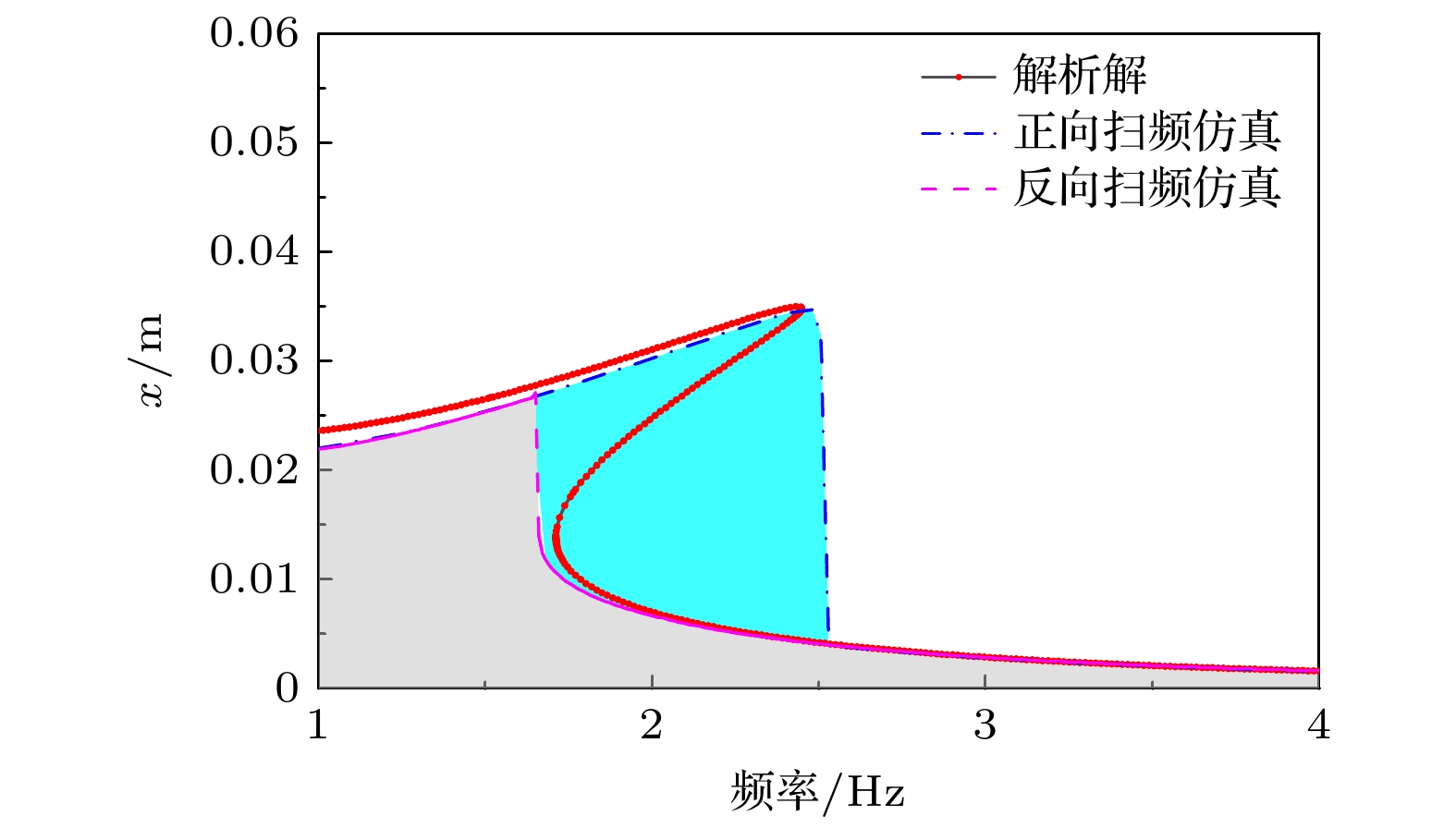
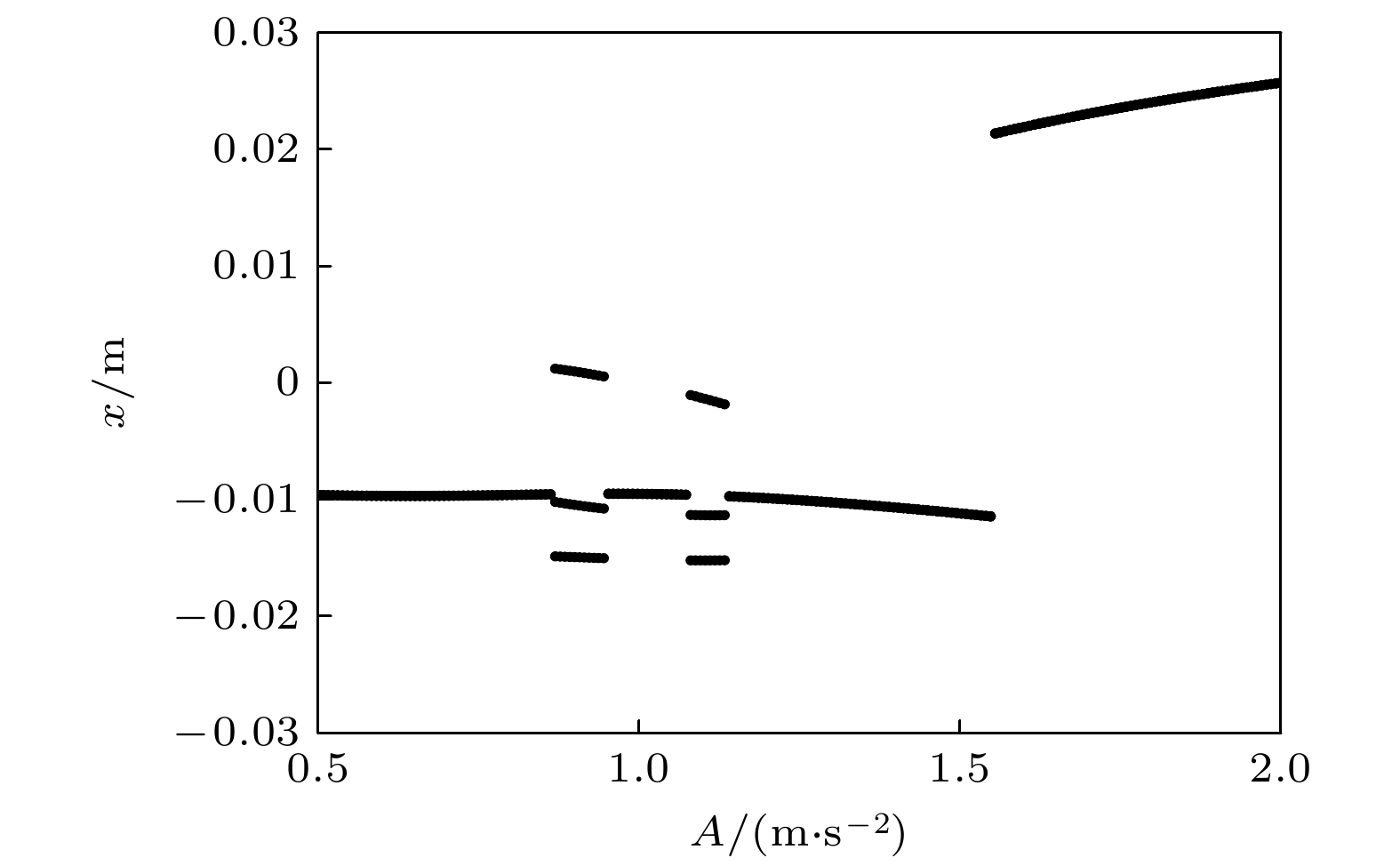
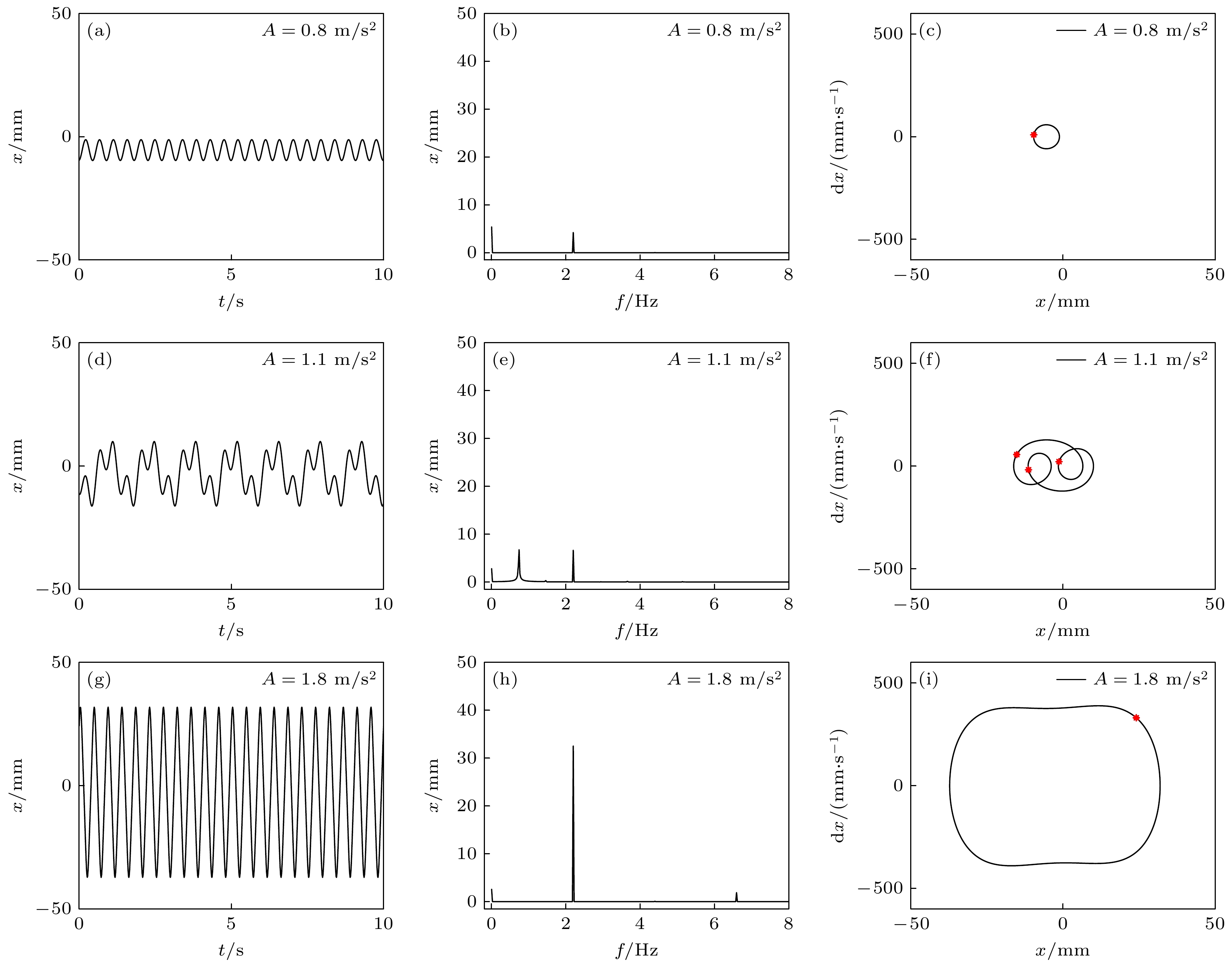
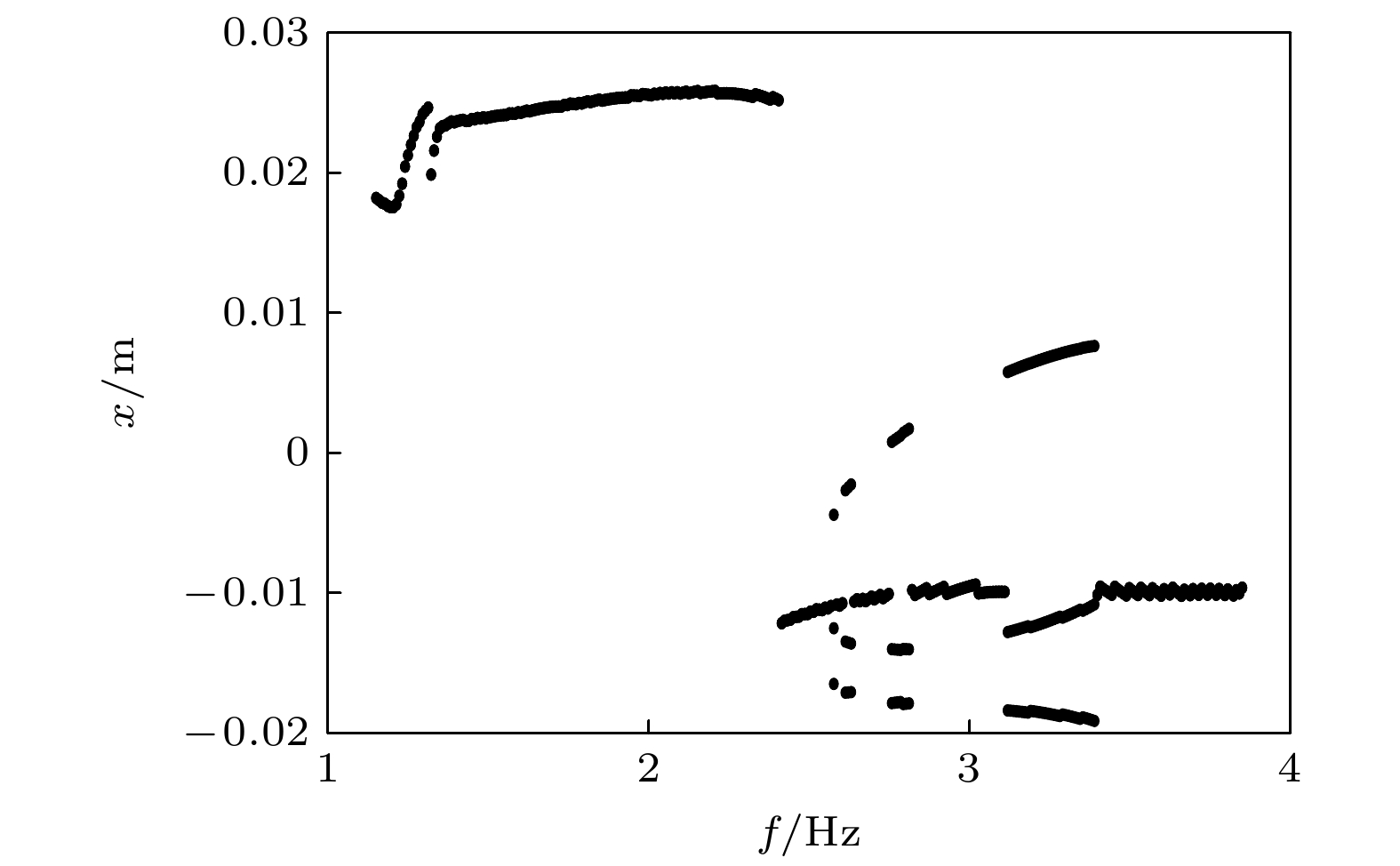
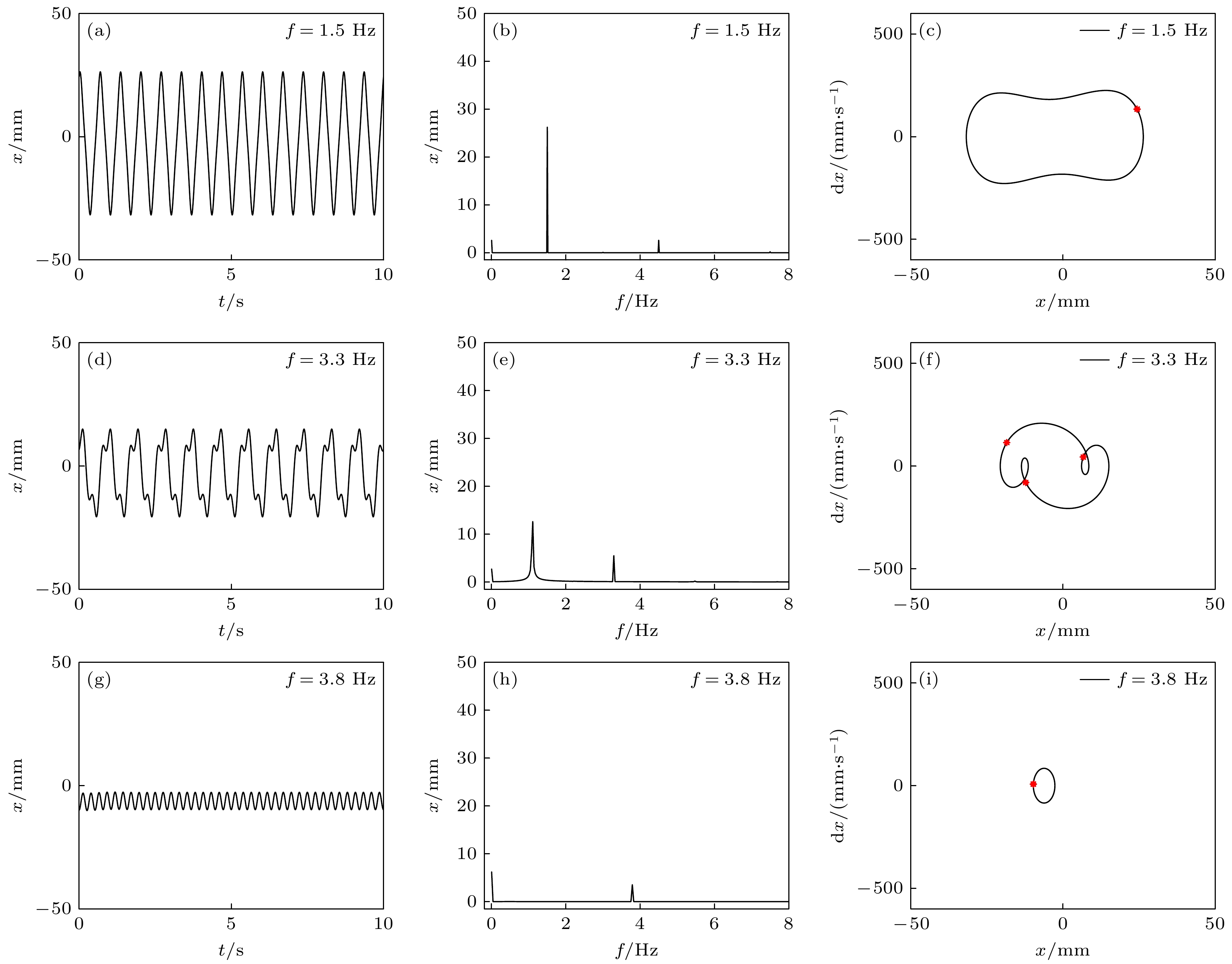
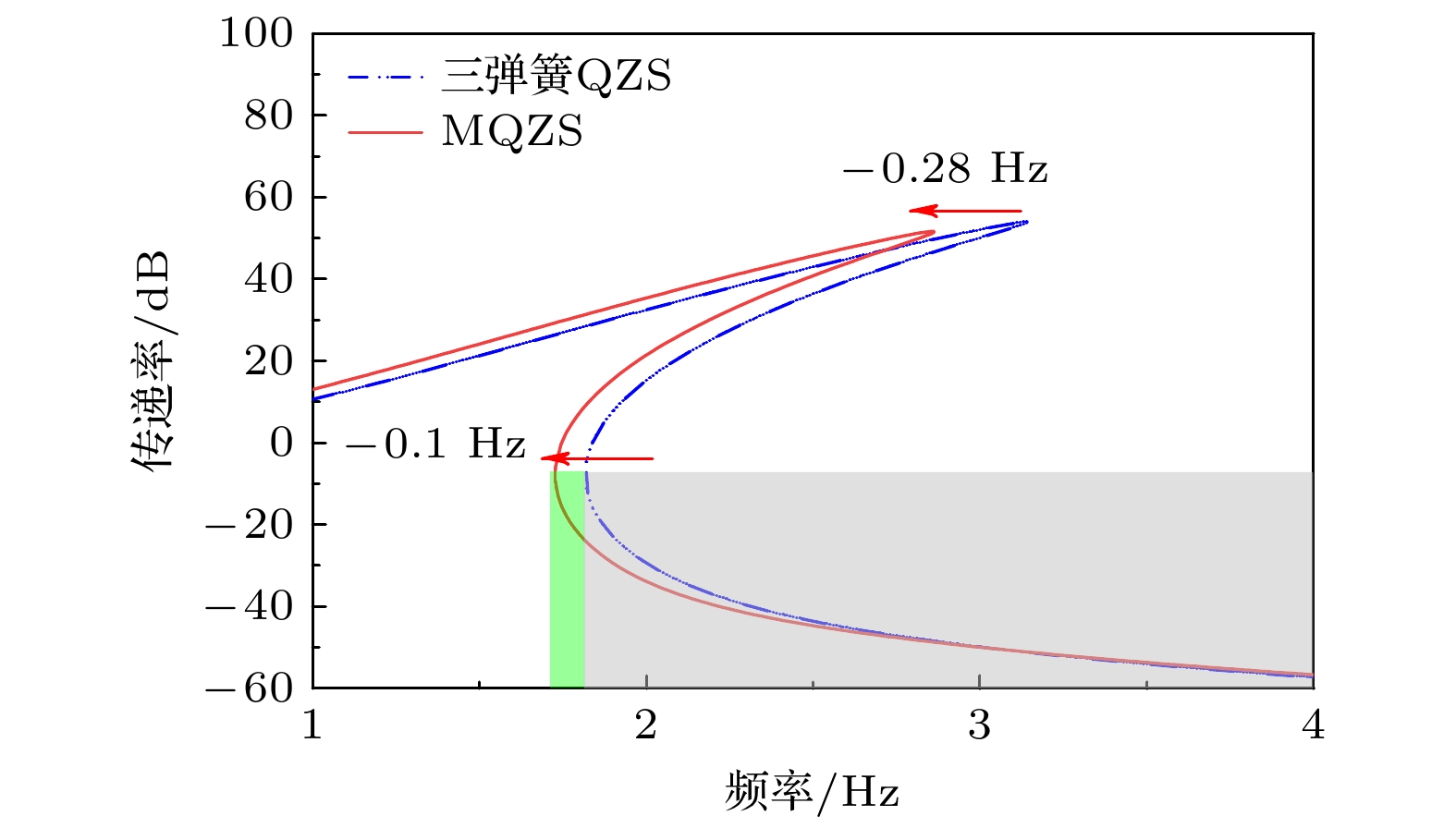
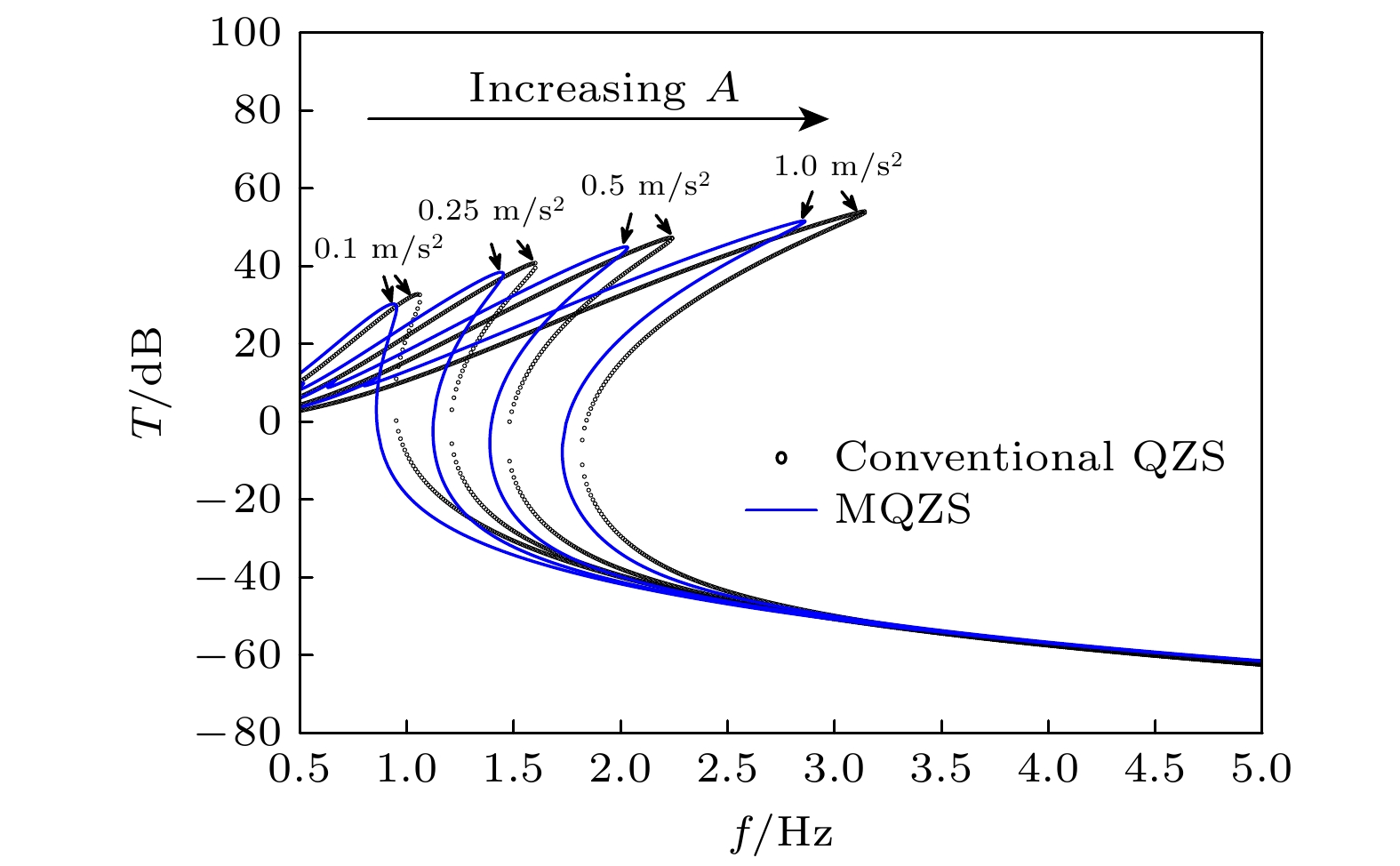
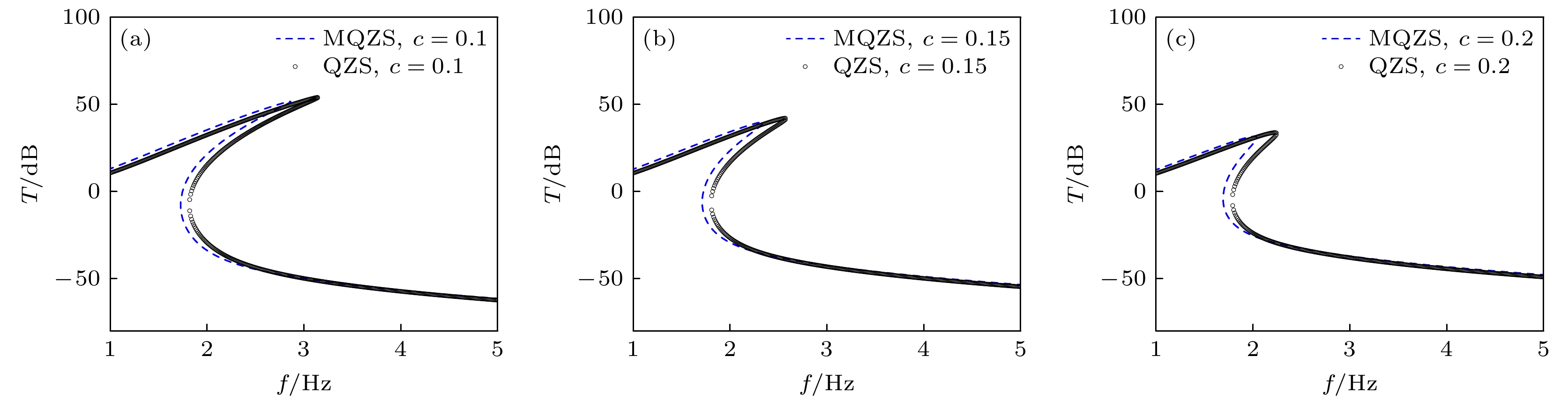
-
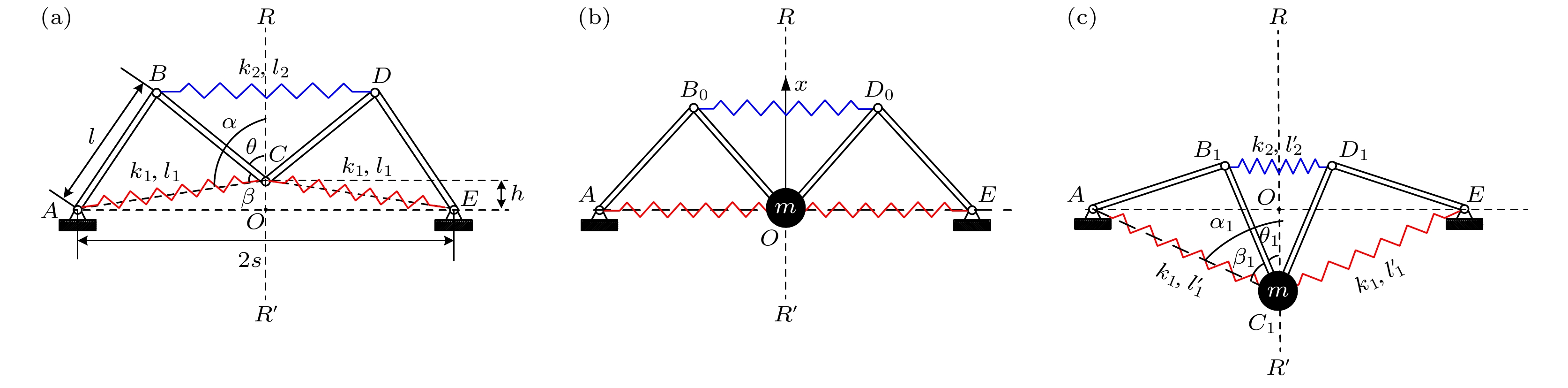
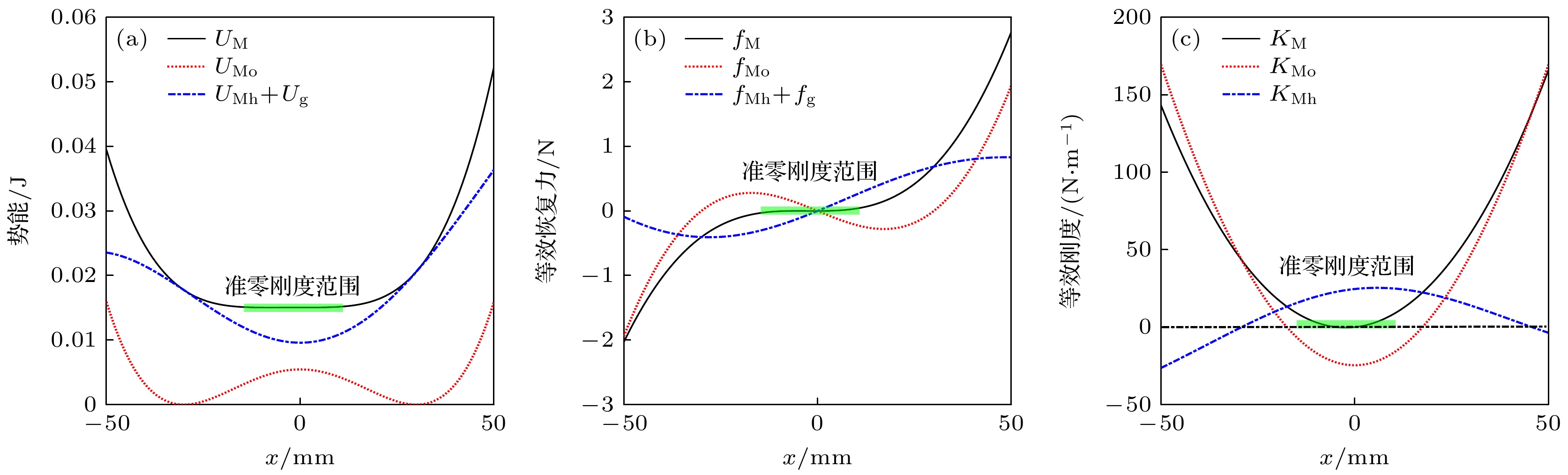
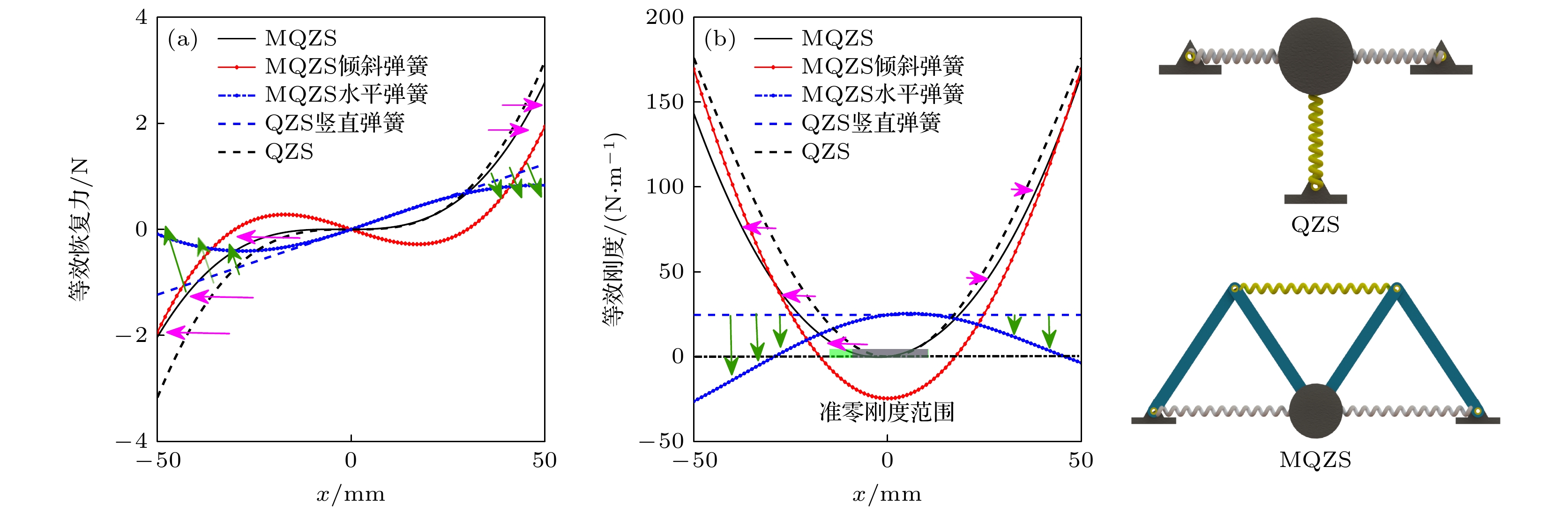
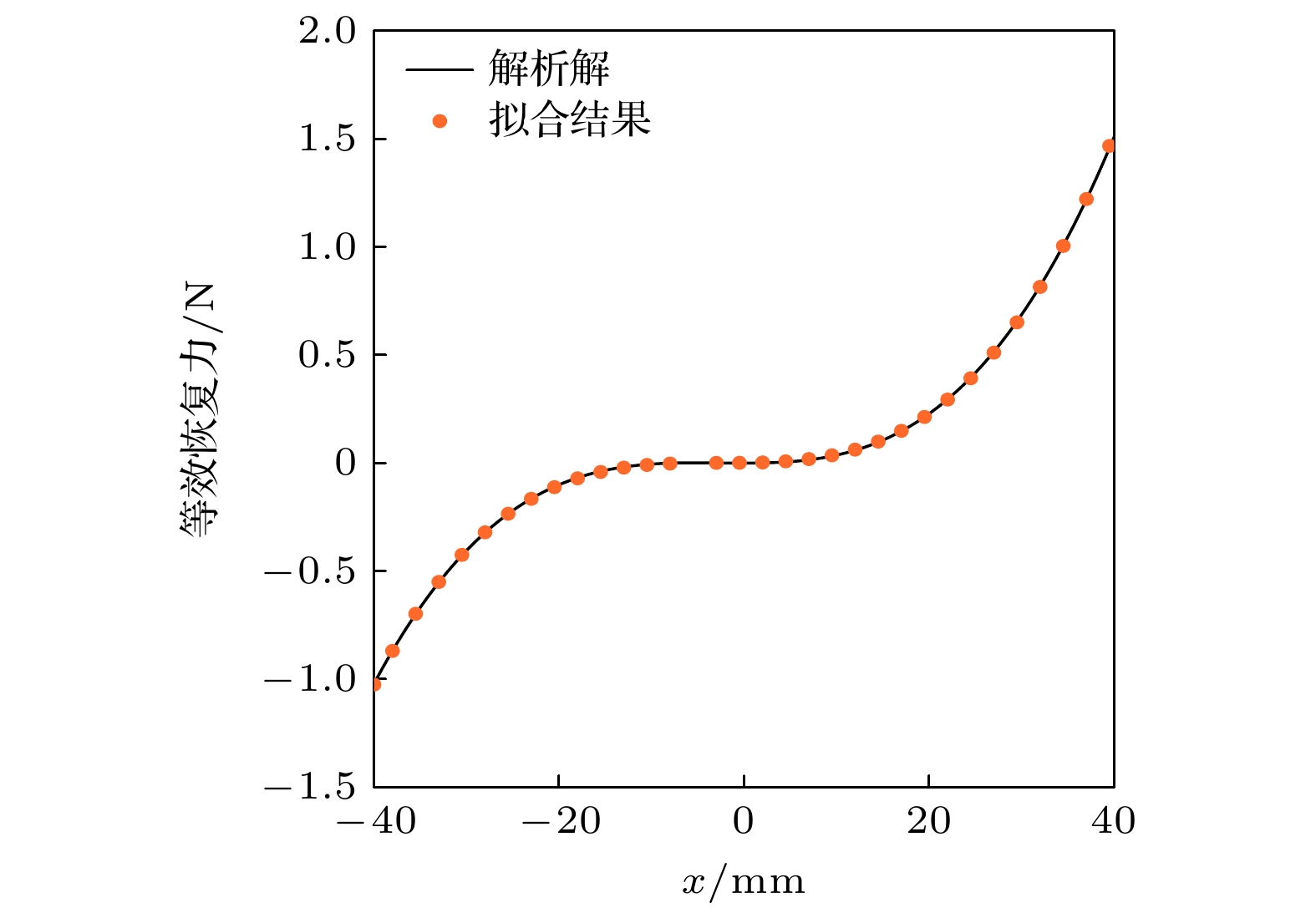
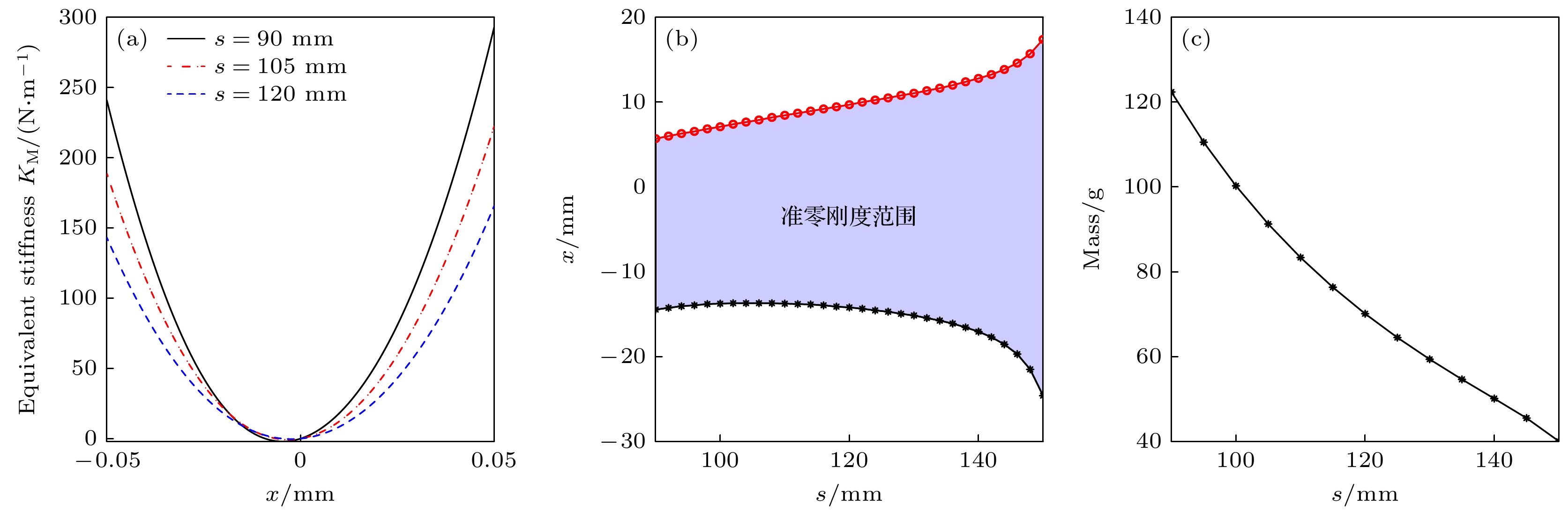
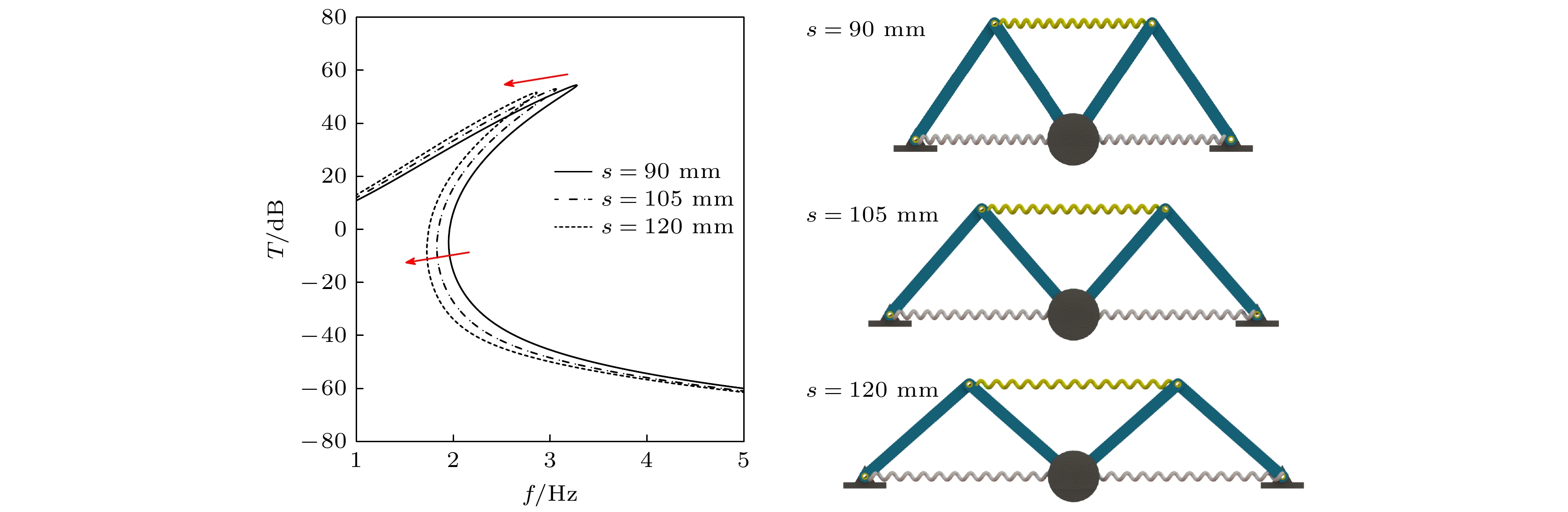
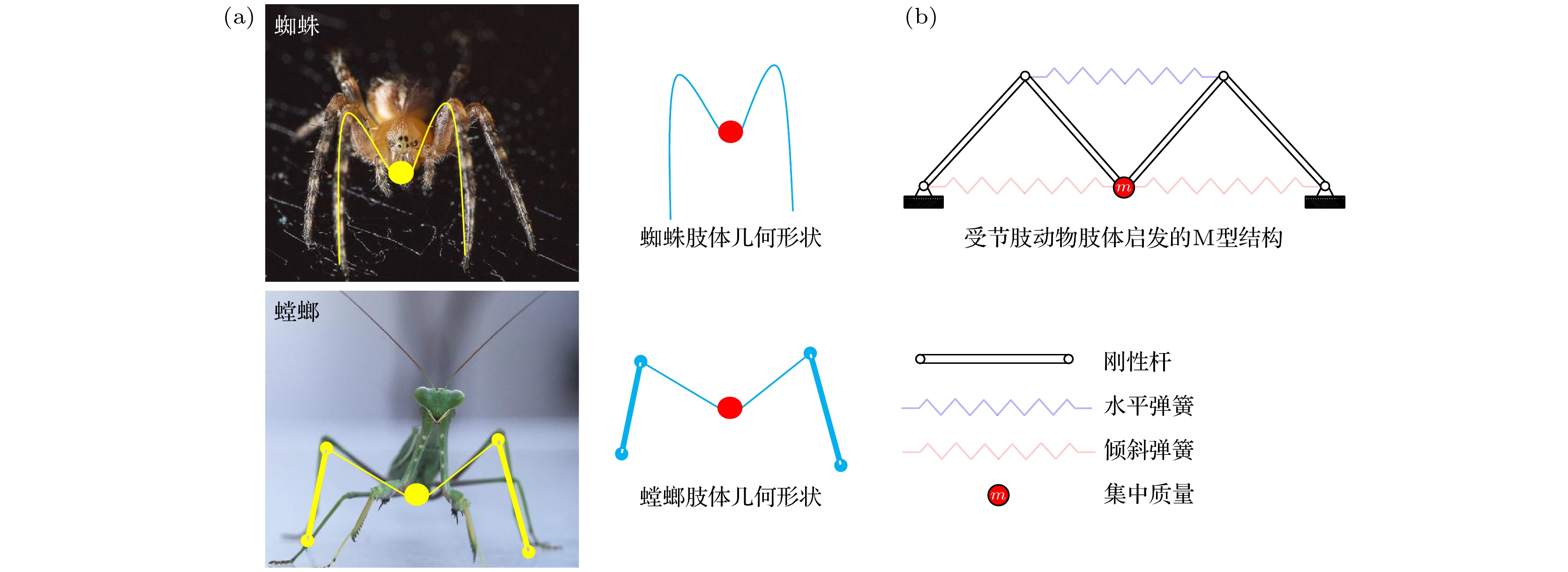
蜘蛛、螳螂等节肢动物能够在晃动的蛛网或树叶上保持身体的稳定性, 其类M形肢体结构的作用不可忽视. 受此启发, 本文提出一种基于节肢动物肢体结构的仿生M形低频隔振结构. 首先, 提出仿生M形低频隔振结构的设计方法, 并建立其动力学模型. 通过对其等效刚度、准零刚度范围等静态特性的对比分析, 发现仿生M形结构的非线性刚度能够有效拓宽准零刚度范围. 运用谐波平衡法进行近似求解, 得到其频率响应特性, 并分析其频率和幅值分岔动力学特性. 通过与经典三弹簧准零刚度结构对比, 发现M形仿生结构能够有效降低隔振频率, 并能降低隔振频带内的传递率. 最后, 研究了M形仿生结构的几何形状对其隔振性能的影响规律. 结果表明, 类似蜘蛛肢体的扁平状M形结构具有更低的隔振频率, 更好的低频隔振效果.Arthropods, including spiders and mantises, can maintain their body stability on shaking surfaces, such as spiderwebs or leaves. This impressive stability can be attributed to the specific geometric shape of their limbs, which exhibit an M-shaped structure. Inspired by this geometry, this work proposes an arthropod-limb-inspired M-shaped structure for low-frequency vibration isolation. First, the design method of the M-shaped quasi-zero-stiffness (QZS) structure is presented. A static analysis of potential energy, restoring force, and equivalent stiffness is conducted, showing that the M-shaped structure enables a horizontal linear spring to generate nonlinear stiffness in the vertical direction. More importantly, this nonlinear stiffness effectively compensates for the negative stiffness in large-displacement responses, thereby achieving a wider quasi-zero-stiffness region than the conventional three-spring-based QZS structure. Subsequently, the harmonic balance method is employed to derive approximate analytical solutions for the M-shaped QZS structure, which are well validated through numerical simulation. A comparison between the proposed M-shaped QZS structure and the conventional three-spring-based QZS structure is performed. Results show that the M-shaped QZS structure is advantageous for reducing both the cut-in isolation frequency and the resonance frequency. In particular, under large excitation or small damping conditions, the performance improvement of the M-shaped QZS structure in terms of reducing the resonance frequency and maximum response becomes more pronounced. The underlying mechanism behind this feature is primarily attributed to the expanded QZS region induced by the M-shaped structure. Finally, since the M-shaped structures vary among different arthropods, the effect of the geometry of M-shaped structures on low-frequency vibration performance is investigated. Interestingly, a trade-off between vibration isolation performance and loading mass is observed. As the M-shaped structure becomes flatter and the QZS region expands, the cut-in isolation frequency, resonance frequency/peak, and loading mass all decrease. This occurs because a flatter M-shaped structure leads to a reduction in the equivalent stiffness generated by the horizontal stiffness. Therefore, as the loading mass capacity decreases, the low-frequency vibration isolation performance is enhanced. This novel finding provides a reasonable explanation for why most arthropods possess many pairs of limbs, allowing the loading mass to be distributed while achieving excellent low-frequency vibration isolation.
-
Keywords:
- bio-inspired structure /
- low-frequency vibration isolation /
- nonlinear vibration /
- arthropods
-
表 1 结构参数
Table 1. Structure Parameters.
MQZS结构参数 取值 三弹簧QZS结构参数 取值 水平间距s/mm 120 水平间距s1/mm 120 杆长l/mm 80 初始高度h1/mm 30 初始高度h/mm 30 斜弹簧刚度k11/(N·m–1) 400 斜弹簧刚度k1/(N·m–1) 400 垂直弹簧刚度k12/(N·m–1) 24.62 -
[1] Jiao X L, Zhang J X, Li W B, Wang Y Y, Ma W L, Zhao Y 2023 Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 138 100898
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li L, Wang L, Yuan L, Zheng R, Wu Y P, Sui J, Zhong J 2021 Acta Astronaut. 180 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20210017871 [2025-05-07]
[4] 孟光, 董瑶海, 周徐斌, 申军烽, 刘兴天 2019 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学 49 024508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Meng G, Dong Y H, Zhou X B, Shen J F, Liu X T 2019 Sci. Sin-Phys. Mech. Astron. 49 024508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] McPherson K, Hrovat K, Kelly E, Keller J 2015 A Researcher’s Guide to Acceleration Environment on the International Space Station (Washington, D. C. : NASA) pp37-41
[6] 刘海平, 张世乘, 门玲鸰, 何振强 2022 71 160701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu H P, Zhang S C, Men L L, He Z Q 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 160701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Luo H T, Fan C H, Li Y X, Liu G M, Yu C S 2023 Eur. J. Mech. A-Solid. 97 104833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Molyneux W G 1958 Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Tec. 30 160
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Carrella A, Brennan M J, Waters T P 2007 J. Sound Vib. 301 678
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张月英 2014 硕士学位论文 (湖南: 湖南大学)
Zhang Y Y 2014 M. S. Thesis (Hunan: Hunan University
[11] Kovacic I, Brennan M J, Waters T P 2008 J. Sound Vib. 315 700
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou J X, Wang X L, Xu D L, Bishop S 2015 J. Sound Vib. 346 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhao F, Ji J C, Ye K, Luo Q T 2020 Mech. Syst. Signal Pr. 144 106975
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Deng T C, Wen G L, Ding H, Lu Z Q, Chen L Q 2020 Mech. Syst. Signal Pr. 145 106967
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu C R, Yu K P, Liao B P, Hu R P 2021 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 95 105654
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 郝志峰 2016 博士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学)
Hao Z F 2016 Ph. D. Dissertation (Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology
[17] 阮子悦 2023 硕士学位论文 (石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学)
Ran Z R 2023 M. S. Thesis (Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang TieDao University
[18] Yan B, Yu N, Wang Z H, Wu C Y, Wang S, Zhang W M 2022 J. Sound Vib. 527 116865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu X T, Huang X C, Hua H X 2013 J. Sound Vib. 332 3359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang K, Zhou J X, Chang Y P, Ouyang H J, Xu D L, Yang Y 2020 Nonlinear Dynam. 101 755
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu W J, Chen X D, Shan Y H 2014 J. Sound Vib. 333 2958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 安隽翰 2021 硕士学位论文 (南京: 南京航空航天大学)
An J H, 2021 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics
[23] Yan G, Zou H X, Wang S, Zhao L C, Wu Z Y, Zhang W M 2021 Appl. Mech. Rev. 73 020801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wu Z J, Jing X J, Bian J, Li F M, Allen R 2015 Bioinspir. Biomim. 10 056015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yan G, Wang S, Zou H X, Zhao L C, Gao Q H, Zhang W M 2020 Sci. China Tech. Sci. 63 2617
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Shi X J, Xu J, Chen T K, Qian C, Tian W J 2023 J. Bionic Eng. 20 2194
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zeng R, Wen G L, Zhou J X, Zhao G 2021 Acta Mech. Sinica-PRC 37 1152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Yan G, Zou H X, Wang S, Zhao L C, Wu Z Y, Zhang W M 2022 Mech. Syst. Signal Pr. 162 108010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Jin G X, Wang Z H, Yang T Z 2022 Appl. Math. Mech. -Engl. Ed. 43 813
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ling P, Miao L L, Zhang W M, Wu C Y, Yan B 2022 Mech. Syst. Signal Pr. 171 108955
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Long S M, Leonard A, Carey A, Jakob E M 2015 J. Arachnol. 43 111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 237
- PDF下载量: 6
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: