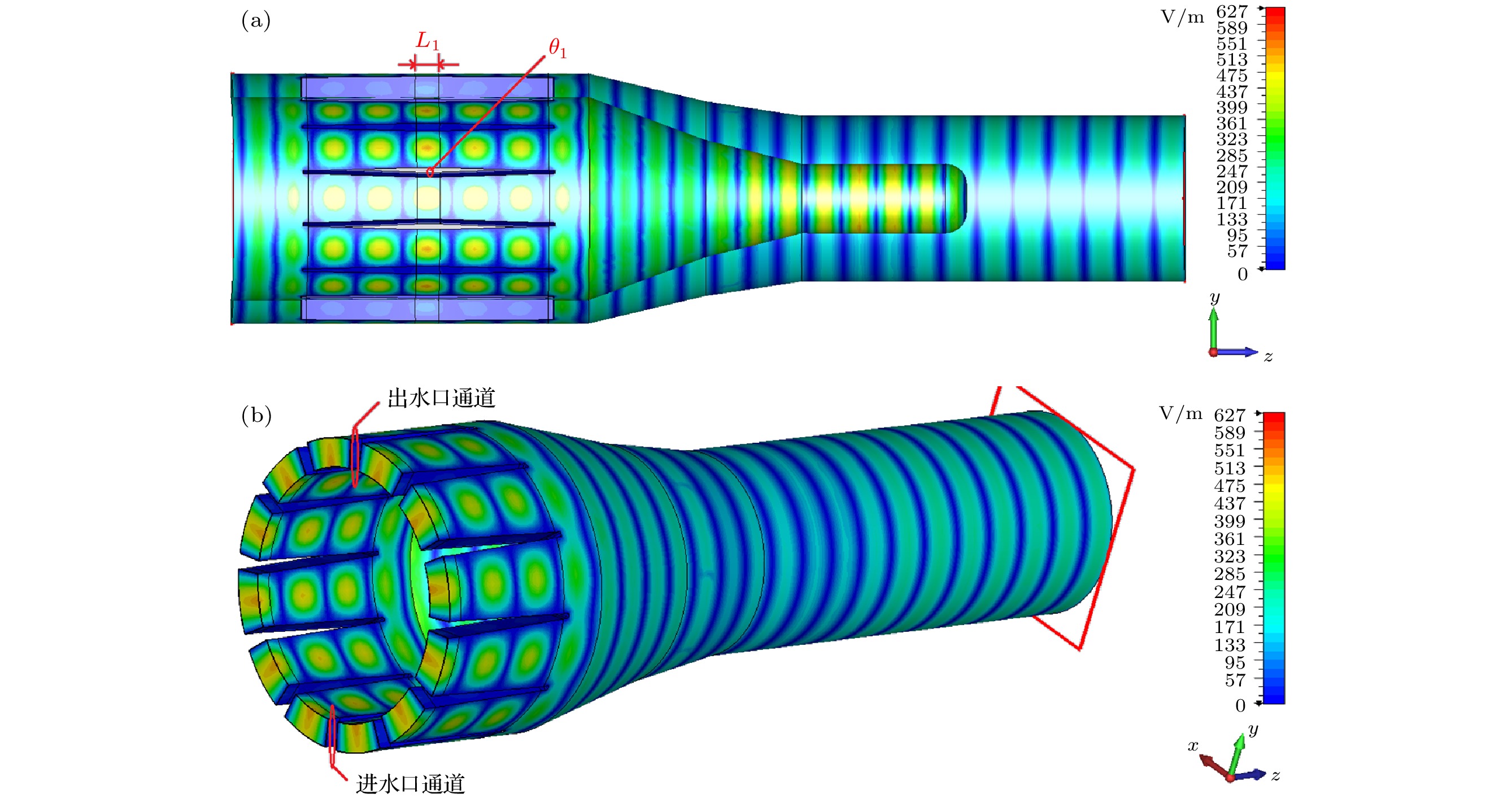
-
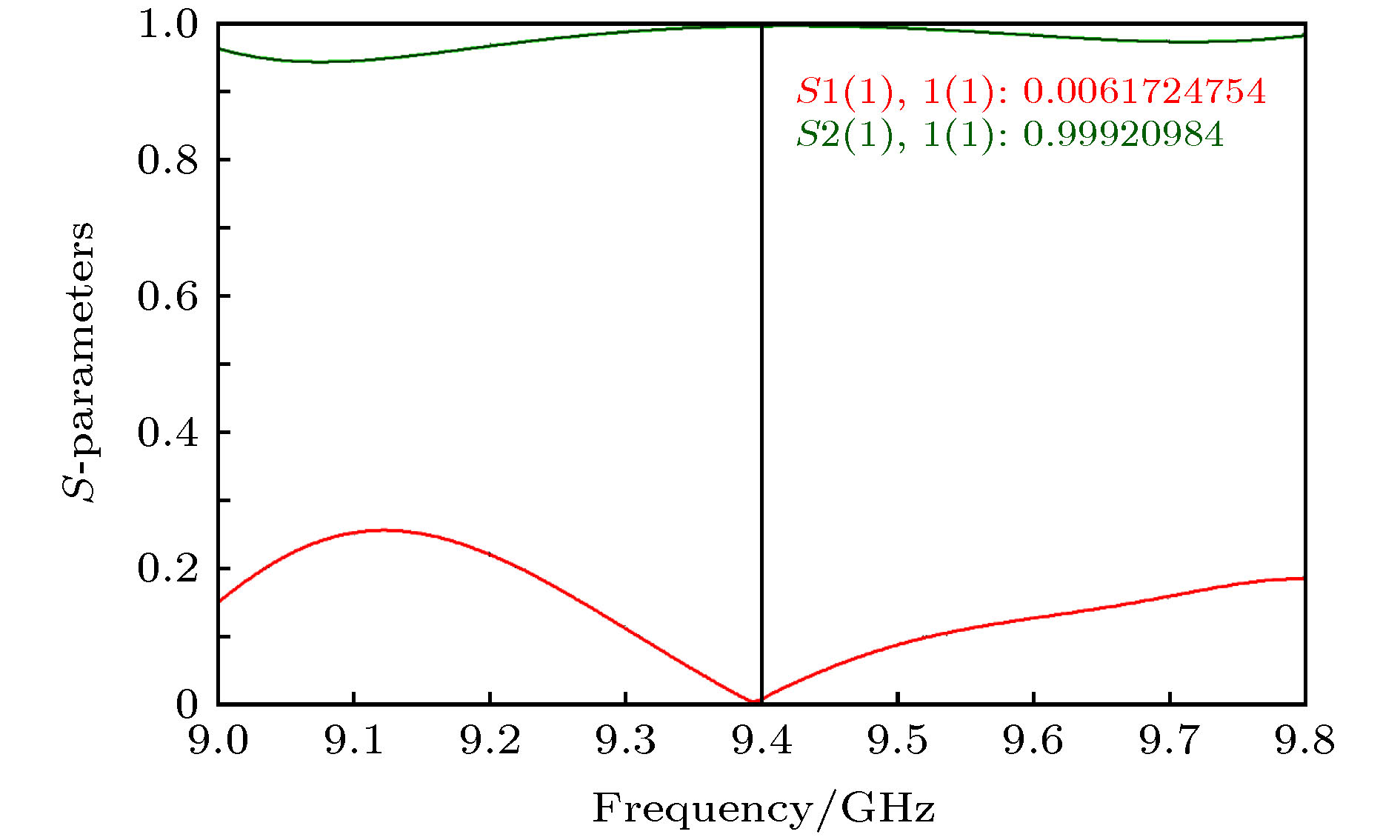
The relativistic klystron amplifier (RKA) is a very important kind of high power microwave device, which has the advantages of high power, high efficiency, stable output phase and amplitude. The development of multi-injection RKA toward engineering and practical application needs to further improve operating frequency and output power of klystron amplifier, while the RKA of conventional circular waveguide drift tubes is restricted by the physical factors such as geometric size, space charge force and high-voltage breakdown. The multi-beam RKA based on the technology of multiple electron beams can work at low voltage and guiding magnetic field, and can also possess high electron beam current and diversion coefficient. The physical limitation of conventional structure RKA is overcome, and the working frequency and the output power are improved. In the experiment, the X-band GW level power of microwave is obtained. The multi-beam RKA needs to further improve its working frequency and working life. In the experiment, the power conversion efficiency of multi-beam RKA is about 35%, and most of the remaining electron energy will accumulate on the collection pole at the end. If the heat dissipation of the collector is not designed appropriately, the collection will be seriously ablated when working at high heavy frequency. Thus a large quantity of plasma and secondary electrons are generated, which affects the stability of the device. To solve the problem of electron reflux bombarding the output cavity after electron beam exchanging energy in the gap of output cavity, the reflux process of relativistic electron beam in the device is analyzed in this paper. On this basis, a coaxial extraction structure with four-gap extension interaction is designed to avoid electron reflux and reduce the gap electric field, thus improving the working life of the device. At the same time, in order to solve the problem that the conventional water cooling channel can affect the output microwave mode in a high-frequency over-mode device, a mode transformation structure of coaxial TEM mode-fan-shaped TE10 mode-coaxial TEM mode-circular waveguide TM01 mode is designed. The mode conversion efficiency is greater than 99.9%, and the influence of collecting polar water cooling channel on the output microwave mode is avoided. The stable operation of multi-beam RKA in the X-band with a repetition rate of 45 Hz is realized experimentally, while the output power is over 1 GW and the microwave pulse width is over 100 ns. At present, the multi-beam RKA runs about 10000 times in total, and the output microwave parameters do not decrease significantly.
-
Keywords:
- relativistic klystron amplifier /
- X-band /
- long pulse /
- high repetition rate
[1] Jerrold S L, Bruce D H 1994 Appl. Phys. Lett. 65 2133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 黄华, 吴洋, 刘振帮, 袁欢, 何琥, 李乐乐, 李正红, 金晓, 马弘舸 2018 67 088402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang H, Wu Y, Liu Z B, Yuan H, He H, Li L L, Li Z H, Jin X, Ma H G 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 088402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Thomas H, Adam B, Rasheda B, Heinz B, Mark C, Edward E, Deepika G, Armand S, Brad S, Lou Z 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ding Y G, Shen B, Cao J, Zhang Y Q, Ruan C J, Gu H H, Zhang D, Wang C Y, Cao M 2009 IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 56 870
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 吴洋, 许州, 周霖, 李文君, 唐传祥 2012 61 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y, Xu Z, Zhou L, Li W J, Tang C X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li R J, Ruan C J, Zhang H F 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 033107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 魏元璋, 李士锋, 王战亮, 黄华, 刘振帮, 何琥, 宫玉彬 2018 强激光与粒子束 30 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei Y Z, Li S F, Wang Z L, Huang H, Liu Z B, He H, Gong Y B 2018 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 30 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张长青, 阮存军, 王树忠, 杨修东 2015 红外与毫米波学报 34 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang C Q, Ruan C J, Wang S Z, Yang X D 2015 J. Infrared Millmeter Waves 34 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Friedman M, Pasour J, Smithe D 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 3724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Edward B A, Andrew N D, Mikhail I F, Nikolay G K, Nikolay F K, Mikhail I P, Alexander V S, Edl S, Eugeny I S, Vladimir V Y 2002 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 30 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhang W, Ju J C, Zhang J, Zhou Y X, Zhong H H 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 053102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Qi Z M, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Zhong H H, Xu L R, Yang L 2016 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 37 782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘振帮, 金晓, 黄华, 陈怀璧 2012 61 128401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Jin X, Huang H, Chen H B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 128401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘振帮, 黄华, 金晓, 袁欢, 戈弋, 何琥, 雷禄容 2015 64 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Yuan H, Ge Y, He H, Lei L R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Lei L R, Zhu L, Li L L, Li S F, Yan W K, He H 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 093110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王淦平, 金晓, 黄华, 刘振帮 2017 66 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G P, Jin X, Huang H, Liu Z B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Carlsten B E, Faehl R J, Fazio M V, Haynes W B, Stringfield R M 1994 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 22 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 彭国良, 梁玉钦 2016 强激光与粒子束 28 053003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng G L, Liang Y Q 2016 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 28 053003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 薛明, 丁耀根, 王勇 2018 真空电子技术 8 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xue M, Ding Y G, Wang R 2018 Vaccum Electron. 8 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 戴宏毅, 肖亚斌, 王同权, 张树发 2001 湖南大学学报 28 6
Dai H Y, Xiao Y B, Wang T Q, Zhang S F 2001 J. Hunan Univ. 28 6
-
-
[1] Jerrold S L, Bruce D H 1994 Appl. Phys. Lett. 65 2133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 黄华, 吴洋, 刘振帮, 袁欢, 何琥, 李乐乐, 李正红, 金晓, 马弘舸 2018 67 088402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang H, Wu Y, Liu Z B, Yuan H, He H, Li L L, Li Z H, Jin X, Ma H G 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 088402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Thomas H, Adam B, Rasheda B, Heinz B, Mark C, Edward E, Deepika G, Armand S, Brad S, Lou Z 2010 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Ding Y G, Shen B, Cao J, Zhang Y Q, Ruan C J, Gu H H, Zhang D, Wang C Y, Cao M 2009 IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 56 870
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 吴洋, 许州, 周霖, 李文君, 唐传祥 2012 61 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wu Y, Xu Z, Zhou L, Li W J, Tang C X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li R J, Ruan C J, Zhang H F 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 033107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 魏元璋, 李士锋, 王战亮, 黄华, 刘振帮, 何琥, 宫玉彬 2018 强激光与粒子束 30 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei Y Z, Li S F, Wang Z L, Huang H, Liu Z B, He H, Gong Y B 2018 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 30 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 张长青, 阮存军, 王树忠, 杨修东 2015 红外与毫米波学报 34 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang C Q, Ruan C J, Wang S Z, Yang X D 2015 J. Infrared Millmeter Waves 34 307
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Friedman M, Pasour J, Smithe D 1997 Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 3724
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Edward B A, Andrew N D, Mikhail I F, Nikolay G K, Nikolay F K, Mikhail I P, Alexander V S, Edl S, Eugeny I S, Vladimir V Y 2002 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 30 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhang W, Ju J C, Zhang J, Zhou Y X, Zhong H H 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 053102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Qi Z M, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Zhong H H, Xu L R, Yang L 2016 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 37 782
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘振帮, 金晓, 黄华, 陈怀璧 2012 61 128401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Jin X, Huang H, Chen H B 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 128401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 刘振帮, 黄华, 金晓, 袁欢, 戈弋, 何琥, 雷禄容 2015 64 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Yuan H, Ge Y, He H, Lei L R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 018401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu Z B, Huang H, Jin X, Lei L R, Zhu L, Li L L, Li S F, Yan W K, He H 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 093110
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 王淦平, 金晓, 黄华, 刘振帮 2017 66 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G P, Jin X, Huang H, Liu Z B 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 044102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Carlsten B E, Faehl R J, Fazio M V, Haynes W B, Stringfield R M 1994 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 22 719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 彭国良, 梁玉钦 2016 强激光与粒子束 28 053003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng G L, Liang Y Q 2016 High Power Laser and Particle Beams 28 053003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 薛明, 丁耀根, 王勇 2018 真空电子技术 8 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xue M, Ding Y G, Wang R 2018 Vaccum Electron. 8 43
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 戴宏毅, 肖亚斌, 王同权, 张树发 2001 湖南大学学报 28 6
Dai H Y, Xiao Y B, Wang T Q, Zhang S F 2001 J. Hunan Univ. 28 6
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7759
- PDF Downloads: 122
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: