-
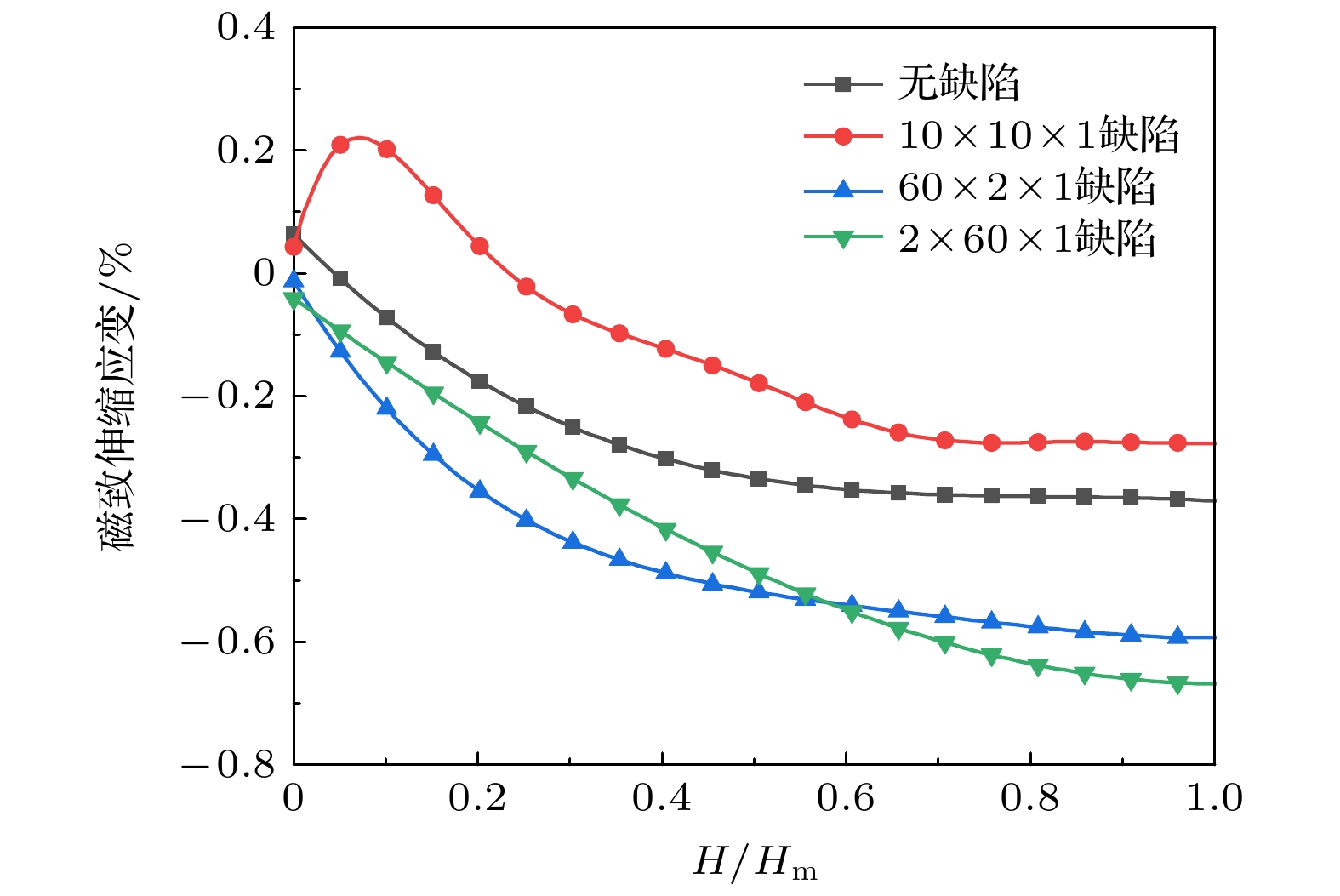
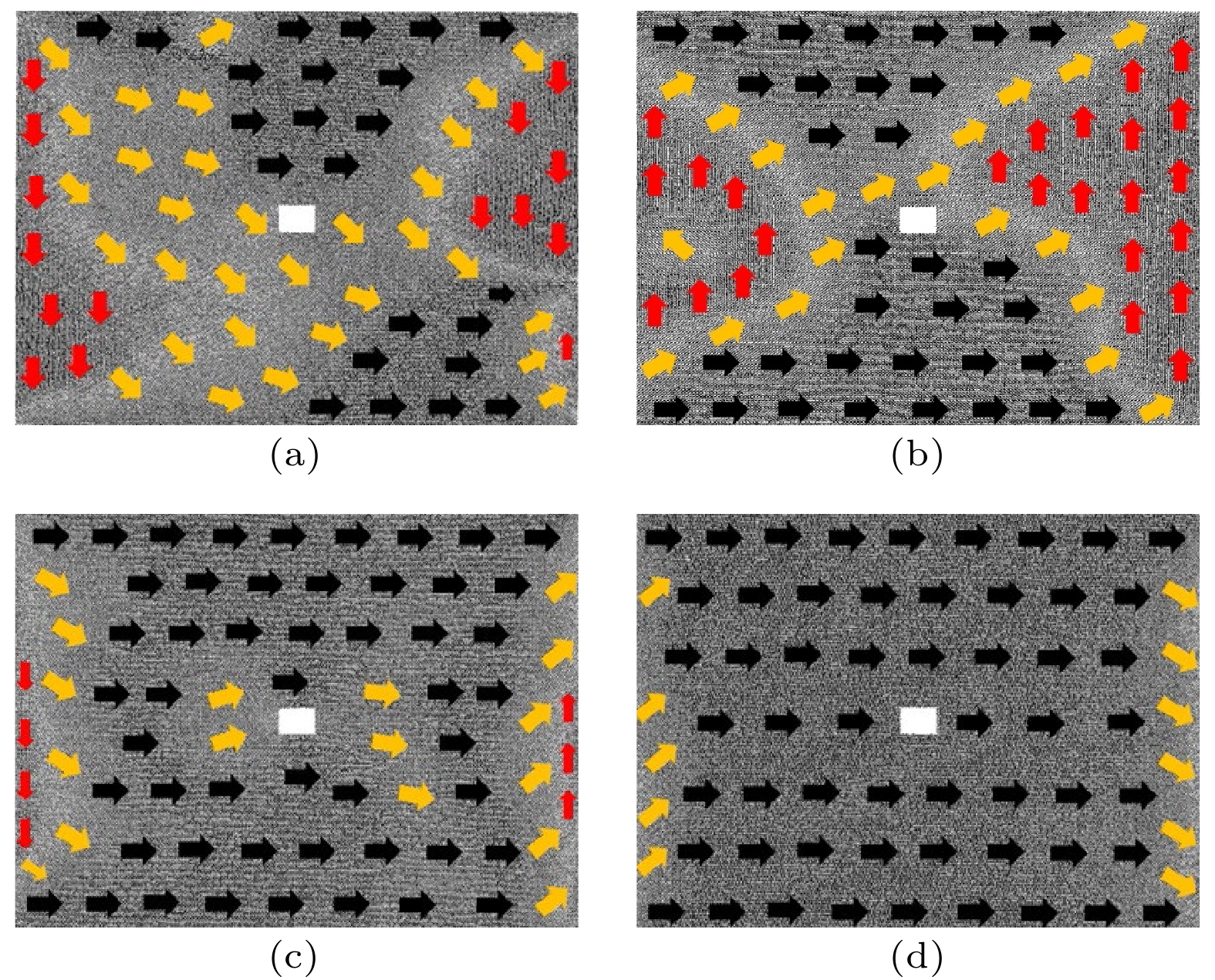
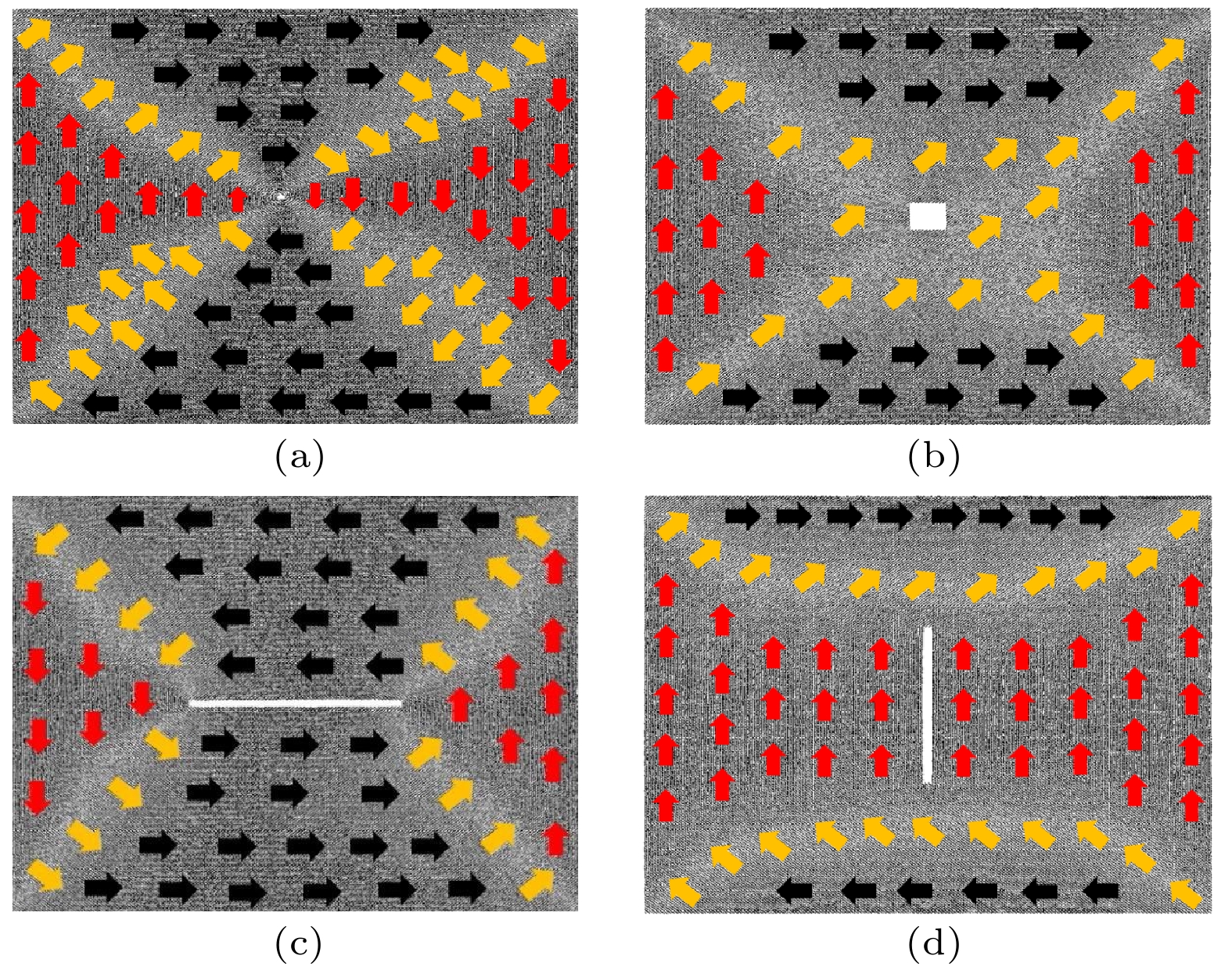
磁致伸缩材料在传感、控制及能量与信息转换等领域应用前景广阔, 此类材料的性能提升及工程应用已成为研究热点, 但材料在制备与使用中不可避免会出现缺陷. 本文以常用的铁磁性材料铁单质为研究对象, 采用分子动力学方法分别建立无缺陷、孔洞缺陷与裂纹缺陷的铁单质磁致伸缩结构模型, 分析了缺陷形式对铁单质薄膜磁致伸缩行为的影响, 并从微观原子磁矩角度解释缺陷对磁致伸缩行为的影响机理. 结果表明: 缺陷会对其周围的原子磁矩产生影响, 从而影响铁单质薄膜磁致伸缩, 其中孔洞形缺陷对磁致伸缩的影响较小, 裂纹形缺陷对磁致伸缩的影响较大. 裂纹的方向会影响铁单质薄膜的磁致伸缩, 与磁化方向平行的裂纹会降低材料在磁化方向上由初始状态至磁化达到饱和的最大磁致伸缩量; 与磁化方向垂直的裂纹会提高材料在磁化方向上由初始状态至磁化达到饱和的最大磁致伸缩量.Magnetostrictive materials have broad application prospects in sensing, control, energy conversion, and information conversion. The improving of the performances and applications of such materials has become a research hotspot, but defects will inevitably appear in the preparation and use of materials. In this study, the magnetostrictive structure model of iron elemental material with no defect or hole defect or crack defect is established by the molecular dynamics method. The influences of different defects on the magnetostrictive behavior of iron thin films are analyzed, and the mechanism of the influence of defects on the magnetostrictive behavior is depicted from the perspective of atomic magnetic moment. The results show that the films with 60 × 2 × 1 defects in the center are the easiest to reach saturation magnetostriction, and the magnetostriction is the least after reaching saturation, with respect to the films without defects. The films with 10 × 10 × 1 and 2 × 60 × 1 defects in the center require a larger magnetic field to approach to saturation, and the magnetostriction of the film with 2 × 60 × 1 defects in the center reaches a maximum value after saturation. This is because the defects will affect the magnetic moment of the surrounding atoms and make them deflect to the direction parallel to the defects, thus affecting the magnetostriction of the iron thin film. Among them, the hole defects have less influence on the magnetostriction, while the crack defects have stronger influence on the magnetostriction. The direction of the crack also has an effect on the magnetostriction of Fe thin film. When the crack is parallel to the direction of magnetization, the maximum magnetostriction of the film in the direction of magnetization from the initial state to the saturation of magnetization will decrease. When the crack is perpendicular to the direction of magnetization, the maximum magnetostriction of the film in the direction of magnetization from the initial state to the saturation of magnetization will increase. These results suggest that the defects affect the magnetostriction of the model as a whole during magnetization by affecting the initial magnetic moment orientation of the surrounding atoms.
-
Keywords:
- elemental iron /
- magnetostriction /
- defects /
- molecular dynamics /
- thin film
[1] Makarova L A, Alekhina Y A, Isaev D A, Khairullin M F, Perov N S 2021 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 54 15003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Garcia M H, Barrera D, Amat R, Kurlyandskaya G V, Sales S 2016 Measurement 80 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pei H F, Jing J H, Zhang S Q 2020 Measurement 151 107172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yu G L, Li Y X, Zeng Y Q, Li J, Zuo L, Li Q, Zhang H W 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 077504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 周勇, 李纯健, 潘昱融 2018 67 077702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y, Li C J, Pan Y R 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 077702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 苏三庆, 刘馨为, 王威, 左付亮, 邓瑞泽, 秦彦龙 2020 工程科学学报 42 1557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su S Q, Liu X W, Wang W, Zuo F L, Deng R Z, Qin Y L 2020 Chin. J. Eng. 42 1557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ren W P, Xu K, Dixon S, Zhang C 2019 NDT E Int. 101 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] M'Zali N, Martin F, Aydin U, Belahcen A, Benabou A, Henneron T 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500 166299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 时朋朋, 郝帅 2021 70 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi P P, Hao S 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao B X, Yao K, Wu L B, Li X L, Wang Y S 2020 Appl. Sci. -Basel 10 7083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dubov A A 1997 Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 39 401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang P, Zhang Y, Yao E T, Mi Y, Zheng Y, Tang C L 2021 Measurement 168 108187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bao S, Gu Y B, Fu M L, Zhang D, Hu S N 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 423 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang J, Jin W L, Mao J H, Xia J, Fan W J 2020 Constr. Build. Mater. 239 117885
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 宋凯, 任吉林, 任尚坤, 唐继红 2007 无损检测 29 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song K, Ren J L, Ren S K, Tang J H 2007 Nondestruct. Test. 29 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张卫民, 刘红光, 孙海涛 2004 北京理工大学学报 24 571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W M, Liu H G, Sun H T 2004 Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 24 571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李川, 刘敬华, 陈立彪, 蒋成保, 徐惠彬 2011 60 097505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C, Liu J H, Chen L B, Jiang C B, Xu H B 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 097505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kharel P, Talebi S, Ramachandran B, Dixit A, Naik V M, Sahana M B, Sudakar C, Naik R, Rao M S R, Lawes G 2009 J. Phys. -Condes. Matter. 21 36001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 张辉, 曾德长 2010 59 2808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Zeng D C 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 2808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Suzuki S, Kawamata T, Simura R, Asano S, Fujieda S, Umetsu R Y, Fujita M, Imafuku M, Kumagai T, Fukuda T 2019 Mater. Trans. 60 2235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tranchida J, Plimpton S J, Thibaudeau P, Thompson, A P 2018 J. Comput. Phys. 372 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jeong J, Goremychkin E A, Guidi T, Nakajima K, Jeon G S, Kim S A, Furukawa S, Kim Y B, Lee S, Kiryukhin V, Cheong S W, Park J G 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 077202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kvashnin Y O, Cardias R, Szilva A, Di Marco I, Katsnelson M I, Lichtenstein A I, Nordstrom L, Klautau A B, Eriksson O 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 217202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
-
[1] Makarova L A, Alekhina Y A, Isaev D A, Khairullin M F, Perov N S 2021 J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 54 15003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Garcia M H, Barrera D, Amat R, Kurlyandskaya G V, Sales S 2016 Measurement 80 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pei H F, Jing J H, Zhang S Q 2020 Measurement 151 107172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Yu G L, Li Y X, Zeng Y Q, Li J, Zuo L, Li Q, Zhang H W 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 077504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 周勇, 李纯健, 潘昱融 2018 67 077702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Y, Li C J, Pan Y R 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 077702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 苏三庆, 刘馨为, 王威, 左付亮, 邓瑞泽, 秦彦龙 2020 工程科学学报 42 1557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su S Q, Liu X W, Wang W, Zuo F L, Deng R Z, Qin Y L 2020 Chin. J. Eng. 42 1557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ren W P, Xu K, Dixon S, Zhang C 2019 NDT E Int. 101 34
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] M'Zali N, Martin F, Aydin U, Belahcen A, Benabou A, Henneron T 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500 166299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 时朋朋, 郝帅 2021 70 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi P P, Hao S 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 034101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao B X, Yao K, Wu L B, Li X L, Wang Y S 2020 Appl. Sci. -Basel 10 7083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Dubov A A 1997 Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 39 401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang P, Zhang Y, Yao E T, Mi Y, Zheng Y, Tang C L 2021 Measurement 168 108187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Bao S, Gu Y B, Fu M L, Zhang D, Hu S N 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 423 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang J, Jin W L, Mao J H, Xia J, Fan W J 2020 Constr. Build. Mater. 239 117885
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 宋凯, 任吉林, 任尚坤, 唐继红 2007 无损检测 29 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song K, Ren J L, Ren S K, Tang J H 2007 Nondestruct. Test. 29 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张卫民, 刘红光, 孙海涛 2004 北京理工大学学报 24 571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W M, Liu H G, Sun H T 2004 Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 24 571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李川, 刘敬华, 陈立彪, 蒋成保, 徐惠彬 2011 60 097505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li C, Liu J H, Chen L B, Jiang C B, Xu H B 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 097505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kharel P, Talebi S, Ramachandran B, Dixit A, Naik V M, Sahana M B, Sudakar C, Naik R, Rao M S R, Lawes G 2009 J. Phys. -Condes. Matter. 21 36001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 张辉, 曾德长 2010 59 2808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Zeng D C 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 2808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Suzuki S, Kawamata T, Simura R, Asano S, Fujieda S, Umetsu R Y, Fujita M, Imafuku M, Kumagai T, Fukuda T 2019 Mater. Trans. 60 2235
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tranchida J, Plimpton S J, Thibaudeau P, Thompson, A P 2018 J. Comput. Phys. 372 406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jeong J, Goremychkin E A, Guidi T, Nakajima K, Jeon G S, Kim S A, Furukawa S, Kim Y B, Lee S, Kiryukhin V, Cheong S W, Park J G 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 108 077202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kvashnin Y O, Cardias R, Szilva A, Di Marco I, Katsnelson M I, Lichtenstein A I, Nordstrom L, Klautau A B, Eriksson O 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 116 217202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6618
- PDF下载量: 142
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: