-
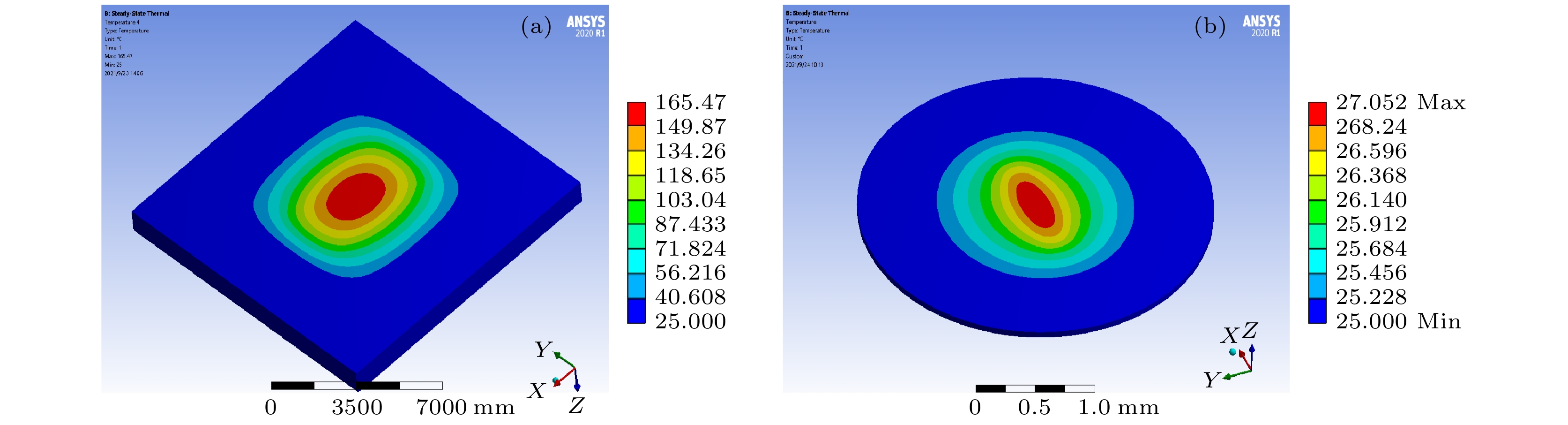
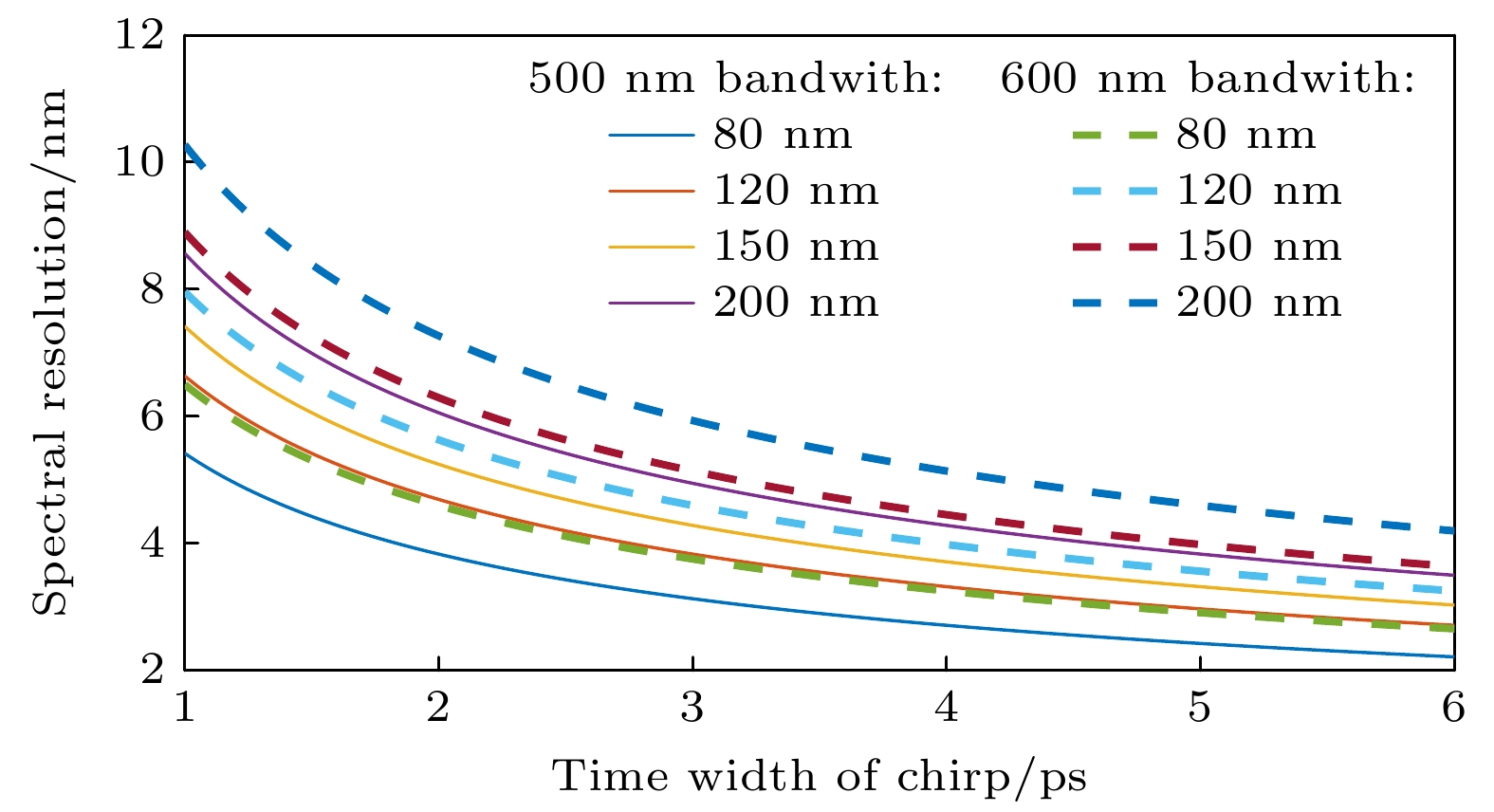
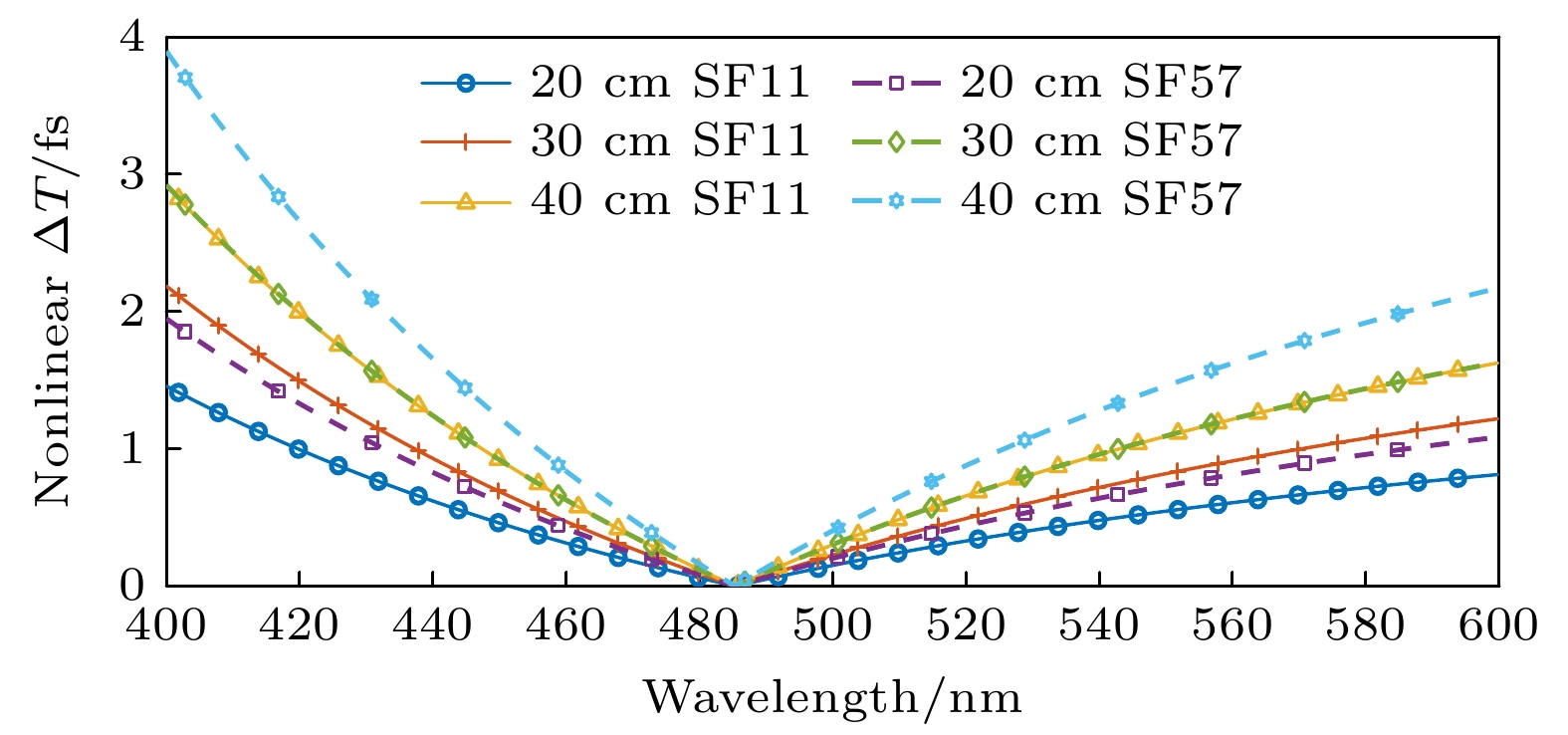
X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) pulse time diagnosis technology is often used to detect the relative arrival time of XFEL pulse and auxiliary laser near the experimental station. It is an important auxiliary technology and provides a reference signal for the pump-probe pulse in the XFEL laser pump-probe experiment. With the development of XFEL towards high repetition frequency and short pulse, higher requirements are put forward for diagnostic frequency, pump sample and resolution in time diagnosis. The technology is realized by the pump-probe method and optical cross-correlation method. When the XFEL pulse is incident on the high-bandwidth semiconductor solid target instantaneously, the complex refractive index of the solid target will change, then the arrival time of XFEL will be encoded in the mutation space. In thiswork, we design an XFEL pulse arrival time diagnostic device based on two methods: spatial coding and spectral coding. In this framework, the interaction between X-ray and solid target is explored by Beer's absorption theory and atomic scattering theory. Therefore, the response to X-ray absorption and refractive index in this process are investigated, and the solid target selection model is developed. This model is used to analyze the influence of solid target type and thickness in diagnosis, while avoiding situations where the sample is too hot due to a lot X-ray absorption. Moreover, the influence of hard X-ray on sample temperature at high frequency is considered, and the samples suitable for different X-ray bands are given. The chirped pulse modulation in spectral coding is analyzed, and the influence of dispersion medium and pulse parameters on the diagnostic resolution of spectral coding are obtained. Finally, the error effects of X-ray, spatial coding and spectral coding on the results are analyzed, and the analysis methods and consideration factors of the two coding methods are given. This work is of great significance in using the XFEL pulse arrival time diagnostic device.
-
Keywords:
- time diagnosis /
- optical cross correlation /
- X-ray free electron laser /
- pump probe
[1] 赵振堂, 冯超 2018 物理 47 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Z T, Feng C 2018 Physics 47 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bostedt C, Boutet S, Fritz D M, Huang Z, Lee H J, Lemke H T, Robert A, Schlotter W F, Turner J J, Williams G J 2016 Rev. Mod. Phys. 88 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Emma P, Akre R, Arthur J, et al. 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Harmand M, Coffee R, Bionta M R, Chollet M, French D, Zhu D, Fritz D M, Lemke H T, Medvedev N, Ziaja B, Toleikis S, Cammarata M 2013 Nat. Photonics 7 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Schulz S, Grguras I, Behrens C, Bromberger H, Costello J T, Czwalinna M K, Felber M, Hoffmann M C, Ilchen M, Liu H Y, Mazza T, Meyer M, Pfeiffer S, Predki P, Schefer S, Schmidt C, Wegner U, Schlarb H, Cavalieri A L 2015 Nat. Commun 6 5938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Grychtol P, Rivas D E, Baumann T M, et al. 2021 Opt. Express 29 37429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sato T, Letrun R, Kirkwood H J, et al. 2020 Optica 7 716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nakajima K, Joti Y, Katayama T, Owada S, Togashi T, Abe T, Kameshima T, Okada K, Sugimoto T, Yamaga M, Hatsui T, Yabashi M 2018 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 25 592
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Düsterer S, Rehders M, Al-Shemmary A, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. Spec. Top. Accel. Beams 17 23545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sanchez-Gonzalez A, Johnson A S, Fitzpatrick A, Hutchison C D M, Fare C, Cordon-Preciado V, Dorlhiac G, Ferreira J L, Morgan R M, Marangos J P, Owada S, Nakane T, Tanaka R, Tono K, Iwata S, van Thor J J 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 203105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hartmann N, Helml W, Galler A, Bionta M R, Grünert J, L. Molodtsov S, Ferguson K R, Schorb S, Swiggers M L, Carron S, Bostedt C, Castagna J C, Bozek J, Glownia J M, Kane D J, Fry A R, White W E, Hauri C P, Feurer T, Coffee R N 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Maltezopoulos T, Photonen D F M, Cunovic S, Wieland M, Drescher M 2008 New J. Phys. 10 1218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Schorb S, Gorkhover T, Cryan J P, Glownia J M, Bionta M R, Coffee R N, Erk B, Boll R, Schmidt C, Rolles D, Rudenko A, Rouzee A, Swiggers M, Carron S, Castagna J C, Bozek J D, Messerschmidt M, Schlotter W F, Bostedt C 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 121107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Beye M, Krupin O, Hays G, Reid A H, Rupp D, Jong S d, Lee S, Lee W S, Chuang Y D, Coffee R, Cryan J P, Glownia J M, Föhlisch A, Holmes M R, Fry A R, White W E, Bostedt C, Scherz A O, Durr H A, Schlotter W F 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 121108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Katayama T, Owada S, Togashi T, Ogawa K, Karvinen P, Vartiainen I, Eronen A, David C, Sato T, Nakajima K, Joti Y, Yumoto H, Ohashi H, Yabashi M 2016 Struct. Dynam. -US 3 034301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Droste S, Zohar S, Shen L, White V E, Diaz-Jacobo E, Coffee R N, Reid A H, Tavella F, Minitti M P, Turner J J, Robinson J S, Fry A R, Coslovich G 2020 Opt. Express 28 23545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bionta M R, Lemke H T, Cryan J P, Glownia J M, Bostedt C, Cammarata M, Castagna J C, Ding Y, Fritz D M, Fry A R, Krzywinski J, Messerschmidt M, Schorb S, Swiggers M L, Coffee R N 2011 Opt. Express 19 21855
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kirkwood H J, Letrun R, Tanikawa T, et al. 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 1650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Diez M, Galler A, Schulz S, Boemer C, Coffee R N, Hartmann N, Heider R, Wagner M S, Helml W, Katayama T, Sato T, Sato T, Yabashi M, Bressler C 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 3562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Owada S, Nakajima K, Togashi T, Katayama T, Yumoto H, Ohashi H, Yabashi M 2019 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 26 887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Krupin O, Trigo M, Schlotter W F, et al. 2012 Opt. Express 20 11396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Attwood D 1999 Soft X-rays and Extreme Ultraviolet Radiation (New York: Cambridge) pp98–122
[23] Teubner U, Wagner U, Forster E 2001 J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 34 2993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang K, Qian L J, Luo H, Yuan P, Zhu H Y 2006 Opt. Express 14 6366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang J, Zhang Y, Shen H, Jiang Y, Wang Z 2017 Opt. Eng. 56 076107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
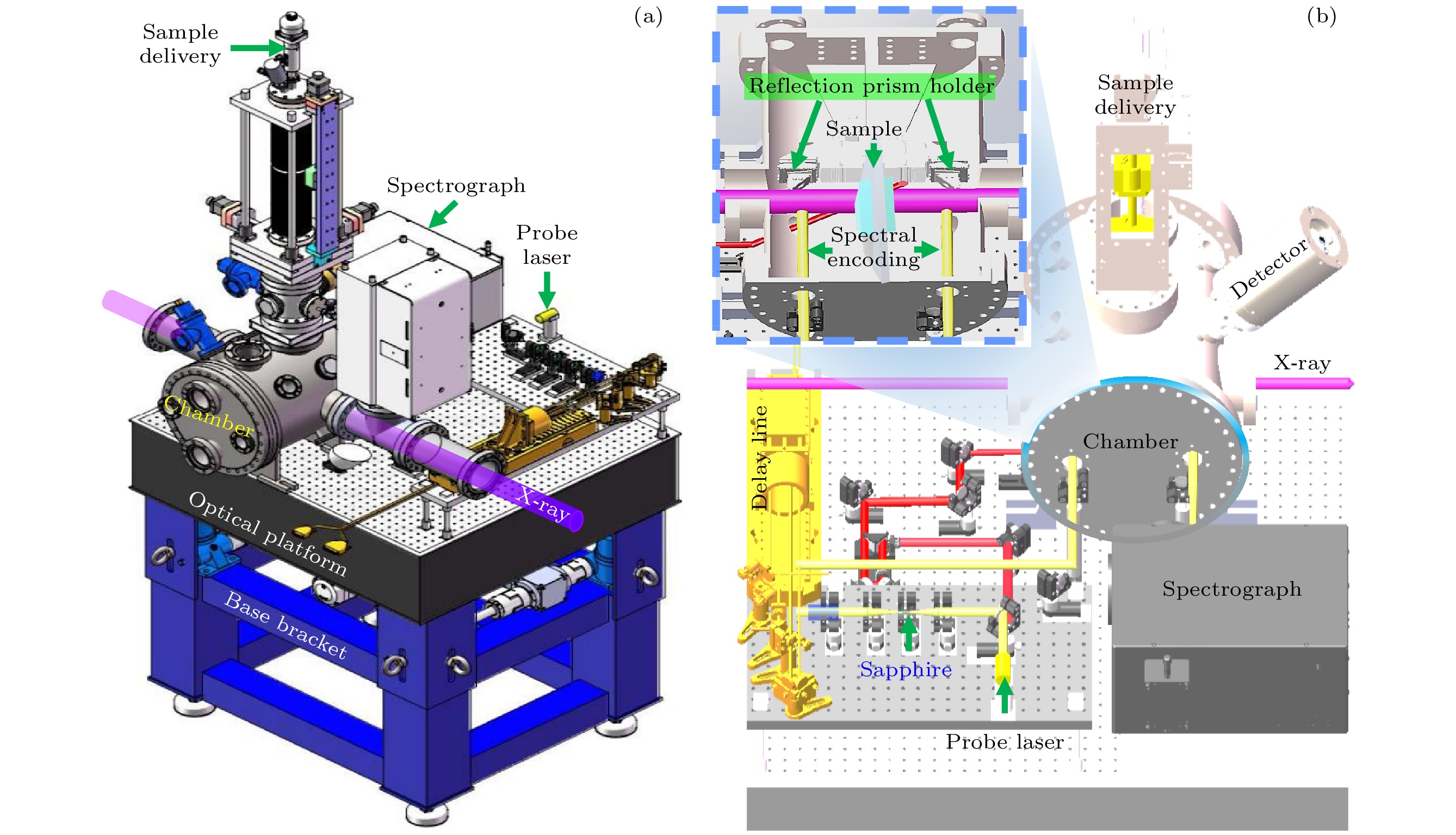
图 1 XFEL脉冲到达时间诊断系统光路示意图, 诊断系统位于XFEL束线末端, 实验线站之前. 其中红色光束为空间编码, 绿色光束为光谱编码光路, 插图为空间编码示意图
Figure 1. Optical layout of PAM (XFEL pulse arrival time monitor), PAM is located before the experimental station, at the end of the XFEL beam line. Red optical layout is spatial coding, green optical layout is spectral coding, illustration is a spatial coding diagram.
表 1 GaAs, Si3N4和金刚石膜三种半导体材料用于到达时间诊断的相关参数
Table 1. Parameters for GaAs, Si3N4 and diamond film semiconductor materials for arriving time diagnosis.
种类 规格 带宽 吸收长度* 密度 熔点 导热系数 mm2 eV nm g/cm3 ℃ W/(cm·K) Si3N4 102 5 360—4431 3.19 1800 1.369 GaAs 102 1.43 321—2166 5.31 1238 0.46 Diamond 102 5.5 367—3714 3.515 3550 23 * X射线波长范围0.4—2 nm 表 2 Si3N4, GaAs和金刚石膜中载流子的有效质量和弛豫时间
Table 2. Effective mass and relaxation time of carriers in GaAs, Si3N4 and diamond film.
样品 $ {m}_{{\rm{e}}}^{*} $ $ {m}_{{\rm{h}}}^{*} $ $ {\tau }_{\text{e}} $/ps $ {\tau }_{{\rm{h}}} $/ps Si3N4 0.3$ {m}_{{\rm{e}}}^{} $ 0.3$ {m}_{{\rm{e}}}^{} $ 0.5 0.5 GaAs 0.067$ {m}_{{\rm{e}}}^{} $ 0.4$ {m}_{{\rm{e}}}^{} $ 4.8 2 Diamond 0.28$ {m}_{{\rm{e}}}^{} $ 1.22$ {m}_{{\rm{e}}}^{} $ 1.5 1.4 -
[1] 赵振堂, 冯超 2018 物理 47 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Z T, Feng C 2018 Physics 47 481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bostedt C, Boutet S, Fritz D M, Huang Z, Lee H J, Lemke H T, Robert A, Schlotter W F, Turner J J, Williams G J 2016 Rev. Mod. Phys. 88 18
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Emma P, Akre R, Arthur J, et al. 2010 Nat. Photonics 4 641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Harmand M, Coffee R, Bionta M R, Chollet M, French D, Zhu D, Fritz D M, Lemke H T, Medvedev N, Ziaja B, Toleikis S, Cammarata M 2013 Nat. Photonics 7 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Schulz S, Grguras I, Behrens C, Bromberger H, Costello J T, Czwalinna M K, Felber M, Hoffmann M C, Ilchen M, Liu H Y, Mazza T, Meyer M, Pfeiffer S, Predki P, Schefer S, Schmidt C, Wegner U, Schlarb H, Cavalieri A L 2015 Nat. Commun 6 5938
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Grychtol P, Rivas D E, Baumann T M, et al. 2021 Opt. Express 29 37429
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sato T, Letrun R, Kirkwood H J, et al. 2020 Optica 7 716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nakajima K, Joti Y, Katayama T, Owada S, Togashi T, Abe T, Kameshima T, Okada K, Sugimoto T, Yamaga M, Hatsui T, Yabashi M 2018 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 25 592
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Düsterer S, Rehders M, Al-Shemmary A, et al. 2014 Phys. Rev. Spec. Top. Accel. Beams 17 23545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Sanchez-Gonzalez A, Johnson A S, Fitzpatrick A, Hutchison C D M, Fare C, Cordon-Preciado V, Dorlhiac G, Ferreira J L, Morgan R M, Marangos J P, Owada S, Nakane T, Tanaka R, Tono K, Iwata S, van Thor J J 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 122 203105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Hartmann N, Helml W, Galler A, Bionta M R, Grünert J, L. Molodtsov S, Ferguson K R, Schorb S, Swiggers M L, Carron S, Bostedt C, Castagna J C, Bozek J, Glownia J M, Kane D J, Fry A R, White W E, Hauri C P, Feurer T, Coffee R N 2014 Nat. Photonics 8 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Maltezopoulos T, Photonen D F M, Cunovic S, Wieland M, Drescher M 2008 New J. Phys. 10 1218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Schorb S, Gorkhover T, Cryan J P, Glownia J M, Bionta M R, Coffee R N, Erk B, Boll R, Schmidt C, Rolles D, Rudenko A, Rouzee A, Swiggers M, Carron S, Castagna J C, Bozek J D, Messerschmidt M, Schlotter W F, Bostedt C 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 121107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Beye M, Krupin O, Hays G, Reid A H, Rupp D, Jong S d, Lee S, Lee W S, Chuang Y D, Coffee R, Cryan J P, Glownia J M, Föhlisch A, Holmes M R, Fry A R, White W E, Bostedt C, Scherz A O, Durr H A, Schlotter W F 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 121108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Katayama T, Owada S, Togashi T, Ogawa K, Karvinen P, Vartiainen I, Eronen A, David C, Sato T, Nakajima K, Joti Y, Yumoto H, Ohashi H, Yabashi M 2016 Struct. Dynam. -US 3 034301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Droste S, Zohar S, Shen L, White V E, Diaz-Jacobo E, Coffee R N, Reid A H, Tavella F, Minitti M P, Turner J J, Robinson J S, Fry A R, Coslovich G 2020 Opt. Express 28 23545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Bionta M R, Lemke H T, Cryan J P, Glownia J M, Bostedt C, Cammarata M, Castagna J C, Ding Y, Fritz D M, Fry A R, Krzywinski J, Messerschmidt M, Schorb S, Swiggers M L, Coffee R N 2011 Opt. Express 19 21855
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kirkwood H J, Letrun R, Tanikawa T, et al. 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 1650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Diez M, Galler A, Schulz S, Boemer C, Coffee R N, Hartmann N, Heider R, Wagner M S, Helml W, Katayama T, Sato T, Sato T, Yabashi M, Bressler C 2021 Sci. Rep. 11 3562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Owada S, Nakajima K, Togashi T, Katayama T, Yumoto H, Ohashi H, Yabashi M 2019 J. Synchrotron Radiat. 26 887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Krupin O, Trigo M, Schlotter W F, et al. 2012 Opt. Express 20 11396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Attwood D 1999 Soft X-rays and Extreme Ultraviolet Radiation (New York: Cambridge) pp98–122
[23] Teubner U, Wagner U, Forster E 2001 J. Phys. B:At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 34 2993
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang K, Qian L J, Luo H, Yuan P, Zhu H Y 2006 Opt. Express 14 6366
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wang J, Zhang Y, Shen H, Jiang Y, Wang Z 2017 Opt. Eng. 56 076107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7285
- PDF Downloads: 147
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: