-
The prevailing Jiles-Atherton (J-A) model and Zheng Xiao-Jing-Liu Xing-En (Z-L) model are extensively used in modeling the magneto-mechanical effect on magnetization in ferromagnetic materials. In the J-A model, a fitting formula of magnetostrictive strain interms of stress and magnetization is adopted to model the stress effect on magnetostriction. However, the fitting formula is not in good accordance with the experimental results obtained by Kuruzar and Culllity. In order to solve this problem, a transcendental function tanh(x) is appropriately selected to describe the nonlinear magnetostrictive strain in the Z-L model, and it is found that the general formula of magnetostrictive strain is more effective to describe the nonlinear relation of magnetostrictive strain with stress and magnetization. Then, the modified law proposed by Jiles and Li is adopted to modify the Z-L model by Shi Pengpeng to describe the hysteretic behavior; nevertheless, the effect of Weiss molecular field, pinning energy and plastic deformation on magnetization are not taken into account, and the modified Z-L model can only describe the elastic stress effect on magnetization. In order to solve these problems above, a modified magneto-mechanical model is established by combining the magnetostrictive constitutive relationships of Z-L model with the modified energy conservation equation of J-A model, as well as taking the effect of elastic stress and plastic strain on the model parameters into account simultaneously. It is found that the predictions of proposed model here are in better accordance with the initial magnetization curves given by Jiles and Atherton and the hysteresis loops obtained by Makar and Tanner under different stresses and plastic deformation than those calculated by the J-A model and Z-L model. The correlation coefficients between experimental data and theoretical results calculated by the modified model are all over 0.98, which indicates that the modified model here is more effective than the existing model. A detailed study also performed to reveal the effects of the elastic tensile and compressive stress and plastic tensile and compressive strain on hysteresis loops, coercivity and remanence. The proposed model reveals that the area of hysteresis loop and coercivity increase nonlinearly with the stress and plastic deformation increasing, while the remanence decreases significantly; the effects of compressive stress and compressive plastic deformation on magnetization characteristic parameters above are more significant than those of tensile stress and tensile plastic deformation, which is consistent with the experimental trend. The proposed model can be used to quantitatively analyze the magneto-mechanical effect on the magnetization of ferromagnetism.
-
Keywords:
- magneto-mechanical effect /
- magnetostriction /
- hysteresis loops /
- Jiles-Atherton model /
- Zheng Xiao-Jing-Liu Xing-En model
[1] Aydin U, Rasilo P, Martin F, Belahcen A, Daniel L, Havisto A, Arkkio A 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Shi P, Jin K, Zheng X J 2017 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 124−125 229
[3] Wang Z D, Deng B, Yao K 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 083928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Roskosz M, Gawrilenko P 2008 NDT & E Int. 41 570
[5] Sablik M J, Landgraf F J G, Magnabosco R, Fukuhara M, de Campos M F, Machado R, Missell F P 2006 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 304 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sablik M J, Kwun H, Burkhardt G L, Jiles D C 1987 J. Appl. Phys. 61 3799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sablik M J, Rubin S W, Riley L A, Jiles D C, Kaminski D A, Biner S B 1993 J. Appl. Phys. 74 480
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jiles D C 1995 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 28 1537
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Craik D J, Wood M J 1970 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 3 1009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jiles D C 1988 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys 21 1196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 任文坚, 孙金立, 陈曦, 王振, 任吉林 2013 机械工程学报 49 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren W J, Shu J L, Chen X, Wang Z, Ren J L 2013 J. Mech. Eng. 49 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 任吉林, 陈晨, 刘昌奎, 陈曦, 舒铭航 2008 航空材料学报 28 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren J L, Chen C, Liu C K, Chen X, Shu M H 2008 J. Aeronaut. Mater. 28 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Makar J M, Tanner B K 1998 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 184 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Makar J M, Tanner B K 2000 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 222 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jiles D C, Atherton D L 1984 J. Appl. Phys. 55 2115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiles D C, Atherton D L 1984 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 17 2491
[17] Sablik M J, Burkhardt G L, Kwun H, Jiles D C 1988 J. Appl. Phys. 63 3930
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sablik M J, Jiles D C 1993 IEEE Trans. Magn. 29 2113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Nouicer A, Nouicer E, Feliachi M 2015 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 373 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Nouicer A, Nouicer E, Mahtali M, Feliachi M 2013 J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26 1489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Abdelmadjid N, Elamine N, Mouloud F 2013 Int. J. Appl. Eletrom. 42 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li J W, Xu M Q 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 63918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sablik M J 1997 IEEE Trans. Magn. 33 3958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li L, Jiles D C 2003 IEEE Trans. Magn. 39 3037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sablik M J, Chen Y, Jiles D C 2000 AIP Conf. Proc. 509 1565
[26] Sablik M J, Stegemann D, Krys A 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 7254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sablik M J 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 5610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lo C C H, Kinser E, Jiles D C 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 6626
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Lo C C H, Lee S J, Li L, Kerdus L C, Jiles D C 2002 IEEE Trans. Magn. 38 2418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Sablik M J, Yonamine T, Landgraf F J G 2004 IEEE Trans. Magn. 40 3219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Li J W, Xu M Q, Leng J C, Xu M X 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 063909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Liu Q Y, Luo X, Zhu H Y, Liu J X, Han Y W 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 077502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 刘清友, 罗旭, 朱海燕, 韩一维, 刘建勋 2017 66 107501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Q Y, Luo X, Zhu H Y, Han Y W, Liu J X 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 107501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zhou Y H, Zhou H M, Zheng X J, Qiang Y, Jing W 2009 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhou Y H, Zhou H M, Zheng X J 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 104 23907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Shi P P, Jin K, Zheng X J 2016 J. Appl. Phys. 119 145103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Shi P P, Zhang P C, Jin K, Chen Z M, Zheng X J 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 123 145102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Kurzar M E, Cullity B D 1971 Intern. J. Magnetism 1 323
[39] Yamasaki T, Yamamoto S, Hirao M 1996 NDT & E Int. 29 263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Sablik M J, Geerts W J, Smith K, Gregory A, Moore C, Palmer D, Bandyopadhyay A, Landgraf F J G, Campos M F 2010 IEEE Trans. Magn. 46 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Schneider C S, Cannell P Y, Watts K T 1992 IEEE Trans. Magn. 28 2626
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 单次磁化条件下不同模型计算得到的
${B_{\rm{e}}}$ -$H$ 曲线对比 (a)修正模型计算结果; (b) J-A模型计算结果; (c) Z-L模型计算结果; (d)不同模型计算结果与试验结果相关系数对比Figure 1. Comparison of initial
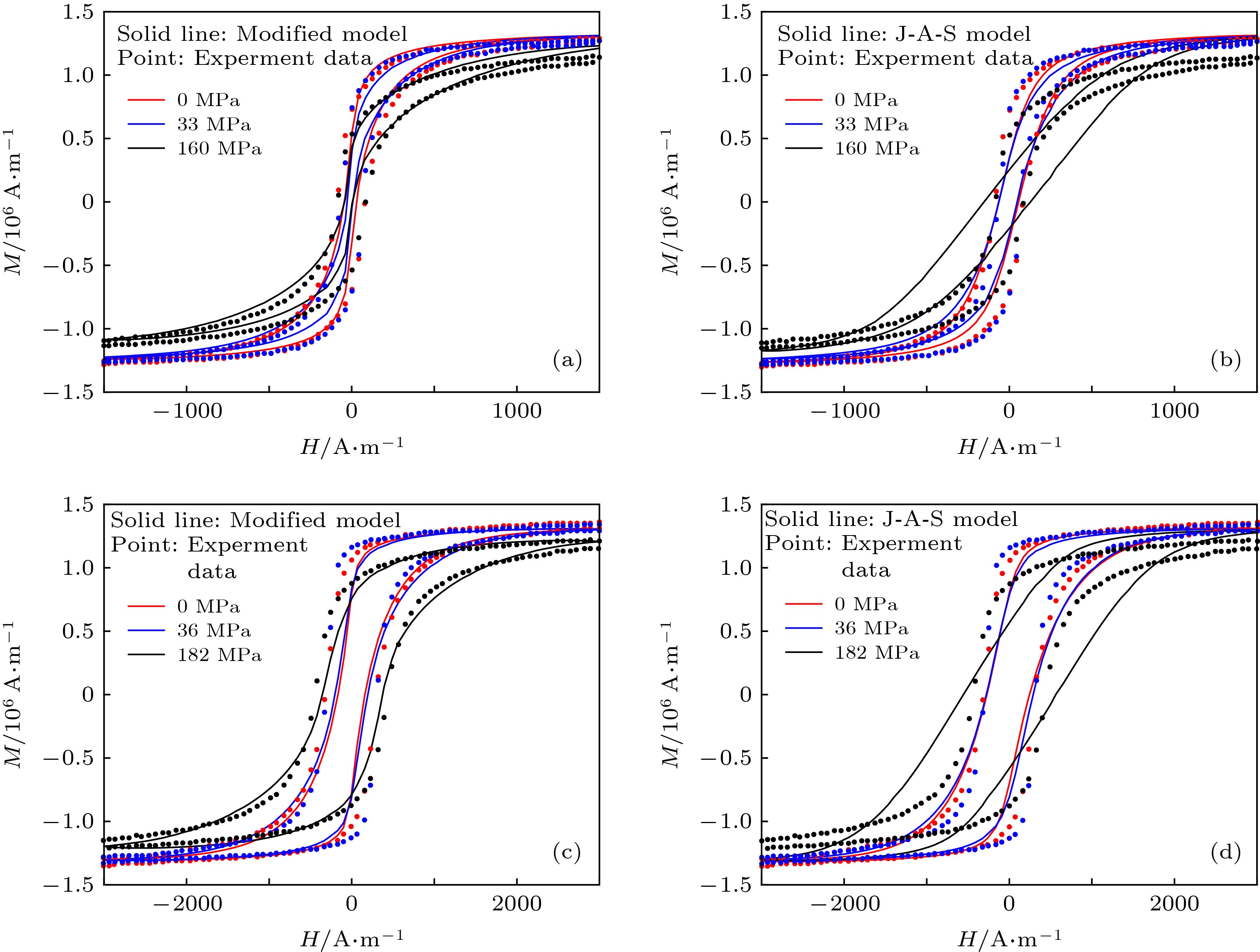
${B_{\rm{e}}}$ -$H$ curves calculated by different models: (a) Our theoretical model; (b) J-A model; (c) Z-L model; (d) correlation coefficients of different models图 2 不同应力条件下修正模型和J-A模型磁滞回线计算结果的对比 (a)含碳量为0.003%时修正模型计算结果; (b)含碳量为0.003%时J-A模型计算结果; (c)含碳量为0.15%时修正模型计算结果; (d)含碳量为0.15%时J-A模型计算结果
Figure 2. Hysteresis loops predicated by modified model and J-A model under different loading stresses: (a) Our modified model for 0.003 wt% C sample; (b) J-A model for 0.003 wt% C sample; (c) our modified model for 0.15 wt% C sample; (d) J-A model for 0.15 wt% C sample
图 3 不同残余塑性变形条件下修正模型和J-A模型磁滞回线计算结果的对比 (a)含碳量0.003%时修正模型计算结果; (b)含碳量0.003%时J-A模型计算结果; (c)含碳量0.15%时修正模型计算结果; (d)含碳量0.15%时J-A模型计算结果
Figure 3. Hysteresis loops predicated by modified model and J-A model under different residual plastic deformation: (a) Our modified model for 0.003 wt% C sample; (b) J-A model for 0.003 wt% C sample; (c) our modified model for 0.15 wt% C sample; (d) J-A model for 0.15 wt% C sample
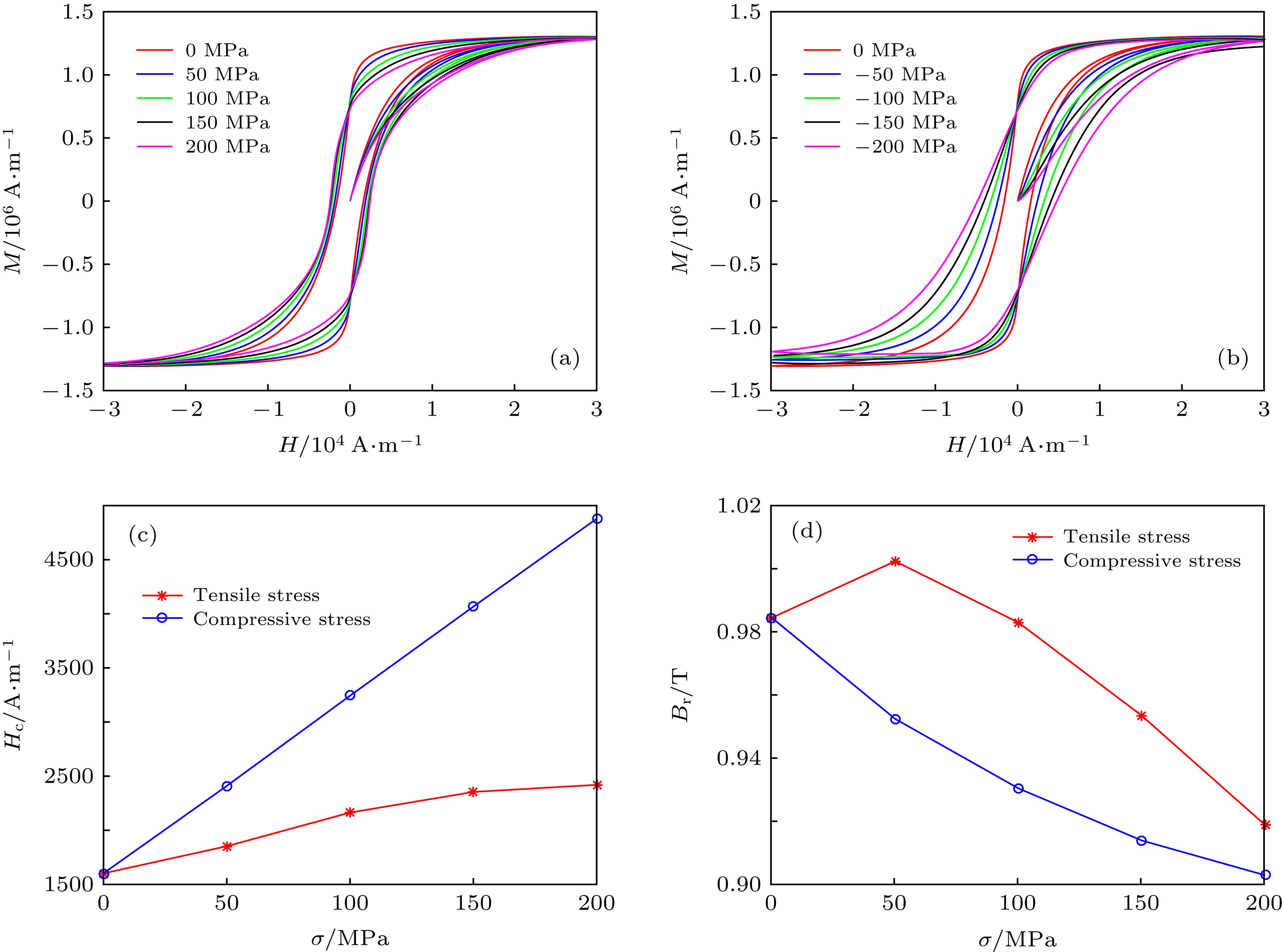
图 4 弹性应力对磁滞回线、矫顽力及剩余磁感应强度的影响 (a)弹性拉应力对磁滞回线的影响; (b)弹性压应力对磁滞回线的影响; (c)弹性拉、压应力对矫顽力的影响; (d)弹性拉、压应力对剩余磁感应强度的影响
Figure 4. Effects of elastic stress on hysteresis loops, coercivity and remanence: (a) Effect of elastic tensile stress on hysteresis loop; (b) effect of elastic compressive stress on hysteresis loop; (c) effect of elastic tensile and compressive stress on coercivity; (d) effect of elastic tensile and compressive stress on remanence
图 5 塑性应变对磁滞回线、矫顽力及剩余磁化强度的影响 (a)拉伸塑性应变对磁滞回线的影响; (b)压缩塑性变形对磁滞回线的影响; (c)塑性变形对矫顽力的影响; (d)塑性变形对剩余磁感应强度的影响
Figure 5. Effects of plastic deformation on hysteresis loops, coercivity and remanence: (a) Effect of plastic tensile deformation on hysteresis loop; (b) effect of plastic compressive deformation on hysteresis loop; (c) effect of plastic tensile and compressive deformation on coercivity; (d) effect of plastic tensile and compressive deformation on remanence
表 1 不同模型的相关系数
${R^2}$ 比较Table 1. Correlation coefficients
${R^2}$ of initial magnetization curve predicated by different models.模型类型 应力值/MPa –200 –100 0 100 200 修正模型${R^2}$ 0.9904 0.9947 0.9973 0.9859 0.9724 Z-L模型${R^2}$ 0.9421 0.9290 0.9333 0.9300 0.8956 J-A模型${R^2}$ 0.6289 0.0394 –0.0289 0.2688 0.6440 表 2 加载条件下不同模型计算得到的磁滞回线与试验曲线相关系数
${R^2}$ 比较Table 2. Correlation coefficients
${R^2}$ of hysteresis loops predicated by different models under loading condition.模型类型 试件含碳量0.003 wt% 试件含碳量0.15 wt% 0 MPa 33 MPa 160 MPa 0 MPa 36 MPa 182 MPa 修正模型${R^2}$ 0.9845 0.9894 0.9898 0.9840 0.9808 0.9937 J-A模型${R^2}$ 0.9133 0.9188 0.8984 0.9485 0.9496 0.9153 表 3 卸载条件下不同模型计算得到的磁滞回线与试验曲线相关系数
${R^2}$ 比较Table 3. Correlation coefficients
${R^2}$ of hysteresis loops predicated by different models under different residual plastic deformation.模型类型 试件含碳量0.003 wt% 试件含碳量0.153 wt% 0 MPa 160 MPa 0 MPa 182 MPa 修正模型${R^2}$ 0.9845 0.9943 0.9840 0.9858 J-A模型${R^2}$ 0.9133 0.9826 0.9485 0.9765 -
[1] Aydin U, Rasilo P, Martin F, Belahcen A, Daniel L, Havisto A, Arkkio A 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469 19
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Shi P, Jin K, Zheng X J 2017 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 124−125 229
[3] Wang Z D, Deng B, Yao K 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 109 083928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Roskosz M, Gawrilenko P 2008 NDT & E Int. 41 570
[5] Sablik M J, Landgraf F J G, Magnabosco R, Fukuhara M, de Campos M F, Machado R, Missell F P 2006 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 304 155
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Sablik M J, Kwun H, Burkhardt G L, Jiles D C 1987 J. Appl. Phys. 61 3799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Sablik M J, Rubin S W, Riley L A, Jiles D C, Kaminski D A, Biner S B 1993 J. Appl. Phys. 74 480
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jiles D C 1995 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 28 1537
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Craik D J, Wood M J 1970 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 3 1009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jiles D C 1988 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys 21 1196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 任文坚, 孙金立, 陈曦, 王振, 任吉林 2013 机械工程学报 49 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren W J, Shu J L, Chen X, Wang Z, Ren J L 2013 J. Mech. Eng. 49 8
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 任吉林, 陈晨, 刘昌奎, 陈曦, 舒铭航 2008 航空材料学报 28 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren J L, Chen C, Liu C K, Chen X, Shu M H 2008 J. Aeronaut. Mater. 28 41
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Makar J M, Tanner B K 1998 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 184 193
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Makar J M, Tanner B K 2000 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 222 291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jiles D C, Atherton D L 1984 J. Appl. Phys. 55 2115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jiles D C, Atherton D L 1984 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 17 2491
[17] Sablik M J, Burkhardt G L, Kwun H, Jiles D C 1988 J. Appl. Phys. 63 3930
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Sablik M J, Jiles D C 1993 IEEE Trans. Magn. 29 2113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Nouicer A, Nouicer E, Feliachi M 2015 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 373 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Nouicer A, Nouicer E, Mahtali M, Feliachi M 2013 J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26 1489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Abdelmadjid N, Elamine N, Mouloud F 2013 Int. J. Appl. Eletrom. 42 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Li J W, Xu M Q 2011 J. Appl. Phys. 110 63918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Sablik M J 1997 IEEE Trans. Magn. 33 3958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Li L, Jiles D C 2003 IEEE Trans. Magn. 39 3037
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sablik M J, Chen Y, Jiles D C 2000 AIP Conf. Proc. 509 1565
[26] Sablik M J, Stegemann D, Krys A 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 7254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Sablik M J 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 5610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Lo C C H, Kinser E, Jiles D C 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 6626
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Lo C C H, Lee S J, Li L, Kerdus L C, Jiles D C 2002 IEEE Trans. Magn. 38 2418
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Sablik M J, Yonamine T, Landgraf F J G 2004 IEEE Trans. Magn. 40 3219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Li J W, Xu M Q, Leng J C, Xu M X 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 111 063909
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Liu Q Y, Luo X, Zhu H Y, Liu J X, Han Y W 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 077502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 刘清友, 罗旭, 朱海燕, 韩一维, 刘建勋 2017 66 107501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Q Y, Luo X, Zhu H Y, Han Y W, Liu J X 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 107501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Zhou Y H, Zhou H M, Zheng X J, Qiang Y, Jing W 2009 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhou Y H, Zhou H M, Zheng X J 2008 J. Appl. Phys. 104 23907
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Shi P P, Jin K, Zheng X J 2016 J. Appl. Phys. 119 145103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Shi P P, Zhang P C, Jin K, Chen Z M, Zheng X J 2018 J. Appl. Phys. 123 145102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Kurzar M E, Cullity B D 1971 Intern. J. Magnetism 1 323
[39] Yamasaki T, Yamamoto S, Hirao M 1996 NDT & E Int. 29 263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Sablik M J, Geerts W J, Smith K, Gregory A, Moore C, Palmer D, Bandyopadhyay A, Landgraf F J G, Campos M F 2010 IEEE Trans. Magn. 46 491
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Schneider C S, Cannell P Y, Watts K T 1992 IEEE Trans. Magn. 28 2626
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 19267
- PDF Downloads: 379
- Cited By: 0



















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: