-
As one of the coherent diffractive imaging (CDI) techniques, coherent modulation imaging (CMI) is a lensless phase imaging technology with diffraction limited resolution in theory. Unlike multiple measurement phase retrieval algorithms, the CMI can achieve fast convergence speed with single-shot measurement by introducing a pre-characterized random phase modulator. Besides, it has simple structure without reference wave based on iterative engine. Despite the fact that the matured phase imaging can be used to implement the on-line wave diagnostics of laser pulse, in this work we accurately measure the face-type of optical component with peak-to-valley value below 0.5λ (λ = 632.8 nm) by using the CMI for the first time. In order to verify its measurement capability, 10 quartz windows with a diameter of 80 mm and PV value between 0.1λ and 0.5λ are repeatedly measured. Compared with the results of commercial interferometer, the root mean square error (Root MSE) of the peak-to-valley (PV) ratio of the results of the CMI is 0.0305λ, and the Root MSE of the root mean square (RMS) is 0.00522λ. The measurement accuracy of PV ratio and RMS can reach 0.1λ and 0.01λ respectively. In addition, the parallel flat with PV ratio = λ/20 is measured and analyzed with CMI, and its noise level is also analyzed. Considering that the potential improvement of CMI is available in the future, the CMI is expected to become a new technique for optical metrology with high precision, which is different from interferometry.
-
Keywords:
- phase retrieval /
- iterative engine /
- optical metrology /
- coherent diffractive imaging
[1] Rodenburg J M 2008 Adv. Imaging Electron Phys. 150 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rodenburg J M, Hurst A C, Cullis A G, Dobson B R, Pfeiffer F, Bunk O, David C, Jefimovs K, Johnson I 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 034801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shahmoradian S, Tsai E, Diaz A, Guizar-Sicairos M, Raabe J, Spycher L, Britschgi M, Ruf A, Stahlberg H, Holler M 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hoppe R, Reinhardt J, Hofmann G, Patommel J, Grunwaldt J D, Damsgaard C D, Wellenreuther G, Falkenberg G, Schroer C G 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 203104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hüe F, Rodenburg J M, Maiden A M, Sweeney F, Midgley P A 2010 Phys. Rev. B. 82 121415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shemilt L, Verbanis E, Schwenke J, Estandarte Ana K, Xiong G, Harder R, Parmar N, Yusuf M, Zhang F, Robinson Ian K 2015 Biophys. J. 108 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Faulkner H M L, Rodenburg J M 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 023903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Pennycook T J, Martinez G T, Nellist P D, Meyer J C 2019 Ultramicroscopy. 196 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kahnt M, Becher J, Brückner D, Fam Y, Sheppard T, Weissenberger T, Wittwer F, Grunwaldt J D, Schwieger W, Schroer C G 2019 Optica 6 1282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Clark J N, Huang X, Harder R J, Robinson I K 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 6066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Odstrčil M, Holler M, Guizar-Sicairos M 2018 Opt. Express 26 12585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang F, Rodenburg J M 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 121104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang F, Chen B, Morrison G R, Vila-Comamala J, Guizar-Sicairos M, Robinson I K 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 13367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dong X, Pan X, Liu C, Zhu J 2019 High Power. Laser. Sci. 7 e48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pan X, Veetil S, Liu C, Tao H, Jiang Y, Lin Q, Li X, Zhu J 2016 Laser Phys. Lett. 13 055001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Dong X, Pan X, Liu C, Zhu J 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 1762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] He X, Tao H, Pan X, Liu C, Zhu J 2018 Opt. Express 26 6239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Haynam C, Wegner P, Auerbach J, Bowers M, Dixit S, Erbert G, Heestand G, Henesian M, Hermann M, Jancaitis K 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 3276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tao H, Veetil S P, Cheng J, Pan X, Wang H, Liu C, Zhu J 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 1776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 柴立群, 于瀛洁, 石琦凯, 许乔, 温圣林, 侯晶 2010 中国激光 37 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chai L Q, Yu Y J, Shi Q K, Xu Q, Wen S L, Hou J 2010 Chin. J. Las. 37 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
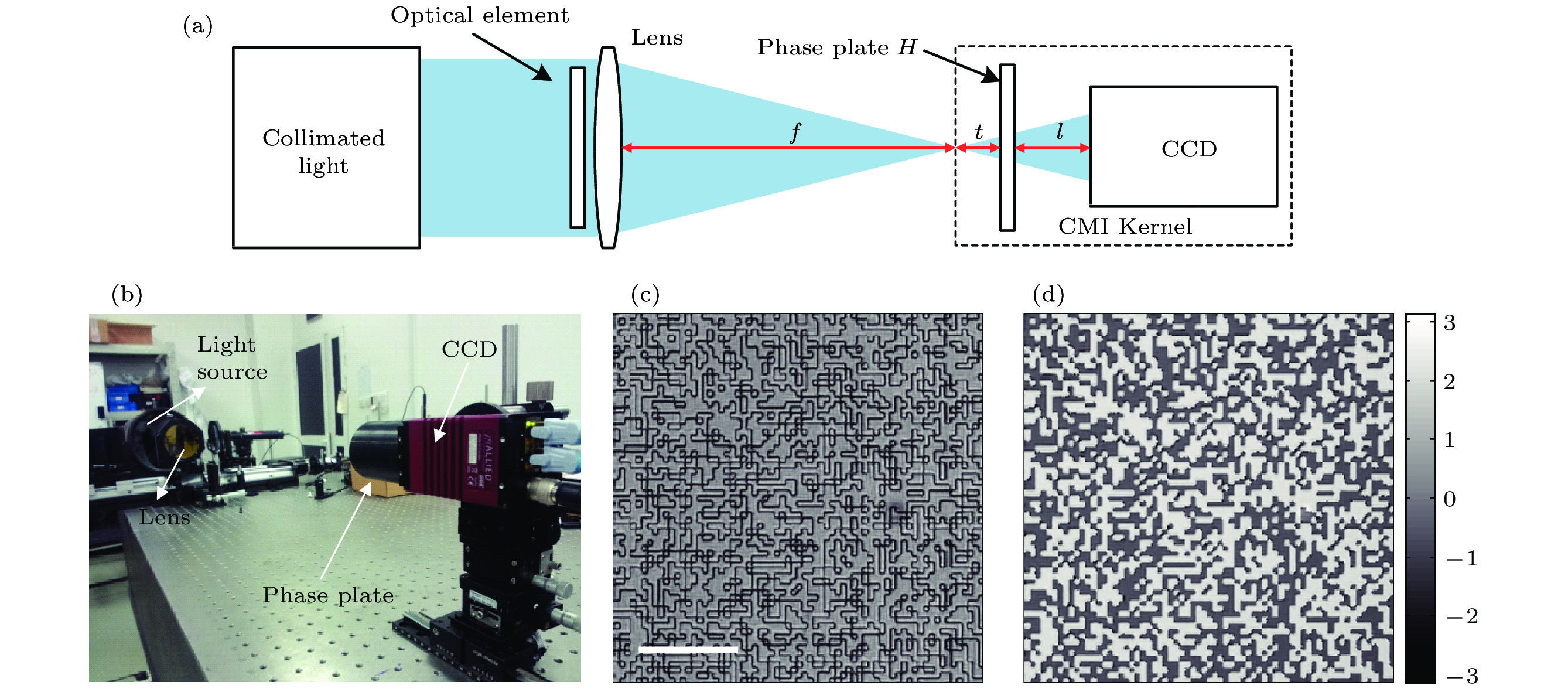
图 1 (a) CMI测量光学元件的基本光路; (b) 实验装置照片; (c), (d) 由ePIE算法标定的随机相位板振幅和相位分布, (c)中标尺长度为0.198 mm
Figure 1. (a) Basic scheme for the measurement of optical components using CMI; (b) photo of the experimental setup; (c) amplitude and (d) phase of the center part of the random phase plate reconstructed by ePIE. The scale bar of (c) is 0.198 mm.
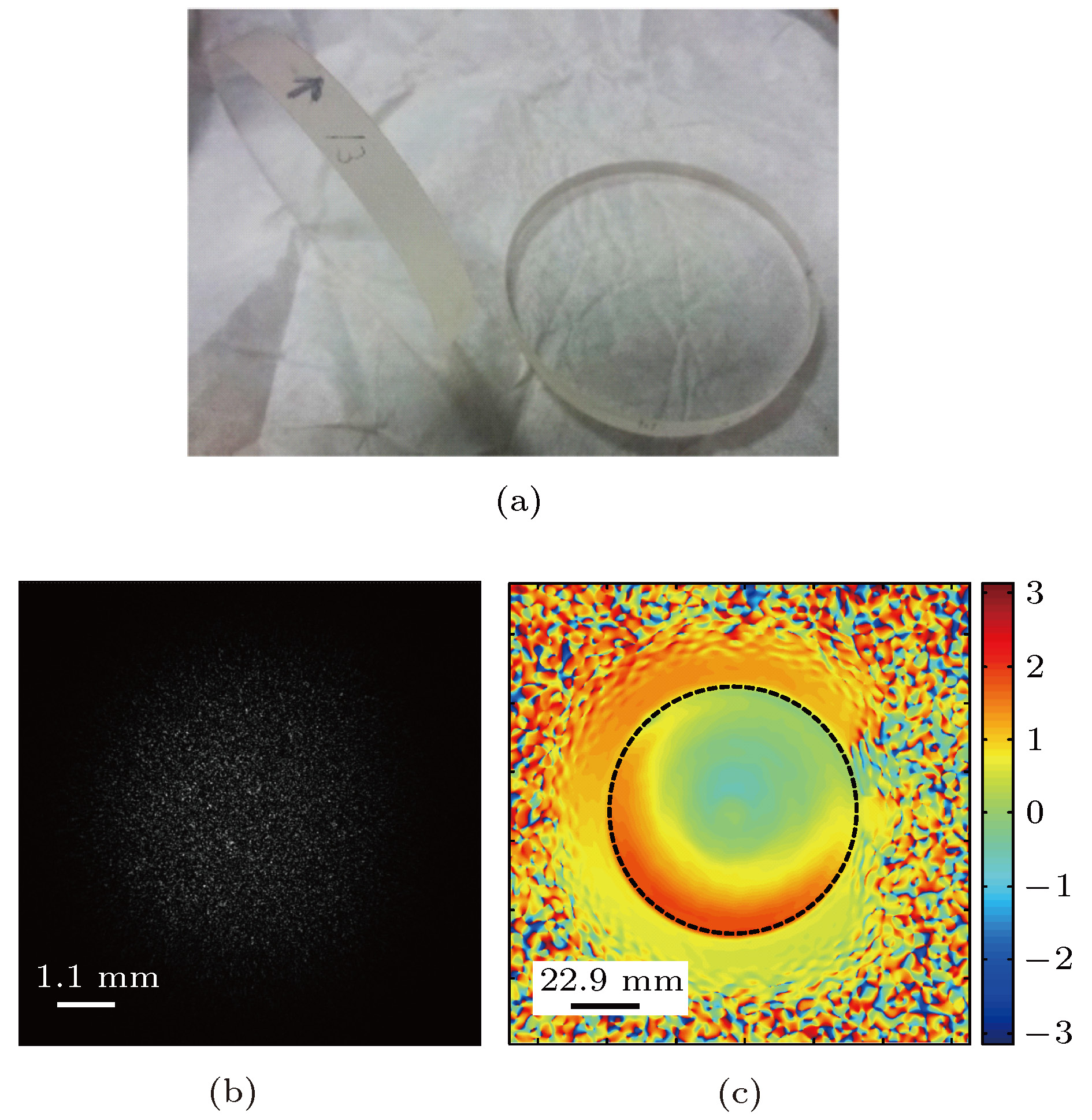
图 3 (a) 作为被测物的石英窗口; (b) CCD记录的衍射光斑; (c) 通过相位相减得到的石英窗口相位图, 其中由黑色虚线标记的区域的直径为79.1 mm
Figure 3. (a) Photo of the plate glasses used in experiments; (b) diffraction pattern recorded by CCD; (c) phase map of plate glass obtained directly by phase subtraction. The section marked by the black dashed circle with a diameter of 79.1 mm is used for the analysis of PV and RMS. The constant phase slope is not removed for these calculations.
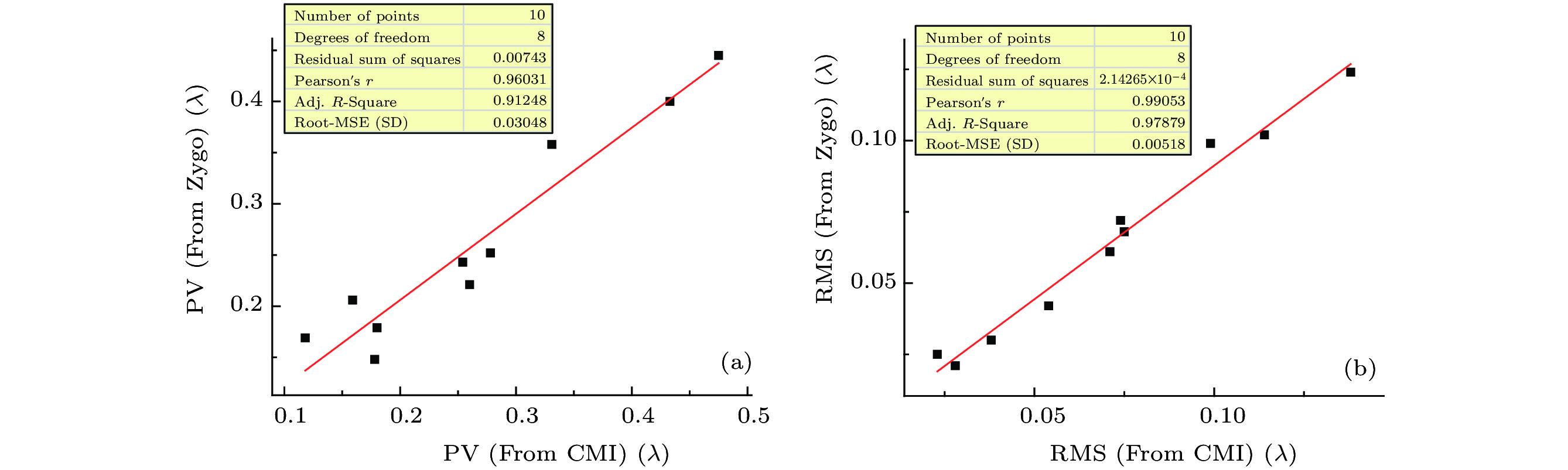
表 1 CMI和干涉仪的测量结果(λ)
Table 1. CMI and interferometer results (λ).
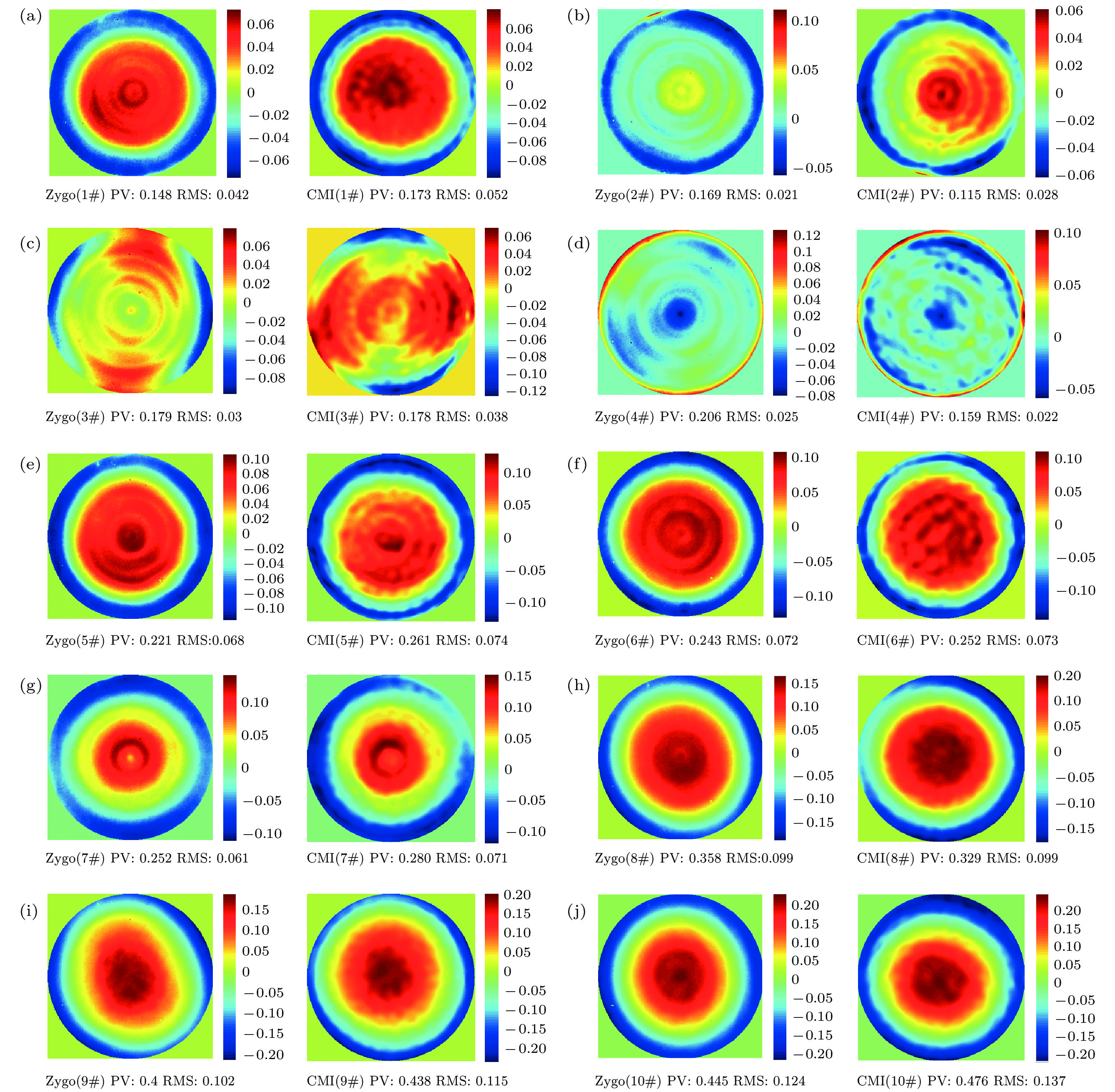
No. ${\overline {{\rm{PV}}} _{{\rm{CMI}}}}$ ${S_{{\rm{pv}}}}$ ${\rm{P}}{{\rm{V}}_{{\rm{Zygo}}}}$ ${\overline {{\rm{RMS}}} _{{\rm{CMI}}}}$ ${S_{{\rm{RMS}}}}$ ${\rm{RM}}{{\rm{S}}_{{\rm{Zygo}}}}$ 1 0.178 2.40 × 10–3 0.148 0.054 6.40 × 10–4 0.042 2 0.118 1.20 × 10–3 0.169 0.028 4.60 × 10–4 0.021 3 0.180 2.40 × 10–3 0.179 0.038 4.80 × 10–4 0.030 4 0.159 6.90 × 10–4 0.206 0.023 2.20 × 10–4 0.025 5 0.260 1.50 × 10–3 0.221 0.075 3.00 × 10–4 0.068 6 0.254 2.30 × 10–3 0.243 0.074 5.90 × 10–4 0.072 7 0.278 3.30 × 10–3 0.252 0.071 7.60 × 10–4 0.061 8 0.331 2.10 × 10–3 0.358 0.099 5.50 × 10–4 0.099 9 0.433 2.60 × 10–3 0.400 0.114 8.10 × 10–4 0.102 10 0.475 2.10 × 10–3 0.445 0.138 3.90 × 10–4 0.124 -
[1] Rodenburg J M 2008 Adv. Imaging Electron Phys. 150 87
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Rodenburg J M, Hurst A C, Cullis A G, Dobson B R, Pfeiffer F, Bunk O, David C, Jefimovs K, Johnson I 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 034801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shahmoradian S, Tsai E, Diaz A, Guizar-Sicairos M, Raabe J, Spycher L, Britschgi M, Ruf A, Stahlberg H, Holler M 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hoppe R, Reinhardt J, Hofmann G, Patommel J, Grunwaldt J D, Damsgaard C D, Wellenreuther G, Falkenberg G, Schroer C G 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 203104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hüe F, Rodenburg J M, Maiden A M, Sweeney F, Midgley P A 2010 Phys. Rev. B. 82 121415
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Shemilt L, Verbanis E, Schwenke J, Estandarte Ana K, Xiong G, Harder R, Parmar N, Yusuf M, Zhang F, Robinson Ian K 2015 Biophys. J. 108 706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Faulkner H M L, Rodenburg J M 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 023903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Pennycook T J, Martinez G T, Nellist P D, Meyer J C 2019 Ultramicroscopy. 196 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Kahnt M, Becher J, Brückner D, Fam Y, Sheppard T, Weissenberger T, Wittwer F, Grunwaldt J D, Schwieger W, Schroer C G 2019 Optica 6 1282
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Clark J N, Huang X, Harder R J, Robinson I K 2014 Opt. Lett. 39 6066
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Odstrčil M, Holler M, Guizar-Sicairos M 2018 Opt. Express 26 12585
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang F, Rodenburg J M 2010 Phys. Rev. B 82 121104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhang F, Chen B, Morrison G R, Vila-Comamala J, Guizar-Sicairos M, Robinson I K 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 13367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dong X, Pan X, Liu C, Zhu J 2019 High Power. Laser. Sci. 7 e48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Pan X, Veetil S, Liu C, Tao H, Jiang Y, Lin Q, Li X, Zhu J 2016 Laser Phys. Lett. 13 055001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Dong X, Pan X, Liu C, Zhu J 2018 Opt. Lett. 43 1762
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] He X, Tao H, Pan X, Liu C, Zhu J 2018 Opt. Express 26 6239
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Haynam C, Wegner P, Auerbach J, Bowers M, Dixit S, Erbert G, Heestand G, Henesian M, Hermann M, Jancaitis K 2007 Appl. Opt. 46 3276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tao H, Veetil S P, Cheng J, Pan X, Wang H, Liu C, Zhu J 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 1776
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 柴立群, 于瀛洁, 石琦凯, 许乔, 温圣林, 侯晶 2010 中国激光 37 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chai L Q, Yu Y J, Shi Q K, Xu Q, Wen S L, Hou J 2010 Chin. J. Las. 37 809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12559
- PDF Downloads: 266
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: