-
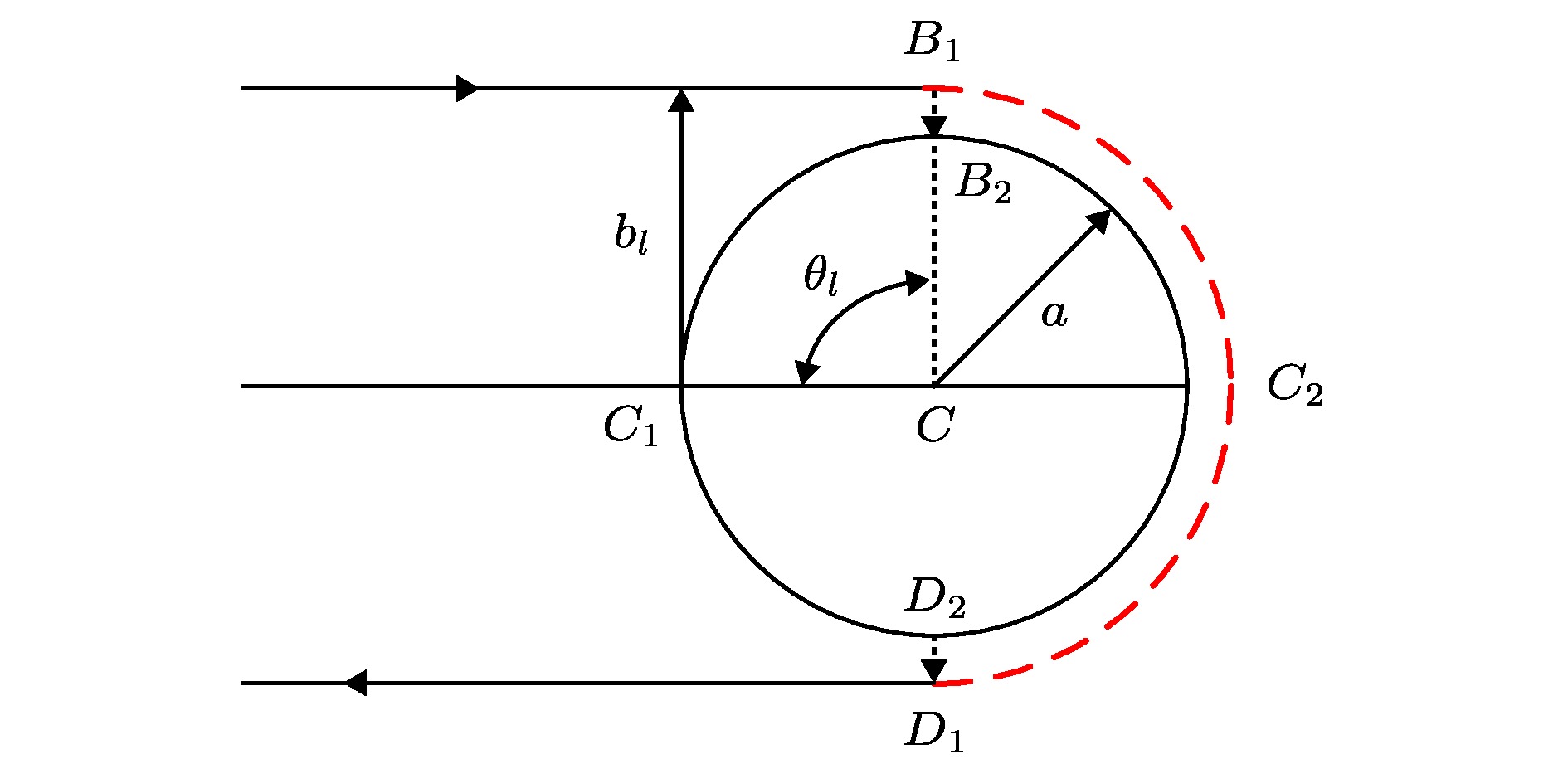
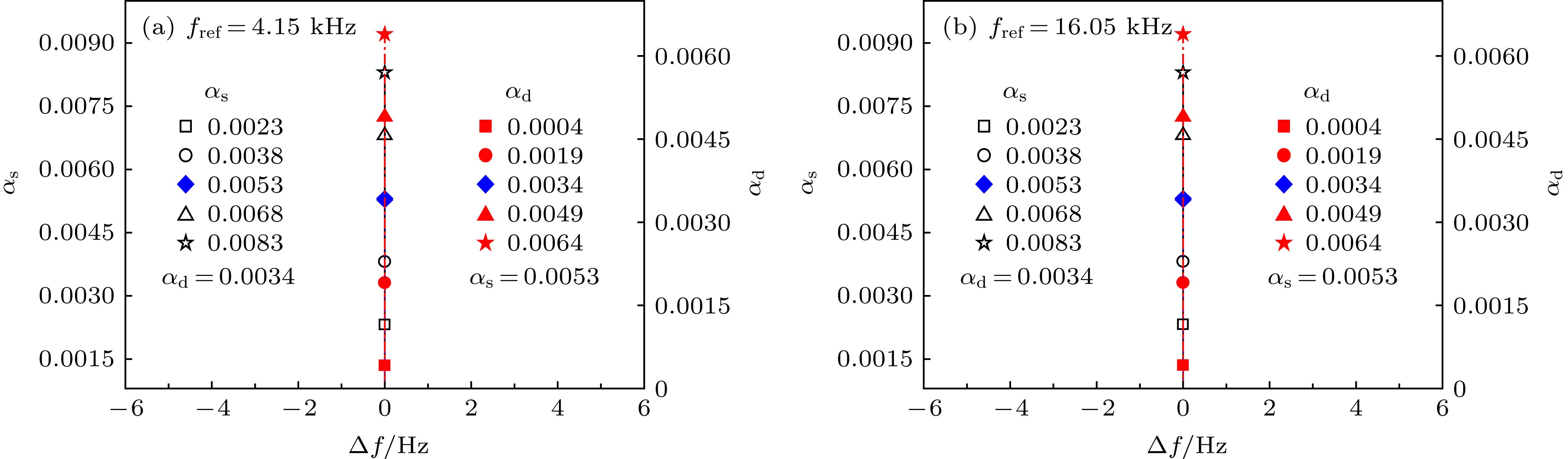
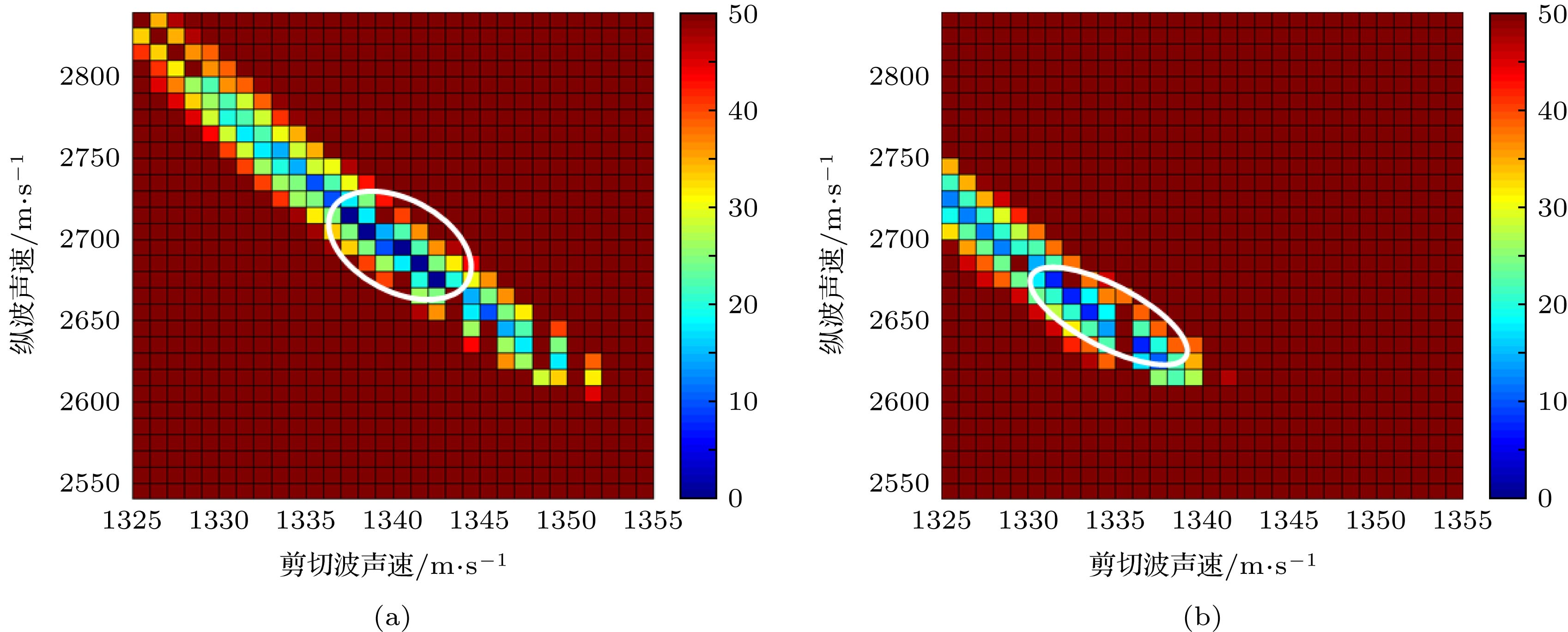
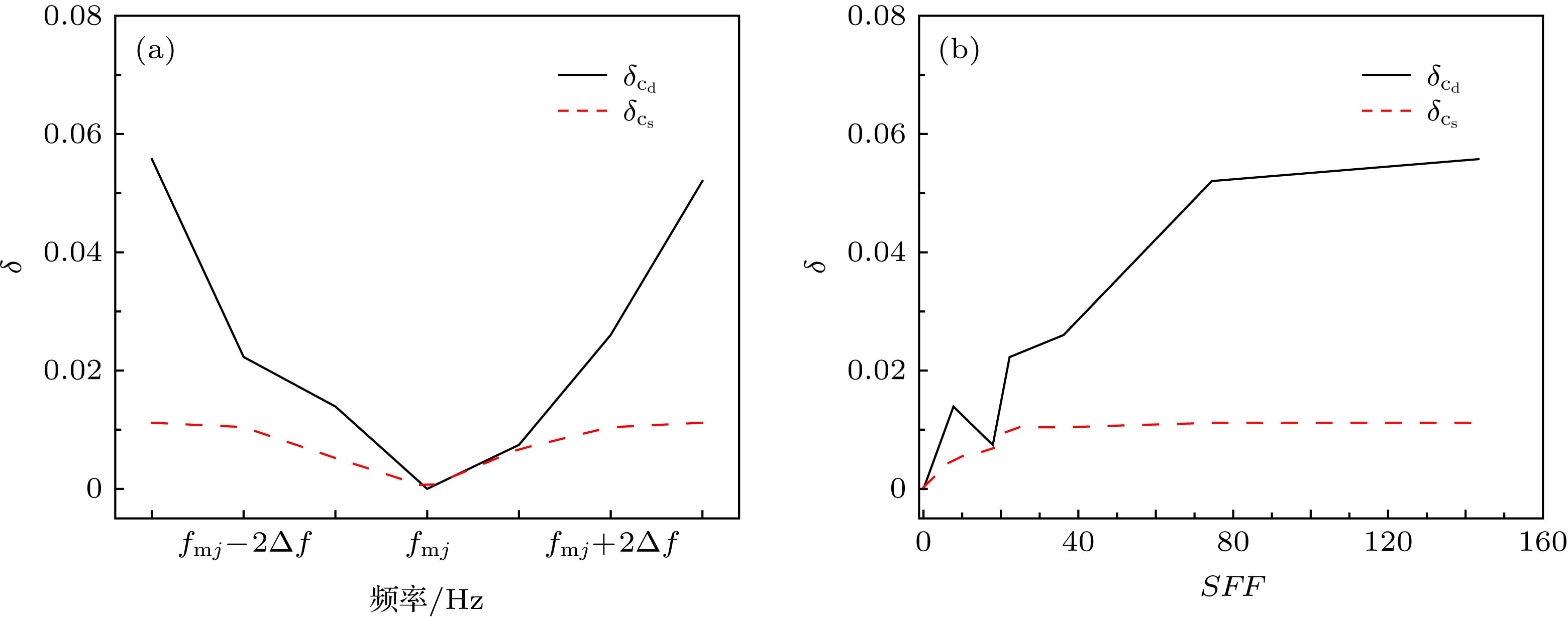
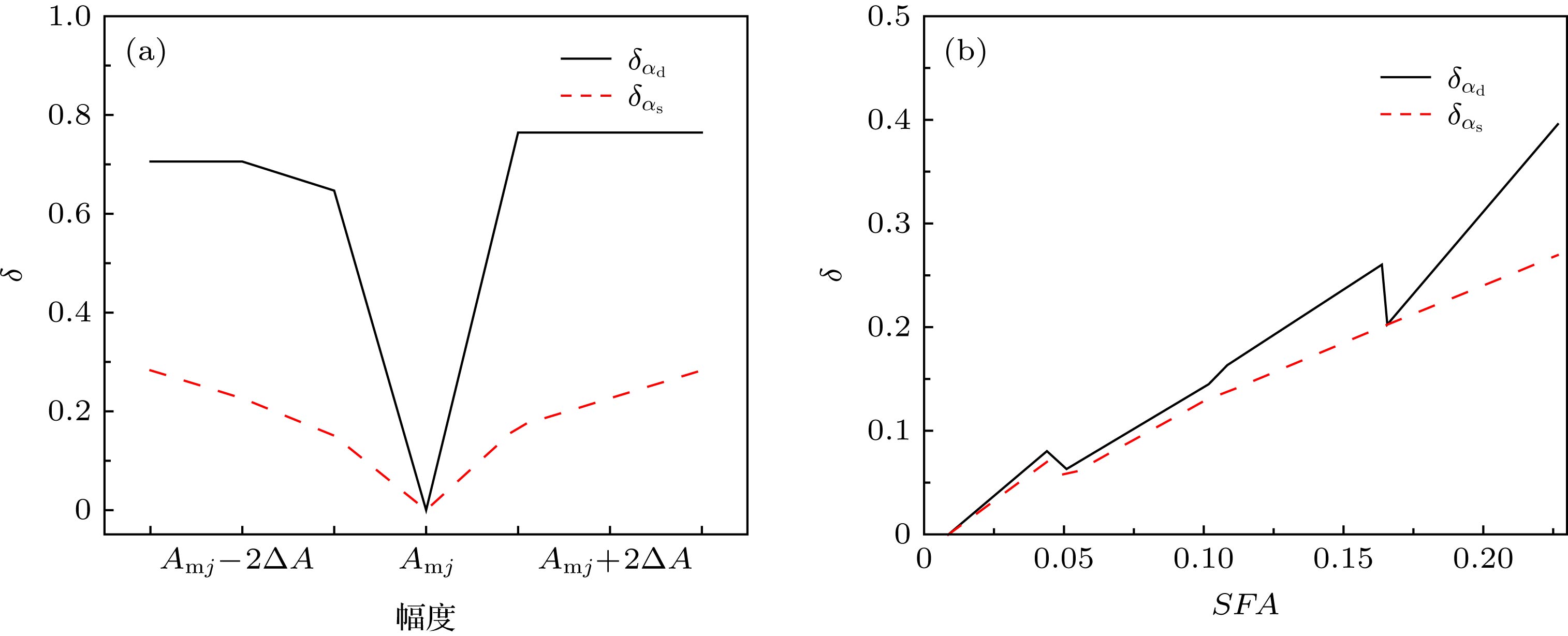
The high-precision molding capability of complex surfaces and structures makes three-dimensional (3D) printing technology more widely used in underwater acoustic models and structural molding. The plastic polymer material, as the main material in the field of 3D printing, possesses the acoustic parameters that are directly related to the acoustic properties of 3D printed underwater acoustic models and structures. Based on the Rayleigh normal series solution for the acoustic scattering of underwater target and the mechanism analysis of the low-frequency resonance which is associated with subsonic Rayleigh waves on the solid plastic polymer spheres, the sensitivity characteristics of the resonance frequency and amplitude to the wave velocity and attenuation coefficient are obtained at low frequencies. It is shown that the transverse wave velocity and the transverse wave attenuation coefficient both have high inversion accuracy at low values of ka, where a is the radius of elastic sphere, as they are quite sensitive to the backscattering resonance frequency and amplitude, respectively. In the frequency band of interest, the backscattering resonance frequency is almost independent of attenuation coefficient. Considering the inversion accuracy, the longitudinal wave velocity and transverse wave velocity are inverted by the resonance frequency separately. Based on these characteristics, the cyclic search method is used to establish an acoustic parameter inversion method for plastic polymer materials, in which the frequency and amplitude of backscattering resonance peak are used as cost functions. Finally, the backscattering acoustic scattering experiment on a solid typical plastic polymer PMMA (methyl methacrylate-acrylic) sphere is conducted in the tank. The experimental results about the backscattering target strength varying with the frequency are in good agreement with the simulation results in a frequency range of 5–20 kHz. The simulation parameters such as the longitudinal wave velocity, transverse wave velocity and attenuation coefficient are obtained by the previously established inversion method. Therefore, the acoustic parameter inversion method provides reliable acoustic parameters for 3D printed underwater acoustic model and structure performance prediction for plastic polymer materials.
-
Keywords:
- plastic polymer /
- acoustic scattering /
- acoustic parameters /
- inversion
[1] 凌绳, 王秀芬, 吴友平 2007 聚合物材料 (北京: 中国轻工业出版社)第1−4页
Ling S, Wang X F, Wu Y P 2007 Polymer Materials (Beijing: China Light Industry Press) pp1−4 (in Chinese)
[2] 王荣津 1983 水声材料手册 (北京: 科学出版社) 第49−64页
Wang R J 1983 The Handbook of Underwater Acoustic Materials (Beijing: Science Press) pp49−64 (in Chinese)
[3] 李永清, 朱锡, 孙卫红, 晏欣 2012 舰船科学技术 34 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y Q, Zhu X, Sun W H, Yan X 2012 Ship Science And Technology 34 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 代阳, 杨建华, 侯宏, 陈建平, 孙亮, 石静 2017 声学学报 42 476
Dai Y, Yang J H, Hou H, Chen J P, Sun L, Shi J 2017 Acta Acustica 42 476
[5] 陈建平, 何元安, 黄爱根 2015 声学技术 34 109
Chen J P, He Y A, Huang A G 2015 Technical Acoustics 34 109
[6] 任群言, 朴胜春, 马力, 郭圣明, 廖天俊 2018 哈尔滨工程大学学报 39 236
Ren Q Y, Piao S C, Ma L, Guo S M, Liao T J 2018 J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 39 236
[7] 杨坤德, 马远良 2009 58 1798
Yang K D, Ma Y L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 1798
[8] 郭晓乐, 杨坤德, 马远良 2015 17 174302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo X L, Yang K D, Ma Y L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 17 174302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 郑广赢, 黄益旺 2017 哈尔滨工程大学学报 38 371
Zheng G Y, Huang Y W 2017 J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 38 371
[10] 金国梁, 尹剑飞, 温激鸿, 温熙森 2016 65 014305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin G L, Yin J F, Wen J H, Wen X S 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 陶猛, 赵阳 2014 振动与冲击 33 85
Tao M, Zhao Y 2014 Journal of Vibration and Shock 33 85
[12] 宋扬, 杨士莪, 黄益旺 2007 材料科学与工艺 15 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song Y, Yang S E, Huang Y W 2007 Material Science and Technology 15 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gaunaurd G C, Überall H 1983 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 73 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hartmann B, Jarzynski J 1972 J. Appl. Phys. 43 4304
[15] 龙云亮, 文希理, 谢处方 1994 数值计算与计算机应用 2 88
You Y L, Wen X L, Xie C F 1994 J. Num. Meth. Computer Appl. 2 88
[16] Dickey J W, Frisk G V, Überall H 1976 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 59 1339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Marston P L 1992 Geometrical and Catastrophe Optics Methods in Scattering (New York: Academic Press) pp47–50
[18] Tesei A, Guerrini P, Zampolli M 2008 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124 827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hefner B T, Marston P L 2000 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 107 1930
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 汤渭霖, 范军, 马忠诚 2018 水中目标声散射 (北京: 科学出版社) 第112−116页
Tang W L, Fan J, Ma Z C 2018 Acoustic Scattering of Underwater Targets (Beijing: Science Press) pp112−116 (in Chinese)
[21] Mitri F G, Fellah Z E A, Chapelon J Y 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115 1411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 计算所用材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters used in the calculations.
材料 密度/kg·m–3 纵波波速/m·s–1 剪切波波速/m·s–1 纵波衰减系数${\alpha _{\rm{d}}}$ 剪切波衰减系数${\alpha _{\rm{s}}}$ PMMA 1190 2690 1340 0.0034 0.0053 钢 7700 5950 3240 水 1000 1500 表 2 实验获取共振峰频率和幅度
Table 2. Resonance frequency and amplitude obtained in experiment.
共振峰频率${f_{{\rm{m}}j}}$/kHz 共振峰幅度${A_{{\rm{m}}j}}$ ${f_{{\rm{m}}1}}$ 7.654 ${A_{{\rm{m}}1}}$ 3.1556 ${f_{{\rm{m}}2}}$ 9.605 ${A_{{\rm{m}}2}}$ 3.1378 ${f_{{\rm{m}}3}}$ 11.48 ${A_{{\rm{m}}3}}$ 2.6025 ${f_{{\rm{m}}4}}$ 14.894 ${A_{{\rm{m}}4}}$ 2.5969 -
[1] 凌绳, 王秀芬, 吴友平 2007 聚合物材料 (北京: 中国轻工业出版社)第1−4页
Ling S, Wang X F, Wu Y P 2007 Polymer Materials (Beijing: China Light Industry Press) pp1−4 (in Chinese)
[2] 王荣津 1983 水声材料手册 (北京: 科学出版社) 第49−64页
Wang R J 1983 The Handbook of Underwater Acoustic Materials (Beijing: Science Press) pp49−64 (in Chinese)
[3] 李永清, 朱锡, 孙卫红, 晏欣 2012 舰船科学技术 34 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Y Q, Zhu X, Sun W H, Yan X 2012 Ship Science And Technology 34 7
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 代阳, 杨建华, 侯宏, 陈建平, 孙亮, 石静 2017 声学学报 42 476
Dai Y, Yang J H, Hou H, Chen J P, Sun L, Shi J 2017 Acta Acustica 42 476
[5] 陈建平, 何元安, 黄爱根 2015 声学技术 34 109
Chen J P, He Y A, Huang A G 2015 Technical Acoustics 34 109
[6] 任群言, 朴胜春, 马力, 郭圣明, 廖天俊 2018 哈尔滨工程大学学报 39 236
Ren Q Y, Piao S C, Ma L, Guo S M, Liao T J 2018 J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 39 236
[7] 杨坤德, 马远良 2009 58 1798
Yang K D, Ma Y L 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 1798
[8] 郭晓乐, 杨坤德, 马远良 2015 17 174302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Guo X L, Yang K D, Ma Y L 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 17 174302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 郑广赢, 黄益旺 2017 哈尔滨工程大学学报 38 371
Zheng G Y, Huang Y W 2017 J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 38 371
[10] 金国梁, 尹剑飞, 温激鸿, 温熙森 2016 65 014305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jin G L, Yin J F, Wen J H, Wen X S 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 陶猛, 赵阳 2014 振动与冲击 33 85
Tao M, Zhao Y 2014 Journal of Vibration and Shock 33 85
[12] 宋扬, 杨士莪, 黄益旺 2007 材料科学与工艺 15 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song Y, Yang S E, Huang Y W 2007 Material Science and Technology 15 44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Gaunaurd G C, Überall H 1983 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 73 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hartmann B, Jarzynski J 1972 J. Appl. Phys. 43 4304
[15] 龙云亮, 文希理, 谢处方 1994 数值计算与计算机应用 2 88
You Y L, Wen X L, Xie C F 1994 J. Num. Meth. Computer Appl. 2 88
[16] Dickey J W, Frisk G V, Überall H 1976 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 59 1339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Marston P L 1992 Geometrical and Catastrophe Optics Methods in Scattering (New York: Academic Press) pp47–50
[18] Tesei A, Guerrini P, Zampolli M 2008 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 124 827
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Hefner B T, Marston P L 2000 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 107 1930
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 汤渭霖, 范军, 马忠诚 2018 水中目标声散射 (北京: 科学出版社) 第112−116页
Tang W L, Fan J, Ma Z C 2018 Acoustic Scattering of Underwater Targets (Beijing: Science Press) pp112−116 (in Chinese)
[21] Mitri F G, Fellah Z E A, Chapelon J Y 2004 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115 1411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 11920
- PDF Downloads: 116
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: